Efficacy of Polymer-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Curcumin and Selected Anticancer Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Curcumin in Cancer Therapy
3. Nanocarriers for Combination Chemotherapy
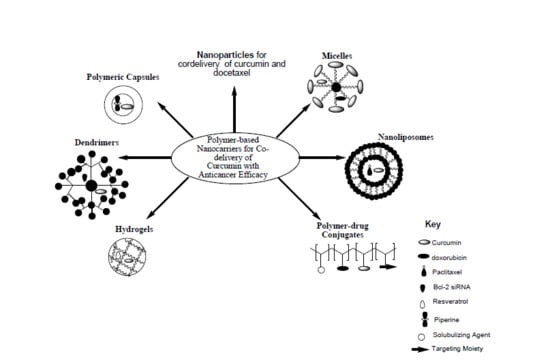
4. Polymer-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Curcumin with Anticancer Drugs
4.1. Polymeric Nanoparticles
4.2. Micelles
4.3. Nanoliposomes
4.4. Polymer-Drug Conjugates
4.5. Dendrimers
4.6. Hydrogels
4.7. Nanocapsules
4.8. Exosomes
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.; Sharma, B.; Kanwar, S.S.; Kumar, A. Lead Phytochemicals for Anticancer Drug Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aderibigbe, B.A.; Naki, T.; Steenkamp, V.; Nwamadi, M.; Ray, S.S.; Balogun, M.O.; Matshe, W.M.R. Physicochemical and in vitro evaluation of polymeric drugs for combination cancer therapy. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakde, D.; Jain, D.; Shrivastava, V.; Kakde, R.; Patil, A.T. Cancer Therapeutics-Opportunities, Challenges and Advances in Drug Delivery. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Chien, S. Chemotherapeutic engineering: Application and further development of chemical engineering principles for chemotherapy of cancer and other diseases. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 4087–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurgali, K.; Jagoe, R.T.; Abalo, R. Editorial: Adverse Effects of Cancer Chemotherapy: Anything New to Improve Tolerance and Reduce Sequelae? Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.; Arvin, A. Chemotherapy-Induced Immunosuppression. Environ. Health Perspect. 1982, 43, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Liu, K.; Shen, Q.; Li, Q.; Hao, J.; Han, F.; Jiang, R.-W. Reversal of multidrug resistance in cancer by multi-functional flavonoids. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug Resistance in Cancer: An Overview. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Lu, T.; Cao, S. Drug Combinations in Cancer Treatments Advances in Pharmacoepidemiology & Drug Safety. Adv. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Schizas, N.; Kazazis, C. “Potential Anticancer Properties and Mechanisms of Action of Curcumin”. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calzoni, E.; Cesaretti, A.; Polchi, A.; Di Michele, A.; Tancini, B.; Emiliani, C. Biocompatible Polymer Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications in Cancer and Neurodegenerative Disorder Therapies. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.; He, G.; Yin, Y.; He, M. Enzyme/pH dual-responsive polymer prodrug nanoparticles based on 10-hydroxycamptothecin-carboxymethylchitosan for enhanced drug stability and anticancer efficacy. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lee, R.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Yu, B. Anticancer activity of polymeric nanoparticles containing linoleic acid-SN38 (LA-SN38) conjugate in a murine model of colorectal cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, R.M.; Metwally, A.A.; El-ahmady, S.H.; Metwally, E.S.; Ghonim, N.A.; Bayoumy, S.A.; Erfan, T.; Ashraf, R.; Fadel, M.; El-kholy, A.I.; et al. Dual stimuli-responsive polypyrrole nanoparticles for anticancer therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 47, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baksi, R.; Pratap, D.; Borse, P.; Rana, R.; Sharma, V.; Nivsarkar, M. In vitro and in vivo anticancer efficacy potential of Quercetin loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, D.; Barenholz, Y. Optimization of vincristine—Topotecan combination—Paving the way for improved chemotherapy regimens by nanoliposomes. J. Control. Release 2010, 146, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, D.; Andriyanov, A.; Steiner, A.; Raviv, U.; Barenholz, Y. Characterization of PEGylated nanoliposomes co-remotely loaded with topotecan and vincristine: Relating structure and pharmacokinetics to therapeutic efficacy. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, E.; Allard-vannier, E.; Falanga, A.; Stiuso, P.; Teresa, M.; Galdiero, M.; Galdiero, S.; Chourpa, I. Quantitative and qualitative effect of gH625 on the nanoliposome-mediated delivery of mitoxantrone anticancer drug to HeLa cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 488, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochicchio, S.; Dapas, B.; Russo, I.; Ciacci, C.; Piazza, O.; Smedt, S.; Pottie, E.; Angela, A.; Grassi, G. In vitro and ex vivo delivery of tailored siRNA-nanoliposomes for E2F1 silencing as a potential therapy for colorectal cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, N.; Merrigan, S.; Turpin, J.; Lavoie, C.; Papavasiliou, V.; Geretti, E.; Espelin, C.W.; Luus, L.; Kamoun, W.S.; Ghasemi, O.; et al. Nanoliposome targeting in breast cancer is influenced by the tumor microenvironment. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 17, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timin, A.S.; Gould, D.J.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Multi-layer microcapsules: Fresh insights and new applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Yan, Y.; Such, G.K.; Liang, K.; Ochs, C.J.; Postma, A.; Caruso, F. Immobilization and Intracellular Delivery of an Anticancer Drug Using Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Capsules. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 2225–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trushina, D.B.; Akasov, R.A.; Khovankina, A.V.; Borodina, T.N.; Bukreeva, T.V.; Markvicheva, E.A. Doxorubicin-loaded biodegradable capsules: Temperature induced shrinking and study of cytotoxicity in vitro. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amgoth, C.; Dharmapuri, G. Synthesis and Characterization of Polymeric Nanoparticles and Capsules as Payload for Anticancer Drugs and Nanomedicines. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 3833–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yin, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, A.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, G.; Liao, W.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.Y. Dual pH/Redox-Responsive Mixed Polymeric Micelles for Anticancer Drug Delivery and Controlled Release. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hruby, M.; Svoboda, J.; Studenovsky, M.; Ve, D.; Ulbrich, K.; Kovár, J.; Kan, D. Polymer conjugates of acridine-type anticancer drugs with pH-controlled activation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4056–4063. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; Zhu, L. Enhancing cancer targeting and anticancer activity by a stimulus-sensitive multifunctional polymer-drug conjugate. J. Control. Release 2015, 212, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, J.; Miranda, A.; Nunes, S.; Cova, T.; Vitorino, C.; Pais, A. Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery Nanosystems for the Treatment of Brain Tumors. Gels 2018, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmanzadeh, D.; Ghaderi, M. A computational study of PAMAM dendrimer interaction with trans isomer of picoplatin anticancer drug. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2018, 80, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Z.; Ding, L.; Huang, A.Y.; Kao, K.; Peng, L. Poly(amidoamine) dendrimers: Covalent and supramolecular synthesis. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 13, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.P.; Pan, J.; Torchilin, V.P. Dendrimers as Nanocarriers for Nucleic Acid and Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2017, 22, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesharwani, P.; Choudhury, H.; Gopal, J.; Pandey, M.; Gorain, B. Dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles as promising nanocarriers for anticancer therapeutics and imaging. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 484–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drbohlavova, J.; Chomoucka, J.; Adam, V.; Ryvolova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Hubalek, J.; Kizek, R. Nanocarriers for Anticancer Drugs-New Trends in Nanomedicine. Curr. Drug Metab. 2013, 14, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilia, A.R.; Isacchi, B.; Righeschi, C.; Guccione, C.; Bergonzi, M.C. Flavoids loaded in nanocarries: An opportunity to increase oral bioavailibity and bioefficacy. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 1212–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Mhlwatika, Z.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Polymeric Nanocarriers for the Delivery of Antimalarials. Molecules 2018, 23, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomeh, M.A.; Hadianamrei, R.; Zhao, X. A Review of Curcumin and Its Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koohpar, Z.K.; Entezari, M.; Movafagh, A.; Hashemi, M. Anticancer Activity of Curcumin on Human Breast Adenocarcinoma: Role of Mcl-1 Gene. Iran. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 8, e2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasr, M.; Awadallah, A.; Al-karaki, R.; Madanat, F.; Alsunna, L.; Sami, K.; Ibrahim, Z.; Makhlouf, O.; Almajali, R. Exploring the unique anticancer properties of curcumin nanoparticles. Clin. Oncol. Res. 2019, 2, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Her, C.; Venier-Julienne, M.-C.; Roger, E. Improvement of Curcumin Bioavailability for Medical Applications. Med. Aromat. Plants 2018, 7, 1000326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutkova, J.; Chorvat, D.; Miskovsky, P.; Jancura, D.; Datta, S. Encapsulation of anticancer drug curcumin and co-loading with photosensitizer hypericin into lipoproteins investigated by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howells, L.M.; Iwuji, C.O.; Irving, G.R.; Barber, S.; Walter, H.; Sidat, Z.; Griffin-Teall, N.; Singh, R.; Foreman, N.; Patel, S.R.; et al. Curcumin Combined with FOLFOX Chemotherapy Is Safe and Tolerable in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in a Randomized Phase IIa Trial. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanai, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Asada, M.; Imaizumi, A.; Suzuki, C.; Matsumoto, S.; Nishimura, T.; Mori, Y.; Masui, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; et al. A phase I/II study of gemcitabine-based chemotherapy plus curcumin for patients with gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayet-Robert, M.; Kwiatowski, F.; Leheurteur, M.; Gachon, F.; Planchat, E.; Abrial, C.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Durando, X.; Barthomeuf, C.; Chollet, P. Phase I dose escalation trial of docetaxel plus curcumin in patients with advanced and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghalaut, V.S.; Sangwan, L.; Dahiya, K.; Ghalaut, P.S.; Dhankhar, R.; Saharan, R. Effect of imatinib therapy with and without turmeric powder on nitric oxide levels in chronic myeloid leukemia. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2012, 18, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahammedi, H.; Planchat, E.; Pouget, M.; Durando, X.; Curé, H.; Guy, L.; Van-Praagh, I.; Savareux, L.; Atger, M.; Bayet-Robert, M.; et al. The new combination docetaxel, prednisone and curcumin in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer: A pilot phase II study. Oncology 2016, 90, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorelli, D.; Fabricio, A.S.; Giovanis, P.; D’Ippolito, S.; Fiduccia, P.; Soldà, C.; Buda, A.; Sperti, C.; Bardini, R.; Da Dalt, G.; et al. Phytosome complex of curcumin as complementary therapy of advanced pancreatic cancer improves safety and efficacy of gemcitabine: Results of a prospective phase II trial. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 132, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Yang, T.S.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, H.H.; Chiang, H.C.; Lin, T.C.; Yeh, C.H.; Ke, T.W.; Chen, J.S.; Hsiao, K.H.; et al. Effectiveness of a novel herbal agent MB-6 as a potential adjunct to 5-fluoracil–based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, Y.; Saadat, A.; Beiraghdar, F.; Sahebkar, A. Adjuvant therapy with bioavailability-boosted curcuminoids suppresses systemic inflammation and improves quality of life in patients with solid tumors: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.L.; Heckler, C.E.; Ling, M.; Katz, A.; Williams, J.P.; Pentland, A.P.; Morrow, G.R. Curcumin for radiation dermatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of thirty breast cancer patients. Radiat. Res. 2013, 180, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esfahani, K.; Boodaghians, L.; Kasymjanova, G.; Agulnik, J.S.; Pepe, C.; Sakr, L.; Small, D.I.; Jagoe, T.R.; Cohen, V. A phase I open prospective cohort trial of curcumin plus tyrosine kinase inhibitors for EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, M.; Otsuka, Y.; Otsuka, K.; Sato, M.; Nishimura, T.; Mori, Y.; Kawaguchi, M.; Hatano, E.; Kodama, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. A phase I study investigating the safety and pharmacokinetics of highly bioavailable curcumin (Theracurmin®) in cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.G.; Veena, M.S.; Basak, S.K.; Han, E.; Tajima, T.; Gjertson, D.W.; Starr, J.; Eidelman, O.; Pollard, H.B.; Srivastava, M.; et al. Curcumin treatment suppresses IKKβ kinase activity of salivary cells of patients with head and neck cancer: A pilot study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5953–5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ide, H.; Tokiwa, S.; Sakamaki, K.; Nishio, K.; Isotani, S.; Muto, S.; Hama, T.; Masuda, H.; Horie, S. Combined inhibitory effects of soy isoflavones and curcumin on the production of prostate-specific antigen. Prostate 2010, 70, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Shi, C.B.; Wen, H.; Li, F.L.; Wang, B.L.; Wang, J. Upregulation of p53 expression in patients with colorectal cancer by administration of curcumin. Cancer Invest. 2011, 29, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.; Dutta, S.; Begum, R.; Mittal, S.; Dutta, P.D.; Bharti, A.C.; Panda, C.K.; Biswas, J.; Dey, B.; Talwar, G.P.; et al. Clearance of cervical human papillomavirus infection by topical application of curcumin and curcumin containing polyherbal cream: A phase II randomized controlled study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5753–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ora-Curcumin Formulation on its Way to Health Product Market. Available online: https://www.newswise.com/articles/ora-curcumin-formulation-on-its-way-to-health-product-market (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Rationalizing combination therapies. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1113. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4426 (accessed on 5 March 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Filipczak, N.; Torchilin, V.P. Polymeric Co-delivery systems in cancer treatment: An overview on component drugs’ dosage ratio effect. Molecules 2019, 24, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahira, S.; Kommineni, N.; Husain, G.M.; Khan, W. Cabazitaxel and silibinin co-encapsulated cationic liposomes for CD44 targeted delivery: A new insight into nanomedicine based combinational chemotherapy for prostate cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Gao, Z.; Huang, W.; Jin, M.; Wang, Q. Nanocarrier-mediated co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and gene agents for cancer treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unsoy, G.; Gunduz, U. Smart Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailaja, A.K.; Amareshwar, P.; Chakravarty, P. Different Technique Used for the Preparation of Nanoparticles Using Natural Polymers and Their Application. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, E.; Peoples, V.A.; Johnson, F.; Bibbs, R.K.; Topps, D.; Bopda-Waffo, A.; Coats, M.T. Utilizing Nanotechnology to Combat Malaria. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2015, 3, 1000229. [Google Scholar]
- Crucho, C.I.C.; Barros, M.T. Polymeric nanoparticles: A study on the preparation variables and characterization methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 80, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawahar, N.; Baruah, U.K.; Singh, V. Co-delivery of chloroquine phosphate and azithromycin nanoparticles to overcome drug resistance in malaria through intracellular targeting. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 11, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Shi, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Mingyuen, S.; Wang, Y.; Leong, K.W.; Chen, M. pH-sensitive polymeric nanoparticles for co-delivery of doxorubicin and curcumin to treat cancer via enhanced pro-apoptotic and anti- angiogenic activities. Acta Biomater. 2017, 58, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Tian, C. Targeted nanomedicine for prostate cancer therapy: Docetaxel and curcumin co-encapsulated lipid—polymer hybrid nanoparticles for the enhanced anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ge, X.; Wang, L. Construction and comparison of different nanocarriers for co-delivery of cisplatin and curcumin: A synergistic combination nanotherapy for cervical cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cai, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Fan, K.; Liu, Z.; et al. PEGylated Lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for co- delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin: Design, characterization and its cytotoxic effect. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Zhao, P.; Li, M.; Fan, T.; Yan, R.; Lu, Y.; Lee, R.J.; et al. Platinum complexes of curcumin delivered by dual-responsive polymeric nanoparticles improve chemotherapeutic efficacy based on the enhanced anti-metastasis activity and reduce side effects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi-attari, J.; Pilehvar-soltanahmadi, Y.; Dadashpour, M.; Alipour, S.; Farajzadeh, R.; Javidfar, S. Co-Delivery of Curcumin and Chrysin by Polymeric Nanoparticles Inhibit Synergistically Growth and hTERT Gene Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medel, S.; Syrova, Z.; Kovacik, L.; Hrdy, J.; Hornacek, M.; Jager, E.; Hruby, M.; Lund, R.; Cmarko, D.; Stepanek, P.; et al. Curcumin-bortezomib loaded polymeric nanoparticles for synergistic cancer therapy. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 93, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immix Doses First Patient in US in its Phase 1b/2a Trial in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours. Available online: https://pharmaceutical-business-review.com/news/immix-doses-first-patient-in-us-in-its-phase-1b-2a-trial-in-patients-with-advanced-solid-tumours/ (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Curcumin/Doxorubicin-Encapsulating Nanoparticle IMX-110. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-drug/def/794327 (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Bisht, S.; Feldmann, G.; Soni, S.; Ravi, R.; Karikar, C.; Maitra, A.; Maitra, A. Polymeric nanoparticle-encapsulated curcumin ("nanocurcumin"): A novel strategy for human cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2007, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, S.S.; Lui, E.; Majeed, M.; Vishwanatha, J.K.; Ranjan, A.P.; Maitra, A.; Pramanik, D.; Smith, J.A.; Helson, L. Differential distribution of intravenous curcumin formulations in the rat brain. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 907–911. [Google Scholar]
- Bisht, S.; Mizuma, M.; Feldmann, G.; Ottenhof, N.A.; Hong, S.M.; Pramanik, D.; Chenna, V.; Karikari, C.; Sharma, R.; Goggins, M.G.; et al. Systemic administration of polymeric nanoparticle-encapsulated curcumin (NanoCurc) blocks tumor growth and metastases in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starov, V.; Zhdanov, V.; Kovalchuk, N. Kinetic models of micelles formation. J. Colloids Surf. 2010, 354, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danafar, H.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Davaran, S.; Hamidi, M. Drug-conjugated PLA–PEG–PLA copolymers: A novel approach for controlled delivery of hydrophilic drugs by micelle formation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseini, G.A.; Pitt, W.G. Micelles and Nanoparticles for Ultrasonic Drug and Gene Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1137–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Guo, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Tu, P. Co-assembly of doxorubicin and curcumin targeted micelles for synergistic delivery and improving anti-tumor efficacy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 112, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, N.; Cheng, R.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Tian, Z. pH multistage responsive micellar system with charge-switch and PEG layer detachment for co-delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin to synergistically eliminate breast cancer stem cells. Biomaterials 2017, 147, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, W.; De Souza, P.; Stenzel, M.H. Dual-drug delivery of curucmin and platinum drugs in polymeric micelles enhances the synergistic effects: A double act for the treatment of multidrug-resistanr cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocher, A.; Schiborr, C.; Behnam, D.; Frank, J. The oral bioavailability of curcuminoids in healthy humans is markedly enhanced by micellar solubilisation but not further improved by simultaneous ingestion of sesamin, ferulic acid, naringenin and xanthohumol. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danaei, M.; Kalantari, M.; Raji, M.; Samareh, F.H.; Saber, R.; Asnani, G.P.; Mortazavi, S.M.; Mozafari, M.R.; Rasti, B.; Taheriazam, A. Probing nanoliposomes using single particle analytical techniques: Effect of excipients, solvents, phase transition and zeta potential. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi-Darani, K.; Mozafari, M. Nanoliposome Potentials in Nanotherapy: A Concise Overview. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Shade, C.W. Liposomes as advanced delivery systems for nutraceuticals. Integr. Med. 2016, 15, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttala, H.B.; Ko, Y.T. Biointerfaces Liposomal co-delivery of curcumin and albumin/paclitaxel nanoparticle for enhanced synergistic antitumor efficacy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barui, S.; Saha, S.; Mondal, G.; Haseena, S.; Chaudhuri, A. Simultaneous delivery of doxorubicin and curcumin encapsulated in liposomes of pegylated RGDK-lipopeptide to tumor vasculature. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storka, A.; Vcelar, B.; Klickovic, U.; Gouya, G.; Weisshaar, S.; Aschauer, S.; Bolger, G.; Helson, L.; Woltz, M. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of liposomal curcumin (Lipocurc™) in healthy humans. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 53, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, G.T.; Licollari, A.; Tan, A.; Greil, R.; Vcelar, B.; Greil-Ressler, S.; Weiss, L.; Schönlieb, C.; Magnes, T.; Radl, B.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of liposomal curcumin (Lipocurc™) infusion: Effect of co-medication in cancer patients and comparison with healthy individuals. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 83, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringsdorf, R. Structure and properties of pharmacologically active polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Smposia 1975, 5, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alven, S.; Aderibigbe, B.A.; Balogun, M.O.; Matshe, W.M.R.; Ray, S.S. Polymer-drug conjugates containing antimalarial drugs and antibiotics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Maniscalco, L.; Giammona, G.; Civiale, C.; Mazzone, M.G.; Enea, V. Chemical conjugation of dexamethasone to a polyaspartamide and in vitro evaluation studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2004, 14, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, N.; Ghandehari, H. Polymeric conjugates for drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2012, 13, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Q.; Tong, R. Anticancer nanoparticulate polymer-drug conjugates for Anti-cancer Drug Delivery. Bioengen. Trans. Med. 2016, 1, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderibigbe, B.A.; Sadiku, E.R.; Ray, S.S.; Mbianda, X.Y.; Fotsing, M.C.; Agwuncha, S.C.; Owonubi, S.J. Synthesis and characterization of polyamidoamine conjugates of neridronic acid. Polym. Bull. 2015, 72, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasini, N.; Haque, S.; Kaminskas, L.M. Polymer-drug conjugates as inhalable drug delivery systems: A review. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 31, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dragojevic, S.; Ryu, J.S.; Raucher, D. Polymer-Based Prodrugs: Improving Tumor Targeting and the Solubility of Small Molecule Drugs in Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2015, 20, 21750–21769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Yadav, T.; Sharma, S.; Nayak, A.; Kumari, A. Polymers in Drug Delivery. J. Biosci. Med. 2016, 4, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Zou, S.; Guo, C.; Wang, K.; Zhao, F.; Fan, H.; Yin, J.; Chen, D. Multifunctional redox-responsive and CD44 receptor targeting polymer-drug nanomedicine based curcumin and alendronate: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S168–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Huang, F.; Chu, L.; Gao, H.; Li, C.; Kong, D.; et al. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and curcumin by pH-sensitive prodrug nanoparticle for combination therapy of cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Che, S.; Hui, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qiang, Y.; Ma, H. Lung cancer therapy using doxorubicin and curcumin combination: Targeted prodrug based, pH sensitive nanomedicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Kanamoto, T.; Nakashima, H.; Yoshida, T. Synthesis of a new amphiphilic glycodendrimer with antiviral functionality. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjwade, B.K.; Bechra, H.M.; Derkar, G.K.; Manvi, F.V.; Nanjwade, V.K. Dendrimers: Emerging polymers for drug-delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqil, F.; Munagala, R.; Jeyabalan, J.; Vadhanam, M.V. Bioavailability of phytochemicals and its enhancement by drug delivery systems. Cancer Lett. 2013, 334, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghaffari, M.; Dehghan, G.; Baradaran, B.; Zarebkohan, A.; Mansoori, B.; Soleymani, J.; Ezzati, J.; Dolatabadi, N.; Hambiln, M.R. Co-delivery of curcumin and Bcl-2 siRNA by PAMAM dendrimers for enhancement of the therapeutic e ffi cacy in HeLa cancer cells. Col. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alven, S.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Combination Therapy Strategies for the Treatment. Molecules 2019, 24, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopecek, J. Hydrogel biomaterials: A smart future? Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5185–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultana, F.; Manirujjaman, M.; Imran-Ul-Haque, M.A.; Sharmin, S. An overview of nanogel drug delivery system. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Selvamuthukumar, S.; Kilimozhi, D. Cyclodextrin nanosponge based hydrogel for the transdermal co-delivery of curcumin and resveratrol: Development, optimization, in vitro and ex vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothamasu, P.; Kanumur, H.; Ravur, N.; Maddu, C.; Parasuramrajam, R.; Thangavel, S. Nanocapsules: The Weapons for Novel Drug Delivery Systems. BioImpacts 2012, 2, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ariga, K.; Lvov, Y.M.; Kawakami, K.; Ji, Q.; Hill, J.P. Layer-by-layer self-assembled shells for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Hemant, K.; Ram, M.; Shivakumar, H. Microencapsulation: A promising technique for controlled drug delivery. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Velasques, K.; Maciel, T.R.; Forno, H.A.; Helena, C.D.; Teixeira, F.E.G.; Fonseca, A.L.F.; Varotti, F.P.; Fajaro, A.R.; Avila, D.S.; Haas, S.E. Co-nanoencapsulation of antimalarial drugs increases their in vitro efficacy against Plasmodium falciparum and decreases their toxicity to Caenorhabditis elegans. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 118, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slika, L.; Moubarak, A.; Borjac, J.; Baydoun, E.; Patra, D. Preparation of curcumin-poly (allyl amine) hydrochloride based nanocapsules: Piperine in nanocapsules accelerates encapsulation and release of curcumin and effectiveness against colon cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 4, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andaloussi, S.E.L.; Mäger, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J.A. Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Deliv. 2013, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Xu, Q. Functions and applications of exosomes. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2014, 71, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, X.; Sansanaphongpricha, K.; Myers, I.; Chen, H.; Yuan, H.; Sun, D. Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.S.; Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Mahajan, V.; Deygen, I.; Klyachko, N.L.; Inskoe, E.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Okolie, O.; et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hood, J.L. Post isolation modification of exosomes for nanomedicine applications. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haney, M.J.; Klyachko, N.L.; Zhao, Y.; Gupta, R.; Plotnikova, E.G.; He, Z.; Patel, T.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V.; et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J. Control. Release 2015, 207, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Zhuang, X.; Xiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Barnes, S.; Grizzle, W.; Miller, D.; Zhang, H.G. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: The anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Han, Y.; An, Y.; Ding, Y.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Tang, Q. NRP-1 targeted and cargo-loaded exosomes facilitate simultaneous imaging and therapy of glioma in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2018, 178, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqil, F.; Munagala, R.; Jeyabalan, J.; Agrawal, A.K.; Gupta, R. Exosomes for the enhanced tissue bioavailability and efficacy of curcumin. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Study Investigating the Ability of Plant Exosomes to Deliver Curcumin to Normal and Colon Cancer Tissue. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01294072 (accessed on 5 March 2020).









| Types of Cancer | Drugs Administration | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metastatic colorectal cancer | 2 g of curcumin plus folinic acid/fluorouracil/oxaliplatin | CXCL1 was not altered over time significantly. The combination was safe and tolerable for the patients | [43] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Combination of curcumin 8 g with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. | The median survival time after the administration of curcumin was 161 days with 1-year survival rate. The plasma curcumin levels in 5 patients were in the range of 29 to 412 ng/mL. The combination was found to be was safe. | [44] |
| Metastatic breast cancer | Combination of 100 mg per day of docetaxel intravenously and curcumin 6000 mg per day orally | The combination was safe and tolerable. | [45] |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | Combination of turmeric powder with imatinib | The levels of nitric oxide were significantly decreased. | [46] |
| Chemotherapy-naive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer | Combination of docetaxel with curcumin 6000 mg/d. | The combination did not result in any adverse effect and it was well tolerated by the patients. | [47] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Combination of curcumin formulation (Meriva®) with gemcitabine. | The median progression free survival and overall survival were 8.4 and 10.2 months, respectively. The combination was safe and can translate into a good response rate in first line therapy of advanced pancreatic cancer. | [48] |
| Metastatic colorectal cancer | MB-6 (composed of fermented soybean extract, green tea extract, Antrodia camphorata mycelia, spirulina, grape seed extract, and curcumin extract) with leucovorin/5-fluorouracil/oxaliplatin | The patients displayed a significant lower rate of disease progression and incidence of adverse events. | [49] |
| Solid tumors | Curcuminoids 180 mg/day in combination with 5-fluoracil–based chemotherapy. | The combination resulted in a significant improvement in health-related quality of life when compared to the placebo (p < 0.001). The magnitude of reductions in the mediators implicated in systemic inflammation were significant. | [50] |
| Radiation dermatitis in breast cancer | 6 g of curcumin per day plus radiotherapy | A reduced severity of radiation dermatitis in breast cancer patients. | [51] |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | Curcumin formulation (CURCUVivaTM) at 80 mg/1 capsule daily in combination with tyrosane kinase inhibitors (TKIs), (gefitinib and erlotinib) | The short-term use of curcumin in combination with EGFR-positive patients treated with TKIs was safe | [52] |
| Pancreatic or biliary tract cancer | Curcumin formulation (400 mg), (Theracurmin®) combination with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. | No adverse effects were observed in all the patients. The repetitive administration of a high dosage of curcumin did not increase the incidence of adverse effects in cancer patients receiving curcumin together with the gemcitabine-based chemotherapy | [53] |
| Squamous cell carcinoma cancer | Curcumin | It inhibits IkB kinase b (IKKb) activity in the saliva of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer patients thereby suppressing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. | [54] |
| Prostate cancer | Curcumin and isoflavones | The combination reduced the level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA). | [55] |
| Colorectal cancer | Curcumin | Increased body weight and reduced serum TNF-alpha levels, increased apoptotic tumor cells, and enhanced expression of p53 molecule in tumor tissue. Improved general health of patients. | [56] |
| Cervical cancer | Curcumin cream formulation (Basant™ containing curcumin extract, amla, aloe vera, reetha) administered via intravaginal route | The HPV clearance rate in Basant cream was significant with (87.7%) with no serious adverse effects. | [57] |
| Nanocarrier | Polymers Used | Drugs Loaded/Incorporated | Cancer Cell Lines Used | Therapeutic Outcomes | Route of Administration In Vivo | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticle | poly(β-amino ester) | Curcumin and doxorubicin | umbilical vein endothelial cancer cell lines (HUVECs) and human liver cancer cell lines (SMMC 7721) | The high cytotoxicity effect of co-encapsulation of doxorubicin and curcumin in polymeric nanoparticles and improved cellular uptake. | - | [68] |
| Nanoparticle | PLGA | Curcumin and docetaxel | Human prostate carcinoma cells (PC3 cells). | In vivo studies using mice-bearing PC3 tumor xenografts showed that the hybrid nanoparticles inhibited tumor growth without causing any severe side effects | Subcutaneous administration | [69] |
| Nanoparticles | PLGA | Curcumin and cisplatin | Cervical cancer | The accumulation of the drug-loaded formulation was enhanced in the tumor tissue when compared to the free drugs. | Subcutaneous administration | [70] |
| Nanoparticles | Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG)-lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles | Curcumin and paclitaxel | Breast cancer cell lines | Controlled and sustained drug release profiles from the nanoparticles. | - | [71] |
| Nanoparticles | mPEG-PLGA | Curcumin and cisplatin | A549 cancer cells | The nanoparticles exhibited high cytotoxicity which was 4-fold effective in cell growth inhibition when compared to the free curcumin on the A549 cancer cells | - | [72] |
| Nanoparticles | PEGylated PLGA | Curcumin and chrysin | Caco-2 Colorectal cancer | A significant synergistic antiproliferative outcome when compared to the free drugs | - | [73] |
| Nanoparticles | methoxy-poly(ethylene glycol)-block-polylactic acid (mPEG-b-PLA)-b c | Curcumin and bortezomib | MCF-7, HeLa, and MDA-MB 231 cancer cells | Significant cytotoxic effects of the nanoparticles loaded with drugs when compared to the free drugs | - | [74] |
| Micelles | Hyaluronic acid-vitamin E succinate graft copolymer | Doxorubicin and curcumin | Lung and breast cancer | Reduced the cardiotoxic and hepatoxic effect of doxorubicin. Enhanced the cytotoxic effects of the drug loaded micelles | Intravenous administration | [83] |
| Micelles | poly(ethylene glycol)-benzoic imine-poly(g-benzyl-L-aspartate)-b-poly(1-vinylimidazole) block copolymer | curcumin and paclitaxel | Breast cancer MCF-7 | Inhibition of tumor growth without any significant recurrence | Subcutaneous administration | [84] |
| Micelles | PEG and polycaprolactone | Curcumin and oxoplatin | A2780 human ovarian cancer cell lines | Cytotoxic effect of the encapsulated drug increased when compared to the free drugs | - | [85] |
| Nanoliposomes | PEG | Curcumin and paclitaxel | MCF-7 and B16F10 | Sustained drug release profile and high cytotoxic effect of the drug-loaded nanoliposomes in vitro | - | [90] |
| Liposomes | Pegylated RGDK-lipopeptide | Curcumin and doxorubicin | B16F10 tumors and HUVEC cancer cell line | The survival rate of the tumor bearing mice was high revealing the efficacy of curcumin in alleviating the adverse side effects of doxorubicin. Enhanced accumulation of doxorubicin in the tumor vasculature. | Intravenously | [91] |
| Polymer-drug conjugates | Hyaluronan | Curcumin and alendronate | Breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) | The uptake and cytotoxic effect of the nanocarriers were higher in MDA-MB-231 cells when compared to MCF-7 cells | - | [103] |
| Polymer-drug conjugates | PEG | Curcumin and doxorubicin | HepG 2 cancer cells | The dual drug-loaded polymeric conjugates displayed a higher anti-tumor efficacy against HepG 2 and HeLa cancer cells when compared to the free drug. | - | [104] |
| Polymer-drug conjugates | poly(L-histidine) and U11 peptide | Curcumin and doxorubicin | A549 Lung cancer | Decorated nanocarriers showed improved inhibition of the tumor growth in vivo. | Subcutaneous administration | [105] |
| Dendrimers | Polyamidoamine | Curcumin and siRNA | HeLa cancer cell | The in vitro cellular uptake of the co-loaded dendrimers into HeLa cells was high. | - | [109] |
| Hydrogel | Cyclodextrin | Curcumin and resveratrol | MCF-7 Breast cancer | A cytotoxic synergistic effect on the MCF-7 breast cancer cells with a combination index value of 0.29 | [113] | |
| Nanocapsules | Poly (allyl amine) hydrochloride | Curcumin and piperine | Caco-2-cancer cell lines | Significant cytotoxic effects. | Intraperitoneal administration | [118] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alven, S.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Efficacy of Polymer-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Curcumin and Selected Anticancer Drugs. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081556
Alven S, Aderibigbe BA. Efficacy of Polymer-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Curcumin and Selected Anticancer Drugs. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(8):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081556
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlven, Sibusiso, and Blessing Atim Aderibigbe. 2020. "Efficacy of Polymer-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Curcumin and Selected Anticancer Drugs" Nanomaterials 10, no. 8: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081556
APA StyleAlven, S., & Aderibigbe, B. A. (2020). Efficacy of Polymer-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Curcumin and Selected Anticancer Drugs. Nanomaterials, 10(8), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081556