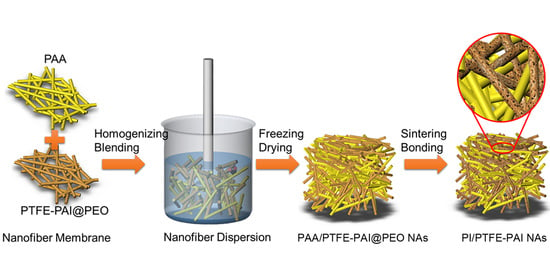
Preparation of PI/PTFE–PAI Composite Nanofiber Aerogels with Hierarchical Structure and High-Filtration Efficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PAA Nanofiber and PTFE–PAI@PEO Composite Nanofiber
2.3. Fabrication of PI/PTFE–PAI Composite NAs
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation PAA and PTFE–PAI@PEO Nanofiber
3.1.1. PAA and PI Nanofiber
3.1.2. PTFE–PAI–PEO and PTFE–PAI Nanofiber
3.2. Fabrication of PI/PTFE–PAI NAs
3.2.1. Influence of Weight Ratio of PAA: PTFE–PAI–PEO Nanofibers
3.2.2. Influence of the Fiber Contents
3.2.3. Influence of the Fiber Contents
3.3. Chemical Analysis
3.4. Thermal Performance of PTFE–PAI/PI NAs
3.5. Mechanical Properties
3.6. Filtration Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Lee, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chu, S.; et al. Nanofiber Air Filters with High-Temperature Stability for Efficient PM2.5 Removal from the Pollution Sources. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C. Experimental and modeling study of pressure drop across electrospun nanofiber air filters. Build. Environ. 2018, 142, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, T.; Jiang, P.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Cleanable Air Filter Transferring Moisture and Effectively Capturing PM2.5. Small 2017, 13, 1603306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, C. Three-layer Composite Filter Media Containing Electrospun Polyimide Nanofibers for the Removal of Fine Particles. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F. Air Filtration in the Free Molecular Flow Regime: A Review of High-efficiency Particulate Air Filters Based on Carbon Nanotubes. Small 2015, 10, 4543–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Anti-deformed Polyacrylonitrile/Polysulfone Composite Membrane with Binary Structures for Effective Air Filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8086–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei., Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Improving Filtration Performance of Electrospun Nanofiber Mats by a Bimodal Method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, H.P.; Kafle, L.; Ojha, D.P.; Song, J.H.; Kim, H.J. Three-dimensional Nanoporous Polyacrylonitrile-based Carbon Scaffold for Effective Separation of Oil from Oil/water Emulsion. Polymer 2018, 153, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, L.; Yin, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Biomimetic Structure Enables Superelastic and Thermostable Nanofibrous Aerogels for Cascade Filtration of PM 2.5. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, H.; Pan, F. An Electrically Renewable Air Filter with Integrated 3D Nanowire Networks. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, M.; Nie, J.; Tan, J.; Yang, B.; Song, S. Design of double-component metal-organic framework air filters with PM2.5 capture, gas adsorption and antibacterial capacities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Zhao, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Kang, W.; Zhuang, X. Preparation and Properties of sc-PLA/PMMA Transparent Nanofiber Air Filter. Polymers 2018, 10, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.; Lee, M.; Kwon, B.; Kim, H.; Shim, I.; Jung, M.; Lee, S.; Park, J.-C. Effective layer by layer cell seeding into non-woven 3D electrospun scaffolds of poly-L-lactic acid microfibers for uniform tissue formation. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.; Zang, R.; Yang, K.K.; Liu, N.; Yang, S.-T. Three-dimensional fibrous scaffolds with microstructures and nanotextures for tissue engineering. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lim, C.T. Fabrication of large pores in electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for cellular infiltration: A review. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2012, 18, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, P.D.; Vaquette, C.; Farrugia, B.L.; Dargaville, T.R.; Brown, T.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Electrospinning and additive manufacturing: Converging technologies. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 2, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibers for high-performance air filtration. Compos. Communs. 2019, 15, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Si, Y.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight and Resilient Electrospun Fiber Sponge with a Lamellar Corrugated Microstructure for Effective Low-Frequency Sound Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 35333–35342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, D.; Deng, B.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Wu, T. Robust polyimide nano/microfibre aerogels welded by solvent-vapour for environmental applications. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Aerogels Derived from Polymer Nanofibers and Their Applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1700724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.; Wang, X.; Dou, L.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight and Fire-resistant Ceramic Nanofibrous Aerogels with Temperature-invariant Superelasticity. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas8925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Wu, T.; He, N.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; He, L.; Huang, C.; Ei-Hamshary, H.A.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Ke, Q.; et al. Three-dimensional polycaprolactone scaffold via needleless electrospinning promotes cell proliferation and infiltration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Tang, X.; Ge, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight Nanofibre-assembled Cellular Aerogels with Superelasticity and Multifunctionality. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, G.; Jiang, S.; Jérôme, V.; Wendorff, J.H.; Fathi, A.; Uhm, J.; Altstädt, V.; Herling, M.; Breu, J.; Freitag, R.; et al. Ultralight, Soft Polymer Sponges by Self-Assembly of Short Electrospun Fibers in Colloidal Dispersions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2850–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuber, F.; Mousavi, S.; Federer, L.; Hofer, M.; Adlhart, C. Exploration of Ultralight Nanofiber Aerogels as Particle Filters: Capacity and Efficiency. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9069–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuber, F.; Mousavi, S.; Hofer, M.; Adlhart, C. Tailoring Pore Structure of Ultralight Electrospun Sponges by Solid Templating. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 5595–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tong, S.; Ge, M.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Superelastic and ultralight polyimide aerogels as thermal insulators and particulate air filters. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Morsi, Y.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Newhy, M.; Fan, C.; Mo, X. Superabsorbent 3D Scaffold Based on Electrospun Nanofibers for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24415–24425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Cheong, J.Y.; Nam, J.S.; Kim, I.D.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. High-density Fibrous Polyimide Sponges with Superior Mechanical and Thermal Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19006–19014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F.; Li, Z. Hybrid aerogels derived from banana peel and waste paper for efficient oil absorption and emulsion separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Si, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight, superelastic and bendable lashing-structured nanofibrous aerogels for effective sound absorption. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Li, Y.; Cao, H.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.; Chang, J.; Duan, F. Novel PTFE hollow fiber membrane fabricated by emulsion electrospinning and sintering for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 583, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Zhao, H.; Ju, J.; Shi, Z.; Qiao, C.; Cheng, B. Electrospun poly(tetrafluoroethylene) nanofiber membranes from PTFE-PVA-BA-H2O gel-spinning solutions. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xiong, T.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Hou, H. Polyamide-imide reinforced polytetrafluoroethylene nanofiber membranes with enhanced mechanical properties and thermal stabilities. Mater. Lett. 2016, 182, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Yop Rhee, K.; Jin, F.-L. Improvement of hydrophilic properties of electrospun polyamide-imide fibrous mats by atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2015, 78, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jin, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Y. Formation and characterization of polytetrafluoroethylene nanofiber membranes for high-efficiency fine particulate filtration. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 13631–13645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| PAI–PTFE–PEO Nanofiber | Weight Ratio of Different Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAI | PTFE | PEO | H2O | PAI:PTFE | |
| Hybrid–1 | 2.5 | 10 | 1 | 19 | 2:8 |
| Hybrid–2 | 4.3 | 10 | 1 | 12 | 3:7 |
| Hybrid–3 | 4.3 | 10 | 1 | 19 | 3:7 |
| Hybrid–4 | 4.3 | 10 | 1 | 24 | 3:7 |
| Hybrid–5 | 4.3 | 10 | 1 | 29 | 3:7 |
| Hybrid–6 | 6.7 | 10 | 1 | 19 | 4:6 |
| Hybrid–7 | 4.3 | 10 | 1 | 39 | 3:7 |
| Hybrid–8 | 4.3 | 10 | 1 | 4 | 3:7 |
| Filtration Performance | Particle Size (μm) | Fiber Contents (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5% | 1% | 1.5% | 2% | ||
| Filtration Efficiency (%) | ≥0.3 | 81.21 | 87.20 | 95.36 | 97.35 |
| ≥0.5 | 91.27 | 95.51 | 98.81 | 99.19 | |
| ≥1.0 | 97.63 | 99.45 | 99.87 | 99.88 | |
| ≥2.0 | 99.34 | 99.92 | 99.88 | 99.98 | |
| ≥5.0 | 99.60 | 99.89 | 99.59 | 99.98 | |
| ≥10.0 | 99.27 | 99.91 | 99.41 | 100 | |
| Pressure drop (Pa) | -- | 180 | 210 | 310 | 440 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Liu, H.; Shen, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Deng, B. Preparation of PI/PTFE–PAI Composite Nanofiber Aerogels with Hierarchical Structure and High-Filtration Efficiency. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091806
Li D, Liu H, Shen Y, Wu H, Liu F, Wang L, Liu Q, Deng B. Preparation of PI/PTFE–PAI Composite Nanofiber Aerogels with Hierarchical Structure and High-Filtration Efficiency. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(9):1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091806
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dawei, Huizhong Liu, Ying Shen, Huiping Wu, Feng Liu, Lanlan Wang, Qingsheng Liu, and Bingyao Deng. 2020. "Preparation of PI/PTFE–PAI Composite Nanofiber Aerogels with Hierarchical Structure and High-Filtration Efficiency" Nanomaterials 10, no. 9: 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091806
APA StyleLi, D., Liu, H., Shen, Y., Wu, H., Liu, F., Wang, L., Liu, Q., & Deng, B. (2020). Preparation of PI/PTFE–PAI Composite Nanofiber Aerogels with Hierarchical Structure and High-Filtration Efficiency. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091806