A Guide for Using Transmission Electron Microscopy for Studying the Radiosensitizing Effects of Gold Nanoparticles In Vitro
Abstract
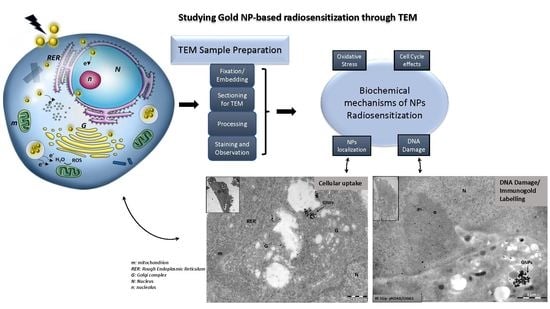
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Results
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Incubation with Gold Nanoparticles
2.3. Irradiation of the Cells
2.4. Cell Fixation and Preparation for TEM
2.4.1. Embedding in Gelatin of Cells Attached to a Substrate (Adherent Cells)
2.4.2. Cells in Suspension (Lymphocytes)
2.5. Processing and Embedding in Epoxy Resin
2.6. Processing and Embedding in Acrylic Resin
2.7. Sectioning of Resin-Embedded Tissue Blocks
2.7.1. Semi-Thin Sections
Staining of Semi-Thin Sections
2.7.2. Thin Sections
Staining of Thin Sections
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Immunocytochemisty
2.8.1. Immunogold Labelling
2.8.2. Post-Embedding Immunogold-Labelling
2.9. Use of TEM to Monitor Gold Nanoparticle Cellular Uptake
2.10. Silver-Enhancement of Gold Nanoparticles
2.11. Immunogold Labelling for DNA Damage Detection
3. Materials
3.1. Equipment
3.2. Reagents
Reagent’s Preparation
3.3. Gold Nanoparticles
3.3.1. Citrate-Capped GNPs 15 nm Preparation
3.3.2. PEG-Capped GNPs Preparation
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayhew, T.M.; Mühlfeld, C.; Vanhecke, D.; Ochs, M. A review of recent methods for efficiently quantifying immunogold and other nanoparticles using TEM sections through cells, tissues and organs. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2009, 191, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skepper, J.N.; Powell, J.M. Ultrastructural Immunochemistry. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb.top47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, J.M.; Takizawa, T.; Vandré, D.D. Enhanced Labeling Efficiency Using Ultrasmall Immunogold Probes: Immunocytochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2000, 48, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C.W. Determining the Size and Shape Dependence of Gold Nanoparticle Uptake into Mammalian Cells. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igaz, N.; Szőke, K.; Kovács, D.; Buhala, A.; Varga, Z.; Bélteky, P.; Rázga, Z.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Vizler, C.; Hideghéty, K.; et al. Synergistic Radiosensitization by Gold Nanoparticles and the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor SAHA in 2D and 3D Cancer Cell Cultures. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazmi, F.; Vallis, K.A.; Vellayappan, B.A.; Bandla, A.; Yukun, D.; Carlisle, R. Megavoltage Radiosensitization of Gold Nanoparticles on a Glioblastoma Cancer Cell Line Using a Clinical Platform. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haume, K.; Rosa, S.; Grellet, S.; Śmiałek, M.A.; Butterworth, K.T.; Solov‘yov, A.V.; Prise, K.M.; Golding, J.; Mason, N.J. Gold nanoparticles for cancer radiotherapy: A review. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barsoumian, H.B.; Ramapriyan, R.; Younes, A.I.; Caetano, M.S.; Menon, H.; Comeaux, N.I.; Cushman, T.R.; Schoenhals, J.E.; Cadena, A.P.; Reilly, T.P.; et al. Low-dose radiation treatment enhances systemic antitumor immune responses by overcoming the inhibitory stroma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branzei, D.; Foiani, M. Regulation of DNA repair throughout the cell cycle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, M.; Lukášová, E.; Kozubek, S. Chromatin structure influences the sensitivity of DNA to γ-radiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 2398–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, D.; Monaghan, P.; Clarke, C.; Atherton, A.J. An appraisal of low-temperature embedding by progressive lowering of temperature into Lowicryl HM20 for immunocytochemical studies. J. Microsc. 1992, 168, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.; Bendayan, M.; Orci, L. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1978, 26, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, M.A. Positive Staining for Electron Microscopy/M. A. Hayat; Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, E.S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, J. The silver anniversary of gold: 25 years of the colloidal gold marker system for immunocytochemistry and histochemistry. Histochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 106, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulk, W.P.; Taylor, G.M. Communication to the editors: An immunocolloid method for the electron microscope. Immunochemistry 1971, 8, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wu, Y.; Jin, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, L.; Liang, X.-J. Gold Nanoparticles Induce Autophagosome Accumulation through Size-Dependent Nanoparticle Uptake and Lysosome Impairment. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8629–8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Liao, J.; Shao, X.; Li, Q.; Lin, Y. The Effect of shape on Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanoparticles in the forms of Stars, Rods, and Triangles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Fu, S.; Wu, J. Gold Nanoparticles as Radiosensitizers in Cancer Radiotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9407–9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Penninckx, S.; Karmani, L.; Heuskin, A.-C.; Watillon, K.; Marega, R.; Zola, J.; Corvaglia, V.; Genard, G.; Gallez, B.; et al. LET-dependent radiosensitization effects of gold nanoparticles for proton irradiation. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 455101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Slatkin, D.N.; Smilowitz, H.M. The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, N309–N315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefančíková, L.; Porcel, E.; Eustache, P.; Li, S.; Salado, D.; Marco, S.; Guerquin-Kern, J.-L.; Réfrégiers, M.; Tillement, O.; Lux, F.; et al. Cell localisation of gadolinium-based nanoparticles and related radiosensitising efficacy in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holgate, C.S.; Jackson, P.; Cowen, P.N.; Bird, C.C. Immunogold-silver staining: New method of immunostaining with enhanced sensitivity. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1983, 31, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danscher, G.; Nörgaard, J.O. Light microscopic visualization of colloidal gold on resin-embedded tissue. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1983, 31, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baude, A.; Nusser, Z.; Molnar, E.; McIlhinney, R.A.J.; Somogyi, P. High-resolution immunogold localization of AMPA type glutamate receptor subunits at synaptic and non-synaptic sites in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 1995, 69, 1031–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piludu, M.; Medda, L.; Cugia, F.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. Silver Enhancement for Transmission Electron Microscopy Imaging of Antibody Fragment–Gold Nanoparticles Conjugates Immobilized on Ordered Mesoporous Silica. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9458–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piludu, M.; Medda, L.; Monduzzi, M.; Salis, A. Gold Nanoparticles: A Powerful Tool to Visualize Proteins on Ordered Mesoporous Silica and for the Realization of Theranostic Nanobioconjugates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baschong, W.; Wrigley, N.G. Small colloidal gold conjugated to fab fragments or to immunoglobulin g as high-resolution labels for electron microscopy: A technical overview. J. Electron Microsc. Tech. 1990, 14, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, S.J.; Hyland, W.B.; Muir, M.F.; Coulter, J.A.; Jain, S.; Butterworth, K.T.; Schettino, G.; Dickson, G.R.; Hounsell, A.R.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; et al. Biological consequences of nanoscale energy deposition near irradiated heavy atom nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimling, J.; Maier, M.; Okenve, B.; Kotaidis, V.; Ballot, H.; Plech, A. Turkevich Method for Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis Revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15700–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Graham, S.; Wang, Z.; Tan, B.; Sherrington, D.C.; Rannard, S.P.; Cooper, A.I.; Brust, M. Size-Controlled Synthesis of Near-Monodisperse Gold Nanoparticles in the 1−4 nm Range Using Polymeric Stabilizers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16398–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitaki, Z.; Pariset, E.; Sudar, D.; Costes, S.V.; Georgakilas, A.G. In Situ Detection of Complex DNA Damage Using Microscopy: A Rough Road Ahead. Cancers 2020, 12, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Resins | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Glycid ether 100 | 30.24 g |
| Araldite CY212 | 17.40 g |
| DDSA | 52.68 g |
| Dibutyl Phthalate (plasticiser) | 2 mL |
| DMP-30 | 74 drops |
| Resins | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Crosslinker D | 7.45 g |
| Monomer E | 42.55 g |
| Initiator C (powder) | 0.25 g |
| Processing Steps | GNPs Cellular Uptake/Morphology | GNPs Radiosensitization through Immunocytochemistry |
|---|---|---|
| Fixation | 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution in 0.01 M PBS | 3% paraformaldehyde and 0.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M PB |
| PLT method/ | ||
| Embedding | Epoxy resin/acrylic resin | Acrylic resin |
| Sectioning/grids | 80 nm/copper grids | 80 nm/formvar coated nickel grids |
| Immunolocalization | - | Single or Double immunogold labelling |
| Silver enhancement | YES (for small GNPs) | YES (for small gold-conjugated antibodies) |
| Staining | 7.5% alcoholic uranyl acetate and 0.4% lead citrate | |
| Observation | TEM operating at 80-kV with an objective aperture of 30 μm and equipped with a digital CCD camera | |
| Quantification | Electron micrographs of 22,000–40,000× original magnification | |
| Image analysis software (e.g., ImageJ) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tremi, I.; Havaki, S.; Georgitsopoulou, S.; Lagopati, N.; Georgakilas, V.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Georgakilas, A.G. A Guide for Using Transmission Electron Microscopy for Studying the Radiosensitizing Effects of Gold Nanoparticles In Vitro. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040859
Tremi I, Havaki S, Georgitsopoulou S, Lagopati N, Georgakilas V, Gorgoulis VG, Georgakilas AG. A Guide for Using Transmission Electron Microscopy for Studying the Radiosensitizing Effects of Gold Nanoparticles In Vitro. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(4):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040859
Chicago/Turabian StyleTremi, Ioanna, Sophia Havaki, Sofia Georgitsopoulou, Nefeli Lagopati, Vasilios Georgakilas, Vassilis G. Gorgoulis, and Alexandros G. Georgakilas. 2021. "A Guide for Using Transmission Electron Microscopy for Studying the Radiosensitizing Effects of Gold Nanoparticles In Vitro" Nanomaterials 11, no. 4: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040859
APA StyleTremi, I., Havaki, S., Georgitsopoulou, S., Lagopati, N., Georgakilas, V., Gorgoulis, V. G., & Georgakilas, A. G. (2021). A Guide for Using Transmission Electron Microscopy for Studying the Radiosensitizing Effects of Gold Nanoparticles In Vitro. Nanomaterials, 11(4), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040859