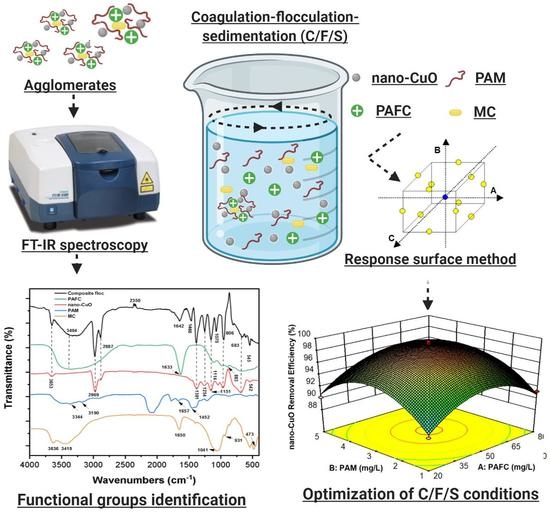
Synergetic Effect of Organic Flocculant and Montmorillonite Clay on the Removal of Nano-CuO by Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Stock Solutions
2.3. C/F/S Experiments
2.4. Analytical Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Coagulant and Flocculant Dosage on the Removal of Nano-CuO
3.2. Influence of pH on the Removal of Nano-CuO
3.3. Influence of Sedimentation Period on the Removal of Nano-CuO
3.4. Influence of Stirring Speed on the Removal of Nano-CuO
3.5. Response Surface Methodology
3.6. Model Validation and Monitoring of Floc
3.7. Characteristics of Composite Flocs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pietroiusti, A.; Stockmann-Juvala, H.; Lucaroni, F.; Savolainen, K. Nanomaterial exposure, toxicity, and impact on human health. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 10, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, F.; Sun, T.; Nowack, B. Environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials: Review of modeling and analytical studies. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 181, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janković, N.Z.; Plata, D.L. Engineered nanomaterials in the context of global element cycles. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2697–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Chung, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, I. The Genotoxic Effect of ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles on Early Growth of Buckwheat, Fagopyrum Esculentum. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, O.; Juganson, K. Angela Ivask, Kaja Kasemets, Monika Mortimer & Anne Kahru. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.T.; Ali, S.A.K. February. Removal lead Pb (II) from wastewater using kaolin clay. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bour, A.; Mouchet, F.; Silvestre, J.; Gauthier, L.; Pinelli, E. Environmentally relevant approaches to assess nanoparticles ecotoxicity: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muna, M.; Blinova, I.; Kahru, A.; Vinković Vrček, I.; Pem, B.; Orupõld, K.; Heinlaan, M. Combined effects of test media and dietary algae on the toxicity of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles to freshwater microcrustaceans Daphnia magna and Heterocypris incongruens: Food for thought. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Ma, Y.; Shannon, K.; Chen, D.-R.; Huang, Y.-W. Toxicity of nano- and micro-sized ZnO particles in human lung epithelial cells. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2009, 11, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduok, S.; Coulon, F. Engineered Nanoparticles in the environments: Interactions with microbial systems and microbial Activity. In Microbial Ecotoxicology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 63–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, K.; Li, X. Influence of copper nanoparticles on the physical-chemical properties of activated sludge. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, N.; Chu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yan, H.; Han, Q. CuO nanoparticle–humic acid (CuONP–HA) composite contaminant removal by coagulation/ultrafiltration process: The application of sodium alginate as coagulant aid. Desalination 2015, 367, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, F.; Laborie, S.; Guigui, C. Removal of SiO2 nanoparticles from industry wastewaters and subsurface waters by ultrafiltration: Investigation of process efficiency, deposit properties and fouling mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalew, T.E.A.; Ajmani, G.; Huang, H.; Schwab, K.J. Evaluating nanoparticle breakthrough during drinking water treatment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, R.J.; Keene, V.; Daniels, L.; Walker, S.L. Removal of TiO2 Nanoparticles during primary water treatment: Role of Coagulant type, dose, and nanoparticle concentration. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2014, 31, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.A.; Park, D.R.; Khan, S.; Akram, M.; Yeom, I.T. The Removal of CuO Nanoparticles from Water by Conventional Treatment C/F/S: The Effect of pH and Natural Organic Matter. Molecules 2019, 24, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, M.; Liu, T.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Sun, M.; Feng, Y. Interactions between magnetic particles and polyaluminum chloride on the coagulation behavior in humic acid-kaolin synthetic water treatment. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.; Zhuang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, H. Efficient Removal of TiO2 nanoparticles by enhanced flocculation–coagulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 14528–14537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Du, B. Impacts of organic coagulant aid on purification performance and membrane fouling of coagulation/ultrafiltration hybrid process with different Al-based coagulants. Desalination 2015, 363, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhou, R.; Guo, X. Behavior of stabilized multiwalled carbon nanotubes in a FeCl3 coagulation system and the structure characteristics of the produced flocs. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 366, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, Y.-N.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Keller, A.A.; Wang, T.; Li, F. Heteroaggregation of engineered nanoparticles and kaolin clays in aqueous environments. Water Res. 2015, 80, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wu, F.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Niu, L.; Fang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, F. Impact of montmorillonite clay on the homo-and heteroaggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (nTiO2) in synthetic and natural waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, D. Process optimization: A statistical approach. J. Qual. Technol. 2008, 40, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.M. Response surface methodology: Process and product optimization using designed experiments, 3rd edition. J. Qual. Technol. 2010, 42, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Lin, A.; Liu, X. Population balance modeling of cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) induced flocculation process for lignin recovery from the pre-hydrolysis liquor of kraft pulping process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, H.; Sun, W.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, X.; You, Z.; Liu, C. Characterization and coagulation behavior of polymeric aluminum ferric silicate for high-concentration oily wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 119, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, V.S.; Corniciuc, C.; Teixeira, M.R. The effect of TiO2 nanoparticles removal on drinking water quality produced by conventional treatment C/F/S. Water Res. 2017, 109, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.T.; Ye, Y.Y.; Qi, J.; Li, F.T.; Tang, Y.L. Removal of titanium dioxide nanoparticles by coagulation: Effects of coagulants, typical ions, alkalinity and natural organic matters. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 7–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanca, C.H.; Yarce, C.J.; Zapata, C.A.; Giraldo, J.A. Relationship between the polymeric ionization degree and powder and surface properties in materials derived from poly (maleic anhydride-alt-octadecene). Molecules 2018, 23, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Coagulation performance and mechanism of polyaluminum ferric chloride (PAFC) coagulant synthesized using blast furnace dust. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, H.; Tan, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Feng, L.; Xiang, X. Synthesis and characterization of composite flocculant PAFS-CPAM for the treatment of textile dye wastewater. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Tang, M.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, H. Effective sludge dewatering technique using the combination of Fenton’s reagent and CPAM. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 96, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chu, J.; Tan, S.K.; Vu, T.T.; Lam, K.P. Sedimentation behavior of flocculant-treated soil slurry. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2016, 35, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, A.; Pan, S.-Y.; Sun, W.; Zhu, C.; Shah, K.J.; Zheng, H. Novel chitosan-based flocculants for chromium and nickle removal in wastewater via integrated chelation and flocculation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; Tan, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Preparation and coagulation performance of hybrid coagulant polyacrylamide-polymeric aluminum ferric chloride. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadighavam, S.; Heiderscheidt, E.; Marttila, H.; Kløve, B. Optimization of gravity-driven hydraulic flocculators to treat peat extraction runoff water. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.-L.; Guo, L.-F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.-W.; Xu, W.; Zhao, H.-Z. Rapid removal of bound water from dredged sediments using novel hybrid coagulants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 205, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhou, S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y. Synthesis and evaluation of cationic flocculant P(DAC-PAPTAC-AM) for flocculation of coal chemical wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Li, X. Synthesis, purification and characterization of polyaluminum ferric chloride (PAFC) with high (Al+Fe)b content. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 146, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrajt, G.; Borg, J.; Raynal, P.I.; Djouadi, Z.; Hendecourt, L.D.; Flynn, G.; Deboffe, D. FTIR and Raman analyses of the Tagish Lake meteorite: Relationship with the aliphatic hydrocarbons observed in the Diffuse Interstellar Medium. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 416, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Tang, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, W.; Liu, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhai, J.; Zheng, H. Characterization of an inorganic polymer coagulant and coagulation behavior for humic acid/algae-polluted water treatment: Polymeric zinc–ferric–silicate–sulfate coagulant. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19856–19862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.A.; Zam, S.Z.; Park, D.R.; Yeom, I.T. Assessment of Key Environmental Factors Influencing the Sedimentation and Aggregation Behavior of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Aquatic Environment. Water 2018, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Gao, C.; Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Huang, X.; Ran, W.; Shen, Q. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by lipopeptides and lipopeptides modified Na-montmorillonite. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, L.; Batouche, K.; Lévêque, J.-M.; Muller, F.; Bény, J.-M.; Kebabi, B.; Duclaux, L. Adsorption of imidazolium and pyridinium ionic liquids onto montmorillonite: Characterisation and thermodynamic calculations. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussein, S.M.; Shihab, O.H.; Ibrahim, S.S. Interaction between Kaolin and DMSO: FTIR, XRD, thermodynamic and Nano studies. J. Univ. Anbar Pure Sci. 2014, 8, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Seifi, S.; Masoum, S. Preparation of copper oxide/oak-based biomass nanocomposite for electrochemical hydrogen storage. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 11979–11988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, P.W. Co-adsorption of metal ions and organic ligands: Formation of ternary surface complexes. Miner. Water Interface Geochem. 2018, 281–308. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.; Behpour, M.; Sobhani-Nasab, A.; Jeddy, M.R. Nanocrystalline Ce-doped copper ferrite: Synthesis, characterization, and its photocatalyst application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 11691–11697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Type | Variables | Coded Level of Variables | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Corresponding Operation Values | ||||
| A | PAFC (mg/L) | 20 | 50 | 80 |
| B | PAM (mg/L) | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| C | Stirring Speed (RPM) | 100 | 200 | 350 |
| Experiment | A | B | C | Nano-CuO Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 92.26 |
| 2 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 90.15 |
| 3 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 91.15 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 98.82 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 88.12 |
| 6 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 87.87 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 98.67 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.15 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 91.95 |
| 10 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 90.23 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.48 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.51 |
| 13 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 87.14 |
| 14 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 93.49 |
| 15 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 89.37 |
| 16 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 91.22 |
| 17 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 91.14 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Prob > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 310.5 | 9 | 34.5 | 80.51 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| A-(PAFC) | 1.05 | 1 | 1.05 | 2.45 | 0.1613 | Not significant |
| B-(PAM) | 1.04 | 1 | 1.04 | 2.42 | 0.1638 | Not significant |
| C-(Stirring Speed) | 26.94 | 1 | 26.94 | 62.86 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| AB | 6.250 ×10−4 | 1 | 6.25 × 10−4 | 1.458 × 10−3 | 0.9706 | Not significant |
| AC | 7.37 | 1 | 7.37 | 17.2 | 0.0043 | Significant |
| BC | 0.19 | 1 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 0.5276 | Not significant |
| A2 | 64.02 | 1 | 64.02 | 149.38 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| B2 | 87.33 | 1 | 87.33 | 203.79 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| C2 | 93.97 | 1 | 93.97 | 219.28 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| Residual | 3 | 7 | 0.43 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 2.42 | 3 | 0.81 | 5.62 | 0.0643 | Not significant |
| Pure Error | 0.57 | 4 | 0.14 | |||
| Cor Total | 313.5 | 16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, R.; Inam, M.A.; Lee, K.-H.; Channa, A.S.; Mallah, M.A.; Wie, Y.-M.; Abbasi, M.N. Synergetic Effect of Organic Flocculant and Montmorillonite Clay on the Removal of Nano-CuO by Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation Process. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102753
Khan R, Inam MA, Lee K-H, Channa AS, Mallah MA, Wie Y-M, Abbasi MN. Synergetic Effect of Organic Flocculant and Montmorillonite Clay on the Removal of Nano-CuO by Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation Process. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102753
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Rizwan, Muhammad Ali Inam, Kang-Hoon Lee, Abdul Sami Channa, Mukhtiar Ali Mallah, Young-Min Wie, and Mahmood Nabi Abbasi. 2021. "Synergetic Effect of Organic Flocculant and Montmorillonite Clay on the Removal of Nano-CuO by Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation Process" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102753
APA StyleKhan, R., Inam, M. A., Lee, K. -H., Channa, A. S., Mallah, M. A., Wie, Y. -M., & Abbasi, M. N. (2021). Synergetic Effect of Organic Flocculant and Montmorillonite Clay on the Removal of Nano-CuO by Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation Process. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102753