Serum Lowers Bioactivity and Uptake of Synthetic Amorphous Silica by Alveolar Macrophages in a Particle Specific Manner
Abstract
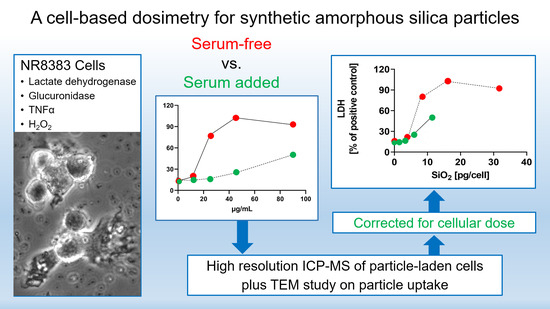
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Particle Suspensions
2.3. Cultivation of NR8383 Macrophages and Cell Culture Assays
2.4. Particle Size Determination under Cell Culture Conditions with Particle Tracking Analysis
2.5. Electron Microscopy of NR8383 Macrophages
2.6. Quantification of Cell-Associated SiO2 NP by High Resolution ICP-MS
2.7. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Particle Characterization
3.2. Quantification of Particle Uptake by NR8383 Cells
3.3. In Vitro Toxicity Determination of SAS and Electron Microscopic Study
3.3.1. AEROSIL® 380 F and AEROSIL® OX50
3.3.2. SIPERNAT® 50 and SIPERNAT® 160
3.4. Evaluation of Data Using the Cell-Associated SiO2 Mass as a Dose Metric
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stark, W.J.; Stoessel, P.R.; Wohlleben, W.; Hafner, A. Industrial Applications of Nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5793–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkler, H.C.; Suter, M.; Naegeli, H. Critical Review of the Safety Assessment of Nano-Structured Silica Additives in Food. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dekkers, S.; Krystek, P.; Peters, R.J.B.; Lankveld, D.P.K.; Bokkers, B.G.H.; van Hoeven-Arentzen, P.H.; Bouwmeester, H.; Oomen, A.G. Presence and Risks of Nanosilica in Food Products. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retamal Marín, R.; Babick, F.; Lindner, G.-G.; Wiemann, M.; Stintz, M. Effects of Sample Preparation on Particle Size Distributions of Different Types of Silica in Suspensions. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bio-Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Food, Biomedical, and Health Sciences; Bagchi, D. (Ed.) Functional Food Science and Technology series; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK; Ames, IA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-470-67037-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, C.; Von Goetz, N.; Scheringer, M.; Wormuth, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Potential Exposure of German Consumers to Engineered Nanoparticles in Cosmetics and Personal Care Products. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L.C.; Lison, D.; Martens, J.A.; Hoet, P.H. The Nanosilica Hazard: Another Variable Entity. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol.-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol.-Gel Processing; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; ISBN 978-0-12-134970-7. [Google Scholar]
- Taeger, D.; McCunney, R.; Bailer, U.; Barthel, K.; Küpper, U.; Brüning, T.; Morfeld, P.; Merget, R. Cross-Sectional Study on Nonmalignant Respiratory Morbidity Due to Exposure to Synthetic Amorphous Silica. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 58, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, J.H.E.; Muijser, H.; Duistermaat, E.; Junker, K.; Kuper, C.F. Five-Day Inhalation Toxicity Study of Three Types of Synthetic Amorphous Silicas in Wistar Rats and Post-Exposure Evaluations for up to 3 Months. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugadoss, S.; Lison, D.; Godderis, L.; Van Den Brule, S.; Mast, J.; Brassinne, F.; Sebaihi, N.; Hoet, P.H. Toxicology of Silica Nanoparticles: An Update. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2967–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.J.; Driscoll, K.E.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Baggs, R.; O’Reilly, M.A.; Carter, J.; Gelein, R.; Oberdörster, G. Pulmonary Chemokine and Mutagenic Responses in Rats after Subchronic Inhalation of Amorphous and Crystalline Silica. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 56, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding Biophysicochemical Interactions at the Nano-Bio Interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, E.K.; Jiang, J.; Leonard, S.S.; Eberly, S.; Castranova, V.; Biswas, P.; Elder, A.; Han, X.; Gelein, R.; Finkelstein, J.; et al. Concept of Assessing Nanoparticle Hazards Considering Nanoparticle Dosemetric and Chemical/Biological Response Metrics. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part. A 2010, 73, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.-S.; Duffin, R.; Bradley, M.; Megson, I.L.; MacNee, W.; Lee, J.K.; Jeong, J.; Donaldson, K. Predictive Value of in Vitro Assays Depends on the Mechanism of Toxicity of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Corson, N.; Wade-Mercer, P.; Gelein, R.; Jiang, J.; Sahu, M.; Biswas, P.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Elder, A.; Oberdörster, G. Assessing the Relevance of in Vitro Studies in Nanotoxicology by Examining Correlations between in Vitro and in Vivo Data. Toxicology 2012, 297, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Driscoll, K.E.; Higgins, J.M.; Leytart, M.J.; Crosby, L.L. Differential Effects of Mineral Dusts on the in Vitro Activation of Alveolar Macrophage Eicosanoid and Cytokine Release. Toxicol. Vitro 1990, 4, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemann, M.; Vennemann, A.; Stintz, M.; Retamal Marín, R.R.; Babick, F.; Lindner, G.-G.; Schuster, T.B.; Brinkmann, U.; Krueger, N. Effects of Ultrasonic Dispersion Energy on the Preparation of Amorphous SiO₂ Nanomaterials for In Vitro Toxicity Testing. Nanomaterials 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vennemann, A.; Alessandrini, F.; Wiemann, M. Differential Effects of Surface-Functionalized Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles on Alveolar Macrophages, Rat Lung, and a Mouse Allergy Model. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, M.G.; Chiu, M.; Taurino, G.; Ruotolo, R.; Marmiroli, N.; Bergamaschi, E.; Cubadda, F.; Bussolati, O. Pyrogenic and Precipitated Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles Differentially Affect Cell Responses to LPS in Human Macrophages. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibe, R.; Hsiao, I.-L.; Fritsch-Decker, S.; Kielmeier, U.; Wagbo, A.M.; Voss, B.; Schmidt, A.; Hessman, S.D.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; et al. The Protein Corona Suppresses the Cytotoxic and Pro-Inflammatory Response in Lung Epithelial Cells and Macrophages upon Exposure to Nanosilica. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peuschel, H.; Ruckelshausen, T.; Cavelius, C.; Kraegeloh, A. Quantification of Internalized Silica Nanoparticles via STED Microscopy. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Rawi, M.; Diabaté, S.; Weiss, C. Uptake and Intracellular Localization of Submicron and Nano-Sized SiO2 Particles in HeLa Cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panas, A.; Marquardt, C.; Nalcaci, O.; Bockhorn, H.; Baumann, W.; Paur, H.-R.; Mülhopt, S.; Diabaté, S.; Weiss, C. Screening of Different Metal Oxide Nanoparticles Reveals Selective Toxicity and Inflammatory Potential of Silica Nanoparticles in Lung Epithelial Cells and Macrophages. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marucco, A.; Aldieri, E.; Leinardi, R.; Bergamaschi, E.; Riganti, C.; Fenoglio, I. Applicability and Limitations in the Characterization of Poly-Dispersed Engineered Nanomaterials in Cell Media by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS). Materials 2019, 12, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Aberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Biomolecular Coronas Provide the Biological Identity of Nanosized Materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docter, D.; Westmeier, D.; Markiewicz, M.; Stolte, S.; Knauer, S.K.; Stauber, R.H. The Nanoparticle Biomolecule Corona: Lessons Learned—Challenge Accepted? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6094–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halamoda-Kenzaoui, B.; Ceridono, M.; Colpo, P.; Valsesia, A.; Urbán, P.; Ojea-Jiménez, I.; Gioria, S.; Gilliland, D.; Rossi, F.; Kinsner-Ovaskainen, A. Dispersion Behaviour of Silica Nanoparticles in Biological Media and Its Influence on Cellular Uptake. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hinderliter, P.M.; Minard, K.R.; Orr, G.; Chrisler, W.B.; Thrall, B.D.; Pounds, J.G.; Teeguarden, J.G. ISDD: A Computational Model of Particle Sedimentation, Diffusion and Target Cell Dosimetry for in Vitro Toxicity Studies. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binnemars-Postma, K.A.; ten Hoopen, H.W.; Storm, G.; Prakash, J. Differential Uptake of Nanoparticles by Human M1 and M2 Polarized Macrophages: Protein Corona as a Critical Determinant. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 2889–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, G.A.; Chrisler, W.B.; Cassens, K.J.; Tan, R.; Tarasevich, B.J.; Markillie, L.M.; Zangar, R.C.; Thrall, B.D. Cellular Recognition and Trafficking of Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles by Macrophage Scavenger Receptor A. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemann, M.; Vennemann, A.; Sauer, U.G.; Wiench, K.; Ma-Hock, L.; Landsiedel, R. An in Vitro Alveolar Macrophage Assay for Predicting the Short-Term Inhalation Toxicity of Nanomaterials. J. Nanobiotechnol 2016, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Großgarten, M.; Holzlechner, M.; Vennemann, A.; Balbekova, A.; Wieland, K.; Sperling, M.; Lendl, B.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Karst, U.; Wiemann, M. Phosphonate Coating of SiO2 Nanoparticles Abrogates Inflammatory Effects and Local Changes of the Lipid Composition in the Rat Lung: A Complementary Bioimaging Study. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Landuyt, K.L.; Cokic, S.M.; Asbach, C.; Hoet, P.; Godderis, L.; Reichl, F.X.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Vennemann, A.; Wiemann, M. Interaction of Rat Alveolar Macrophages with Dental Composite Dust. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiemann, M.; Vennemann, A.; Wohlleben, W. Lung Toxicity Analysis of Nano-Sized Kaolin and Bentonite: Missing Indications for a Common Grouping. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiemann, M.; Sauer, U.G.; Vennemann, A.; Bäcker, S.; Keller, J.-G.; Ma-Hock, L.; Wohlleben, W.; Landsiedel, R. In Vitro and In Vivo Short-Term Pulmonary Toxicity of Differently Sized Colloidal Amorphous SiO2. Nanomaterials 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, D.G.; Smith, J.N.; Thrall, B.D.; Baer, D.R.; Jolley, H.; Munusamy, P.; Kodali, V.; Demokritou, P.; Cohen, J.; Teeguarden, J.G. ISD3: A Particokinetic Model for Predicting the Combined Effects of Particle Sedimentation, Diffusion and Dissolution on Cellular Dosimetry for in Vitro Systems. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aureli, F.; Ciprotti, M.; D’Amato, M.; do Nascimento da Silva, E.; Nisi, S.; Passeri, D.; Sorbo, A.; Raggi, A.; Rossi, M.; Cubadda, F. Determination of Total Silicon and SiO2 Particles Using an ICP-MS Based Analytical Platform for Toxicokinetic Studies of Synthetic Amorphous Silica. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossert, D.; Urban, D.A.; Maceroni, M.; Ackermann-Hirschi, L.; Haeni, L.; Yajan, P.; Spuch-Calvar, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Petri-Fink, A.; et al. A Hydrofluoric Acid-Free Method to Dissolve and Quantify Silica Nanoparticles in Aqueous and Solid Matrices. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Chen, S. Macrophage Autophagy and Silicosis: Current Perspective and Latest Insights. IJMS 2021, 22, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turci, F.; Pavan, C.; Leinardi, R.; Tomatis, M.; Pastero, L.; Garry, D.; Anguissola, S.; Lison, D.; Fubini, B. Revisiting the Paradigm of Silica Pathogenicity with Synthetic Quartz Crystals: The Role of Crystallinity and Surface Disorder. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fubini, B.; Zanetti, G.; Altilia, S.; Tiozzo, R.; Lison, D.; Saffiotti, U. Relationship between Surface Properties and Cellular Responses to Crystalline Silica: Studies with Heat-Treated Cristobalite. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1999, 12, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokel, R.A.; Hancock, M.L.; Cherian, B.; Brooks, A.J.; Ensor, M.L.; Vekaria, H.J.; Sullivan, P.G.; Grulke, E.A. Simulated Biological Fluid Exposure Changes Nanoceria’s Surface Properties but Not Its Biological Response. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemann, M.; Vennemann, A.; Blaske, F.; Sperling, M.; Karst, U. Silver Nanoparticles in the Lung: Toxic Effects and Focal Accumulation of Silver in Remote Organs. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathé, C.; Devineau, S.; Aude, J.-C.; Lagniel, G.; Chédin, S.; Legros, V.; Mathon, M.-H.; Renault, J.-P.; Pin, S.; Boulard, Y.; et al. Structural Determinants for Protein Adsorption/Non-Adsorption to Silica Surface. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wattiez, R.; Hermans, C.; Bernard, A.; Lesur, O.; Falmagne, P. Human Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid: Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis, Amino Acid Microsequencing and Identification of Major Proteins. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 1634–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël-Georis, I.; Bernard, A.; Falmagne, P.; Wattiez, R. Database of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Proteins. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 771, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, M.; Kreyling, W.G. Deposition and Biokinetics of Inhaled Nanoparticles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wohlleben, W.; Hellack, B.; Nickel, C.; Herrchen, M.; Hund-Rinke, K.; Kettler, K.; Riebeling, C.; Haase, A.; Funk, B.; Kühnel, D.; et al. The NanoGRAVUR Framework to Group (Nano)Materials for Their Occupational, Consumer, Environmental Risks Based on a Harmonized Set of Material Properties, Applied to 34 Case Studies. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17637–17654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Material | Size of Primary Structures (nm) (1) | Aggregate Size (nm) (1) | BET (m2/g) (2) | Zeta Potential (mV) (3) | Solubility (mg/L) (4) | pH (5) | SEARs No. (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEROSIL® 380F | 8.0 ± 2.7 | 101.9 | 390 | −36 | 226.0 | 4.2 | 14.5 |
| AEROSIL® OX50 | 41.4 ± 18.3 | 233.7 | 45 | −40 | 117.9 | 4.6 | 1.8 |
| SIPERNAT® 50 | 3.1. ± 0.7 | 59.8 | 460 | −21 | 113.9 | 6.3 | 16.3 |
| SIPERNAT® 160 | 12.2. ± 2.7 | 58.3 | 180 | −53 | 112.1 | 6.1 | 11.1 |
| 10% FCS | FCS-Free | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Cell-Associated SiO2 (µg) (1) | % Total (2) | Cell-Associated SiO2 (µg) (1) | % Total (2) | Ratio FCS-Free/10% FCS (3) |
| AEROSIL® 380 F | 4.4/4.4 | 6.6/6.6 | 13.3/15.6 | 19.9/23.4 | 3.28 |
| AEROSIL® OX50 | 5.7/5.8 | 8.4/8.6 | 33.3/37.8 | 49.5/56.2 | 6.18 |
| SIPERNAT® 50 | 25.5/26.7 | 42.3/44.3 | 27.8/30.1 | 46.1/49.9 | 1.11 |
| SIPERNAT® 160 | 13.3/14.4 | 21.1/22.8 | 34.4/38.9 | 54.5/61.6 | 2.65 |
| Control (4) | 1.2/1.6 | -/- | 1.2/1.3 | -/- | - |
| Low Observed Adverse Effect Concentration (LOAEC) Shift (µg/mL) (2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | LDH (1) | GLU (1) | TNFα (1) | LDH | GLU | H2O2 | TNFα |
| AEROSIL® 380F | −92.6% | −81.2% | −87.4% | 11.25⟶90 | 11.25⟶90 | 90⟶≥90 | 45⟶≥90 |
| AEROSIL® OX50 | −68.9% | −65.9% | −81.2% | 45⟶90 | 45⟶90 | 90⟶≥90 | 45⟶≥90 |
| SIPERNAT® 50 | −72.3% | −64.1% | −81.9% | 22.5⟶90 | 45⟶90 | 45⟶≥90 | 45⟶≥90 |
| SIPERNAT® 160 | −79.6% | −71.6% | −79.6% | 11.25⟶45 | 22.5⟶90 | 90⟶≥90 | 45⟶≥90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiemann, M.; Vennemann, A.; Venzago, C.; Lindner, G.-G.; Schuster, T.B.; Krueger, N. Serum Lowers Bioactivity and Uptake of Synthetic Amorphous Silica by Alveolar Macrophages in a Particle Specific Manner. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030628
Wiemann M, Vennemann A, Venzago C, Lindner G-G, Schuster TB, Krueger N. Serum Lowers Bioactivity and Uptake of Synthetic Amorphous Silica by Alveolar Macrophages in a Particle Specific Manner. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(3):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030628
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiemann, Martin, Antje Vennemann, Cornel Venzago, Gottlieb-Georg Lindner, Tobias B. Schuster, and Nils Krueger. 2021. "Serum Lowers Bioactivity and Uptake of Synthetic Amorphous Silica by Alveolar Macrophages in a Particle Specific Manner" Nanomaterials 11, no. 3: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030628
APA StyleWiemann, M., Vennemann, A., Venzago, C., Lindner, G. -G., Schuster, T. B., & Krueger, N. (2021). Serum Lowers Bioactivity and Uptake of Synthetic Amorphous Silica by Alveolar Macrophages in a Particle Specific Manner. Nanomaterials, 11(3), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030628