Facile Synthesis of L-Cysteine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as a Bioimaging and Photosensitive Agent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Pristine GQDs and Gamma-Irradiated GQDs
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Ultraviolet–Visible Spectroscopy
2.2.2. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
2.2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.2.6. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.2.7. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
2.2.8. Bioimaging
2.2.9. MTT Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. UV–Vis Spectroscopy
3.2. PL Spectroscopy
3.3. AFM Microscopy
3.4. DLS Analysis
3.5. SEM-EDS
3.6. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.7. EPR Spectroscopy with 1O2 Trap
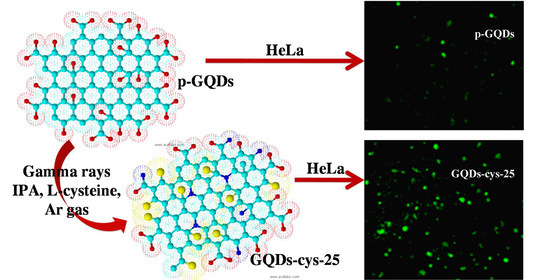
3.8. Bioimaging
3.9. Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ponomarenko, L.A.; Schedin, F.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Yang, R.; Hill, E.W.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. Chaotic Dirac Billiard in Graphene Quantum Dots. Science 2008, 320, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safardoust-Hojaghan, H.; Amiri, O.; Hassanpour, M.; Panahi-Kalamuei, M.; Moayedi, H.; Salavati-Niasari, M. S,N co-doped graphene quantum dots-induced ascorbic acid fluorescent sensor: Design, characterization and performance. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.T.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Luo, K.Q.; Chen, P. Glowing Graphene Quantum Dots and Carbon Dots: Properties, Syntheses, and Biological Applications. Small 2015, 11, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.-H.; Ha, H.D.; Lee, E.-S.; Liu, F.; Kim, Y.-H.; Seo, T.S.; Cho, Y.-H. Is the Chain of Oxidation and Reduction Process Reversible in Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots? Small 2015, 11, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gao, W.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Liao, P.; Fu, W.; Luo, Y. Graphene quantum dots in biomedical applications: Recent advances and future challenges. Front. Lab. Med. 2017, 1, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, T.; Gooding, J.J.; Liu, J. Review of Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots for Sensing. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Tang, L.; Teng, K.S.; Lau, S.P. Graphene quantum dots from chemistry to applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 10, 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Sun, Z. Tailoring color emissions from N-doped graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Light Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prekodravac, J.R.; Kepić, D.P.; Colmenares, J.C.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Jovanović, S.P. A comprehensive review on selected graphene synthesis methods: From electrochemical exfoliation through rapid thermal annealing towards biomass pyrolysis. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 6722–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, S. Creating high yield water soluble luminescent graphene quantum dots via exfoliating and disintegrating carbon nanotubes and graphite flakes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10177–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, D. Shining luminescent graphene quantum dots: Synthesis, physicochemical properties, and biomedical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, S.P.; Syrgiannis, Z.; Budimir, M.D.; Milivojević, D.D.; Jovanovic, D.J.; Pavlović, V.B.; Papan, J.M.; Bartenwerfer, M.; Mojsin, M.M.; Stevanović, M.J.; et al. Graphene quantum dots as singlet oxygen producer or radical quencher-The matter of functionalization with urea/thiourea. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Hai, X.; Xia, C.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, J.H. Preparation of excitation-independent photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with visible-light excitation/emission for cell imaging. Chemistry 2013, 19, 15918–15923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, T.V.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, W.M. Facile synthesis of cysteine–functionalized graphene quantum dots for a fluorescence probe for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 97598–97603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Haddad, R.E.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.T.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R.; Ryan, C.; Pota, K.; Green, K.; Coffer, J.L.; Naumov, A.V. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots: Optical properties modification and photovoltaic applications. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rui, M.; Song, J.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, H. Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots for Optoelectronic and Energy Devices: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Deshpande, S.; Shinde, D.B.; Pillai, V.K.; Singh, N. Mitigating the Cytotoxicity of Graphene Quantum Dots and Enhancing Their Applications in Bioimaging and Drug Delivery. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Paunovic, V.; Markovic, Z.; Simovic Markovic, B.; Misirkic-Marjanovic, M.; Todorovic-Markovic, B.; Bojic, S.; Vucicevic, L.; Jovanovic, S.; Arsenijevic, N.; et al. Large graphene quantum dots alleviate immune-mediated liver damage. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12098–12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurunnabi, M.; Khatun, Z.; Huh, K.M.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Cho, K.J.; Lee, Y.-k. In Vivo Biodistribution and Toxicology of Carboxylated Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6858–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurunnabi, M.; Khatun, Z.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Lee, D.-g.; Lee, Y.-k. Surface Coating of Graphene Quantum Dots Using Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine for Biomedical Optical Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2013, 5, 8246–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Qiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; et al. Surface Chemistry Routes to Modulate the Photoluminescence of Graphene Quantum Dots: From Fluorescence Mechanism to Up-Conversion Bioimaging Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bai, L.; Shang, W.; Xie, W.; Ma, H.; Fu, Y.; Fang, D.; Sun, H.; Fan, L.; Han, M.; et al. Facile synthesis of water-soluble, highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a robust biological label for stem cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7461–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Electrochemical synthesis of small-sized red fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a bioimaging platform. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2544–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, C.T.J.; Walsh, F.C.; Chakrabarti, M.H.; Hashim, M.A.; Hussain, M.A. Electrochemical approaches to the production of graphene flakes and their potential applications. Carbon 2013, 54, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirwar, S.; Mallick, S.; Bahadur, D. Electrochemical Method To Prepare Graphene Quantum Dots and Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8343–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, H.; Gan, W.; Yuan, Q. Graphene quantum dots: Recent progress in preparation and fluorescence sensing applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110775–110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Optimizing oxygen functional groups in graphene quantum dots for improved antioxidant mechanism. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; You, X.; Mao, B.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; He, P.; et al. Electrochemical Cutting in Weak Aqueous Electrolytes: The Strategy for Efficient and Controllable Preparation of Graphene Quantum Dots. Langmuir 2018, 34, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansón-Casaos, A.; Puértolas, J.A.; Pascual, F.J.; Hernández-Ferrer, J.; Castell, P.; Benito, A.M.; Maser, W.K.; Martínez, M.T. The effect of gamma-irradiation on few-layered graphene materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 301, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovanović, S.P.; Syrgiannis, Z.; Marković, Z.M.; Bonasera, A.; Kepić, D.P.; Budimir, M.D.; Milivojević, D.D.; Spasojević, V.D.; Dramićanin, M.D.; Pavlović, V.B.; et al. Modification of Structural and Luminescence Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots by Gamma Irradiation and Their Application in a Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2015, 7, 25865–25874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, S.; Dorontić, S.; Jovanović, D.; Ciasca, G.; Budimir, M.; Bonasera, A.; Scopelliti, M.; Marković, O.; Todorović Marković, B. Gamma irradiation of graphene quantum dots with ethylenediamine: Antioxidant for ion sensing. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 23611–23622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, S.; Marković, Z.; Budimir, M.; Spitalsky, Z.; Vidoeski, B.; Todorović Marković, B. Effects of low gamma irradiation dose on the photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2016, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Yan, L. Efficient preparation of highly hydrogenated graphene and its application as a high-performance anode material for lithium ion batteries. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2124–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, R.; Song, K.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Fluorescence Enhancement and Radiolysis of Carbon Dots through Aqueous γ Radiation Chemistry. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 15826–15832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, S.P.; Marković, Z.M.; Kleut, D.N.; Dramićanin, M.D.; Holclajtner-Antunović, I.D.; Milosavljević, M.S.; La Parola, V.; Syrgiannis, Z.; Todorović Marković, B.M. Structural analysis of single wall carbon nanotubes exposed to oxidation and reduction conditions in the course of gamma irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 16147–16155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Lei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, J.; Lin, Y. Preparation and Specific Capacitance Properties of Sulfur, Nitrogen Co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, L.; Yuan, Q.; Gan, W. Time-efficient syntheses of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots with tunable luminescence and their sensing applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36554–36560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-X.; Gao, H.; Li, X.-L. Synthesis and optical properties of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4615–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thannon, A.A.; Barton, J.P.; Packer, J.E.; Sims, R.J.; Trumbore, C.N.; Winchester, R.V. The radiolysis of aqueous solutions of cysteine in the presence of oxygen. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 1974, 6, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Than, A.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Sun, L.; Duan, H.; Xu, C.; Chen, P. Ultrasensitive Profiling of Metabolites Using Tyramine-Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3622–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, K.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Lin, H. A graphene quantum dot-based fluorescent nanoprobe for hypochlorite detection in water and in living cells. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3833–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, A.; Rosenthal, M.; Neuhaus, S.; Huber, K.; Brassat, K.; Lindner, J.K.N.; Grothe, R.; Grundmeier, G.; Bremser, W.; Wilhelm, R. A Novel Lubricant Based on Covalent Functionalized Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweetman, M.J.; Hickey, S.M.; Brooks, D.A.; Hayball, J.D.; Plush, S.E. A Practical Guide to Prepare and Synthetically Modify Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fan, H.; Jiang, W.; Ni, G.; Qu, S. Amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots prepared using high-softening point asphalt and their application in Fe3+ detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, G.; Tang, T.; Wen, J.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots decorated with TiO2 nanocomposites. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 97, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeyani, D.; Shojaei, S.; Kandjani, S.A.; Wlodarski, W. Synthesizing Graphene Quantum Dots for Gas Sensing Applications. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Jang, M.-H.; Chung, J.; Jin, S.H.; Kim, B.H.; Hur, S.-H.; Yoo, S.; Cho, Y.-H.; Jeon, S. Highly Efficient Light-Emitting Diode of Graphene Quantum Dots Fabricated from Graphite Intercalation Compounds. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Jin, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, Y.; An, D. Mechanisms behind excitation- and concentration-dependent multicolor photoluminescence in graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Ding, X.; Feng, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q. Photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots enhanced by microwave post-treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, S. Graphene Quantum Dots—A New Member of the Graphene Family: Structure, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. In Handbook of Graphene Set, I-VIII; Edvige Celasco, A.N.C., Tobias, S., Mei, Z., Cengiz, O., Cengiz, O., Umit, O., Barbara, P., Sulaiman, W.H., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 267–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Shao, J.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Du, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. Investigating the surface state of graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7927–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, S.-J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Qu, S.-N.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.-H.; Chen, Q.-D.; Xu, H.-L.; Han, W.; Yang, B.; et al. Common Origin of Green Luminescence in Carbon Nanodots and Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, D.; Shao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yuwen, L.; Weng, L.; Luo, Z.; Wang, L. Reduction of graphene oxide quantum dots to enhance the yield of reactive oxygen species for photodynamic therapy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 17262–17267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonta, W.; Talodthaisong, C.; Sattayaporn, S.; Chaicham, C.; Chaicham, A.; Sahasithiwat, S.; Kangkaew, L.; Kulchat, S. The synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots for fluorescence detection of cobalt(II) ions in water. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Hai, X.; Chen, X.-W.; Wang, J.-H. Simultaneously fabrication of free and solidified N, S-doped graphene quantum dots via a facile solvent-free synthesis route for fluorescent detection. Talanta 2017, 168, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tian, B.; Xue, Y.; Li, R.; Zhai, T.; Tan, L. Determination of aminophylline based on fluorescence quenching of amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots induced by photoilluminated riboflavin-aminophylline system. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 235, 118306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Du, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Tan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Sun, Z. Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12272–12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, N.-J.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wu, C.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chan, Y.-H.; Chen, I.W.P. One-Pot Synthesis of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots via Exfoliating and Disintegrating Graphite Flakes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kocherginsky, N.; Swartz, H. Nitroxide Spin Labels: Reactions in Biology and Chemistry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Li, Y.M.; Seo, J.G.; Jang, T.S.; Knowles, J.C.; Song, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Biological Potential of Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)-Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots in In Vitro Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Song, B.; Liang, H.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Shao, L. Toxicity of graphene-family nanoparticles: A general review of the origins and mechanisms. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Sample | Position (nm) | Sample | Position (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-GQDs | 426Ex300 | GQDs-cys-50 | 440Ex300 |
| 439Ex320 | 445Ex320 | ||
| 452Ex340 | 457Ex340 | ||
| 464Ex360 | 465Ex360 | ||
| 477Ex380 | 478Ex380 | ||
| 494Ex400 | 493Ex400 | ||
| GQDs-cys-25 | 443Ex300 | GQDs-cys-200 | 435Ex300 |
| 447Ex320 | 442Ex320 | ||
| 457Ex340 | 456Ex340 | ||
| 466Ex360 | 467Ex360 | ||
| 480Ex380 | 478Ex380 | ||
| 495Ex400 | 494Ex400 |
| Sample | Iex360 | A360 | QY (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-GQDs | 23,450,791340nm | 0.144340nm | 1.45340nm [33] |
| GQDs-cys-25 | 35,957,065 | 0.073 | 21.60 |
| GQDs-cys-50 | 17,488,510 | 0.149 | 5.15 |
| GQDs-cys-200 | 14,572,620 | 0.205 | 3.12 |
| Rhodamine B | 66,440,340 | 0.094 | 31 |
| Sample | Diameter (nm) | Height (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| p-GQD | 20.4 | 2.6 |
| GQDs-cys-25 | 25.5 | 1.6 |
| GQDs-cys-50 | 28.0 | 1.5 |
| GQDs-cys-200 | 29.0 | 1.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milenković, M.; Mišović, A.; Jovanović, D.; Popović Bijelić, A.; Ciasca, G.; Romanò, S.; Bonasera, A.; Mojsin, M.; Pejić, J.; Stevanović, M.; et al. Facile Synthesis of L-Cysteine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as a Bioimaging and Photosensitive Agent. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081879
Milenković M, Mišović A, Jovanović D, Popović Bijelić A, Ciasca G, Romanò S, Bonasera A, Mojsin M, Pejić J, Stevanović M, et al. Facile Synthesis of L-Cysteine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as a Bioimaging and Photosensitive Agent. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(8):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081879
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilenković, Mila, Aleksandra Mišović, Dragana Jovanović, Ana Popović Bijelić, Gabriele Ciasca, Sabrina Romanò, Aurelio Bonasera, Marija Mojsin, Jelena Pejić, Milena Stevanović, and et al. 2021. "Facile Synthesis of L-Cysteine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as a Bioimaging and Photosensitive Agent" Nanomaterials 11, no. 8: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081879
APA StyleMilenković, M., Mišović, A., Jovanović, D., Popović Bijelić, A., Ciasca, G., Romanò, S., Bonasera, A., Mojsin, M., Pejić, J., Stevanović, M., & Jovanović, S. (2021). Facile Synthesis of L-Cysteine Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as a Bioimaging and Photosensitive Agent. Nanomaterials, 11(8), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081879