Covalent Organic Framework-Functionalized Magnetic CuFe2O4/Ag Nanoparticles for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
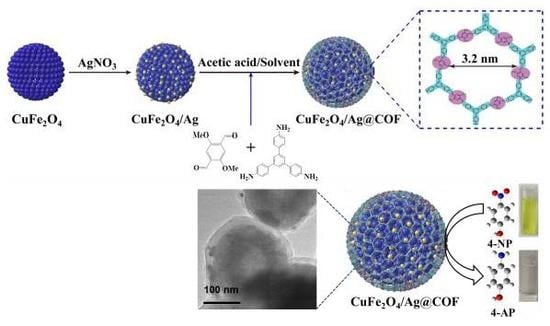
2.3. Synthesis of CuFe2O4/Ag Nanoparticles
2.4. Preparation of Core-Shell Structured CuFe2O4/Ag@COF Nanocomposites
2.5. Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol (4-NP)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of CuFe2O4/Ag@COF Nanocomposite
3.2. Catalytic Reduction of 4-NP
3.3. Plausible Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Nitrophenols: 2-Nitrophenol, 4-Nitrophenol; U.S. Public Health Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- Tang, A.; Long, M.; He, Z. Electrodeposition of Sb2Se3 on TiO2 nanotube arrays for catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol. Electrochimica Acta 2014, 146, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, K.; Kantam, M.L.; Shirai, M.; Nishio-Hamane, D.; Sasaki, T.; Maheswaran, H. Gold nanoparticles stabilized on nanocrystalline magnesium oxide as an active catalyst for reduction of nitroarenes in aqueous medium at room temperature. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 3164–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Safaie, N.; Hosseini, S.H.; Bennett, C. Graphene oxide/poly(imidazole/imidazolium) nanocomposite: An effective support for immobilization of large amounts of Pd nanoparticles. J. Ind. Eng. 2016, 38, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Tang, K.; Verpoort, F.; Sun, T. Polymer-based stimuli-responsive recyclable catalytic systems for organic synthesis. Small 2014, 10, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Shao, Y.; Liao, H.G.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Yin, G.; Lin, Y. Graphene decorated with PtAu alloy nanoparticles: Facile synthesis and promising application for formic acid oxidation. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.N.; Lv, J.J.; Li, S.S.; Xue, M.W.; Wang, A.J.; Feng, J.J. One-pot synthesis of reduced graphene oxide supported hollow Ag@Pt core-shell nanospheres with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for ethylene glycol oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3445–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lin, L.; Ma, J.; Feng, J.; Lin, L.Q.; Ren, Y.M. Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, P.; Zou, B.; Ma, J. Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.R.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, Q.D.; Li, Y.H.; Sun, C.Z.; Cao, Y.Q. Photocatalytic performances and activities of Ag-doped CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 2927–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.H.; Lan, W.Z.; Gong, H.M.; Bai, J.L.; Ramachandran, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, F. Highly sensitive acetone-sensing properties of Pt-decorated CuFe2O4 nanotubes prepared by electrospinning. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 2856–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, A.P.; Benin, A.I.; Ockwig, N.W.; O’keeffe, M.; Matzger, A.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Porous, Crystalline, Covalent Organic Frameworks. Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waller, P.J.; Gándara, F.; Yaghi, O.M. Chemistry of Covalent Organic Frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, A.G.; Cooper, A.I. Function-Led Design of New Porous Materials. Science 2015, 348, 6238–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuerle, F.; Gole, B. Covalent Organic Frameworks and Cage Compounds: Design and Applications of Polymeric and Discrete Organic Scaffolds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4850–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, H.; Cahill, J.F.; Prather, K.A.; Cohen, S.M. Tandem Postsynthetic Metal Ion and Ligand Exchange in Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 4011–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Pan, Q.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Guan, X.Y.; Xue, M.; Fang, Q.R.; Yan, Y.S.; Valtchev, V.; Qiu, S.L. Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with dual linkages for bifunctional cascade catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14783–14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmaier, J.F.; Medina, D.D.; Dogru, M.; Knochel, P.; Bein, T.; Heckl, W.M.; Lackinger, M. Isoreticular two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks synthesized by on-surface condensation of diboronic acids. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7234–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.M.; Sheng, J.L.; Yang, Z.D.; Sun, X.J.; Tang, H.L.; Lu, M.; Dong, H.; Shen, F.C.; Liu, J.; Lan, Y.Q. Rational Design MOF/COF Hybrid Materials for Photocatalytic H2 Evolution in the Presence of Sacrificial Electron Donors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 130, 12282–12286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylianakis, E.; Klontzasa, E.; Froudakis, G.E. Multi-scale theoretical investigation of hydrogen storage in covalent organic frameworks. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Deng, S.B.; Ren, L.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, W.J.; Vakili, M.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Yu, G. Stable Covalent Organic Frameworks as Efficient Adsorbents for High and Selective Removal of an Aryl-Organophosphorus Flame Retardant from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30265–30272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogru, M.; Bein, T. On the road towards electroactive covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5531–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, H.L.; Yang, C.X.; Yan, X.P. Bottom-up synthesis of chiral covalent organic frameworks and their bound capillaries for chiral separation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12104–12111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Li, J.; Gao, M.X.; Zhang, X.M. Self-assembling covalent organic frameworks functionalized magnetic graphene hydrophilic biocomposite as an ultrasensitive matrix for N-linked glycopeptide recognition. Nanoscale 2017, 30, 10750–10756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, J.T.; Cho, S.J.; Jung, G.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.K.; Kwak, S.K.; Lee, S.Y. COF-Net on CNT-Net as a Molecularly Designed, Hierarchical Porous Chemical Trap for Polysulfides in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3292–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.X.; Yan, X.P. Controllable preparation of core-shell magnetic covalent-organic framework nanospheres for efficient adsorption and removal of bisphenols in aqueous solution. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2511–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.; Zhai, L.P.; Coupry, D.E.; Addicoat, M.A.; Okushita, K.; Nishimura, K.; Heine, T.; Jiang, D.L. Multiple-component covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12325–12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Gao, J.; Jiang, D. Stable, Crystalline, Porous, Covalent Organic Frameworks as A Platform for Chiral Organocatalysts. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Li, S.; Guo, Z.; Farha, O.K.; Hauser, B.G.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Imparting Functionality to A Metal-Organic Framework Material by Controlled Nanoparticle Encapsulation. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Su, L.; Ma, Y.H.; Ren, C.L.; Guo, Q.; Chen, X.G. CuFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles: A simple and efficient catalyst for the reduction of nitrophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 221, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshkumar, M.; Lee, P.N.; Lee, C.K. Stepwise assembly of multimetallic nanoparticles via self-polymerized polydopamine. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 12316–12320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.F.; Yao, Y.J.; Xu, Y.L.; Liu, K.; Zhu, G.S.; Chi, L.F.; Lu, G. Imparting Catalytic Activity to a Covalent Organic Framework Material by Nanoparticle Encapsulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7481–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.S.; Zhu, X.Y.; Meng, H.B.; Feng, J.J.; Wang, A.J. One-pot synthesis of highly branched Pt@Ag core-shell nanoparticles as a recyclable catalyst with dramatically boosting the catalytic performance for 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 538, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandambeth, S.; Venkatesh, V.; Shinde, D.B.; Kumari, S.; Halder, A.; Verma, S.; Banerjee, R. Self-Templated Chemically Stable Hollow Spherical Covalent Organic Framework. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altincekica, T.G.; Boz, I.; Baykal, A.; Kazan, S.; Topkaya, R.; Toprak, M.S. Synthesis and characterization of CuFe2O4 nanorods synthesized by polyol route. J. Alloy Compd. 2010, 493, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Meng, D.; Wang, C.; Diao, G. Facile fabrication of hierarchically porous CuFe2O4 nanospheres with enhanced capacitance property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6030–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Tao, C.; Xiao, G.; Wei, G.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Su, H. Controlled synthesis and photocatalysis of sea urchin-like Fe3O4@TiO2@Ag nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5313–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, G.; Cui, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Yan, W.; Xing, C.; Chi, Y.R.; Yang, Y.; Huo, F. A Family of Metal-Organic Frameworks Exhibiting Size-Selective Catalysis with Encapsulated Noble-Metal Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4056–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, C.; Zhao, D.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Liang, C. Covalent Organic Framework-Functionalized Magnetic CuFe2O4/Ag Nanoparticles for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030426
Hou C, Zhao D, Chen W, Li H, Zhang S, Liang C. Covalent Organic Framework-Functionalized Magnetic CuFe2O4/Ag Nanoparticles for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(3):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030426
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Chen, Dongyan Zhao, Wenqiang Chen, Hao Li, Sufeng Zhang, and Chen Liang. 2020. "Covalent Organic Framework-Functionalized Magnetic CuFe2O4/Ag Nanoparticles for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol" Nanomaterials 10, no. 3: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030426
APA StyleHou, C., Zhao, D., Chen, W., Li, H., Zhang, S., & Liang, C. (2020). Covalent Organic Framework-Functionalized Magnetic CuFe2O4/Ag Nanoparticles for the Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Nanomaterials, 10(3), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030426