Influence of Polysaccharides’ Molecular Structure on the Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Green Synthesized Composites Based on Silver Nanoparticles and Carboxymethyl-Cellulose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
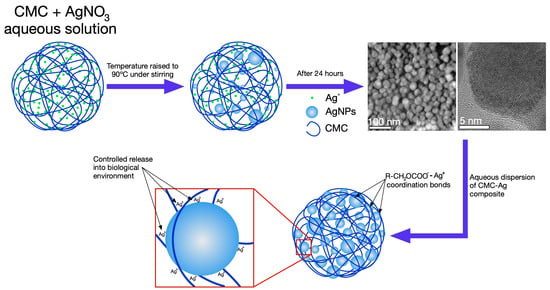
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CMC-AgNPs Composite
2.2. Antibacterial Assay
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological and Crystalline Features of CMC-AgNPs Composites
3.2. Spectroscopic Characterization
3.3. Antibacterial Activity
3.4. Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stathopoulou, M.-E.K.; Banti, C.N.; Kourkoumelis, N.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Kalampounias, A.G.; Hadjikakou, S.K. Silver complex of salicylic acid and its hydrogel-cream in wound healing chemotherapy. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 181, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prucek, R.; Tuček, J.; Kilianová, M.; Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Filip, J.; Kolář, M.; Tománková, K.; Zbořil, R. The targeted antibacterial and antifungal properties of magnetic nanocomposite of iron oxide and silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4704–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Donia, D.T.; Sabbatella, G.; Antiochia, R. Silver nanoparticles in polymeric matrices for fresh food packaging. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2016, 28, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farshchi, E.; Pirsa, S.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Alizadeh, M.; Rezazad, M. Photocatalytic/biodegradable film based on carboxymethyl cellulose, modified by gelatin and TiO2-Ag nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as antibacterial agent: Ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Tschulik, K.; Neumann, C.C.M.; Laborda, E.; Compton, R.G. Why are silver nanoparticles more toxic than bulk silver? Towards understanding the dissolution and toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Bapat, R.A.; Chaubal, T.V.; Joshi, C.P.; Bapat, P.R.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Gorain, B.; Kesharwani, P. An overview of application of silver nanoparticles for biomaterials in dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, M.C.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Kunzelman, S.; Hussain, S.M.; Varma, R.S. Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility of “green” synthesized silver nanoparticles using tea polyphenols. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid-ul-Islam; Butola, B.S.; Kumar, A. Green chemistry based in-situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles for multifunctional finishing of chitosan polysaccharide modified cellulosic textile substrate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, P.; Yaswant, G.; Kavitha, S.; Chandramohan, E.; Kowsalya, G.; Vijay, R.; Sudhagar, B.; Kumar, D.S.R.S. Preparation and characterization of hybrid chitosan-silver nanoparticles (Chi-Ag NPs); A potential antibacterial agent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Antibacterial activities of aliphatic polyester nanocomposites with silver nanoparticles and/or graphene oxide sheets. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Evtugyn, V.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Nanohydrogel formation within the halloysite lumen for triggered and sustained release. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8265–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basta, A.H.; El-Saied, H.; Hasanin, M.S.; El-Deftar, M.M. Green carboxymethyl cellulose-silver complex versus cellulose origins in biological activity applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, M.A.; Garza-Navarro, M.A.; Moreno-Cortez, I.E.; Lucio-Porto, R.; González-González, V.A. Silver/polysaccharide-based nanofibrous materials synthesized from green chemistry approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; Chakraborty, I.; Ghosh, S. Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose−CTAB Interaction: A detailed thermodynamic study of polymer−surfactant interaction with opposite charges. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9905–9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadagouda, M.N.; Varma, R.S. Synthesis of thermally stable carboxymethyl cellulose/metal biodegradable nanocomposites for potential biological applications. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2762–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Navarro, M.A.; Aguirre-Rosales, J.A.; Llanas-Vázquez, E.E.; Moreno-Cortez, I.E.; Torres-Castro, A.; González-González, V.A. Totally ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles from aqueous dissolutions of polysaccharides. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 2013, 436021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laredo-Naranjo, M.A.; Carrillo-Gonzalez, R.; De La Garza-Ramos, M.A.; Garza-Navarro, M.A.; Torre-Martinez, H.H.H.; Del Angel-Mosqueda, C.; Mercado-Hernandez, R.; Carrillo-Fuentevilla, R. Antimicrobial properties and dental pulp stem cell cytotoxicity using carboxymethyl cellulose-silver nanoparticles deposited on titanium plates. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Scand. 2016, 2, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemp, M.M.; Kumar, A.; Mousa, S.; Park, T.-J.; Ajayan, P.; Kubotera, N.; Mousa, S.A.; Linhardt, R.J. Synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles stabilized with glycosaminoglycans having distinctive biological activities. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Roberts, C.B. Stabilization of Fe−Pd nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for enhanced transport and dechlorination of trichloroethylene in soil and groundwater. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, F.; Gunn, T.M.; Zhao, D.; Roberts, C.B. Precise seed-mediated growth and size-controlled synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using a green chemistry approach. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7116–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, I.; Travan, A.; Pelillo, C.; Scarpa, T.; Coslovi, A.; Bonifacio, A.; Sergo, V.; Paoletti, S. Polyol synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of reduction by alditol bearing polysaccharides. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivleva, N.P.; Wagner, M.; Horn, H.; Niessner, R.; Haisch, C. In situ surface-enhanced Raman scattering analysis of biofilm. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8538–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H. Facile synthesis of carboxymethyl curdlan-capped silver nanoparticles and their application in SERS. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarska, K.; Grabowska, B.; Spychaj, T.; Zdanowicz, M.; Sitarz, M.; Bobrowski, A.; Cukrowicz, S. Effect of microwave treatment on structure of binders based on sodium carboxymethyl starch: FT-IR, FT-Raman and XRD investigations. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 199, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambjörnsson, H.A.; Schenzel, K.; Germgård, U. Carboxymethyl cellulose produced at different mercerization conditions and characterized by nir ft raman spectroscopy in combination with multivariate analytical methods. BioResources 2013, 8, 1918–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Schuck, P.J.; Nico, P.S.; Gilbert, B. Surface enhanced raman spectroscopy of organic molecules on magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alee, K.S.; Kuladeep, R.; Rao, D.N. In-situ investigation of the formation of silver nanoparticles in polyvinyl alcohol through micro-Raman spectroscopy. Opt. Commun. 2013, 293, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Ko, H.; Gunawidjaja, R.; Tsukruk, V.V. Raman markers from silver nanowire crossbars. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4387–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.; Shao, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jiao, W. Chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose-multilayered magnetic fluorescent systems for reversible protein immobilization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, A.A.P.; de Carvalho, F.G.; Mansur, R.L.; Carvalho, S.M.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Mansur, H.S. Carboxymethylcellulose/ZnCdS fluorescent quantum dot nanoconjugates for cancer cell bioimaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Ma, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mao, Z. The preparation and antibacterial effects of dopa-cotton/AgNPs. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 6799–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lv, M.; Deng, B.; Li, J.; Yu, M.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. Laundering durable antibacterial cotton fabrics grafted with pomegranate-shaped polymer wrapped in silver nanoparticle aggregations. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Ke, X.; Shen, L.; Ge, N.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, F.; Liu, X. Surface modification by carboxymethy chitosan via pad-dry-cure method for binding Ag NPs onto cotton fabric. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xie, L.; Diao, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, F.; Liu, X. Antibacterial cotton fabric with enhanced durability prepared using silver nanoparticles and carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Jones, A.M.; Garg, S.; Pham, A.N.; Waite, T.D. Silver nanoparticle−reactive oxygen species interactions: Application of a charging−discharging model. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 5461–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Arumugam, V.; Vasaviah, S.K. The MIC and MBC of silver nanoparticles against enterococcus faecalis a facultative anaerobe. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1000285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küp, F.Ö.; Çoşkunçay, S.; Duman, F. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Aesculus hippocastanum (horse chestnut): Evaluation of their antibacterial, antioxidant and drug release system activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipankar, C.; Murugan, S. The green synthesis, characterization and evaluation of the biological activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Iresine herbstii leaf aqueous extracts. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 98, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odabaş, M.E.; Çinar, Ç.; Akça, G.; Araz, İ.; Ulusu, T.; Yücel, H. Short-term antimicrobial properties of mineral trioxide aggregate with incorporated silver-zeolite. Dent. Traumatol. 2011, 27, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcântara, M.T.S.; Lincopan, N.; Santos, P.M.; Ramirez, P.A.; Brant, A.J.C.; Riella, H.G.; Lugão, A.B. Simultaneous hydrogel crosslinking and silver nanoparticle formation by using ionizing radiation to obtain antimicrobial hydrogels. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 165, 108369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, J.K.; Jafari, S.; Eghbal, M.A. A review of molecular mechanisms involved in toxicity of nanoparticles. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | AgNO3 Weight (mg) | [AgNO3] (mg/mL) | CMC Weight (mg) | [CMC] (mg/mL) | CMC/AgNO3 Weight Ratio | CMC/Ag Weight Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7Ag1 | 2.41 | 0.24 | 300 | 15.0 | 124.5 | 200.0 |
| 0.7Ag2 | 4.82 | 0.48 | 300 | 15.0 | 62.2 | 100.0 |
| 0.7Ag3 | 9.45 | 0.94 | 300 | 15.0 | 31.8 | 50.0 |
| 0.7Ag4 | 12.59 | 1.26 | 300 | 15.0 | 23.8 | 37.5 |
| 0.9Ag1 | 2.41 | 0.24 | 300 | 15.0 | 124.5 | 200.0 |
| 0.9Ag2 | 4.82 | 0.48 | 300 | 15.0 | 62.2 | 100.0 |
| 0.9Ag3 | 9.45 | 0.94 | 300 | 15.0 | 31.8 | 50.0 |
| 0.9Ag4 | 12.59 | 1.26 | 300 | 15.0 | 23.8 | 37.5 |
| 1.2Ag1 | 2.41 | 0.24 | 300 | 15.0 | 124.5 | 200.0 |
| 1.2Ag2 | 4.82 | 0.48 | 300 | 15.0 | 62.2 | 100.0 |
| 1.2Ag3 | 9.45 | 0.94 | 300 | 15.0 | 31.8 | 50.0 |
| 1.2Ag4 | 12.59 | 1.26 | 300 | 15.0 | 23.8 | 37.5 |
| Sample | Mean Particle Size (nm) | Standard Deviation (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.7Ag1 | 13.1 | 5.3 |
| 0.7Ag2 | 26.0 | 17.7 |
| 0.7Ag3 | 24.6 | 17.0 |
| 0.7 Ag4 | 10.6 | 5.1 |
| 0.9Ag1 | 32.6 | 8.9 |
| 0.9Ag2 | 28.8 | 14.0 |
| 0.9Ag3 | 28.3 | 16.4 |
| 0.9Ag4 | 44.1 | 28.8 |
| 1.2Ag1 | 11.0 | 4.0 |
| 1.2Ag2 | 20.4 | 7.1 |
| 1.2Ag3 | 22.3 | 11.1 |
| 1.2 Ag4 | 19.1 | 14.8 |
| Characterization Technique | Obtained Results |
|---|---|
| HAADF-STEM imaging and particle size measuring | The particle size distribution change according to the weight of AgNO3 added for the synthesis of nanoparticles, as well as the DS and Mw of CMC used as reducing agent and immobilization medium. The 1.2CMC reagent provides better control on particle size distribution than 0.7CMC and 0.9CMC reagents at the CMC/AgNO3 weight ratios used for samples preparation. |
| BF imaging | The synthesized nanoparticles depict a regular atomic arrangement with an interplanar spacing that is congruent with the family planes {111} of silver. |
| SAED patterns | The synthesized nanoparticles show diffraction rings related to family planes {111}, {220}, {220} and {311} of the face-centered cubic (FCC) packing of silver. |
| UV-vis spectroscopy | The UV-Vis spectra obtained from CMC-AgNPs composites show that there are no detectable traces related to Ag+ ions, suggesting full reduction of added Ag+ to Ag0. |
| ATR-FTIR spectroscopy | The ATR-FTIR spectra recorded from CMC-AgNPs composites suggest an interaction between CMC molecules and AgNPs, that could be attributed to the adsorption of R-CH2OCOO− groups onto nanoparticles. |
| Raman spectroscopy | The Raman spectra obtained from the selected samples confirms the adsorption of CMC chains onto nanoparticles and suggest the formation of a bond between Ag and O in the COO− moieties of CMC. |
| XPS spectroscopy | The XPS spectra measured from selected composites confirms that the silver in samples is only Ag0 and indicates that the AgNPs are immobilized into CMC by coordination bonds. Accordingly, these bonds are attributed to those Ag-O among AgNPs and COO− moieties of CMC. Hence, the key factor for the control of particle size distribution of synthesized AgNPs is the quantity of R-CH2OCOO− available for their immobilization. The quantity of these groups varies in direct proportion with the DS of CMC. |
| Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity assays | The antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of the tested samples increase by the use of CMC with higher DS as AgNPs immobilization medium. Therefore, the Ag-O coordination bonds among AgNPs and COO− moieties of CMC modify the ability of nanoparticles to produce and release Ag+ into aqueous dispersion, adjusting their antibacterial activity and the induction of cytotoxicity into the tested biological environments. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Rodríguez, M.d.l.Á.; Madla-Cruz, E.; Urrutia-Baca, V.H.; de la Garza-Ramos, M.A.; González-González, V.A.; Garza-Navarro, M.A. Influence of Polysaccharides’ Molecular Structure on the Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Green Synthesized Composites Based on Silver Nanoparticles and Carboxymethyl-Cellulose. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061164
Martínez-Rodríguez MdlÁ, Madla-Cruz E, Urrutia-Baca VH, de la Garza-Ramos MA, González-González VA, Garza-Navarro MA. Influence of Polysaccharides’ Molecular Structure on the Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Green Synthesized Composites Based on Silver Nanoparticles and Carboxymethyl-Cellulose. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061164
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Rodríguez, María de los Ángeles, Elizabeth Madla-Cruz, Victor H. Urrutia-Baca, Myriam A. de la Garza-Ramos, Virgilio A. González-González, and Marco A. Garza-Navarro. 2020. "Influence of Polysaccharides’ Molecular Structure on the Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Green Synthesized Composites Based on Silver Nanoparticles and Carboxymethyl-Cellulose" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061164
APA StyleMartínez-Rodríguez, M. d. l. Á., Madla-Cruz, E., Urrutia-Baca, V. H., de la Garza-Ramos, M. A., González-González, V. A., & Garza-Navarro, M. A. (2020). Influence of Polysaccharides’ Molecular Structure on the Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Green Synthesized Composites Based on Silver Nanoparticles and Carboxymethyl-Cellulose. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061164