Antiviral Activities of High Energy E-Beam Induced Copper Nanoparticles against H1N1 Influenza Virus
Abstract
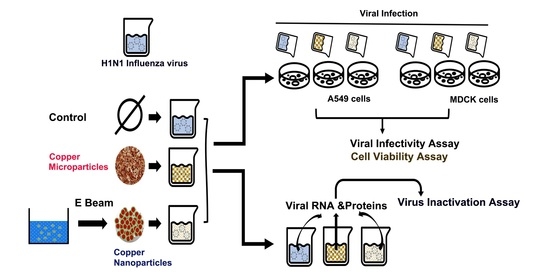
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Cu NPs
2.3. Characterization of Cu NPs
2.4. Cell Culture and Virus Propagation
2.5. Fifty Percent Tissue Culture Infectious Dose (TCID50) Assay
2.6. Virus Infection
2.7. Virus Inactivation Assay
2.8. Cellular RNA Isolation and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
2.9. Cell Viability Assay
2.10. Western Blot and Coomassie Blue Staining
2.11. Confocal Microscopy
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Morphological Analysis of Cu NPs and Cu MPs
3.2. Characteristic Analysis of Cu NPs
3.3. Virus Inactivation by Cu NPs
3.4. Infectivity of Cu NPs-Treated Virus
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Lai, S.; Gao, G.F.; Shi, W. The emergence, genomic diversity and global spread of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 600, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, R.; Azzopardi-Muscat, N.; Kirkby, V.; Lessof, S.; Nathan, N.L.; Pastorino, G.; Permanand, G.; van Schalkwyk, M.C.; Torbica, A.; Busse, R.; et al. Drawing light from the pandemic: Rethinking strategies for health policy and beyond. Health Policy 2021, 126, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreepadmanabh, M.; Sahu, A.K.; Chande, A. COVID-19: Advances in diagnostic tools, treatment strategies, and vaccine development. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind, V.; Bharadwaj, S.; Sai Ganesh, M.R.; Vishnu, J.; Shankar, K.V.; Shankar, B.; Rajesh, R. Antiviral properties of copper and its alloys to inactivate COVID-19 virus: A review. Biometals 2021, 34, 1217–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, M.; Uauy, R. Copper as an essential nutrient. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 791s–796s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceloux, D.G. Copper. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, M.; Duval, R.E.; Hartemann, P.; Engels-Deutsch, M. Contact killing and antimicrobial properties of copper. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dollwet, H.H. Historic uses of copper compounds in medicine. Trace Elem. Med. 1985, 2, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Bouraguba, M.; Glattard, E.; Naudé, M.; Pelletier, R.; Aisenbrey, C.; Bechinger, B.; Raibaut, L.; Lebrun, V.; Faller, P. Copper-binding motifs Xxx-His or Xxx-Zzz-His (ATCUN) linked to an antimicrobial peptide: Cu-binding, antimicrobial activity and ROS production. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 213, 111255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addae, E.; Dong, X.; McCoy, E.; Yang, C.; Chen, W.; Yang, L. Investigation of antimicrobial activity of photothermal therapeutic gold/copper sulfide core/shell nanoparticles to bacterial spores and cells. J. Biol. Eng. 2014, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezza, F.A.; Tichapondwa, S.M.; Chirwa, E.M.N. Fabrication of monodispersed copper oxide nanoparticles with potential application as antimicrobial agents. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, G.; Rensing, C.; Solioz, M. Metallic copper as an antimicrobial surface. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gross, T.M.; Lahiri, J.; Golas, A.; Luo, J.; Verrier, F.; Kurzejewski, J.L.; Baker, D.E.; Wang, J.; Novak, P.F.; Snyder, M.J. Copper-containing glass ceramic with high antimicrobial efficacy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zerbib, S.; Vallet, L.; Muggeo, A.; de Champs, C.; Lefebvre, A.; Jolly, D.; Kanagaratnam, L. Copper for the Prevention of Outbreaks of Health Care-Associated Infections in a Long-term Care Facility for Older Adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 68–71.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, B.; Patra, S.; Jampílek, J.; Králová, K.; Bakirhan, N.; Uslu, B.; Ozkan, S.; Alfredo, N.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Bernstein, A. Nanostructures for Antimicrobial Therapy: Nanostructures in Therapeutic Medicine Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Avilala, J.; Golla, N. Antibacterial and antiviral properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized by marine actinomycetes. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 10, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Sreekanth, T.V.M.; Nagajyothi, P.C.; Muthuraman, P.; Enkhtaivan, G.; Vattikuti, S.V.P.; Tettey, C.O.; Kim, D.H.; Shim, J.; Yoo, K. Ultra-sonication-assisted silver nanoparticles using Panax ginseng root extract and their anti-cancer and antiviral activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 188, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdiero, S.; Falanga, A.; Vitiello, M.; Cantisani, M.; Marra, V.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antiviral agents. Molecules 2011, 16, 8894–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orłowski, P.; Kowalczyk, A.; Tomaszewska, E.; Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Węgrzyn, A.; Grzesiak, J.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J.; Eriksson, K.; Krzyzowska, M. Antiviral Activity of Tannic Acid Modified Silver Nanoparticles: Potential to Activate Immune Response in Herpes Genitalis. Viruses 2018, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaikwad, S.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A.; Rai, M.; Falanga, A.; Incoronato, N.; Russo, L.; Galdiero, S.; Galdiero, M. Antiviral activity of mycosynthesized silver nanoparticles against herpes simplex virus and human parainfluenza virus type 3. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4303–4314. [Google Scholar]
- Elechiguerra, J.L.; Burt, J.L.; Morones, J.R.; Camacho-Bragado, A.; Gao, X.; Lara, H.H.; Yacaman, M.J. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with HIV-1. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2005, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gherasim, O.; Puiu, R.A.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Burdușel, A.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. An Updated Review on Silver Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.X.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Curcumin modified silver nanoparticles for highly efficient inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3040–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, M.; Xu, T.; Wang, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Zhu, B. The inhibition of H1N1 influenza virus-induced apoptosis by silver nanoparticles functionalized with zanamivir. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, B.C. Oxidation Stability of Conductive Copper Paste Prepared through Electron Beam Irradiation. Appl. Sci. Converg. Tec. 2020, 29, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method of Estimating Fifty per cent Endpoints12. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhou, R.; Hao, X.; Wu, X.; Rao, W.; Chen, Y.; Gao, D. Influences of surfactant (PVA) concentration and pH on the preparation of copper nanoparticles by electron beam irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2008, 77, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Ghazy, O.; Meligi, G.; Saleh, H.; Bekhit, M. Radiation-induced synthesis of Copper/Poly (vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites and their catalytic activity. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Patil, S.; Iyer, V.; Mahumuni, S. Radiation induced synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles. Nanost. Mater. 1998, 10, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bando, Y. A novel method for preparing copper nanorods and nanowires. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki, I.; Billoudet, F.; Pileni, M. Control of the shape and the size of copper metallic particles. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 4160–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, S.; Nakanishi, H.; Matsubara, E.; Matsubara, S.; Ichitsubo, T.; Hosoya, K.; Matsuba, Y. Formation of Cu nanoparticles by electroless deposition using aqueous CuO suspension. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, D474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeju, N.; Rufus, A.; Philip, D. Microwave-assisted rapid synthesis of copper nanoparticles with exceptional stability and their multifaceted applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.; Guedes, M.; Ferro, A.C. Microstructural changes in copper-graphite-alumina nanocomposites produced by mechanical alloying. Microsc. Microanal. 2015, 21, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroui, H.; Wilson, D.S.; Dalmasso, G.; Salaita, K.; Murthy, N.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Merlin, D. Nanomedicine in GI. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G371–G383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper, A.; Hou, H.; Greiner, A.; Schneider, R.; Phillipp, F. Copper nanoparticles encapsulated in multi-shell carbon cages. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 78, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergolese, B.; Muniz-Miranda, M.; Bigotto, A. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering investigation of the adsorption of 2-mercaptobenzoxazole on smooth copper surfaces doped with silver colloidal nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 9241–9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, X.; Peng, H.; Song, H.; Qi, Z.; Miao, X.; Xu, W. Antiviral activity of cuprous oxide nanoparticles against Hepatitis C Virus in vitro. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 222, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, A.; Hashemzadeh, M.S. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 by copper oxide nanoparticles. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 275, 113688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoshima, M.; Lu, Y.; Kimura, T.; Nakano, R.; Ishiguro, H.; Kubota, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Sunada, K. Comparison of the antiviral effect of solid-state copper and silver compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 312, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, D.B.; An, J.S.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Chung, M.S.; Kim, K.H. Divalent cation-induced conformational changes of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.A.; McGuire, K.L.; Wallentine, S.K.; Mohl, G.A.; Lynch, J.D.; Harrison, R.G.; Busath, D.D. Divalent copper complexes as influenza A M2 inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2017, 147, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, C.S.; Shuck, K.; Lear, J.D.; Dieckmann, G.R.; DeGrado, W.F.; Lamb, R.A.; Pinto, L.H. Cu(II) inhibition of the proton translocation machinery of the influenza A virus M2 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5474–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raha, S.; Mallick, R.; Basak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Is copper beneficial for COVID-19 patients? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 142, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, D.; Revol, R.; Östbye, H.; Wang, H.; Daniels, R. Influenza A Virus Cell Entry, Replication, Virion Assembly and Movement. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Sneyd, H.; Dekant, R.; Wang, J. Influenza A Virus Nucleoprotein: A Highly Conserved Multi-Functional Viral Protein as a Hot Antiviral Drug Target. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanley, W.M. The size of influenza virus. J. Exp. Med. 1944, 79, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amodeo, A.A.; Skotheim, J.M. Cell-Size Control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a019083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, T.; Pham, T.T.M.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, K.-M.; Ha, E. Antiviral Activities of High Energy E-Beam Induced Copper Nanoparticles against H1N1 Influenza Virus. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020268
Ha T, Pham TTM, Kim M, Kim Y-H, Park J-H, Seo JH, Kim K-M, Ha E. Antiviral Activities of High Energy E-Beam Induced Copper Nanoparticles against H1N1 Influenza Virus. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(2):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020268
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Taesung, Thi Tuyet Mai Pham, Mikyung Kim, Yeon-Hee Kim, Ji-Hyun Park, Ji Hae Seo, Kyung-Min Kim, and Eunyoung Ha. 2022. "Antiviral Activities of High Energy E-Beam Induced Copper Nanoparticles against H1N1 Influenza Virus" Nanomaterials 12, no. 2: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020268
APA StyleHa, T., Pham, T. T. M., Kim, M., Kim, Y. -H., Park, J. -H., Seo, J. H., Kim, K. -M., & Ha, E. (2022). Antiviral Activities of High Energy E-Beam Induced Copper Nanoparticles against H1N1 Influenza Virus. Nanomaterials, 12(2), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020268