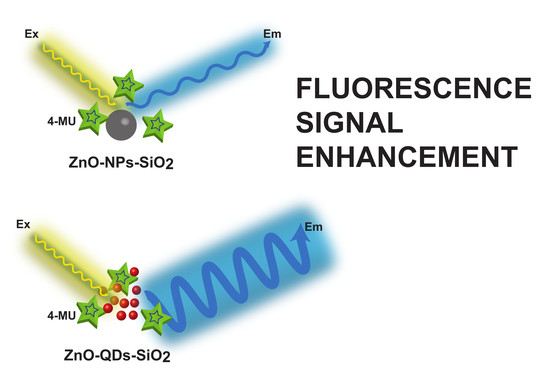
Amplified Fluorescence by ZnO Nanoparticles vs. Quantum Dots for Bovine Mastitis Acute Phase Response Evaluation in Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of TEOS Modified ZnO-QDs
2.3. Fabrication of TEOS Modified ZnO-NPs
2.4. Milk Sampling
2.5. Quantification of NAGase Activity
2.6. Instrumentation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ZnO-Nanomaterials Characterization
3.2. FL Amplification Characterization
3.3. Comparative Studies of NAGase Activity with and without ZnO-Nanomaterials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalmus, P.; Simojoki, H.; Pyörälä, S.; Taponen, S.; Holopainen, J.; Orro, T. Milk haptoglobin, milk amyloid A, and N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase activity in bovines with naturally occurring clinical mastitis diagnosed with a quantitative PCR test. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pyörälä, S.; Hovinen, M.; Simojoki, H.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Eckersall, P.; Orro, T. Acute phase proteins in milk in naturally acquired bovine mastitis caused by different pathogens. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguier, C.; Arora, S.; Gilmartin, N.; Welbeck, K.; O’Kennedy, R. Mastitis detection: Current trends and future perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seegers, H.; Fourichon, C.; Beaudeau, F. Production effects related to mastitis and mastitis economics in dairy cattle herds. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mujawar, L.H.; Moers, A.; Norde, W.; van Amerongen, A. Rapid mastitis detection assay on porous nitrocellulose membrane slides. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7469–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovinen, M.; Simojoki, H.; Pösö, R.; Suolaniemi, J.; Kalmus, P.; Suojala, L.; Pyörälä, S. N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase activity in cow milk as an indicator of mastitis. J. Dairy Res. 2016, 83, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koess, C.; Hamann, J. Detection of mastitis in the bovine mammary gland by flow cytometry at early stages. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, P.M.; McCarthy, K.K. Diagnosis of mastitis for therapy decisions. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Large Anim. Pract. 2003, 19, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffon, R.; Sayasith, K.; Khalil, H.; Dubreuil, P.; Drolet, M.; Lagacé, J. Development of a rapid and sensitive test for identification of major pathogens in bovine mastitis by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2584–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nirala, N.R.; Pinker, N.; Desitti, C.; Shtenberg, G. Milk haptoglobin detection based on enhanced chemiluminescence of gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2019, 197, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirala, N.R.; Shtenberg, G. Gold Nanoparticle Size-Dependent Enhanced Chemiluminescence for Ultra-Sensitive Haptoglobin Biomarker Detection. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitchen, B.; Middleton, G.; Salmon, M. Bovine milk N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase and its significance in the detection of abnormal udder secretions. J. Dairy Res. 1978, 45, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirala, N.R.; Shtenberg, G. Enhanced fluorescence of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase activity by ZnO quantum dots for early stage mastitis evaluation. Front. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Hassabo, A.G.; Mohamed, A.L.; Shaheen, T.I. Surface modification of SiO2 coated ZnO nanoparticles for multifunctional cotton fabrics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 498, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, K.; Previte, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Geddes, C.D. Metal-enhanced fluorescence from nanoparticulate zinc films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 18368–18375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Nahhal, I.M.; Salem, J.K.; Kuhn, S.; Hammad, T.; Hempelmann, R.; Al Bhaisi, S. Synthesis & characterization of silica coated and functionalized silica coated zinc oxide nanomaterials. Powder Technol. 2016, 287, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagura, N.; Ogi, T.; Shirahama, T.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Highly luminescent silica-coated ZnO nanoparticles dispersed in an aqueous medium. J. Lumin. 2011, 131, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Manoth, M.; Singh, V.; Gowd, G.S.; Choudhry, V.; Vadera, S.; Kumar, N. Synthesis of stable dispersion of ZnO quantum dots in aqueous medium showing visible emission from bluish green to yellow. J. Lumin. 2009, 129, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Centeno, A.; Darvill, D.; Pang, J.S.; Ryan, M.P.; Xie, F. Tuneable fluorescence enhancement of nanostructured ZnO arrays with controlled morphology. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 14828–14834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, D.; Song, H.; Hao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Y. Luminescent ZnO quantum dots for sensitive and selective detection of dopamine. Talanta 2013, 107, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znaidi, L. Sol–gel-deposited ZnO thin films: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 174, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Tok, A.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Zeng, X.T.; Zhang, X.H. Surface modification of ZnO nanocrystals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 5473–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshchenko, A.; Fedorenko, V.; Smyntyna, V.; Konup, I.; Konup, A.; Eriksson, M.; Yakimova, R.; Ramanavicius, A.; Balme, S.; Bechelany, M. ZnO films formed by atomic layer deposition as an optical biosensor platform for the detection of Grapevine virus A-type proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xie, W.; Li, X. Enhanced fluorescence detection of proteins using ZnO nanowires integrated inside microfluidic chips. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Metkar, S.K.; Girigoswami, A.; Girigoswami, K. ZnO nanoflower based sensitive nano-biosensor for amyloid detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtenberg, G.; Massad-Ivanir, N.; Fruk, L.; Segal, E. Nanostructured porous Si optical biosensors: Effect of thermal oxidation on their performance and properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16049–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Chen, L. Janus nanostructures formed by mesoporous silica coating Au nanorods for near-infrared chemo–photothermal therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8833–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Yoo, R.; Park, S.R.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, H.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, W. Highly sensitive and selective isoprene sensing performance of ZnO quantum dots for a breath analyzer. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 290, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tăbăcaru, A.; Muşat, V.; Ţigău, N.; Vasile, B.Ş.; Surdu, V.-A. Vinyltrimethoxysilane-modified zinc oxide quantum dots with tuned optical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 359, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswick, T.; Jones, W.; Pacuła, A.; Serwicka, E.; Podobinski, J. The role of anhydrous zinc nitrate in the thermal decomposition of the zinc hydroxy nitrates Zn5(OH)8(NO3)2·2H2O and ZnOHNO3·H2O. J. Solid State Chem. 2007, 180, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, T.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Hou, D.; Wang, J. Fluorometric determination of the antibiotic kanamycin by aptamer-induced FRET quenching and recovery between MoS2 nanosheets and carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, B.J.; Kwee, W.S.; Middleton, G.; Andrews, R.J. Relationship between the level of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAGase) in bovine milk and the presence of mastitis pathogens. J. Dairy Res. 1984, 51, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Han, Q.; Dong, J.; Zheng, H. Solution-based metal enhanced fluorescence with gold and gold/silver core–shell nanorods. Opt. Commun. 2015, 357, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontero, D.; Veglia, A.V.; Bracamonte, A.G.; Boudreau, D. Synthesis of ultraluminescent gold core–shell nanoparticles as nanoimaging platforms for biosensing applications based on metal-enhanced fluorescence. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10252–10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nirala, N.R.; Harel, Y.; Lellouche, J.-P.; Shtenberg, G. Ultrasensitive haptoglobin biomarker detection based on amplified chemiluminescence of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, X.; Guan, P.; Zhang, L.; Fujita, T.; Chen, M. Size dependence of molecular fluorescence enhancement of nanoporous gold. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 73701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, R.; Grady, N.K.; Halas, N.J. Nanoscale Control of Near-Infrared Fluorescence Enhancement Using Au Nanoshells. Small 2008, 4, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, M.A.; Monier, G.; Robert-Goumet, C.; Réveret, F.; Echabaane, M.; Chaudanson, D.; Petit, M.; Bideux, L.; Gruzza, B. Synthesis and Study of Stable and Size-Controlled ZnO–SiO2 Quantum Dots: Application as a Humidity Sensor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 11652–11662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, F.; Valledor, M.; Campo, J. Screening method for early detection of mastitis in cows. Measurement 2014, 47, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample * | SCC (×103) Cells mL−1 | Bacteria |
|---|---|---|
| H | 60 | N/A |
| S1 | 350 | Strep. dysgalactiae |
| S2 | 800 | Strep. dysgalactiae |
| S3 | >1000 | Strep. dysgalactiae |
| Sample *,** | NAGase Activity Conventional Assay (µM min−1) | NAGase Activity with ZnO-NPs-SiO2 (µM min−1) | NAGase Activity with ZnO-QDs-SiO2 (µM min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 0.33 ± 0.01 |
| S1 | 0.73 ± 0.12 | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 0.94 ± 0.02 |
| S2 | 0.86 ± 0.16 | 1.11 ± 0.05 | 1.21 ± 0.03 |
| S3 | 1.50 ± 0.06 | 1.56 ± 0.05 | 1.64 ± 0.04 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nirala, N.R.; Shtenberg, G. Amplified Fluorescence by ZnO Nanoparticles vs. Quantum Dots for Bovine Mastitis Acute Phase Response Evaluation in Milk. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030549
Nirala NR, Shtenberg G. Amplified Fluorescence by ZnO Nanoparticles vs. Quantum Dots for Bovine Mastitis Acute Phase Response Evaluation in Milk. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(3):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030549
Chicago/Turabian StyleNirala, Narsingh R., and Giorgi Shtenberg. 2020. "Amplified Fluorescence by ZnO Nanoparticles vs. Quantum Dots for Bovine Mastitis Acute Phase Response Evaluation in Milk" Nanomaterials 10, no. 3: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030549
APA StyleNirala, N. R., & Shtenberg, G. (2020). Amplified Fluorescence by ZnO Nanoparticles vs. Quantum Dots for Bovine Mastitis Acute Phase Response Evaluation in Milk. Nanomaterials, 10(3), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030549