Morphological Analysis of PSMA/PEI Core–Shell Nanoparticles Synthesized by Soap-Free Emulsion Polymerization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Core–Shell Nanoparticles
2.3. Chemical Analysis of PSMA and Core–Shell Nanoparticles
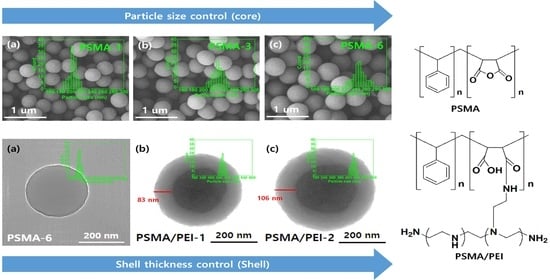
2.4. Morphological Analysis of PSMA and Core–Shell Nanoparticles
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Analysis of PSMA and Core–Shell Nanoparticles
3.2. Morphological Characteristics of PSMA Based on Various Factors
3.3. Core–Shell Nanoparticle Size Distribution Based on the Feed Ratio of PEI
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaudhuri, R.G.; Paria, S. Core/shell nanoparticles: Classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2373–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Mirin, N.A.; Levit, S.D.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Nanosphere-in-a-nanoshell: A simple nanomatryushka. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7378–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radloff, C.; Halas, N.J. Plasmonic properties of concentric nanoshells. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Brynda, M.; Britt, R.D.; Carroll, E.C.; Larsen, D.S.; Louie, A.Y.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Synthesis and characterization of manganese-doped silicon nanoparticles: Bifunctional paramagnetic-optical nanomaterial. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10668–10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Brandl, D.W.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Plasmonic nanostructures: Artificial molecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, A.C. A comparison of mechanochemical methods for the synthesis of nanoparticulate nickel oxide. Powder Technol. 2009, 196, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. Polymer/silica nanocomposites: Preparation, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3893–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, D.; Tang, D.; Niessner, R. Bioanalytical applications of biomolecule-functionalized nanometer-sized doped silica particles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 647, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.; Julián, B.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M. Applications of hybrid organic–Inorganic nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3559–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schärtl, W. Crosslinked spherical nanoparticles with core–shell topology. Adv. Mater. 2001, 12, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.-C.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, F.; Spasova, M.; Salgueiriño-Maceira, V.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Multilayer assemblies of silica-encapsulated gold nanoparticles on decomposable colloid templates. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortan, A.R.; Hull, R.; Opila, R.L.; Bawendi, M.G.; Steigerwald, M.L.; Carroll, P.J.; Brus, L.E. Nucleation and growth of cdse on zns quantum crystallite seeds, and vice versa, in inverse micelle media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Ma, J.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, Z. Synthesis and characterization of mixed CdS-ZnS nanoparticles in reverse micelles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1996, 111, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henglein, A. Small-Particle Research: Physicochemical properties of extremely small colloidal metal and semiconductor particles. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhel, L.; Weller, H.; Henglein, A. Photochemistry of semiconductor colloids. 22. electron ejection from illuminated cadmium sulfide into attached titanium and zinc oxide particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 6632–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H.C.; Baral, S.; Fendler, J.H. Dihexadecyl phosphate, vesicle-stabilized and in situ generated mixed cadmium sulfide and zinc sulfide semiconductor particles: Preparation and utilization for photosensitized charge separation and hydrogen generation. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 6320–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Jiang, M.; Wang, T.-W.; Guo, C.-F.; Xie, S.-S.; Wang, Z.-L. The shape evolution of gold seeds and gold@silver core–shell nanostructures. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 305602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, G.; Gutiérrez, H.; Nunzi, J.-M.; Chitanu, G.C.; Sylla, M.; Simionescu, B.C. Second harmonic generation diagnostic of layer-by-layer deposition from disperse red 1–functionalized maleic anhydride copolymer. Opt. Mater. 2007, 29, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłucińska, K.; Stelmach, E.; Bartosińska, P.; Kisiel, A.; Maksymiuk, K.; Michalska, A. Critical assessment of polymeric nanostructures used as colorimetric ions probes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyerle, A.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Kissel, T.; Stoeger, T. Toxicity pathway focused gene expression profiling of pei-based polymers for pulmonary applications. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.Y.; Lee, D.W.; Yoon, T.Y.; Kim, J.B.; Chae, J.-Y.; Paik, T. Sub-100-nm nearly monodisperse n-paraffin/pmma phase change nanobeads. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yammine, E.; Adumeau, L.; Abboud, M.; Mornet, S.; Nakhl, M.; Duguet, E. Towards polymeric nanoparticles with multiple magnetic patches. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.; Lim, J.; Son, H.-y.; Choi, Y.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; Huh, Y.-M.; Haam, S.; Lim, E.-K. PEGylated magnetic nano-assemblies as contrast agents for effective T2-weighted MR imaging. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Li, G.; Sha, Z. Preparation and structural analysis of nano-silver loaded poly(styrene-co-acrylic acid) core-shell nanospheres with defined shape and composition. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vowinkel, S.; Paul, S.; Gutmann, T.; Gallei, M. Free-standing and self-crosslinkable hybrid films by core–shell particle design and processing. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suckeveriene, Y.; Rahman, R.; Shtein, I.; Kharlamova, N.; Narkis, M. Synthesis of styrene-acrylamide copolymer by surfactant–free sonicated dynamic interfacial polymerization, polymers for advanced technologies. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankan, Z.; Xiaopeng, P.; Chao, W.; Yukun, D.; Ying, T.; Yungang, B.; Baichao, Z.; Kun, X.; Pixin, W. Water-in-oil pickering emulsion polymerization of N-isopropyl acrylamide using starch-based nanoparticles as emulsifier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, T.; Ford, W.T. Particle Size control in suspension copolymerization of styrene, chloromethylstyrene, and divinylbenzene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1982, 27, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelet, T.; Bartholin, M.; Guyot, A. Functionalized Resins, 2. Grafting of functionalized monomers on macroporous styrene-divinyl benzene resins. Angew. Makromol. Chem. Appl. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1982, 106, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonde, Y.; Liu, L.J.; Krieger, I.M. Preparation and surface modification of poly (vinylbenzyl chloride) latices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1980, 25, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, M.D.; Danielson, S.J.; Daiss, J.L.; Goppert, K.E.; Sutton, R.C. Influence of copolymer composition on protein adsorption and structural rearrangements at the polymer surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 132, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugelstad, J.; Mork, P.C.; Kaggerud, K.H.; Ellingsen, T.; Berge, A. Swelling of oligomer-polymer particles. New methods of preparation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 13, 101–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.M.; Yang, W.T. A Novel, Facile method for the preparation of uniform, reactive maleic anhydride/vinyl acetate copolymer micro-and nanospheres. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.M.; Yang, W.T. Stabilizer-free dispersion copolymerization of maleic anhydride and vinyl acetate. I. Effects of principal factors on microspheres. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 3760–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Kook, J.-W.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.-H.; Hwang, K.-S.; Lee, J.-Y. Colorimetric visualization using polymeric core–shell nanoparticles: Enhanced sensitivity for formaldehyde gas sensors. Polymers 2020, 12, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Du, Y.; Ma, G.; Nagai, M.; Omi, S. Mechanism of soap-free emulsion polymerization of styrene and 4-vinylpyridine: Characteristics of reaction in the monomer phase, aqueous phase, and their interface. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 6577–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Nie, J.; He, Y. Investigation of stabilizer-free dispersion polymerization process of styrene and maleic anhydride copolymer microspheres. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 5652–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample Name | Ratio (wt%) | Atomic Ratio (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copolymer of Styrene (St) | MA | C | O | H | |
| PS | 100 | 0 | 99.84 | X | 0.16 |
| PSMA-1 | 95 | 5 | 96.69 | 3.06 | 0.25 |
| PSMA-2 | 90 | 10 | 90.16 | 9.63 | 0.21 |
| PSMA-3 | 85 | 15 | 86.76 | 13.01 | 0.23 |
| PSMA-4 | 80 | 20 | 80.28 | 19.54 | 0.18 |
| PSMA-5 | 75 | 25 | 75.47 | 24.31 | 0.22 |
| PSMA-6 | 70 | 30 | 72.92 | 26.83 | 0.25 |
| Sample Name | Ratio (mol) | Atomic Ratio (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEI:MA | C | N | O | H | |
| PSMA | 0:1 | 72.92 | X | 26.83 | 0.19 |
| PSMA/PEI-1 | 0.02:1 | 72.44 | 7.43 | 11.15 | 8.98 |
| PSMA/PEI-2 | 0.04:1 | 71.92 | 9.79 | 7.65 | 10.64 |
| PSMA/PEI-3 | 0.06:1 | 72.58 | 10.54 | 5.76 | 11.12 |
| PSMA/PEI-4 | 0.08:1 | 72.34 | 12.57 | 4.48 | 10.61 |
| PSMA/PEI-5 | 0.10:1 | 71.57 | 13.01 | 4.54 | 10.88 |
| PSMA/PEI-6 | 0.12:1 | 72.23 | 13.35 | 4.32 | 10.10 |
| PSMA/PEI-7 | 0.14:1 | 72.06 | 6.55 | 12.21 | 9.18 |
| PSMA/PEI-8 | 0.16:1 | 73.93 | 4.58 | 13.32 | 8.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.-J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, D.; Choi, W.; Kwon, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Hwang, K.-S.; Lee, J.-Y. Morphological Analysis of PSMA/PEI Core–Shell Nanoparticles Synthesized by Soap-Free Emulsion Polymerization. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081958
Park J-J, Kim Y, Lee C, Kim D, Choi W, Kwon H, Kim J-H, Hwang K-S, Lee J-Y. Morphological Analysis of PSMA/PEI Core–Shell Nanoparticles Synthesized by Soap-Free Emulsion Polymerization. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(8):1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081958
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jae-Jung, Yongsoo Kim, Chanmin Lee, Donghyun Kim, Wonjun Choi, Hyukjun Kwon, Jung-Hyun Kim, Ki-Seob Hwang, and Jun-Young Lee. 2021. "Morphological Analysis of PSMA/PEI Core–Shell Nanoparticles Synthesized by Soap-Free Emulsion Polymerization" Nanomaterials 11, no. 8: 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081958
APA StylePark, J. -J., Kim, Y., Lee, C., Kim, D., Choi, W., Kwon, H., Kim, J. -H., Hwang, K. -S., & Lee, J. -Y. (2021). Morphological Analysis of PSMA/PEI Core–Shell Nanoparticles Synthesized by Soap-Free Emulsion Polymerization. Nanomaterials, 11(8), 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081958