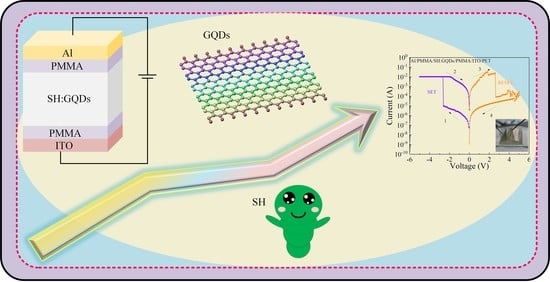
Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Device Fabrication
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Xuan, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Smith, C.G.; Luo, J. Transient Resistive Switching Devices Made from Egg Albumen Dielectrics and Dissolvable Electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10954–10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgunde, B.K.; Rabinal, M.K. Solution processed bilayer junction of silk fibroin and semiconductor quantum dots as multilevel memristor devices. Org. Electron. 2017, 48, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, B.; Elshekh, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Hou, W.; Zhao, Y. The pH-controlled memristive effect in a sustainable bioelectronic device prepared using lotus root. Mater. Today Sustain. 2020, 7–8, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.; Dugasani, S.R.; Raza, M.T.; Jeon, Y.R.; Park, S.H.; Choi, C. The observation of resistive switching characteristics using transparent and biocompatible Cu2+-doped salmon DNA composite thin film. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 335203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Sun, B.; Fu, G.; Li, T.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, L.; Mao, S.; Kan, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, Y. A nonvolatile organic resistive switching memory based on lotus leaves. Chem. Phys. 2019, 516, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, S.; Sun, B.; Li, X.; Guo, B.; Zeng, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, W. From natural biomaterials to environmentally friendly and sustainable nonvolatile memory device. Chem. Phys. 2018, 513, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, M.; Guerrini, A.; Ballestri, M.; Aluigi, A.; Zamboni, R.; Sotgiu, G.; Posati, T. Bioactive Keratin and Fibroin Nanoparticles: An Overview of Their Preparation Strategies. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Lan, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, S.; Stegmann, A.E.; Yu, R.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.Y. Flexible and Insoluble Artificial Synapses Based on Chemical Cross-Linked Wool Keratin. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Sushko, M.L.; Qiu, W.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.Y. Silk Flexible Electronics: From Bombyx mori Silk Ag Nanoclusters Hybrid Materials to Mesoscopic Memristors and Synaptic Emulators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, C.; Hota, M.K.; Naskar, D.; Kundu, S.C.; Maiti, C.K. Resistive switching in natural silk fibroin protein-based biomemristors. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2013, 210, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, M.K.; Bera, M.K.; Kundu, B.; Kundu, S.C.; Maiti, C.K. A Natural Silk Fibroin Protein-Based Transparent Bio-Memristor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4493–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Lee, J.S. Artificial Synapses with Short- and Long-Term Memory for Spiking Neural Networks Based on Renewable Materials. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8962–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.X.; Cheong, K.Y. Effects of drying temperature and ethanol concentration on bipolar switching characteristics of natural Aloe vera-based memory devices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 26833–26853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.X.; Sreenivasan, S.; Wong, Y.H.; Zhao, F.; Cheong, K.Y. Effects of Electrode Materials on Charge Conduction Mechanisms of Memory Device Based on Natural Aloe Vera. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.Y.; Cho, W.J. High-Performance Resistive Switching in Solution-Derived IGZO: N Memristors by Microwave-Assisted Nitridation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoman, M.; Aldrigo, M.; Dragoman, D. Perspectives on Atomic-Scale Switches for High-Frequency Applications Based on Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tan, L.; Sun, B.; Lei, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Memristive effect with nonzero-crossing current-voltage hysteresis behavior based on Ag doped Lophatherum gracile Brongn. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogurla, N.; Mondal, S.P.; Sinha, A.K.; Katiyar, A.K.; Banerjee, W.; Kundu, S.C.; Ray, S.K. Transparent and flexible resistive switching memory devices with a very high ON/OFF ratio using gold nanoparticles embedded in a silk protein matrix. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 345202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Lee, J.-S. Controlling the Resistive Switching Behavior in Starch-Based Flexible Biomemristors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7326–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Sun, F.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Hao, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T. Bioinspired flexible artificial synapses for pain perception and nerve injuries. Npj Flex. Electron. 2020, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yarimaga, O.; Choi, S.-J.; Choi, Y.-K. Highly durable and flexible memory based on resistance switching. Solid·State Electron. 2010, 54, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, K.; Bocchini, S.; Chiappone, A.; Roppolo, I.; Perrone, D.; Bejtka, K.; Ricciardi, C.; Pirri, C.F.; Chiolerio, A. Spin-coated silver nanocomposite resistive switching devices. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 168, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Jang, J.; Park, S.; Ji, G.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, D.-B.; Yoon, K.-H.; Chung, C.-M.; Cho, S. Flexible and transparent electrode based on Ag-nanowire embedded colorless poly (amide-imide). Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Tay, R.Y.; Nguyen, V.C.; Wang, J.; Cai, G.; Chen, T.; Teo, E.H.T.; Lee, P.S. Hexagonal Boron Nitride Thin Film for Flexible Resistive Memory Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.-S. Flexible Artificial Synaptic Devices Based on Collagen from Fish Protein with Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Rho, J. Solution-Processed Flexible Biomemristor Based on Gold-Decorated Chitosan. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5445–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wen, D. Nonvolatile Bio-Memristor Based on Silkworm Hemolymph Proteins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Yan, X. Enhanced memory characteristics of charge trapping memory by employing graphene oxide quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J. Highly improved performance in Zr0.5Hf0.5O2 films inserted with graphene oxide quantum dots layer for resistive switching nonvolatile memory. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 11046–11052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Large magnetization modulation in ZnO-based memory devices with embedded graphene quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 16047–16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Self-rectifying resistive switching and short-term memory characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN artificial synaptic device. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Meng, F.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Sericin for resistance switching device with multilevel nonvolatile memory. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5498–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Baeg, K.-J.; Khim, D.; Noh, Y.-Y.; Kim, D.-Y. Printed, Flexible, Organic Nano-Floating-Gate Memory: Effects of Metal Nanoparticles and Blocking Dielectrics on Memory Characteristics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3503–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, W.; Wen, D. Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203709
Wang L, Yang J, Zhu H, Li W, Wen D. Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(20):3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203709
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Jing Yang, Hongyu Zhu, Wenhao Li, and Dianzhong Wen. 2022. "Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph" Nanomaterials 12, no. 20: 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203709
APA StyleWang, L., Yang, J., Zhu, H., Li, W., & Wen, D. (2022). Flexible Threshold-Type Switching Devices with Low Threshold and High Stability Based on Silkworm Hemolymph. Nanomaterials, 12(20), 3709. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203709