Impact of Physico-Chemical Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Silver Nanoparticle Hybrid Suspensions on Their Biocidal and Toxicological Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of CNC/AgNP Hybrid Suspensions and H2O2 Post-Reaction
2.3. UV/Vis Spectroscopy
2.4. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)
2.5. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM)
2.6. X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure (XANES) and Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (EXAFS)
2.7. X-ray Diffraction Spectroscopy (XRD)
2.8. Ag+ Relesase Analysis
2.9. Biocidal Tests
2.10. Toxicological Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Variation of AgNP Content in CNC/AgNP Hybrids
3.2. Morphological Variation from Spherical AgNPs to AgNPrisms by H2O2 Redox Post-Treatment
3.3. Short-Term Biocidal Activity: Impact of AgNP Content and Oxidation State
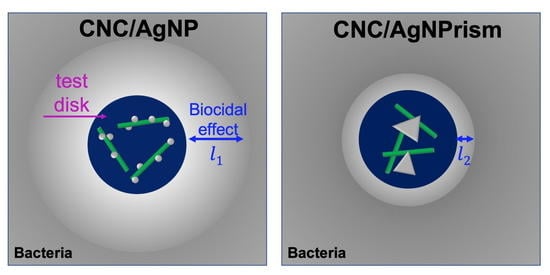
3.4. Short-Term Biocidal Activity: Impact of AgNP Size–Shape Variation by H2O2
3.5. Long-Term Biocidal Activity of CNC/AgNP Hybrids
3.6. Impact of the Variation of AgNP Content on Macrophage Viability and Function
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiu, Z.M.; Zhang, Q.B.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harish, B.S.; Uppuluri, K.B.; Anbazhagan, V. Synthesis of fibrinolytic active silver nanoparticle using wheat bran xylan as a reducing and stabilizing agent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, M.; Allen, N.S.; Turner, D.; Robinson, J.; Seal, K. The enhanced performance of biocidal additives in paints and coatings. Prog. Org. Coatings 2001, 43, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulit-Prociak, J.; Chwastowski, J.; Siudek, M.; Banach, M. Incorporation of Metallic Nanoparticles into Cosmetic Preparations and Assessment of Their Physicochemical and Utility Properties. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2018, 21, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.M.; Fan, W.; Kishen, A.; Gutmann, F.B. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyaei, B.; Azizian, S.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Pajohi-Alamoti, M. Preparation of clay/alumina and clay/alumina/Ag nanoparticle composites for chemical and bacterial treatment of waste water. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 247, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruparelia, J.P.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Duttagupta, S.P.; Mukherji, S. Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klasen, H. A historical review of the use of silver in the treatment of burns. II. Renewed interest for silver. Burns 2000, 26, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, S.Y.; Read, D.C.; Pugh, W.J.; Furr, J.R.; Russell, A.D. Interaction of silver nitrate with readily identifiable groups: Relationship to the antibacterial action of silver ions. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 25, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H.; Odermatt, E.K.; Berndt, I.; Joerg, C. Long-term active antimicrobial coatings for surgical sutures based on silver nanoparticles and hyperbranched polylysine. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korani, M.; Ghazizadeh, E.; Korani, S.; Hami, Z.; Mohammadi-Bardbori, A. Effects of silver nanoparticles on human health. Eur. J. Nanomed. 2015, 7, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, Z.; Nemmar, A. Health Impact of Silver Nanoparticles: A Review of the Biodistribution and Toxicity Following Various Routes of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- León-Silva, S.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; López-Valdez, F. Silver Nanoparticles (AgNP) in the Environment: A Review of Potential Risks on Human and Environmental Health. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyala, N.R.; Peña-Méndez, E.M.; Havel, J. Silver or silver nanoparticles: A hazardous threat to the environment and human health? J. Appl. Biomed. 2008, 6, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. Triple Helical Polysaccharide-Induced Good Dispersion of Silver Nanoparticles in Water. Biomacromolecules 2011, 26, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimala, K.; Mohan, Y.M.; Sivudu, K.S.; Varaprasad, K.; Ravindra, S.; Reddy, N.N.; Padma, Y.; Sreedhar, B.; Mohanaraju, K. Fabrication of porous chitosan films impregnated with silver nanoparticles: A facile approach for superior antibacterial application. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimala, K.; Sivudu, K.S.; Mohan, Y.M.; Sreedhar, B.; Raju, K.M. Controlled silver nanoparticles synthesis in semi-hydrogel networks of poly (acrylamide) and carbohydrates: A rational methodology for antibacterial application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinchi, L.; Cotana, F.; Fortunati, E.; Kenny, J.M. Production of nanocrystalline cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass: Technology and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.S.; Villalobos, M.; Cranston, E.D. Benchmarking Cellulose Nanocrystals: From the Laboratory to Industrial Production. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1583–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Gomi, S.; Maeda, Y.; Matsunaga, M.; Hikino, S.; Uto, K.; Tsuji, T.; Kawazumi, H. Rapid transformation from spherical nanoparticles, nanorods, cubes, or bipyramids to triangular prisms of silver with PVP, citrate, and H2O2. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8845–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, M.; Dille, J.; Godet, S. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastoriza-santos, I.; Liz-marza, L.M. Synthesis of Silver Nanoprisms in DMF. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xie, J.; Hong, F.; Cao, Z.; Yang, X. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticle impregnated bacterial cellulose membrane: Effect of fermentation carbon sources of bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Hsieh, Y. Lo Synthesis of cellulose nanofibril bound silver nanoprism for surface enhanced raman scattering. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3608–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lokanathan, A.R.; Uddin, K.M.A.; Rojas, O.J.; Laine, J. Cellulose nanocrystal-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Role of sulfate groups in nucleation phenomena. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, G.; He, J.; Huang, L. Size control of silver nanoparticles deposited on silica dielectric spheres by electroless plating technique. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 2955–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Tang, J.; Chen, L.; Yan, C.; Tanvir, S.; Anderson, W.A.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Enhanced Colloidal Stability and Antibacterial Performance of Silver Nanoparticles/Cellulose Nanocrystal Hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, U.; Castell, A.Z.; Pöppl, K.; Schneider, S. Silver colloid produced by reduction with hydrazine as support for highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Langmuir 2000, 16, 9087–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, M.; Moores, A. Review: Nanocelluloses as versatile supports for metal nanoparticles and their applications in catalysis. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musino, D.; Rivard, C.; Novales, B.; Landrot, G.; Rabilloud, T.; Capron, I. Hydroxyl Groups on Cellulose Nanocrystal Surfaces form Nucleation Points for Silver Nanoparticles of Varying Shapes and Sizes (Accepted). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa-Cristóbal, L.F.; Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Martínez-Martínez, R.E.; Loyola-Rodríguez, J.P.; Patiño-Marín, N.; Reyes-Macías, J.F.; Ruiz, F. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 2603–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Castañon, G.A.; Nino-Martinez, N.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F.; Martinez-Mendoza, J.R.; Ruiz, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drogat, N.; Granet, R.; Sol, V.; Memmi, A.; Saad, N.; Klein Koerkamp, C.; Bressollier, P.; Krausz, P. Antimicrobial silver nanoparticles generated on cellulose nanocrystals. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errokh, A.; Magnin, A.; Putaux, J.L.; Boufi, S. Hybrid nanocellulose decorated with silver nanoparticles as reinforcing filler with antibacterial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, M.; Park, H.S.; Shin, U.S.; Gong, M.S.; Kim, H.W. Size-dependent cellular toxicity of silver nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Hirani, A.A.; Colacino, K.R.; Lee, Y.W.; Roman, M. Cytotoxicity and Cellular Uptake of Cellulose Nanocrystals. Nano Life 2012, 2, 1241006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, J.; Ilves, M.; Jarventaus, H.; Hannukainen, K.-S.; Kontturi, E.; Vanhala, E.; Alenius, H.; Savolainen, K.M.; Norppa, H. Genotoxic and Immunotoxic Effects of Cellulose Nanocrystals In Vitro. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, M. Toxicity of cellulose nanocrystals: A review. Ind. Biotechnol. 2015, 11, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Khaliullin, T.O.; Shurin, M.R.; Kisin, E.R.; Yanamala, N.; Fadeel, B.; Chang, J.; Shvedova, A.A. Fibrous nanocellulose, crystalline nanocellulose, carbon nanotubes, and crocidolite asbestos elicit disparate immune responses upon pharyngeal aspiration in mice. J. Immunotoxicol. 2018, 15, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Depend on the Shape of the Nanoparticle ? A Study of the Gram-Negative Bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parnklang, T.; Lamlua, B.; Gatemala, H.; Thammacharoen, C.; Kuimalee, S.; Lohwongwatana, B.; Ekgasit, S. Shape transformation of silver nanospheres to silver nanoplates induced by redox reaction of hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 153, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Métraux, G.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Rapid thermal synthesis of silver nanoprisms with chemically tailorable thickness. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millstone, J.E.; Hurst, S.J.; Métraux, G.S.; Cutler, J.I.; Mirkin, C.A. Colloidal gold and silver triangular nanoprisms. Small 2009, 5, 646–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dong, P.; Ha, C.H.; Binh, L.T.; Kasbohm, J. Chemical synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel-shaped silver nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size- and shape-dependent antibacterial studies of silver nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Badawy, A.M.E.L.; Silva, R.G.; Morris, B.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T. Surface Charge-Dependent Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gondikas, A.P.; Marinakos, S.M.; Auffan, M.; Liu, J.; Hsu-kim, H.; Meyer, J.N. Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticle Toxicity Is Dependent on Dissolved Silver and Surface Coating in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Levard, C.; Marinakos, S.M.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Michel, F.M.; Brown, G.E.; Lowry, G.V. Size-controlled dissolution of organic-coated silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Vemula, P.K.; Ajayan, P.M.; John, G. Silver-nanoparticle-embedded antimicrobial paints based on vegetable oil. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musino, D.; Rivard, C.; Landrot, G.; Novales, B.; Capron, I. Tunable Ag Nanoparticle Properties in Cellulose Nanocrystals/Ag Nanoparticle Hybrid Suspensions by H2O2 Redox Post-Treatment: The Role Of The H2O2/Ag Ratio. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. Athena, artemis, hephaestus: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, I.K.; Ohta, H.; Waseda, Y. High-temperature thermal expansion of six metallic elements measured by dilatation method and X-ray diffraction. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhsa, P.; Narain, R.; Manuspiya, H. Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals (BCNC) Preparation and Characterization from Three Bacterial Cellulose Sources and Development of Functionalized BCNCs as Nucleic Acid Delivery Systems. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.D.; Hesterberg, D.; Ravel, B. Analysis of Soils and Minerals Using X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. Mineral. Methods 2015, 5, 387–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Yao, Y.; Sullivan, N.; Chen, Y. Modeling the primary size effects of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles on their ion release kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4422–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.S.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Shameli, K.; Zainuddin, N.; Salama, M.; Ibrahim, N.A. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties of copper nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4467–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopinath, V.; MubarakAli, D.; Priyadarshini, S.; Priyadharsshini, N.M.; Thajuddin, N.; Velusamy, P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tribulus terrestris and its antimicrobial activity: A novel biological approach. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 96, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, T.I.; Fouda, A. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Green approach for one-pot synthesis of silver nanorod using cellulose nanocrystal and their cytotoxicity and antibacterial assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merril, C. Development and Mechanisms of Silver Stains for Electrophoresis. ACTA Histochem. Cytochem. 1986, 19, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gianazza, E.; Astrua-Testori, S.; Righetti, P.G. Some more formulations for immobilized pH gradients. Electrophoresis 1985, 6, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalzon, B.; Torres, A.; Diemer, H.; Ravanel, S.; Collin-Faure, V.; Pernet-Gallay, K.; Jouneau, P.H.; Bourguignon, J.; Cianférani, S.; Carrière, M.; et al. How reversible are the effects of silver nanoparticles on macrophages? A proteomic-instructed view. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 3133–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalzon, B.; Aude-Garcia, C.; Diemer, H.; Bons, J.; Marie-Desvergne, C.; Pérard, J.; Dubosson, M.; Collin-Faure, V.; Carapito, C.; Cianférani, S.; et al. The longer the worse: A combined proteomic and targeted study of the long-term: Versus short-term effects of silver nanoparticles on macrophages. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 2032–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.V.D.Z.; Neigh, A.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; de la Fonteyne, L.J.J.; Verharen, H.W.; Briedé, J.J.; van Loveren, H.; de Jong, W.H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9810–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lim, D.H.; Lim, H.J.; Kwon, T.; Choi, J.S.; Jeong, S.; Choi, I.H.; Cheon, J. Size dependent macrophage responses and toxicological effects of Ag nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4382–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivask, A.; Kurvet, I.; Kasemets, K.; Blinova, I.; Aruoja, V.; Suppi, S.; Vija, H.; Kakïnen, A.; Titma, T.; Heinlaan, M.; et al. Size-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles to bacteria, yeast, algae, crustaceans and mammalian cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratsinis, A.; Hervella, P.; Leroux, J.C.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Sotiriou, G.A. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in macrophages. Small 2013, 9, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliga, A.; Skoglound, S.; Wallinder, I.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H. Size-dependent cytotocicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: The role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samulin Erdem, J.; Alswady-Hoff, M.; Ervik, T.K.; Skare, Ø.; Ellingsen, D.G.; Zienolddiny, S. Cellulose nanocrystals modulate alveolar macrophage phenotype and phagocytic function. Biomaterials 2019, 203, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toybou, D.; Celle, C.; Aude-Garcia, C.; Rabilloud, T. A toxicology-informed, safer by design approach for the fabrication of transparent electrodes based on silver nanowires. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvedova, A.A.; Kisin, E.R.; Yanamala, N.; Farcas, M.T.; Menas, A.L.; Williams, A.; Fournier, P.M.; Reynolds, J.S.; Gutkin, D.W.; Star, A.; et al. Gender differences in murine pulmonary responses elicited by cellulose nanocrystals. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| AgNO3 Vol. (μL, 50 mM) | NaBH4/AgNO3 Molar Ratio | AgNP Content (mg Ag/g Hybrid, wt%) 1 | Avg. Feret’s Diam. (nm) 2 | CS (nm) 3 | Ag0 (%) 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 67.7 | 0.4 ± 0.03 | 10.5 ± 4.8 | 3.5 | - |
| 30 | 33.4 | 0.9 ± 0.04 | - | - | - |
| 60 | 16.7 | 1.6 ± 0.02 | - | - | - |
| 110 | 9.1 | 3.0 ± 0.03 | 11.3 ± 8.3 | - | 91 ± 9 |
| 160 | 6.3 | 6.0 ± 0.01 | 10.0 ± 7.4 | 3.7 | 75 ± 8 |
| 240 | 4.2 | 8.7 ± 0.05 | 9.9 ± 7.3 | 3.1 | 65 ± 7 |
| 330 | 3.0 | 12.5 ± 0.16 | 12.1 ± 9.2 | 3.2 | 57 ± 6 |
| 550 | 1.8 | 18.6 ± 0.14 | 12.2 ± 8.2 | - | 32 ± 3 |
| 700 | 1.5 | 24.7 ± 0.34 | 11.2 ± 9.1 | 3.0 | 34 ± 3 |
| AgNP Content (wt%) | H2O2 Vol. (µL) | H2O2/AgNP Mass Ratio, α | NP Shape/Size 1 (nm) | Ag0 (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.7 | 0 | 0 | Nanospheres (~10) | 65 ± 7 |
| 12.5 | 0 | 0 | Nanospheres (~10) | 57 ± 6 |
| 18.6 | 0 | 0 | Nanospheres (~10) | 32 ± 3 |
| 24.7 | 0 | 0 | Nanospheres (~10) | 34 ± 3 |
| 6.9 (AgNP_H2O2) | 160 | 0.27 | Nanoprisms (~150–300) | 95 ± 10 |
| 9.3 (AgNP_H2O2) | 160 | 0.20 | Nanoprisms (~150–300) | 97 ± 10 |
| 17.1 (AgNP_H2O2) | 160 | 0.12 | Nanospheres (~15) | 50 ± 10 |
| 24.1 (AgNP_H2O2) | 160 | 0.09 | Nanospheres (~15) | 29 ± 3 |
| Hybrid (Code) | AgNP Content (mg/g of Hybrid), % | Ag+ (%) by XANES | Inhibition Halo (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 3.0 | 9 | 2.9 ± 1.4 |
| H2 | 8.7 | 35 | 7.1 ± 0.2 |
| H3 | 18.6 | 68 | 10.0 ± 0.9 |
| H3/2 (eq. H2) | 9.3 | 68 | 7.4 ± 0.8 |
| H3/6 (eq. H1) | 3.1 | 68 | 4.2 ± 1.1 |
| Sample Code | Relative AgNP Content in Hybrid (wt%) | AgNP in Culture Medium (µg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 v% | 1 v% | 2 v% | 5 v% | 10 v% | ||
| A30 | 3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 3 |
| A60 | 6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 3 | 6 |
| A87 | 8.7 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 4.4 | 8.7 |
| A186 | 18.6 | 0.9 | 1.9 | 3.7 | 9.3 | 18.6 |
| A247 | 24.7 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 4.9 | 12.4 | 24.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musino, D.; Devcic, J.; Lelong, C.; Luche, S.; Rivard, C.; Dalzon, B.; Landrot, G.; Rabilloud, T.; Capron, I. Impact of Physico-Chemical Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Silver Nanoparticle Hybrid Suspensions on Their Biocidal and Toxicological Effects. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071862
Musino D, Devcic J, Lelong C, Luche S, Rivard C, Dalzon B, Landrot G, Rabilloud T, Capron I. Impact of Physico-Chemical Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Silver Nanoparticle Hybrid Suspensions on Their Biocidal and Toxicological Effects. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(7):1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071862
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusino, Dafne, Julie Devcic, Cécile Lelong, Sylvie Luche, Camille Rivard, Bastien Dalzon, Gautier Landrot, Thierry Rabilloud, and Isabelle Capron. 2021. "Impact of Physico-Chemical Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Silver Nanoparticle Hybrid Suspensions on Their Biocidal and Toxicological Effects" Nanomaterials 11, no. 7: 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071862
APA StyleMusino, D., Devcic, J., Lelong, C., Luche, S., Rivard, C., Dalzon, B., Landrot, G., Rabilloud, T., & Capron, I. (2021). Impact of Physico-Chemical Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Silver Nanoparticle Hybrid Suspensions on Their Biocidal and Toxicological Effects. Nanomaterials, 11(7), 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071862