Novel Concept of Micro Patterned Micro Titer Plates Fabricated via UV-NIL for Automated Neuronal Cell Assay Read-Out
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mastering
2.2. P2P UV-NIL Imprints
2.3. Converting to R2R UV-NIL
2.4. Cytotoxicity Validation
2.5. Neuronal Growth
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mastering
3.2. P2P UV-NIL Imprints
3.3. Converting to R2R UV-NIL
3.4. Cytotoxicity Validation
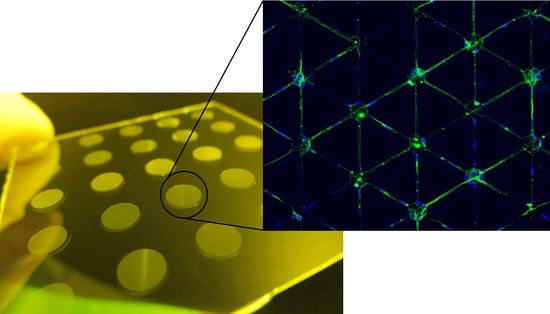
3.5. Neuronal Growth
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deleglise, B.; Lassus, B.; Soubeyre, V.; Alleaume-Butaux, A.; Hjorth, J.J.; Vignes, M.; Schneider, B.; Brugg, B.; Viovy, J.-L.; Peyrin, J.-M. Synapto-Protective Drugs Evaluation in Reconstructed Neuronal Network. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsson, P.; Engqvist, H.; Biermann, J.; Rönnerman, E.W.; Forssell-Aronsson, E.; Kovács, A.; Karlsson, P.; Helou, K.; Parris, T.Z. Optimization of cell viability assays to improve replicability and reproducibility of cancer drug sensitivity screens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nierode, G.; Kwon, P.S.; Dordick, J.S.; Kwon, S.-J. Cell-Based Assay Design for High-Content Screening of Drug Candidates. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kepp, O.; Galluzzi, L.; Lipinski, M.; Yuan, J.; Kroemer, G. Cell death assays for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, R.; Li, D.; Tang, I.C.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.T. Cell-Based Assays in High-Throughput Screening for Drug Discovery. Int. J. Biotechnol. Wellness Ind. 2012, 1, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.A. Redox cycling compounds generate H2O2 in HTS buffers containing strong reducing reagents—Real hits or promiscuous artifacts? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drewe, J.; Kasibhatla, S.; Tseng, B.; Shelton, E.; Sperandio, D.; Yee, R.M.; Litvak, J.; Sendzik, M.; Spencer, J.R.; Cai, S.X. Discovery of 5-(4-hydroxy-6-methyl-2-oxo-2H-pyran-3-yl)-7-phenyl-(E)-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1,4-thiazepines as a new series of apoptosis inducers using a cell- and caspase-based HTS assay. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4987–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peuhu, E.; Paul, P.; Remes, M.; Holmbom, T.; Eklund, P.; Sjöholm, R.; Eriksson, J.E. The antitumor lignan Nortrachelogenin sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced cell death by inhibition of the Akt pathway and growth factor signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiloh, Y.; Andegeko, Y.; Tsarfaty, I. In search of drug treatment for genetic defects in the DNA damage response: The example of ataxia-telangiectasia. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2004, 14, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeyeodu, S.T.; Witherspoon, S.M.; Gilyazova, N.; Ibeanu, G.C. A Rapid, Inexpensive High Throughput Screen Method for Neurite Outgrowth. Curr. Chem. Genom. 2010, 4, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roach, P.; Parker, T.; Gadegaard, N.; Alexander, M. Surface strategies for control of neuronal cell adhesion: A review. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2010, 65, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hardy, C.; Chen, C.-M.; Yang, S.; Voloshin, A.S.; Liu, Y. Enhanced Cell Adhesion and Alignment on Micro-Wavy Patterned Surfaces. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusuma, S.; Smith, Q.; Facklam, A.; Gerecht, S. Micropattern size-dependent endothelial differentiation from a human induced pluripotent stem cell line. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joo, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, E.; Hong, N.; Sun, W.; Nam, Y. Effects of ECM protein micropatterns on the migration and differentiation of adult neural stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buzanska, L.; Zychowicz, M.; Ruiz, A.; Rossi, F. Stem Cell Technologies in Neuroscience; Neuromethods; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 126, pp. 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lücker, P.B.; Javaherian, S.; Soleas, J.P.; Halverson, D.; Zandstra, P.W.; McGuigan, A.P. A microgroove patterned multiwell cell culture plate for high-throughput studies of cell alignment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, P.; Parker, T.; Gadegaard, N.; Alexander, M.R. A bio-inspired neural environment to control neurons comprising radial glia, substrate chemistry and topography. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendler, C.; Harberts, J.; Rafeldt, L.; Loers, G.; Zierold, R.; Blick, R.H. Neurite guidance and neuro-caging on steps and grooves in 2.5 dimensions. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 5192–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, Q.Y.; Jadhav, A.D.; Narang, A.; Qian, W.X.; Shi, P.; Pang, S.W. Large-scale Topographical Screen for Investigation of Physical Neural-Guidance Cues. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcus, M.; Baranes, K.; Park, M.; Choi, I.S.; Kang, K.; Shefi, O. Interactions of Neurons with Physical Environments. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, M.J.; Gadegaard, N.; Tare, R.; Andar, A.; Riehle, M.O.; Herzyk, P.; Wilkinson, C.D.W.; Oreffo, R.O.C. The control of human mesenchymal cell differentiation using nanoscale symmetry and disorder. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, P.M.; Pedersen, R.H.; Stormonth-Darling, J.; Dalby, M.J.; Riehle, M.O.; Gadegaard, N. Label-Free Segmentation of Co-cultured Cells on a Nanotopographical Gradient. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; McNamara, L.E.; Gadegaard, N.; Alakpa, E.V.; Burgess, K.V.; Meek, R.M.D.; Dalby, M.J. Nanotopographical Induction of Osteogenesis through Adhesion, Bone Morphogenic Protein Cosignaling, and Regulation of MicroRNAs. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9941–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahfeldt, T.; Litterman, N.K.; Rubin, L.L. Studying human disease using human neurons. Brain Res. 2017, 1656, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gladkov, A.; Pigareva, Y.; Kutyina, D.; Kolpakov, V.; Bukatin, A.; Mukhina, I.; Kazantsev, V.; Pimashkin, A. Design of Cultured Neuron Networks in vitro with Predefined Connectivity Using Asymmetric Microfluidic Channels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forró, C.; Thompson-Steckel, G.; Weaver, S.; Weydert, S.; Ihle, S.; Dermutz, H.; Aebersold, M.J.; Pilz, R.; Demkó, L.; Vörös, J. Modular microstructure design to build neuronal networks of defined functional connectivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 122, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrin, J.-M.; Deleglise, B.; Saias, L.; Vignes, M.; Gougis, P.; Magnifico, S.; Betuing, S.; Pietri, M.; Caboche, J.; Vanhoutte, P.; et al. Axon diodes for the reconstruction of oriented neuronal networks in microfluidic chambers. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3663–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Park, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Yeon, J.H.; Kwon, J.; Ko, J.J.; Oh, S.-H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, A.; Han, B.S.; et al. Monitoring the differentiation and migration patterns of neural cells derived from human embryonic stem cells using a microfluidic culture system. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-T.; Karthikeyan, K.; Chirvi, S.; Dave, D.P. Neuro-optical microfluidic platform to study injury and regeneration of single axons. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2576–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, B.G.C.; Vieira, J.; Larramendy, F.; Honegger, T. Microchannel patterning strategies for in vitro structural connectivity modulation of neural networks. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Vignes, M.; Bureau, C.; Mamane, A.; Venzac, B.; Descroix, S.; Viovy, J.-L.; Villard, C.; Peyrin, J.-M.; Malaquin, L. In-mold patterning and actionable axo-somatic compartmentalization for on-chip neuron culture. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toren, P.; Smolka, M.; Haase, A.; Palfinger, U.; Nees, D.; Ruttloff, S.; Kuna, L.; Schaude, C.; Jauk, S.; Rumpler, M.; et al. High-throughput roll-to-roll production of polymer biochips for multiplexed DNA detection in point-of-care diagnostics. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 4106–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thesen, M.W.; Nees, D.; Ruttloff, S.; Rumler, M.; Rommel, M.; Schlachter, F.; Grützner, S.; Vogler, M.; Schleunitz, A.; Grützner, G. Inkjetable and photo-curable resists for large-area and high-throughput roll-to-roll nanoimprint lithography. J. Micro/Nano Lithogr. MEMS MOEMS 2014, 13, 43003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.; Heinrich, M.; Grützner, S.; Haase, A.; Ramos, I.; Salado, C.; Thesen, M.W.; Grützner, G. Versatile fabrication method for multiscale hierarchical structured polymer masters using a combination of photo- and nanoimprint lithography. Micro Nano Eng. 2021, 21, 100079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schift, H.; Saxer, S.; Park, S.; Padeste, C.; Pieles, U.; Gobrecht, J. Controlled co-evaporation of silanes for nanoimprint stamps. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, S171–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleunitz, A.; Vogler, M.; Fernandez-Cuesta, I.; Schift, H.; Gruetzner, G. Innovative and Tailor-made Resist and Working Stamp Materials for Advancing NIL-based Production Technology. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2013, 26, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decrop, D.; Pardon, G.; Brancato, L.; Kil, D.; Shafagh, R.Z.; Kokalj, T.; Haraldsson, T.; Puers, R.; Van Der Wijngaart, W.; Lammertyn, J. Single-Step Imprinting of Femtoliter Microwell Arrays Allows Digital Bioassays with Attomolar Limit of Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10418–10426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Koh, D.; Xu, L.; Row, S.; Andreadis, S.T.; Oh, K.W. A Simple Method for Fabrication of Microstructures Using a PDMS Stamp. Micromachines 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajrala, V.S.; Suraniti, E.; Rigoulet, M.; Devin, A.; Sojic, N.; Arbault, S. PDMS microwells for multi-parametric monitoring of single mitochondria on a large scale: A study of their individual membrane potential and endogenous NADH. Integr. Biol. 2016, 8, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okulova, N. High Speed Fabrication of Large-Scale Micro-Patternedthermoplastic Films for Industrial Applications NNT 2018; NNT: Braga, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Bong, J.; Ha, Y.-G.; Park, S.; Ju, S. Durability of self-assembled monolayers on aluminum oxide surface for determining surface wettability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 330, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Yi, P.; Wu, H.; Lai, X. Study on bubble defects in roll-to-roll UV imprinting process for micropyramid arrays II: Numerical study. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2016, 34, 051203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Light Source | λ (nm) | Intensity I (mW/cm2) | Dose D (mJ/cm2) | Cell Viability (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hg | UV | 10 | 2000 | 97 ± 4 |
| Hg | UV | 20 | 500 | 101 ± 5 |
| Hg | UV | 20 | 1000 | 99 ± 5 |
| Hg | UV | 20 | 2000 | 95 ± 3 |
| LED | 365 | 10 | 2000 | 93 ± 4 |
| LED | 365 | 20 | 500 | 96 ± 4 |
| LED | 365 | 20 | 1000 | 91 ± 6 |
| LED | 365 | 20 | 2000 | 96 ± 4 |
| LED | 365 | 30 | 2000 | 91 ± 4 |
| LED | 365 | 50 | 2000 | 91 ± 4 |
| LED | 390 | 20 | 2000 | 97 ± 4 |
| LED (R2R) 1 | 395 | - | - | 93 ± 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lohse, M.; Thesen, M.W.; Haase, A.; Smolka, M.; Iceta, N.B.; Ayerdi Izquierdo, A.; Ramos, I.; Salado, C.; Schleunitz, A. Novel Concept of Micro Patterned Micro Titer Plates Fabricated via UV-NIL for Automated Neuronal Cell Assay Read-Out. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040902
Lohse M, Thesen MW, Haase A, Smolka M, Iceta NB, Ayerdi Izquierdo A, Ramos I, Salado C, Schleunitz A. Novel Concept of Micro Patterned Micro Titer Plates Fabricated via UV-NIL for Automated Neuronal Cell Assay Read-Out. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(4):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040902
Chicago/Turabian StyleLohse, Mirko, Manuel W. Thesen, Anja Haase, Martin Smolka, Nerea Briz Iceta, Ana Ayerdi Izquierdo, Isbaal Ramos, Clarisa Salado, and Arne Schleunitz. 2021. "Novel Concept of Micro Patterned Micro Titer Plates Fabricated via UV-NIL for Automated Neuronal Cell Assay Read-Out" Nanomaterials 11, no. 4: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040902
APA StyleLohse, M., Thesen, M. W., Haase, A., Smolka, M., Iceta, N. B., Ayerdi Izquierdo, A., Ramos, I., Salado, C., & Schleunitz, A. (2021). Novel Concept of Micro Patterned Micro Titer Plates Fabricated via UV-NIL for Automated Neuronal Cell Assay Read-Out. Nanomaterials, 11(4), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040902