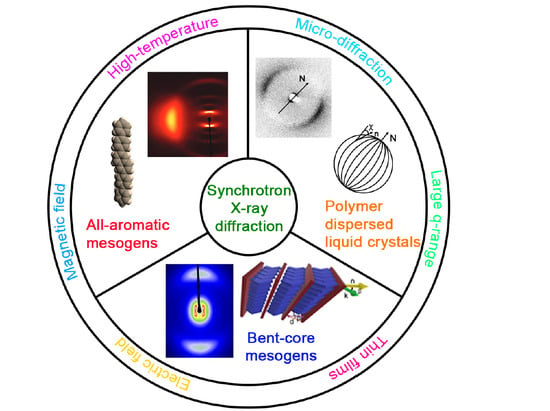
Nanostructure of Unconventional Liquid Crystals Investigated by Synchrotron Radiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bent-Core Mesogens
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Cybotactic Order
2.3. Ferroelectric Switching
2.4. Ferroelectric Switching in Liquid Crystal Polymers Based on Bent-Core Mesogens
2.5. Field-Induced Phase Transitions
2.6. Local Biaxial Order
3. All-Aromatic Liquid Crystals
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Positional Order
3.3. Orientational Order
4. Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystals
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Materials and Methods
4.3. Single Droplet Director Configuration
4.4. Droplet Order Parameter
4.5. Molecular Director Map
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, R.A.L. Soft Condensed Matter; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- de Gennes, P.G.; Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Takezoe, H.; Takanishi, Y. Bent-core liquid crystals: Their mysterious and attractive world. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 597–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelzl, G.; Diele, S.; Weissflog, W. Banana-shaped compounds—A new field of liquid crystals. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jákli, A. Liquid crystals of the twenty-first century—Nematic phase of bent-core molecules. Liq. Cryst. Rev. 2013, 1, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, F.; Adamo, F.C.; Francescangeli, O. Polar order in bent-core nematics: An overview. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 267, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C.; Photinos, D.J. Biaxial nematic phases. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4263–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, F. Search for nematic biaxiality in bent-core mesogens: An X-ray diffraction perspective. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 43, 2254–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, O.; Torgova, S.I.; Karamysheva, L.; Geivandova, T.; Strigazzi, A.; Stanic, V.; Ferrero, C.; Dolbnya, I. X-ray diffraction study of new banana-shaped 1,2,4-oxadiazoles. In Proceedings of the Book of Abstracts of the 19th International Liquid Crystal Conference, Edinburgh, UK, 30 June–5 July 2002; p. 137. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, P.B.J.; Bouchenoire, L.; Brown, S.D.; Mannix, D.; Paul, D.F.; Lucas, C.; Kervin, J.; Cooper, M.J.; Arakawa, P.; Laughon, G. New developments at the XMaS beamline for magnetic and high resolution diffraction. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–29 August 2003; Volume 705, pp. 428–431. [Google Scholar]
- Francescangeli, O.; Stanic, V.; Torgova, S.I.; Strigazzi, A.; Scaramuzza, N.; Ferrero, C.; Dolbnya, I.P.; Weiss, T.M.; Berardi, R.; Muccioli, L.; et al. Ferroelectric response and induced biaxiality in the nematic phase of bent-core mesogens. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.R.; Primak, A.; Kumar, S. Biaxial nematic phase in bent-core thermotropic mesogens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 145506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acharya, B.R.; Kang, S.W.; Prasad, V.; Kumar, S. Role of molecular structure on x-ray diffraction in uniaxial and biaxial phases of thermotropic liquid crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 3845–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, O.; Samulski, E.T. Insights into the cybotactic nematic phase of bent-core molecules. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, O.; Vita, F.; Ferrero, C.; Dingemans, T.; Samulski, E.T. Cybotaxis dominates the nematic phase of bent-core mesogens: A small-angle diffuse X-ray diffraction study. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, O.; Vita, F.; Samulski, E.T. The cybotactic nematic phase of bent-core mesogens: State of the art and future developments. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 7685–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubb, D.; Murthy, N.S.; Francescangeli, O. Elliptical small-angle X-ray scattering patterns from aligned lamellar arrays. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samulski, E.T. Meta-cybotaxis and nematic biaxiality. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 37, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemans, T.J.; Madsen, L.A.; Francescangeli, O.; Vita, F.; Photinos, D.J.; Poon, C.D.; Samulski, E.T. The biaxial nematic phase of oxadiazole biphenol mesogens. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 40, 1655–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, V. Dynamics in the isotropic and nematic phases of bent-core liquid crystals: NMR perspectives. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojadinovic, S.; Adorjan, A.; Sprunt, S.; Sawade, H.; Jakli, A. Dynamics of the nematic phase of a bent-core liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 060701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salamon, P.; Éber, N.; Buka, A.; Gleeson, J.T.; Sprunt, S.; Jákli, A. Dielectric properties of mixtures of a bent-core and a calamitic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 031711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tadapatri, P.; Hiremath, U.S.; Yelamaggad, C.V.; Krishnamurthy, K.S. Permittivity, conductivity, elasticity, and viscosity measurements in the nematic phase of a bent-core liquid crystal. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Panov, V.P.; Kocot, A.; Lehmann, A.; Tschierske, C.; Vij, J.K. Short-range correlations seen in the nematic phase of bent-core liquid crystals by dielectric and electro-optic studies. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 060701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgova, S.; Sreenilayam, S.P.; Panarin, Y.P.; Francescangeli, O.; Vita, F.; Vij, J.K.; Pozhidaev, E.; Minchenko, M.; Ferrero, C.; Strigazzi, A. Short bent-core molecules: X-ray, polarization, dielectricity, texture and electro-optics investigations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 22946–22956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.H.; Williams, J.C.; Twieg, R.J.; Jákli, A.; Gleeson, J.; Sprunt, S.; Ellman, B. Second-harmonic generation in a bent-core nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 041710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peláez, J.; Wilson, M.R. Atomistic simulations of a thermotropic biaxial liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 267801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peroukidis, S.D.; Vanakaras, A.G.; Photinos, D.J. Molecular simulation of hierarchical structures in bent-core nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 010702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, M.; Diorio, N.; Weissflog, W.; Baumeister, U.; Sprunt, S.; Gleeson, J.T.; Jákli, A. Direct observation of smectic layers in thermotropic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 107802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Gleeson, J.T.; Jákli, A.; Sprunt, S. A comparison of short-range molecular order in bent-core and rod-like nematic liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, M.; Panarin, Y.P.; Manna, U.; Vij, J.K.; Keith, C.; Tschierske, C. Electric field induced biaxiality and the electro-optic effect in a bent-core nematic liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 011106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanker, G.; Nagaraj, M.; Kocot, A.; Vij, J.K.; Prehm, M.; Tschierske, C. Nematic phases in 1,2,4-oxadiazole-based bent-core liquid crystals: Is there a ferroelectric switching? Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissflog, W.; Baumeister, U.; Tamba, M.G.; Pelzl, G.; Kresse, H.; Friedemann, R.; Hempel, G.; Kurz, R.; Roos, M.; Merzweiler, K.; et al. Unexpected liquid crystalline behaviour of three-ring bent-core mesogens: Bis(4-subst.-phenyl) 2-methyl-iso-phthalates. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 2671–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, G.; Prehm, M.; Nagaraj, M.; Vij, J.K.; Weyland, M.; Eremin, A.; Tschierske, C. 1,2,4-oxadiazole-based bent-core liquid crystals with cybotactic nematic phases. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Begum, N.; Turlapati, S.; Roy, S.K.; Das, A.K.; Rao, N.V.S. Ferroelectric-like switching in the nematic phase of four-ring bent-core liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlapati, S.; Khan, R.K.; Ghosh, S.; Tadapatri, P.; Pratibha, R.; Rao, N.V.S. Existence of polar switching in the nematic and orthogonal smectic phases in novel four-ring bent-core compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 174101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaasar, M.; Poppe, S.; Kerzig, C.; Klopp, C.; Eremin, A.; Tschierske, C. Cluster phases of 4-cyanoresorcinol derived hockey-stick liquid crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 8454–8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Prasad, V. Ferroelectric nematic and ferrielectric smectic mesophases in an achiral bent-core azo compound. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2998–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, F.; Sparnacci, K.; Panzarasa, G.; Placentino, I.F.; Marino, S.; Scaramuzza, N.; Portale, G.; Di Cola, E.; Ferrero, C.; Torgova, S.I.; et al. Evidence of cybotactic order in the nematic phase of a main-chain liquid crystal polymer with bent-core repeat unit. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, W. Effect of electric fields on the temperature of phase transitions of liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 24, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, C. Magnetic field dependence of the nematic-isotropic transition temperature. Phys. Rev. A 1981, 24, 2236–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapenko, T.; Wiant, D.B.; Sprunt, S.N.; Jákli, A.; Gleeson, J.T. Magnetic-field induced isotropic to nematic liquid crystal phase transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 247801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francescangeli, O.; Vita, F.; Fauth, F.; Samulski, E.T. Extraordinary magnetic field effect in bent-core liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 207801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, F.; Placentino, I.F.; Ferrero, C.; Singh, G.; Samulski, E.T.; Francescangeli, O. Electric field effect on the phase diagram of a bent-core liquid crystal. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 6475–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanakaras, A.G.; Photinos, D.J. Thermotropic biaxial nematic liquid crystals: Spontaneous or field stabilized? J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 154512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckhurst, G. Biaxial nematic liquid crystals: Fact or fiction? Thin Solid Film. 2001, 393, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.A.; Dingemans, T.J.; Nakata, M.; Samulski, E.T. Thermotropic biaxial nematic liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 145505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, M. Biaxial nematics from their prediction to the materials and the vicious circle of molecular design. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 1389–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, F.; Tauscher, T.; Speetjens, F.; Samulski, E.T.; Scharrer, E.; Francescangeli, O. Evidence of biaxial order in the cybotactic nematic phase of bent-core mesogens. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4671–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speetjens, F.; Lindborg, J.; Tauscher, T.; LaFemina, N.; Nguyen, J.; Samulski, E.T.; Vita, F.; Francescangeli, O.; Scharrer, E. Low nematic onset temperatures and room temperature cybotactic behavior in 1,3,4-oxadiazole-based bent-core mesogens possessing lateral methyl groups. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22558–22564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, F.; Tauscher, T.; Speetjens, F.; Ferrero, C.; Samulski, E.T.; Scharrer, E.; Francescangeli, O. Insights into biaxial ordering of bent-core nematics: X-ray diffraction evidence. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 611, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glebowska, A.; Vita, F.; Francescangeli, O.; Dingemans, T.; Samulski, E. Molecular engineering room-temperature bent-core nematics. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Wonderly, W.; Tauscher, T.; Harkins, R.; Vita, F.; Portale, G.; Francescangeli, O.; Samulski, E.T.; Scharrer, E. The effects of lateral halogen substituents on the low-temperature cybotactic nematic phase in oxadiazole based bent-core liquid crystals. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Cukrov, G.; Vita, F.; Scharrer, E.; Samulski, E.T.; Francescangeli, O.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Search for microscopic and macroscopic biaxiality in the cybotactic nematic phase of new oxadiazole bent-core mesogens. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 062701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harkins, R.; Tauscher, T.; Nguyen, J.; Lewis, S.; Adamo, F.C.; Pisani, M.; Hermida-Merino, D.; Samulski, E.T.; Vita, F.; Francescangeli, O.; et al. Biaxial ordering in the supercooled nematic phase of bent-core mesogens: Effects of molecular symmetry and outer wing lateral groups. Liq. Cryst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrell, P.L.; Crellin, D.A. Susceptibilities and order parameters of nematic liquid crystals. J. Phys. Colloq. 1979, 40, C3-211–C3-216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemans, T.; Madsen, L.; Zafiropoulos, N.; Lin, W.; Samulski, E. Uniaxial and biaxial nematic liquid crystals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2006, 364, 2681–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, S.; Norder, B.; Jager, W.F.; Dingemans, T.J.; van Turnhout, J.; Picken, S.J. Elucidation of the orientational order and the phase diagram of p-quinquephenyl. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, F.; Hegde, M.; Portale, G.; Bras, W.; Ferrero, C.; Samulski, E.T.; Francescangeli, O.; Dingemans, T. Molecular ordering in the high-temperature nematic phase of an all-aromatic liquid crystal. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leadbetter, A.J.; Richardson, R.M.; Colling, C.N. The structure of a number of nematogens. J. Phys. Colloq. 1975, 36, C1–37–C1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, P.; Petermann, D.; Levelut, A.M. The measurement of the nematic order parameter by x-ray scattering reconsidered. J. Phys. II Fr. 1995, 5, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droulias, S.; Vanakaras, A.G.; Photinos, D.J. Extending the Maier–Saupe theory to cybotactic nematics. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 37, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, Y.; Muccioli, L.; Zannoni, C. Quinquephenyl: The simplest rigid-rod-like nematic liquid crystal, or is it? An atomistic simulation. ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, O. To be submitted.
- Drzaic, P.S. Liquid Crystal Dispersions; World Scientific: Singapore, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, J.P.; Doane, J.W. Polymer dispersed liquid crystals. Condens. Matter. News 1992, 1, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Simoni, F.; Francescangeli, O. Optical properties of polymer-dispersed liquid crystals. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2000, 45, 381–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumi, M.; Bunning, T.J.; De Sio, L. Polymer dispersed liquid crystals. In Polymer-Modified Liquid Crystals; Dierking, I., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 61–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bronnikov, S.; Kostromin, S.; Zuev, V. Polymer-dispersed liquid crystals: Progress in preparation, investigation, and application. J. Macromol. Sci. Part. B Phys. 2013, 52, 1718–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Srivastava, J.K.; Singh, R.K. Polymer dispersed liquid crystals. In Liquid Crystalline Polymers, Volume 1–Structure and Chemistry; Thakur, V.K., Kessler, M.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 195–249. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchetti, L.; Simoni, F. Coarsening and phase separation in ultraviolet cured polymer dispersed liquid crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 3934–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, I.-C.; Wu, S.-T. Electro-optical properties of liquid crystals. In Optics and Nonlinear Optics of Liquid Crystals; Khoo, I.-C., Wu, S.-T., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 1993; pp. 100–268. [Google Scholar]
- Simoni, F. Nonlinear Optical Properties of Liquid Crystals and Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystals; World Scientific: Singapore, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mucha, M.; Nastal, E. Complex study of reorientational dynamics of the liquid crystal in PDLC films. Liq. Cryst. 1997, 23, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, G.P.; Zumer, S. Historical perspective of liquid crystals confined to curved geometries. In Liquid Crystals in Complex Geometries; Crawford, G.P., Zumer, S., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1995; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann, J.H.; Žumer, S.; Doane, J.W. Configuration transition in a nematic liquid crystal confined to a small spherical cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 1907–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golemme, A.; Žumer, S.; Doane, J.W.; Neubert, M.E. Deuterium NMR of polymer dispersed liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 37, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, O.; Ferrero, C.; Lucchetti, L.; Simoni, F.; Burghammer, M. Ordering and director-field configuration in single droplets of liquid crystals probed by X-ray microdiffraction. Eur. Lett. 2002, 59, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Violette, E.; Parodi, O. Émulsions nématiques. Effets de champ magnétiques et effets piézoélectriques. J. Phys. Colloq. 1969, 30, C4–57–C4–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francescangeli, O.; Stanic, V.; Lucchetti, L.; Ferrero, C.; Burghammer, M. X-ray microdiffraction study of the liquid crystal ordering in confined geometries. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 412, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.R.; Palffy-Muhoray, P. The optical response of polymer dispersed liquid crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol. Sect. A 1994, 243, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Lee, M.A.; West, J.L. Optical field induced scattering in polymer dispersed liquid crystal films. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Inc. Nonlinear Opt. 1990, 179, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, F.; Bloisi, F.; Vicari, L.; Simoni, F. Optical phase shift of polymer-dispersed liquid crystals. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 48, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, D.A.; Luther, B.J. Watching molecules reorient in liquid crystal droplets with multiphoton-excited fluorescence microscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 3935–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, P.S.; Carbone, G.; Botcherby, E.J.; Wilson, T.; Elston, S.J.; Raynes, E.P. Liquid crystal director dynamics imaged using two-photon fluorescence microscopy with remote focusing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 257803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francescangeli, O.; Stanic, V.; Gobbi, L.; Bruni, P.; Iacussi, M.; Tosi, G.; Bernstorff, S. Structure of self-assembled liposome-DNA-metal complexes. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 011904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francescangeli, O.; Pisani, M.; Stanić, V.; Bruni, P.; Weiss, T.M. Evidence of an inverted hexagonal phase in self-assembled phospholipid-DNA-metal complexes. Europhys. Lett. 2004, 67, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, P.; Pisani, M.; Amici, A.; Marchini, C.; Montani, M.; Francescangeli, O. Self-assembled ternary complexes of neutral liposomes, deoxyribonucleic acid, and bivalent metal cations. Promising vectors for gene transfer? Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 073901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorova, L.A.; Erokhina, S.I.; Pisani, M.; Barucca, G.; Marcaccio, M.; Koifman, O.I.; Salnikov, D.S.; Gromova, O.A.; Astolfi, P.; Ricci, V.; et al. Encapsulation of vitamin B12 into nanoengineered capsules and soft matter nanosystems for targeted delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 182, 110366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, P.; Giorgini, E.; Gambini, V.; Rossi, B.; Vaccari, L.; Vita, F.; Francescangeli, O.; Marchini, C.; Pisani, M. Lyotropic liquid-crystaline nanosystems as drug delivery agents for 5-fluororacil: Structure and cytotoxicity. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12369–12378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, P.; Giorgini, E.; Adamo, F.C.; Vita, F.; Logrippo, S.; Francescangeli, O.; Pisani, M. Lyotropic effects of a cationic surfactant incorporation in phytantriol bulk cubic phases and dispersions loaded with the anticancer drug 5-fluororacil. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 286, 110954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, M.; Quassinti, L.; Bramucci, M.; Galassi, G.; Maggi, F.; Rossi, B.; Damin, A.; Carloni, P.; Astolfi, P. Nanostructured liquid crystalline particles as delivery vectors for isofuranodiene: Characterization and in-vitro anticancer activity. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 192, 111050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, W.D.; Ahmed, Z.; Zeng, X.B.; Welch, C.; Ungar, G.; Mehl, G.H. Molecular organization in the twist–bend nematic phase by resonant X-ray scattering at the Se K-edge and by SAXS, WAXS and GIXRD. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 13449–13454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abberley, J.P.; Killah, R.; Walker, R.; Storey, J.M.D.; Imrie, C.T.; Salamończyk, M.; Zhu, C.; Gorecka, E.; Pociecha, D. Heliconical smectic phases formed by achiral molecules. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salamończyk, M.; Mandle, R.J.; Makal, A.; Liebman-Peláez, A.; Feng, J.; Goodby, J.W.; Zhu, C. Double helical structure of the twist-bend nematic phase investigated by resonant X-ray scattering at the carbon and sulfur K-edges. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 9760–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, M.; Yang, L.; Vita, F.; Fox, R.J.; van de Watering, R.; Norder, B.; Lafont, U.; Francescangeli, O.; Madsen, L.A.; Picken, S.J.; et al. Strong graphene oxide nanocomposites from aqueous hybrid liquid crystals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vita, F.; Adamo, F.C.; Pisani, M.; Heist, L.M.; Li, M.; Hegde, M.; Dingemans, T.J.; Samulski, E.T.; Francescangeli, O. Liquid crystal thermosets. A new class of high-performance materials. Liq. Cryst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Pol, E.; Petukhov, A.V.; Thies-Weesie, D.M.E.; Byelov, D.V.; Vroege, G.J. Experimental realization of biaxial liquid crystal phases in colloidal dispersions of boardlike particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 258301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, P.; Penisson, C.; Constantin, D.; Gabriel, J.-C.P. Isotropic, nematic, and lamellar phases in colloidal suspensions of nanosheets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6662–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshino, T.; Nakayama, M.; Fujinami, S.; Nakatani, T.; Kohmura, Y.; Kato, T. Static structure and dynamical behavior of colloidal liquid crystals consisting of hydroxyapatite-based nanorod hybrids. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





























© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vita, F.; Adamo, F.C.; Pisani, M.; Francescangeli, O. Nanostructure of Unconventional Liquid Crystals Investigated by Synchrotron Radiation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091679
Vita F, Adamo FC, Pisani M, Francescangeli O. Nanostructure of Unconventional Liquid Crystals Investigated by Synchrotron Radiation. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(9):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091679
Chicago/Turabian StyleVita, Francesco, Fabrizio Corrado Adamo, Michela Pisani, and Oriano Francescangeli. 2020. "Nanostructure of Unconventional Liquid Crystals Investigated by Synchrotron Radiation" Nanomaterials 10, no. 9: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091679
APA StyleVita, F., Adamo, F. C., Pisani, M., & Francescangeli, O. (2020). Nanostructure of Unconventional Liquid Crystals Investigated by Synchrotron Radiation. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091679