Large Optical Nonlinearity of the Activated Carbon Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
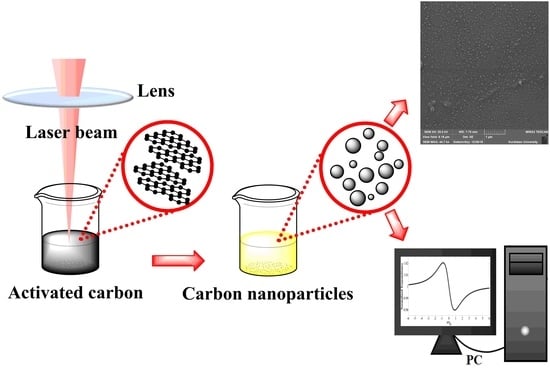
2.2. Laser Ablation of Suspended AC
2.3. Z-Scan Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khashan, K.; Jabir, M.; Abdulameer, F. In Preparation and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles decorated carbon nanoparticles using laser ablation in liquid. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1003, 012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Shojaei, A.F.; Tabatabaeian, K.; Karimi, F.; Shakeri, S.; Moradi, R. Simultaneous determination of 6-mercaptopruine, 6-thioguanine and dasatinib as three important anticancer drugs using nanostructure voltammetric sensor employing Pt/MWCNTs and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluoro phosphate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadian, E.; Ghalkhani, M.; Shahrokhian, S. Electrochemical sensing based on carbon nanoparticles: A review. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 293, 183–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Arotiba, O.A. Simultaneous determination of cholesterol, ascorbic acid and uric acid as three essential biological compounds at a carbon paste electrode modified with copper oxide decorated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite and ionic liquid. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogesh, G.K.; Shuaib, E.; Sastikumar, D. Photoluminescence properties of carbon nanoparticles synthesized from activated carbon powder (4% ash) by laser ablation in solution. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 91, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahernejad-Javazmi, F.; Shabani-Nooshabadi, M.; Karimi-Maleh, H. Analysis of glutathione in the presence of acetaminophen and tyrosine via an amplified electrode with MgO/SWCNTs as a sensor in the hemolyzed erythrocyte. Talanta 2018, 176, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Chen, R.; He, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, K. Hollow core–shell structured silicon@carbon nanoparticles embed in carbon nanofibers as binder-free anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 342, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Jiang, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Dong, A.; Hu, J.; Yang, D. Ionic liquid assist to prepare Si@N-doped carbon nanoparticles and its high performance in lithium ion batteries. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 691, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, D.; Duan, H.; Lv, Y.; Li, L.; Gan, L. Ultramicroporous carbon nanoparticles derived from metal–organic framework nanoparticles for high-performance supercapacitors. Mater. Chem. Phy. 2018, 211, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W. Template-assisted synthesized hollow sphere-like NiCoP/carbon nanoparticles composites for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 880, 114862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedira, S.; Mendaci, B. Hydrothermal synthesis of spherical carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) for supercapacitor electrodes uses. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2020, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Ming, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; He, X.; Huang, H.; Pan, K.; Kang, Z.; Lee, S.-T. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles: Electrochemical synthesis and their pH sensitive photoluminescence properties. New J. Chem 2011, 35, 2666–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Das, P.; Bag, S.; Laha, D.; Pramanik, P. Synthesis, functionalization and bioimaging applications of highly fluorescent carbon nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazbayev, S.; Zhunisbekov, A.; Ramazanov, T.; Omirbekov, D.; Dosbolayev, M.; Gabdullin, M.; Zhumadylov, R. Synthesis of carbon nanoparticles in combined RF-DC plasma. Mater. Today 2018, 5, 22819–22824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemizadeh, F.; Malekfar, R.; Parvin, P. Pulsed laser ablation synthesis of carbon nanoparticles in vacuum. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 104, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Rosowski, A.; Koperkiewicz, A.; Grobelny, J.; Wach, R.; Sharp, M.; French, P.; Janasz, L.; Kozanecki, M. Carbon nanoparticles fabricated by infrared laser ablation of graphite and polycrystalline diamond targets. Phys. Status Solidi 2017, 214, 1600318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semaltianos, N. Nanoparticles by laser ablation. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2010, 35, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S. Laser synthesis and processing of colloids: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3990–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khashan, K.S.; Abdulameer, F.A.; Jabir, M.S.; Hadi, A.A.; Sulaiman, G.M. Anticancer activity and toxicity of carbon nanoparticles produced by pulsed laser ablation of graphite in water. Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 035010. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Zeng, A.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, C.; Wei, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Xie, F. Carbon Quantum Dots: In vitro and in vivo Studies on Biocompatibility and Biointeractions for Optical Imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Dong, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, S. Simultaneous synthesis of luminescent carbon nanoparticles and carbon nanocages by laser ablation of carbon black suspension and their optical limiting properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1957–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małolepszy, A.; Błonski, S.; Chrzanowska-Giżyńska, J.; Wojasiński, M.; Płocinski, T.; Stobinski, L.; Szymanski, Z. Fluorescent carbon and graphene oxide nanoparticles synthesized by the laser ablation in liquid. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohazzab, B.F.; Jaleh, B.; Kakuee, O.; Fattah-Alhosseini, A. Formation of titanium carbide on the titanium surface using laser ablation in n-heptane and investigating its corrosion resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Du, X.W.; Singh, S.C.; Kulinich, S.A.; Yang, S.; He, J.; Cai, W. Nanomaterials via laser ablation/irradiation in liquid: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1333–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.; Reinoso, F.R. Activated Carbon; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, W.; Fu, J.; Mao, X.; Kang, Q.; Ran, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, G. Microwave assisted preparation of activated carbon from biomass: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 92, 958–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Sharma, V.K.; Kumar, E.A.; Gayathri, V. Hydrogen storage in carbon materials—A review. Energy Stor. 2019, 1, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Kränkel, C.; Kannari, F. Transition-metal-doped saturable absorbers for passive Q-switching of visible lasers. Opt. Mater. Express 2020, 10, 1827–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundén, H.; Glimsdal, E.; Lindgren, M.; Lopes, C. How to assess good candidate molecules for self-activated optical power limiting. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 030802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, K.; Zhu, J.; Wolenski, C.; Das, A.; Horning, T.M.; Pampel, S.; Grayson, M.B.; Zohrabi, M.; Gopinath, J.T.; Park, W. Indium Tin Oxide Nanoparticle-Coated Silica Microsphere with Large Optical Nonlinearity and High Quality Factor. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 3042–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfer, C.; Hits, D.; Kasmi, L.; Kramberger, G.; Lucchini, M.; Mikuž, M.; Wallny, R. Three-dimensional charge transport mapping by two-photon absorption edge transient-current technique in synthetic single-crystalline diamond. Appl. Phys. Lett 2019, 114, 203504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewart, P. Encyclopedia of Modern Optics. In SPECTROSCOPY|Nonlinear Laser Spectroscopy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Papagiannouli, I.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Bakandritsos, A.; Couris, S. Nonlinear optical properties of colloidal carbon nanoparticles: Nanodiamonds and carbon dots. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40152–40160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, K.; Hu, J.; Liu, R.; Zhu, H. Nitrogen and sulphur co-doped carbon quantum dots and their optical power limiting properties. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 3176–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Lu, D.; Tian, W.; Zhang, R.; Yu, H.; Gorecka, E.; Pociecha, D.; Godbert, N.; Hao, J.; Li, H. Ordered Structures of Alkylated Carbon Dots and Their Applications in Nonlinear Optics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 8980–8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlinos, A.B.; Trivizas, G.; Karakassides, M.A.; Baikousi, M.; Kouloumpis, A.; Gournis, D.; Bakandritsos, A.; Hola, K.; Kozak, O.; Zboril, R. Green and simple route toward boron doped carbon dots with significantly enhanced non-linear optical properties. Carbon 2015, 83, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xiang, W.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Ni, Y.; Liang, X. Facile synthesis of tunable fluorescent carbon dots and their third-order nonlinear optical properties. Dyes Pigm. 2016, 128, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijesh, K.; Musfir, P.; Thomas, T.; Vaishakh, M.; Nampoori, V.; Thomas, S. Enhanced nonlinear optical properties of solution dispersed carbon dots decorated graphene oxide with varying viscosity. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 121, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bai, L.; Shen, L.; Yao, B.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Kang, Z. Nonlinear optical switching behavior of nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Opt. Mater. 2019, 95, 109216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Qiao, S.; Li, H.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Kang, Z. N-Doped carbon dot with surface dominant non-linear optical properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 95476–95482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Chang, Q. AOPC 2015: In Advances in Laser Technology and Applications. In Nonlinear Absorption Characteristics of Carbon Quantum Dots; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; p. 96710A. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Contreras, D.; Camacho-López, M.; Camacho-López, M.A.; Camacho-López, S.; Rodríguez-Beltrán, R.I.; Mayorga-Rojas, M. Influence of the per pulse laser fluence on the optical properties of carbon nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation of solids in liquids. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 74, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiling, T.T.; Cywiński, P.J.; Bald, I. White carbon: Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles with tunable quantum yield in a reproducible green synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; He, J.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Dey, S.; Zhao, J.; Lei, Y. Microwave-assisted ultrafast and facile synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles from a single precursor: Preparation, characterization and their application for the highly selective detection of explosive picric acid. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4161–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshni, V.; Ottoor, D. Synthesis of carbon nanoparticles using one step green approach and their application as mercuric ion sensor. J. Lumin. 2015, 161, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wu, S.; Du, X. Gated mesoporous carbon nanoparticles as drug delivery system for stimuli-responsive controlled release. Carbon 2016, 101, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharker, S.M.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.E.; Jeong, J.H.; In, I.; Lee, K.D.; Lee, H.; Park, S.Y. In situ synthesis of luminescent carbon nanoparticles toward target bioimaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5468–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, S. Sweet potato-derived carbon nanoparticles as anode for lithium ion battery. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40737–40741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, P.Z.Z.; Chia, S.P.P.; Fong, J.F.Y.; Ng, S.M. Synthesis of carbon nanoparticles from waste rice husk used for the optical sensing of metal ions. New Carbon Mater. 2016, 31, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekaliuk, M.; Pyrshev, K.; Demchenko, A. Visualization and detection of live and apoptotic cells with fluorescent carbon nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.; Mishra, A.K. Green and cost-effective fluorescent carbon nanoparticles for the selective and sensitive detection of iron (III) ions in aqueous solution: Mechanistic insights and cell line imaging studies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xuan, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Li, H. A facile, green synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon nanoparticles from oatmeal for cell imaging. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 9514–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Cao, B.; Li, L.; Zhu, Z. Light-induced synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanoparticles for Fe 3+ sensing and photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcudi, F.; Đorđević, L.; Prato, M. Synthesis, Separation, and Characterization of Small and Highly Fluorescent Nitrogen-Doped Carbon NanoDots. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaleh, B.; Rouzbahani, M.G.; Abedi, K.; Azizian, S.; Ebrahimi, H.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Varma, R.S. Photocatalytic decomposition of VOCs by AC–TiO2 and EG–TiO2 nanocomposites. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik-Bahae, M.; Said, A.A.; Van Stryland, E.W. High-sensitivity, single-beam n2 measurements. Opt. Lett. 1989, 14, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik-Bahae, M.; Said, A.A.; Wei, T.-H.; Hagan, D.J.; Van Stryland, E.W. Sensitive measurement of optical nonlinearities using a single beam. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1990, 26, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Stryland, E.W.; Sheik-Bahae, M. Characterization Techniques and Tabulations for Organic Nonlinear Optical Materials, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 671–708. [Google Scholar]
- MR, R.V. Role of the aperture in Z-scan experiments: A parametric study. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 114206. [Google Scholar]
- Vaziri, M.R. Comment on “Nonlinear refraction measurements of materials using the moiré deflectometry”. Opt. Commun. 2015, 357, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvar, A.; RashidianVaziri, M.; Jaleh, B. Enhancing the nonlinear optical properties of graphene oxide by repairing with palladium nanoparticles. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2018, 103, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, P.; Vaziri, M.R.; Jaleh, B.; Shabestari, N.P. Nonlocal nonlinear optical response of graphene oxide-Au nanoparticles dispersed in different solvents. J. Opt. 2015, 18, 015502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, M.R.R. Z-scan theory for nonlocal nonlinear media with simultaneous nonlinear refraction and nonlinear absorption. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 4843–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, M.R. Describing the propagation of intense laser pulses in nonlinear Kerr media using the ducting model. Laser Phys 2013, 23, 105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, R.A.; Mohsin, M.H.; Ali, A.K.; Hassoon, K.I.; Erten-Ela, S. Preparation and characterization of carbon nanotubes by pulsed laser ablation in water for optoelectronic application. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2020, 119, 113997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganash, E.A.; Al-Jabarti, G.A.; Altuwirqi, R.M. The synthesis of carbon-based nanomaterials by pulsed laser ablation in water. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 7, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Lv, J.-J.; Zhou, D.-L.; Bao, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, A.-J.; Feng, J.-J. One-pot green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles as fluorescent probes for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21691–21696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.C.; Lefumeux, C.; Pino, T. Differential Raman backscattering cross sections of black carbon nanoparticles. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cárdenas, J.F.; Cadenbach, T.; Zhang, Z.-B.; Costa-Vera, C.; Debut, A.; Vaca, A.; Zhang, S.-L.; Paz, J. Raman spectroscopy of carbon nano-particles synthesized by laser ablation of graphite in water. Rev. Mex. Fis. 2017, 63, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, X.; Liang, C. Carbon-encapsulated metal/metal carbide/metal oxide core–shell nanostructures generated by laser ablation of metals in organic solvents. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 2, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, M.; Jaleh, B.; Vaziri, M.R.; Omidvar, A. Study of nonlinear optical properties of TiO2–polystyrene nanocomposite films. Quantum Electron. 2019, 49, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, C.H.; Lee, Y.L.; Kim, S.G. Analysis of asymmetric Z-scan measurement for large optical nonlinearities in an amorphous As2S3 thin film. JOSA B 1999, 16, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousova, I.M.; Videnichev, D.A.; Kislyakov, I.M.; Krisko, T.K.; Rozhkova, N.N.; Rozhkov, S.S. Comparative studies of optical limiting in fullerene and shungite nanocarbon aqueous dispersions. Opt. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, G.; Vazquez, P.; Agullo-Lopez, F.; Torres, T. Role of structural factors in the nonlinear optical properties of phthalocyanines and related compounds. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3723–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, S.; Marder, S.R. Nonlinear Optical Properties of Organic Materials; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Sahu, S.; Anilkumar, P.; Kong, C.Y.; Sun, Y.-P. Linear and nonlinear optical properties of modified graphene-based materials. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Dong, H.; Ju, Y.; He, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, K.; Liao, K.-S.; Zhang, L. Graphene and carbon nanotube polymer composites for laser protection. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2011, 21, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, X.F.; Chen, Z.P. A Review of Carbon Dots Produced from Biomass Wastes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Nanostructure | CNPs Synthesis Method | CNPs Size (nm) | Properties and Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon nanoparticles | LAL | 4–20 | -Good photoluminescence -Can be used for bioimaging | [42] |
| Nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots (N-CND) and Starch Derived Carbon Nanodots (C-CND) | microwave-assisted hydrothermal precursor carbonization | 2.0 ± 0.24 (C-CND) and 2.4 ± 0.25 (N-CND) | -High photoluminescence quantum yield -Long-term stability -Having stable emission | [43] |
| Boron-doped carbon dots | Microwave heating | 2–6 | -Robust blue fluorescence under UV excitation -Large nonlinear optical | [36] |
| Nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles | Microwave oven | 5.5 ± 1.5 | -Highly fluorescent | [44] |
| Carbon nanoparticles | Thermal pyrolysis | 20–50 | -Highly fluorescent -Excellent photoluminescent -Used as a metal sensing probe | [45] |
| Carbon nanoparticles | Thermal carbonization | - | -Synthesized nanoscale particle size -Used as a supercapacitor -Highly specific capacitance and excellent long-term cycle stability | [9] |
| Carbon nanoparticles | Stirring and reflux method | 115 | - Improved release of the drugs | [46] |
| Carbon nanoparticles | Dehydration of hyaluronic acid and carbonized hyaluronic acid | <20 | -Flexibility -Biocompatible and low cytotoxicity -Used for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging | [47] |
| Carbon Nanoparticles | Hydrothermal carbonization and high-temperature annealing | 120 | -Used as an anode for lithium-ion Battery | [48] |
| Carbon Nanoparticles | Thermally-assisted carbonization | - | -synthesized nanoparticles in small size -Strong blue luminescence -Used for sensing of metal ions | [49] |
| Carbon dots | Microwave oven | <10 | -Highly biocompatible -Great fluorescent property -Used for cell imaging | [50] |
| Carbon Nanoparticles | acid treatment of naturally occurring d-glucose followed by heating | <5 | -Used for sensing of metal ions -Used for in vivo imaging | [51] |
| Carbon Nanoparticles | Hydrothermal treatment | 20–40 | - Highly photoluminescent and photo-stability -Low toxicity and good biocompatibility -Used for in vitro and in vivo imaging | [52] |
| Carbon Nanoparticles | Light-induced process | 40 | -Used for sensing of metal ions -Used as a photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution | [53] |
| Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots | Microwave-assisted | 2.47 ± 0.84 | -Size and surface controllable of synthesized NPs -Fluorescent emission -Excellent solubility in water | [54] |
| Carbon nanoparticles | Laser ablation in n-heptane | 23.84 | -Large optical nonlinearities with 442 nm laser radiation | This work |
| Excitation Wavelength (nm) | Fluorescence Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|
| 320 | 395 |
| 340 | 421 |
| 360 | 435 |
| 372 | 442 |
| 380 | 449 |
| 420 | 477 |
| 440 | 494 |
| 460 | 514 |
| n2 (cm2/W) | β (cm/W) |
|---|---|
| −1.15 ± 0.09 × 10−9 | 1.49 ± 0.11 × 10−4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orooji, Y.; Ghanbari Gol, H.; Jaleh, B.; Rashidian Vaziri, M.R.; Eslamipanah, M. Large Optical Nonlinearity of the Activated Carbon Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030737
Orooji Y, Ghanbari Gol H, Jaleh B, Rashidian Vaziri MR, Eslamipanah M. Large Optical Nonlinearity of the Activated Carbon Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(3):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030737
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrooji, Yasin, Hamed Ghanbari Gol, Babak Jaleh, Mohammad Reza Rashidian Vaziri, and Mahtab Eslamipanah. 2021. "Large Optical Nonlinearity of the Activated Carbon Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation" Nanomaterials 11, no. 3: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030737
APA StyleOrooji, Y., Ghanbari Gol, H., Jaleh, B., Rashidian Vaziri, M. R., & Eslamipanah, M. (2021). Large Optical Nonlinearity of the Activated Carbon Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation. Nanomaterials, 11(3), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030737