Insight on Photocatalytic and Photoinduced Antimicrobial Properties of ZnO Thin Films Deposited by HiPIMS through Thermal Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of ZnO Thin Films
2.2. Sample Characterization
2.3. Optical Properties Characterization
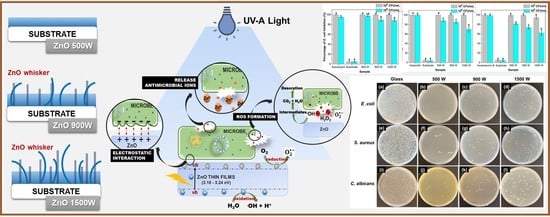
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. ZnO Structure Analysis
3.2. ZnO Thin Film Microstructure
3.3. Optical Properties and Band Gap Energy
3.4. Photocatalytic Activity
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vyas, S. A short review on properties and applications of ZnO based thin film and devices. Johns. Matthey Technol. Rev. 2020, 64, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Ahmad, A.; Anjum, M.A.R.; Haleem, A.; Siddiq, M.; Shah, S.S.; Al Kahtani, A. Photocatalytic degradation of malachite green and methylene blue over reduced graphene oxide (rGO) based metal oxides (rGO-Fe3O4/TiO2) nanocomposite under UV-visible light irradiation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharshini, S.S.; Shubha, J.P.; Shivalingappa, J.; Adil, S.F.; Kuniyil, M.; Hatshan, M.R.; Shaik, B.; Kavalli, K. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue and Metanil Yellow Dyes Using Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanocrystals. Crystals 2022, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-Y.; Widyastuti, E.; Lin, T.-C.; Chiu, C.-T.; Xu, F.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Lee, Y.-C. The Phase Evolution and Photocatalytic Properties of a Ti-TiO2 Bilayer Thin Film Prepared Using Thermal Oxidation. Coatings 2021, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Jamal, M.A.; Iftikhar, M.; Ahmad, A.; Hussain, S.; Asghar, H.; Saeed, M.; Yousaf, A.B.; Karri, R.R.; Al-kadhi, N.S. Lanthanum-Zinc Binary Oxide Nanocomposite with Promising Heterogeneous Catalysis Performance for the Active Conversion of 4-Nitrophenol into 4-Aminophenol. Coatings 2021, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, B.; Khan, M.I.; Iqbal, M.; Mahmood, A.; Al-Masry, W. Structural and optical properties of Ti and Cu co-doped ZnO thin films for photovoltaic applications of dye sensitized solar cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 2445–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Tomar, M.; Gupta, V.; Kapoor, A. Investigation of cadmium incorporated ZnO thin films for photodetector applications. Superlattices Microstruct. 2021, 151, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, J. Atomic layer deposition of ZnO thin film on ZrO2 dental implant surface for enhanced antibacterial and bioactive performance. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 128854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyastuti, E.; Xu, F.-Y.; Chiu, C.-T.; Jan, J.-H.; Hsu, J.-L.; Lee, Y.-C. A Study on the Characteristic and Antibacterial Activity of Ti3Ox Thin Films. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, K.; Kamidaira, M.; Kashiwaba, Y.; Sekiguchi, T.; Watanabe, H. ZnO thin films prepared by remote plasma-enhanced CVD method. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 214, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Chang, J.H.; Minegishi, T.; Park, J.S.; Im, I.H.; Ito, M.; Taishi, T.; Hong, S.K.; Oh, D.C.; Cho, M.W. Investigation on the ZnO: N films grown on (0 0 0 1) and (0 0 0 1) ZnO templates by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 2167–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, C.M.; Rizam, M.S.B.S.; Rusop, M.; Hidayah, S.R. Characterization of ZnO and ZnO: TiO2 thin films prepared by sol-gel spray-spin coating technique. Procedia Eng. 2012, 41, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naouar, M.; Ka, I.; Gaidi, M.; Alawadhi, H.; Bessais, B.; El Khakani, M.A. Growth, structural and optoelectronic properties tuning of nitrogen doped ZnO thin films synthesized by means of reactive pulsed laser deposition. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 57, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbiner, C.R.; Veedu, M.A.A.; Kekuda, D. Influence of oxygen flow rate on the structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO films grown by DC magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrec, A.; Keraudy, J.; Jacq, S.; Schuster, F.; Jouan, P.-Y.; Djouadi, M.A. Correlation between mass-spectrometer measurements and thin film characteristics using dcMS and HiPIMS discharges. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 250, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Hultman, L. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: Towards reliable binding energy referencing. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 107, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Chen, Q. The semi-conductor of ZnO deposited in reactive HiPIMS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, S.; Hemberg, A.; Dauchot, J.P.; Hecq, M. Deposition of zinc oxide layers by high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanom. Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2007, 25, L19–L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, J.G.; Mayes, E.L.H.; McDougall, N.L.; Bilek, M.M.M.; McCulloch, D.G. Characterization and device applications of ZnO films deposited by high power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 165105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becherescu, N.; Mihailescu, I.; Tiron, V.; Luculescu, C. Preparation and characterization of ZnO Thin films by PLD and HIPIMS. UPB Sci. Bull. Ser. A Appl. Math. Phys. Учредители Univ. Politeh. Bucur. 2017, 79, 297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Mickan, M.; Helmersson, U.; Rinnert, H.; Ghanbaja, J.; Muller, D.; Horwat, D. Room temperature deposition of homogeneous, highly transparent and conductive Al-doped ZnO films by reactive high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 157, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Chen, Q. N doped ZnO (N: ZnO) film prepared by reactive HiPIMS deposition technique. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 35122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reed, A.N. Materials for flexible thin-film transistors: High-power impulse magnetron sputtering of zinc oxide. In Women in Aerospace Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kubart, T.; Gudmundsson, J.T.; Lundin, D. Reactive high power impulse magnetron sputtering. In High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 223–263. [Google Scholar]
- Tiron, V.; Velicu, I.-L.; Stanescu, D.; Magnan, H.; Sirghi, L. High visible light photocatalytic activity of nitrogen-doped ZnO thin films deposited by HiPIMS. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 324, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lou, B.-S.; Yang, Y.-C.; Qiu, Y.-X.; Diyatmika, W.; Lee, J.-W. Hybrid high power impulse and radio frequency magnetron sputtering system for TiCrSiN thin film depositions: Plasma characteristics and film properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouanane, I.; Kabir, A.; Boulainine, D.; Zerkout, S.; Schmerber, G.; Boudjema, B. Characterization of ZnO thin films prepared by thermal oxidation of zn. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 3307–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, G.G.; Gǐrtan, M.; Rusu, M. Preparation and characterization of ZnO thin films prepared by thermal oxidation of evaporated Zn thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 2007, 42, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chakrabarti, P. Optical characterization of ZnO thin films grown by thermal oxidation of metallic zinc. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2013, 5, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Gao, W.; Reeves, R.J. Zinc oxide films by thermal oxidation of zinc thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 198, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.C.; Louder, R.; Thompson, C. V Photocatalytic activity and stability of porous polycrystalline ZnO thin films grown via a two-step thermal oxidation process. Coatings 2014, 4, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.W.; Zhong, M.L.; Tang, C.M. Large-Scale Oxide Nanostructures Grown by Thermal Oxidation. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 60, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.G.; Lau, S.P.; Zhang, X.H.; Lee, H.W.; Yu, S.F.; Tay, B.K.; Hng, H.H. Evolution of visible luminescence in ZnO by thermal oxidation of zinc films. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 375, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Deng, H.; Yi, J.; Liu, S. A new method for preparation of zinc oxide whiskers. Mater. Res. Bull. 1999, 34, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongjai, K.; Choopun, S.; Hongsith, N.; Gardchareon, A. Zinc oxide whiskers by thermal oxidation method. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2011, 38, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kado, H.; Yokoyama, K.; Tohda, T. A novel ZnO whisker tip for atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 1992, 42, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-S.; Ting, J.-M. Growth of ZnO thin films and whiskers. Thin Solid Film. 2001, 398, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, W.-T.; Wu, W.-Y.; Ting, J.-M. Growth of single crystal ZnO nanowires using sputter deposition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 1841–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.X.; Sun, X.W.; Chen, B.J.; Dong, Z.L.; Yu, M.B.; Zhang, X.H.; Chua, S.J. Network array of zinc oxide whiskers. Nanotechnology 2004, 16, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renitta, A.; Vijayalakshmi, K. Highly sensitive hydrogen safety sensor based on Cr incorporated ZnO nano-whiskers array fabricated on ITO substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.K.; Lyon, D.Y.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3527–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, T.; Perlstein, B.; Houbara, O.; Felner, I.; Banin, E.; Margel, S. Synthesis and characterization of zinc/iron oxide composite nanoparticles and their antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 374, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.M.; Feris, K.; Bell, J.; Wingett, D.G.; Hanley, C.; Punnoose, A. Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 213902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thongsuriwong, K.; Amornpitoksuk, P.; Suwanboon, S. Structure, morphology, photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel dip-coating method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.; Sampaio, P.; Azevedo, S.; Vaz, C.; Espinós, J.P.; Teixeira, V.; Carneiro, J.O. Influence of thickness and coatings morphology in the antimicrobial performance of zinc oxide coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, D.; Borges, J.; Mota, M.F.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Pereira-Silva, P.; Ferreira, A.; Pereira, C.S.; Sampaio, P.; Vaz, F. Effect of microstructural changes in the biological behavior of magnetron sputtered ZnO thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Film. 2019, 37, 11501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedade, A.P.; Pinho, A.C.; Branco, R.; Morais, P. V Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of ZnO based nanocomposites for the coating of non-critical equipment in medical-care facilities. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 513, 145818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Silva, P.; Costa-Barbosa, A.; Costa, D.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Carvalho, P.; Borges, J.; Vaz, F.; Sampaio, P. Antifungal activity of ZnO thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition. Thin Solid Film. 2019, 687, 137461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilgies, D.-M. Scherrer grain-size analysis adapted to grazing-incidence scattering with area detectors. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ton, N.Q.T.; Le, T.N.T.; Kim, S.; Dao, V.A.; Yi, J.; Vu, T.H.T. High-efficiency photo-generated charges of ZnO/TiO2 heterojunction thin films for photocatalytic and antibacterial performance. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, A. Tutorial: Reactive high power impulse magnetron sputtering (R-HiPIMS). J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Cui, H. Sol–gel preparation of transparent zinc oxide films with highly preferential crystal orientation. Vacuum 2004, 77, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailova, I.; Gerbreders, V.; Tamanis, E.; Sledevskis, E.; Viter, R.; Sarajevs, P. Synthesis of ZnO nanoneedles by thermal oxidation of Zn thin films. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2013, 377, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-M.; Hwang, W.-S.; Liu, W.Y.; Yang, J.S. Effect of RF power on optical and electrical properties of ZnO thin film by magnetron sputtering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 72, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittinger, V.; Lenck, O.; Vergöhl, M.; Szyszka, B.; Bräuer, G. Applications of HIPIMS metal oxides. Thin Solid Film. 2013, 548, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaceri, H.; Boujnah, M.; Erfurt, D.; Rappich, J.; Lifei, X.; Khaldoun, A.; Benyoussef, A.; Ennaoui, A.; Taleb, A. Influence of stress on the photocatalytic properties of sprayed ZnO thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 201, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Cui, Y.; Wang, L. Effect of preheating and annealing temperatures on quality characteristics of ZnO thin film prepared by sol–gel method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 97, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel-Schäuble, N.; Romanyuk, Y.E.; Yoon, S.; Saji, K.J.; Populoh, S.; Pokrant, S.; Aguirre, M.H.; Weidenkaff, A. Thermoelectric properties of nanostructured Al-substituted ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2012, 520, 6869–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, D.; Shen, J.; Zhou, W.; Luo, Q.; Jin, A.; Yang, H.; Gu, C. Growth and electrical properties of zinc oxide nanowires. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Bian, L.; Wei, Y. Simple fabrication and photocatalytic activity of ZnO particles with different morphologies. Powder Technol. 2011, 207, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Xu, X.; Duan, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, X. Photocatalytic activity and stability of ZnO particles with different morphologies. Rare Met. 2011, 30, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Tanaka, N.; Ueda, Y.; Ohshio, S.; Saitoh, H. Epitaxial growth of zinc oxide whiskers by chemical-vapor deposition under atmospheric pressure. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 38, L586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaken, S.M.; Farzana, E.; Podder, J. Effect of Fe-doping on the structural and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. J. Semicond. 2013, 34, 73003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, S.A.; Chan, K.-Y.; Yow, H.-K.; Sahdan, M.Z.; Saim, H.; Knipp, D. Zinc oxide films prepared by sol–gel spin coating technique. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 104, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Gong, W.; Huang, K.; Zhu, J.; Meng, F.; Song, X.; Sun, Z. Effect of annealing temperature on photocatalytic activity of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. Superlattices Microstruct. 2011, 50, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, O.A.; Ismail, A.A.; Zaki, Z.I.; Mohamed, R.M. Zinc oxide thin films prepared by thermal evaporation deposition and its photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yao, B.; He, Y.; Cao, B.; Ma, W.; Chang, L. Oxygen defect-rich In-doped ZnO nanostructure for enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 244, 122672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; An, S.J.; Park, W.I.; Yi, G.; Choi, W. Photocatalysis using ZnO thin films and nanoneedles grown by metal–organic chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Haneda, H. Morphologies of zinc oxide particles and their effects on photocatalysis. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongnavakit, P.; Amornpitoksuk, P.; Suwanboon, S.; Ratana, T. Surface and photocatalytic properties of ZnO thin film prepared by sol–gel method. Thin Solid Film. 2012, 520, 5561–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, A.; Fragala, M.E.; Privitera, V.; Impellizzeri, G. ZnO for application in photocatalysis: From thin films to nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 69, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, S.; Panigrahi, P.; Kumaar, S.; Nagarajan, G.S. Effect of conducting polymer on photoluminescence quenching of green synthesized ZnO thin film and its photocatalytic properties. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2020, 22, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemets, K.; Ivask, A.; Dubourguier, H.-C.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanoparticles of ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquet, J.; Chevalier, Y.; Pelletier, J.; Couval, E.; Bouvier, D.; Bolzinger, M.-A. The contribution of zinc ions to the antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, Y.; Povey, M.; York, D. ZnO nanofluids–A potential antibacterial agent. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2008, 18, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, R.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Abareshi, M.; Moosavi, M.; Yousefi, A.; Nancarrow, P. ZnO nanofluids: Green synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 121, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, A.; Park, S.-H.; Shim, K.-D.; Kim, D.-J.; Jhee, K.-H.; Lee, H.-W.; Heo, C.-H.; Kim, H.-M.; Jang, E.-S. Antibacterial mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles under dark conditions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 45, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devirgiliis, C.; Murgia, C.; Danscher, G.; Perozzi, G. Exchangeable zinc ions transiently accumulate in a vesicular compartment in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, J. Quantitative evaluation of antibacterial activities of metallic oxide powders (ZnO, MgO and CaO) by conductimetric assay. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 54, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Mashayekhi, H.; Xing, B. Bacterial toxicity comparison between nano-and micro-scaled oxide particles. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin Sevinç, B.; Hanley, L. Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brayner, R.; Ferrari-Iliou, R.; Brivois, N.; Djediat, S.; Benedetti, M.F.; Fiévet, F. Toxicological impact studies based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagvenkar, A.P.; Deokar, A.; Perelshtein, I.; Gedanken, A. A one-step sonochemical synthesis of stable ZnO–PVA nanocolloid as a potential biocidal agent. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeto, H.H. Cell-permeable, mitochondrial-targeted, peptide antioxidants. AAPS J. 2006, 8, E277–E283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinu, R.; Madras, G. Environmental remediation by photocatalysis. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2010, 90, 189–230. [Google Scholar]
- Yemmireddy, V.K.; Hung, Y. Using photocatalyst metal oxides as antimicrobial surface coatings to ensure food safety—Opportunities and challenges. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Soares, N.d.F.F.; dos Reis Coimbra, J.S.; de Andrade, N.J.; Cruz, R.S.; Medeiros, E.A.A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antimicrobial activity and food packaging applications. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 1447–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.S.H.; Karthikeyan, C.; Ahamed, A.P.; Thajuddin, N.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Ravi, G. In vitro antibacterial activity of ZnO and Nd doped ZnO nanoparticles against ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, L.S.; Nisha, M.M.; Joice, M.; Shilpa, P.N. Antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticle against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, A. A review on bidirectional analogies between the photocatalysis and antibacterial properties of ZnO. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 783, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.; Murthy, H.C.A.; Amare, E. Enhancing the photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO: Defects, heterojunction, and optimization. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, U.S.; Tan, B.W.Q.; Vellayappan, B.A.; Jeyasekharan, A.D. ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, Y.; Mustapha, A.; Lin, M. Antifungal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium expansum. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 166, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Peral, F.J.; Zaragoza, O.; Pedreno, Y.; Argüelles, J.-C. Protective role of trehalose during severe oxidative stress caused by hydrogen peroxide and the adaptive oxidative stress response in Candida albicans. Microbiology 2002, 148, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, O. Influence of particle size on the antibacterial activity of zinc oxide. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 3, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applerot, G.; Perkas, N.; Amirian, G.; Girshevitz, O.; Gedanken, A. Coating of glass with ZnO via ultrasonic irradiation and a study of its antibacterial properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 256, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Parameter | Zn500 | Zn900 | Zn1500 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sputtering Power (watt) | 500 | 900 | 1500 |
| Argon flows (sccm) | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| Base Pressure (torr) | 2.5 × 10−5 | 2.5 × 10−5 | 2.5 × 10−5 |
| Working Pressure (torr) | 3.6 × 10−3 | 3.6 × 10−3 | 3.6 × 10−3 |
| Voltage (Volt) | 561 | 652 | 755 |
| Current (A) | 0.73 | 1.38 | 1.74 |
| Deposition Rate (nm/min) | 141 | 236 | 310 |
| Sample | Thickness (nm) | Grain Size (D) (nm) | Roughness * (rms) (nm) | Lattice Parameter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a = b (Å)(100) | c (Å)(002) | ||||
| Zn 500 W | 146 | 18.155 | 34.25 | 3.261 | 5.225 |
| Zn 900 W | 147.65 | 15.602 | 44.51 | 3.263 | 5.220 |
| Zn 1500 W | 225.50 | 14.117 | 46.62 | 3.265 | 5.227 |
| Fabrication | Thickness (nm) | Irradiation Time (min) | Photolysis (Concentration) | Photocatalytic Activity (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOCVD | 250 | 300 | Dye (Orange II) (3.50 mg/L) * | 23 | [68] |
| 910 | 50 | ||||
| DC-MS | 400 | 180 | MO (5 mg/L) | 73.4 | [65] |
| Sol-gel | 500 | 180 | MB (3.20 mg/L) * | 70.34 | [70] |
| Sol-gel | 218 | 240 | MB (3.20 mg/L) * | 77 | [44] |
| ALD | 30 | 240 | MB (4.78 mg/L) * | ~53 ** | [71] |
| SILAR | 1870 | 300 | R6G (5 mg/L) | 87 | [72] |
| ILGR | 100 | 80 | MB (1.60 mg/L) * | ~58 ** | [56] |
| HiPIMS, thermal oxidation | 140 | 180 240 300 | MB (10 mg/L) | 73.69 83.68 89.90 | This Work |
| Thin Films (Thickness) | Initial Microbe Concentration (CFU/mL) | Irradiation Time (min) | Microbial Inhibition (%) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | S. aureus | C. albicans | ||||
| Sol-gel (218 nm) | 2.3 × 106 | 30 | 94.17 | - | - | [44] |
| 2.3 × 106 | 60 | 99.50 | - | - | ||
| 2.3 × 105 | 30 | 99.53 | - | - | ||
| 2.3 × 105 | 60 | 100 | - | - | ||
| DC-MS (200–600 nm) | 8 × 107 * | 35 | 45 ** | - | - | [45] |
| DC-MS (148 nm) | ~4.9 × 107 | 480 | - | - | 4.08 ** | [46] |
| (655 nm) | ~4.9 × 107 | 480 | - | - | 53.06 | |
| DC-MS (650 nm) | 1 × 108 * | 1500 | - | - | 68 | [48] |
| RF-MS (400 nm) | 4 × 108 * | 15 | - | 66.27 ** | - | [47] |
| HiPIMS (140 nm) | 1 × 105 | 30 | 100 | 99.98 | 99.20 | This work |
| 1 × 106 | 30 | 97.43 | 88.39 | 81.01 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Widyastuti, E.; Hsu, J.-L.; Lee, Y.-C. Insight on Photocatalytic and Photoinduced Antimicrobial Properties of ZnO Thin Films Deposited by HiPIMS through Thermal Oxidation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030463
Widyastuti E, Hsu J-L, Lee Y-C. Insight on Photocatalytic and Photoinduced Antimicrobial Properties of ZnO Thin Films Deposited by HiPIMS through Thermal Oxidation. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030463
Chicago/Turabian StyleWidyastuti, Endrika, Jue-Liang Hsu, and Ying-Chieh Lee. 2022. "Insight on Photocatalytic and Photoinduced Antimicrobial Properties of ZnO Thin Films Deposited by HiPIMS through Thermal Oxidation" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030463
APA StyleWidyastuti, E., Hsu, J.-L., & Lee, Y.-C. (2022). Insight on Photocatalytic and Photoinduced Antimicrobial Properties of ZnO Thin Films Deposited by HiPIMS through Thermal Oxidation. Nanomaterials, 12(3), 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030463