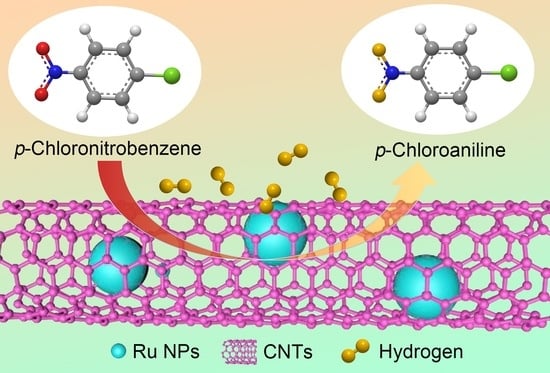
Ru@Carbon Nanotube Composite Microsponge: Fabrication in Supercritical CO2 for Hydrogenation of p-Chloronitrobenzene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of Catalysts
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Catalysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brea, R.J.; Reiriz, C.; Granja, J.R. ChemInform Abstract: Towards Functional Bionanomaterials Based on Self-Assembling Cyclic Peptide Nanotubes. ChemInform 2010, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, A.; Pacini, A.; Pasini, D. Chiral nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoş, G.D.; Pengo, P.; Sanders, J.K.M. Hydrogen-Bonded Helical Organic Nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 46, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Li, C. Catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over Fe3O4 modified Ru/Carbon nanotubes catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 45, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidick, D.; Herlitschke, M.; Poleunis, C.; Delcorte, A.; Hermann, R.P.; Devillers, M.; Hermans, S. Comparison of functionalized carbon nanofibers and multi-walled carbon nanotubes as supports for Fe–Co nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2012, 1, 2050–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuganathan, N.; Chroneos, A. Ru-doped single walled carbon nanotubes as sensors for SO2 and H2S detection. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Hu, D.; Kuang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. High dispersion of platinum–ruthenium nanoparticles on the 3,4,9,10-perylene tetracarboxylic acid-functionalized carbon nanotubes for methanol electro-oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5253–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Kim, B.G.; Seo, S.; Shawky, A.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, K.; Mikladal, B.; Kauppinen, E.I.; Maruyama, S.; Jeon, I.; et al. Strong dark current suppression in flexible organic photodetectors by carbon nanotube transparent electrodes. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Wan, X. Carbon Nanotubes-Coated Conductive Elastomer: Electrical and Near Infrared Light Dual-Stimulated Shape Memory, Self-Healing, and Wearable Sensing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 2954–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; Li, L.; Liang, G.; Jin, Y.Q.; Huang, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Xie, F.; et al. Fe-Nx doped carbon nanotube as a high efficient cathode catalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lan, G.; Fu, W.; Lai, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, H.; Liu, H. Role of surface defects of carbon nanotubes on catalytic performance of barium promoted ruthenium catalyst for ammonia synthesis. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 41, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Chu, W.; Vipin, A.K.; Sun, L. Environmental Remediation Applications of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide: Adsorption and Catalysis. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Fan, Z.; Pan, X.; Bao, X. Effect of Confinement in Carbon Nanotubes on the Activity of Fischer−Tropsch Iron Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9414–9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Bao, X. The Effects of Confinement inside Carbon Nanotubes on Catalysis. Accounts Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillejos, E.; Jahjah, M.; Favier, I.; Orejón, A.; Pradel, C.; Teuma, E.; Masdeu-Bultó, A.M.; Serp, P.; Gómez, M. Synthesis of Platinum-Ruthenium Nanoparticles under Supercritical CO2 and their Confinement in Carbon Nanotubes: Hydrogenation Applications. ChemCatChem 2011, 4, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Pan, X.; Willinger, M.-G.; Su, D.S.; Bao, X. Facile Autoreduction of Iron Oxide/Carbon Nanotube Encapsulates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3136–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.-H.; Feng, M.; Lu, H.; Kong, X.-X.; Cao, G.-P. Nitrile Butadiene Rubber Hydrogenation over a Monolithic Pd/CNTs@Nickel Foam Catalysts: Tunable CNTs Morphology Effect on Catalytic Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Pan, X.; Bao, X. Tuning of Redox Properties of Iron and Iron Oxides via Encapsulation within Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7421–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Pan, X.; Guo, S.; Ren, P.; Bao, X. Toward Fundamentals of Confined Catalysis in Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 137, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, M.; Li, M.; Pan, X.; Chen, J.; Bao, X. Facile encapsulation of nanosized SnO2 particles in carbon nanotubes as an efficient anode of Li-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 9527–9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Takai, C.; Razavi-Khosroshahi, H.; EL Salmawy, M.S.; Fuji, M. Effect of CNTs on morphology and electromagnetic properties of non-firing CNTs/silica composite ceramics. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Bao, R.; Fang, D.; Yi, J.H.; Li, L. A facile synthesis of CNTs/Cu2O-CuO heterostructure composites by spray pyrolysis and its visible light responding photocatalytic properties. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Takai, C.; Razavi-Khosroshahi, H.; Fuji, M. Effect of silane modification on CNTs/silica composites fabricated by a non-firing process to enhance interfacial property and dispersibility. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubenali, M.; Vanucci, G.; Machado, B.; Kacimi, M.; Ziyad, M.; Faria, J.; Raspolli-Galetti, A.; Serp, P. Hydrogenation of p-Chloronitrobenzene over Nanostructured-Carbon-Supported Ruthenium Catalysts. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Fan, Z.; Chen, W.; Ding, Y.; Luo, H.; Bao, X. Enhanced ethanol production inside carbon-nanotube reactors containing catalytic particles. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Meseguer, J.; Cabrero-Antonino, J.R.; Domínguez, I.; Leyva-Pérez, A.; Corma, A. Small Gold Clusters Formed in Solution Give Reaction Turnover Numbers of 10 7 at Room Temperature. Science 2012, 338, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Liang, J.; Zhu, W.; Song, H.; Wang, K.; Li, C. In-Situ Liquid Hydrogenation of m-Chloronitrobenzene over Fe-Modified Pt/Carbon Nanotubes Catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Z.; Gui, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Jia, Y.; Cao, A.; Zhu, Y.; Xiang, R.; Wu, T.; Tang, Z. Carbon Nanotube Sponge-Array Tandem Composites with Extended Energy Absorption Range. Adv. Mater. 2012, 25, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, Z.; Gan, Q.; Xiang, R.; Cao, A.; Tang, Z. Three-Dimensional Carbon Nanotube Sponge-Array Architectures with High Energy Dissipation. Adv. Mater. 2013, 26, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, E.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Hou, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Cao, A.; Fang, Y. Carbon Nanotube Network Embroidered Graphene Films for Monolithic All-Carbon Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2014, 27, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Wei, H.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Ru nanoparticles confined in carbon nanotubes: Supercritical CO2 assisted preparation and improved catalytic performances in hydrogenation of d-glucose. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 7079–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessop, P.G.; Subramaniam, B. Gas-expanded liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2666–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutz, F.; Andanson, J.-M.; Baiker, A. Ionic Liquids and Dense Carbon Dioxide: A Beneficial Biphasic System for Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 111, 322–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, C.S.; Kumar, V.P.; Viswanadham, B.; Srikanth, A.; Chary, K.V.R. Vapor Phase Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene to Aniline Over Carbon Supported Ruthenium Catalysts. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 5403–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, A.; Roggan, S.; Simakova, O.A.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D.Y. Structure sensitivity in catalytic hydrogenation of glucose over ruthenium. Catal. Today 2014, 241, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, S.; Arslan, F.; Ozpozan, N.K. Ru(II) impregnated Al2O3, Fe3O4, SiO2 and N-coordinate ruthenium(II) arene complexes: Multifunctional catalysts in the hydrogenation of nitroarenes and the transfer hydrogenation of aryl ketones. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 164, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Microemulsion-Controlled Synthesis of One-Dimensional Ir Nanowires and Their Catalytic Activity in Selective Hydrogenation of o-Chloronitrobenzene. Langmuir 2014, 31, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M.; Tao, K.; Xiong, C.; Zhou, S. Controlled synthesis of Pd–NiO@SiO2 mesoporous core-shell nanoparticles and their enhanced catalytic performance for p-chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation with H2. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Wang, X.; Lamey, D.; Li, M.; Keane, M.A.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. An examination of catalyst deactivation in p-chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation over supported gold. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xing, Y. Pt−Ru Nanoparticles Supported on Carbon Nanotubes as Methanol Fuel Cell Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ni, X.; Zhang, W.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Girgsdies, F.; Liang, C.; Schlögl, R.; Su, D.S. Structural rearrangements of Ru nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes under microwave irradiation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10716–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, M.; Tabei, S.; Nemati, A.; Eder, D.; Pradeep, T. Synthesis and crystallization of lead–zirconium–titanate (PZT) nanotubes at the low temperature using carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as sacrificial templates. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Rudolph, V.; Zhu, Z. Nanotubules-supported Ru nanoparticles for preferential CO oxidation in H2-rich stream. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-S.; Huang, C.-I.; Yang, R.-Y.; Wang, C.-P. The effect of SWCNT with the functional group deposited on the counter electrode on the dye-sensitized solar cell. Adv. Powder Technol. 2010, 21, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, C.; Oubenali, M.; Galletti, A.M.R.; Serp, P.; Vannucci, G. Novel microwave synthesis of ruthenium nanoparticles supported on carbon nanotubes active in the selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene to p-chloroaniline. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 421-422, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Q.; Guan, R.; Zhao, L.; Yang, H. Controlled synthesis of dendritic ruthenium nanostructures under microwave irradiation and their catalytic properties for p-chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation. Transit. Met. Chem. 2020, 46, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. Experimental Evidence for the Interface Interaction in Ag/C60 Nanocomposite Catalyst and Its Crucial Influence on Catalytic Performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 21526–21530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, X.; Liu, H.; Ding, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Li, B. Ru@Carbon Nanotube Composite Microsponge: Fabrication in Supercritical CO2 for Hydrogenation of p-Chloronitrobenzene. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030539
Ge X, Liu H, Ding X, Liu Y, Li X, Wu X, Li B. Ru@Carbon Nanotube Composite Microsponge: Fabrication in Supercritical CO2 for Hydrogenation of p-Chloronitrobenzene. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030539
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Xianghong, Hui Liu, Xingxing Ding, Yanyan Liu, Xingsheng Li, Xianli Wu, and Baojun Li. 2022. "Ru@Carbon Nanotube Composite Microsponge: Fabrication in Supercritical CO2 for Hydrogenation of p-Chloronitrobenzene" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030539
APA StyleGe, X., Liu, H., Ding, X., Liu, Y., Li, X., Wu, X., & Li, B. (2022). Ru@Carbon Nanotube Composite Microsponge: Fabrication in Supercritical CO2 for Hydrogenation of p-Chloronitrobenzene. Nanomaterials, 12(3), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030539