Bio-Mediated Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles from Chenopodium album: Their Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
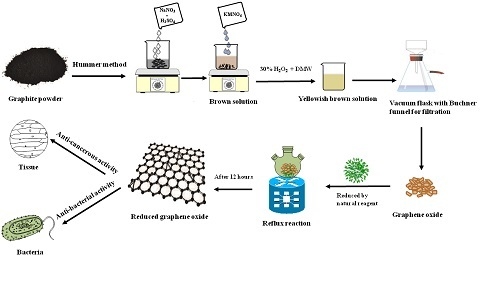
2.2. Preparation of Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGOX)
2.3. Characterization of Graphene Oxide (GOX) and Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGOX)
2.4. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity Determination by Agar Well Diffusion Assay
2.6. Biofilm Inhibition Employing Fluorescence Microscopy
2.7. XTT Biofilm Assay
2.8. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy (UV-Vis) Analysis
3.2. Fourier Transforms Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis.
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
3.5. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration of GOX and RGOX against Bacterial and Fungal Isolates
3.6. Agar Diffusion Assay
3.7. Antibiofilm Activity Revealed by Fluorescence Microscopy by GOX and RGOX
3.8. XTT Assay Employing to Determine Anti-Biofilm Potential of GOX and RGOX
3.9. Cytotoxicity of GOX and RGOX Towards MCF-7 Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dibsdall, L.; Lambert, N.; Bobbin, R.; Frewer, L. Low-income consumers’ attitudes and behaviour towards access, availability and motivation to eat fruit and vegetables. Public Health Nutr. 2003, 6, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishangulyyev, R.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.H. Understanding food loss and waste—Why are we losing and wasting food? Foods 2019, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Somanathan, T.; Prasad, K.; Ostrikov, K.; Saravanan, A.; Krishna, V. Graphene Oxide Synthesis from Agro Waste. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, U.; Sagar, V.R. Quality characteristics of dehydrated leafy vegetables influenced by packaging materials and storage temperature. J. Sci. Ind. Res. (India) 2010, 69, 785–789. [Google Scholar]
- Laghari, A.H.; Memon, S.; Nelofar, A.; Khan, K.M.; Yasmin, A. Determination of free phenolic acids and antioxidant activity of methanolic extracts obtained from fruits and leaves of Chenopodium album. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Salimi, A.; Hallaj, R.; Fathi, F.; Soleimani, F. CuO/WO3 nanoparticles decorated graphene oxide nanosheets with enhanced peroxidase-like activity for electrochemical cancer cell detection and targeted therapeutics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M.K.; Thakur, M.; Bahadur, R.; Kaku, T.; Prabhuraj, R.S.; Ninawe, A.; Srivastava, R. Preparation of graphene oxide-graphene quantum dots hybrid and its application in cancer theranostics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños, K.; Kogan, M.J.; Araya, E. Capping gold nanoparticles with albumin to improve their biomedical properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6387–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Yin, J. Facile synthesis of soluble graphene via a green reduction of graphene oxide in tea solution and its biocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhao, F.; Li, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Low-toxic and safe nanomaterials by surface-chemical design, carbon nanotubes, fullerenes, metallofullerenes, and graphenes. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 362–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, E.S.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kwon, D.-N.; Kim, J.-H. Reduced graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle nanocomposite: A potential anticancer nanotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6257–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Mei, N. Assessment of the toxic potential of graphene family nanomaterials. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, J.; Peng, C.; Hu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Distribution and biocompatibility studies of graphene oxide in mice after intravenous administration. Carbon N. Y. 2011, 49, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.M.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Magalhães, F.D. Graphene-based materials biocompatibility: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.S.A.; Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K. Oxidative stress and antibacterial properties of a graphene oxide-cystamine nanohybrid. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAllister, M.J.; Li, J.-L.; Adamson, D.H.; Schniepp, H.C.; Abdala, A.A.; Liu, J.; Herrera-Alonso, M.; Milius, D.L.; Car, R.; Prud’homme, R.K.; et al. Single sheet functionalized graphene by oxidation and thermal expansion of graphite. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4396–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, A.; Pumera, M. Precise tuning of surface composition and electron-transfer properties of graphene oxide films through electroreduction. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 4748–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Han, G.; Chang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, H. Capacitive performances of reduced graphene oxide hydrogel prepared by using sodium hypophosphite as reducer. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon N. Y. 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Ruoff, R.S. Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, N.; Nagaraja, A.; Armesto, J.; Berry, V. High-throughput, ultrafast synthesis of solution-dispersed graphene via a facile hydride chemistry. Small 2010, 6, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, H.; Ahmed, M.S.; Cho, S.; Jeon, S. Simultaneous reduction and nitrogen functionalization of graphene oxide using lemon for metal-free oxygen reduction reaction. J. Power Sources 2017, 372, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosa, A.; Noori Jaafar, J. Green reduction of graphene oxide using tea leaves Extract with applications to lead Ions removal from water. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 7, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Vusa, C.S.R.; Berchmans, S.; Alwarappan, S. Facile and green synthesis of graphene. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 22470–22475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xia, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Gao, J. Graphene oxide reduced and modified by environmentally friendly glycylglycine and its excellent catalytic performance. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 135707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarod, M.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M. Green synthesis of a Cu/reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4 nanocomposite using Euphorbia wallichii leaf extract and its application as a recyclable and heterogeneous catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and rhodamine B. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 91532–91543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.F.; Nasar, A. Reduced graphene oxide/polypyrrole/nitrate reductase deposited glassy carbon electrode (GCE/RGO/PPy/NR): Biosensor for the detection of nitrate in wastewater. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, D.N.H.; Kabiri, S.; Losic, D. A green approach for the reduction of graphene oxide nanosheets using non-aromatic amino acids. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 76, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujeeb, A.A.; Khan, N.A.; Jamal, F.; Badre Alam, K.F.; Saeed, H.; Kazmi, S.; Alshameri, A.W.F.; Kashif, M.; Ghazi, I.; Owais, M. Olax scandens mediated biogenic synthesis of Ag-Cu nanocomposites: Potential against inhibition of drug-resistant microbes. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, S.N.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, L. Synthesis of graphene oxide (GO) by modified hummers method and its thermal reduction to obtain reduced graphene Oxide (rGO)*. Graphene 2017, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, L.A.; Kolter, R. Genetic analysis of Escherichia coli biofilm formation: Roles of flagella, motility, chemotaxis and type I pili. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, C.G.; Uppuluri, P.; Tristan, A.R.; Wormley, F.L.; Mowat, E.; Ramage, G.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. A simple and reproducible 96-well plate-based method for the formation of fungal biofilms and its application to antifungal susceptibility testing. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Xing, C.; Guo, M.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Gruber, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J. Sodium citrate: A universal reducing agent for reduction / decoration of graphene oxide with au nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Merino, M.J.; Guardia, L.; Paredes, J.I.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Solís-Fernández, P.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Vitamin C is an ideal substitute for hydrazine in the reduction of graphene oxide suspensions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6426–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, A.; Upadhayay, A. Chenopodium album Linn: Review of nutritive value and biological properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3977–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aunkor, M.T.H.; Mahbubul, I.M.; Saidur, R.; Metselaar, H.S.C. The green reduction of graphene oxide. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27807–27828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, P.; Zuo, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Preparation and characterization of a PMMA/Ce(OH)3, Pr2O3/graphite nanosheet composite. Polymer (Guildf) 2005, 46, 12670–12676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-L.; Wang, X.-F.; Qian, Q.-Y.; Wang, F.-B.; Xia, X.-H. A green approach to the synthesis of graphene nanosheets. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriary, L.; Athawale, A.A. Graphene oxide synthesized by using modified hummers approach. Int. J. Renew. Energy Environ. Eng. 2014, 2, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, J.I.; Villar-Rodi, S.; Martinez-Alonsa, A.; Tascon, J.M.D. Graphene oxide dispersion in organic solvents. Langmuirr 2008, 24, 10560–10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.; Siddiqui, S.W.A.; Siddiqui, Z.N. Efficient reduction of graphene oxide to graphene nanosheets using a silica-based ionic liquid: Synthesis, charcterisation and catalytic properties of IMD-Si/FeCl4-@GNS. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 4822–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, W.; An, J.; Kim, S.; Nah, J.; Yang, D.; Piner, R.; Velamakanni, A.; Jung, I.; Tutuc, E.; et al. Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science 2009, 324, 1312–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuila, B.K.; Zaeem, S.M.; Daripa, S.; Kaushik, K.; Gupta, S.K.; Das, S. Mesoporous Mn3O4 coated reduced graphene oxide for high-performance supercapacitor applications. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 015037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoulas, G.; Gold, H.S.; Venkataraman, L.; Moellering, R.C.; Ferraro, J.M.Y.; Eliopoulos, G.M. Introduction of erm (C) into a linezolid- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus does not restore linezolid susceptibility. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 1039–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, R.; Cola, B.A.; Haram, N.; Barisci, J.N.; Lee, S.; Stoughon, S.; Wallace, G.; Too, C.; Thomas, M.; Gestos, A.; et al. Harvesting waste thermal energy using a carbon-nanotube-based thermo-electrochemical cell. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Aburto, R.; Narayanan, T.N.; Nagaoka, Y.; Hasumura, T.; Mitcham, T.M.; Fukuda, T.; Cox, P.J.; Bouchard, R.R.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S.; et al. Fluorintead graphene oxide; a new multimodal material for biological application. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5632–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallabani, N.V.S.; Mittal, S.; Shukla, R.; Pandey, A.; Dhakate, S.; Pasricha, R.; Dhawan, A. Toxicity of graphene in normal human lung cells (BEAS-2B). J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.-H.; Lin, Y.-S.; Macosko, C.W.; Haynes, C.L. Cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and graphene in human erythrocytes and skin fibroblastas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2607–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammel, T.; Boisseaux, P.; Fernandez-Cruz, M.L.; Navas, J.M. Internalization and cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and carboxyl graphene nanoplatelets in the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line help G2. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajeshwari, R.; Prabu, H.G. Synthesis characterization, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities of ZnO nanorods on reduced graphene oxide. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2018, 28, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Wei, F.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y. Folic acid-conjugated graphene–ZnO nanohybrid for targeting photodynamic therapy under visible light irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, F.; Hammad Aziz, M.; Fakhar-e-Alam, M.; Atif, M.; Fatima, M.; Ahmad, R.; Hanif, A.; Anwar, S.; Zafar, F.; Abbas, G.; et al. An In Vitro Study of the photodynamic effectiveness of GO-Ag nanocomposites against human breast cancer cells. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








| Bacterial Strains | GOX | RGOX |
| S. aureus | 6.6 ± 2.0 | 8.6 ± 3.2 |
| E. coli | 6.3 ± 2 | 7.6 ± 2.0 |
| Fungal strain | GOX | RGOX |
| C. albicans | 1.4 ± 2.4 | 2.3 ± 2.09 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umar, M.F.; Ahmad, F.; Saeed, H.; Usmani, S.A.; Owais, M.; Rafatullah, M. Bio-Mediated Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles from Chenopodium album: Their Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061096
Umar MF, Ahmad F, Saeed H, Usmani SA, Owais M, Rafatullah M. Bio-Mediated Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles from Chenopodium album: Their Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061096
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmar, Mohammad Faisal, Faizan Ahmad, Haris Saeed, Saad Ali Usmani, Mohammad Owais, and Mohd Rafatullah. 2020. "Bio-Mediated Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles from Chenopodium album: Their Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061096
APA StyleUmar, M. F., Ahmad, F., Saeed, H., Usmani, S. A., Owais, M., & Rafatullah, M. (2020). Bio-Mediated Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles from Chenopodium album: Their Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061096