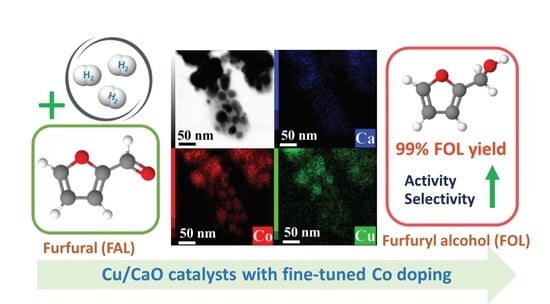
Effect of Co-Doping on Cu/CaO Catalysts for Selective Furfural Hydrogenation into Furfuryl Alcohol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Catalyst Preparation
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.3. Evolution of Catalytic Performance for FAL Hydrogenation to FOL
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fine-Tuning the Activities of Cu/CaO Catalysts by Co-Doping for FAL Hydrogenation to FOL
3.2. Physical and Chemical Properties of the Catalysts
3.2.1. Elemental Composition and Textural Properties of the Catalysts
3.2.2. Reducibility of the Catalysts
3.2.3. Structural Properties of the Catalysts
3.2.4. Acidity and Basicity of the Catalysts
3.2.5. Morphology of the Catalysts
3.3. Optimization of FAL Hydrogenation to FOL over the Co1.40Cu1/CaO Catalyst
3.4. Reusability Experiment of the Co1.40Cu1/CaO Catalyst
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khemthong, P.; Yimsukanan, C.; Narkkun, T.; Srifa, A.; Witoon, T.; Pongchaiphol, S.; Kiatphuengporn, S.; Faungnawakij, K. Advances in catalytic production of value-added biochemicals and biofuels via furfural platform derived lignocellulosic biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 148, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srifa, A.; Chaiwat, W.; Pitakjakpipop, P.; Anutrasakda, W.; Faungnawakij, K. Chapter 6—Advances in bio-oil production and upgrading technologies. In Sustainable Bioenergy; Rai, M., Ingle, A.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 167–198. [Google Scholar]
- Chuseang, J.; Nakwachara, R.; Kalong, M.; Ratchahat, S.; Koo-amornpattana, W.; Klysubun, W.; Khemthong, P.; Faungnawakij, K.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Itthibenchapong, V.; et al. Selective hydrogenolysis of furfural into fuel-additive 2-methylfuran over a rhenium-promoted copper catalyst. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangkoch, S.; Boonkum, S.; Ratchahat, S.; Koo-Amornpattana, W.; Eiad-Ua, A.; Kiatkittipong, W.; Klysubun, W.; Srifa, A.; Faungnawakij, K.; Assabumrungrat, S. Solvent-Free Hydrodeoxygenation of Triglycerides to Diesel-like Hydrocarbons over Pt-Decorated MoO2 Catalysts. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6956–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Tang, X.; He, L.; Peng, L. Selective Hydrogenation of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)furan over a Cheap Carbon-Nanosheets-Supported Zr/Ca Bimetallic Catalyst. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 8432–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaola, Y.; Leangsiri, W.; Pongsiriyakul, K.; Kiatkittipong, W.; Srifa, A.; Lim, J.W.; Reubroycharoen, P.; Kiatkittipong, K.; Eiad-ua, A.; Assabumrungrat, S. Catalytic Hydrotreating of Crude Pongamia pinnata Oil to Bio-Hydrogenated Diesel over Sulfided NiMo Catalyst. Energies 2022, 15, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratchahat, S.; Srifa, A.; Koo-amornpattana, W.; Sakdaronnarong, C.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Wu, K.C.W.; Show, P.-L.; Kodama, S.; Tanthapanichakoon, W.; Sekiguchi, H. Syngas production with low tar content from cellulose pyrolysis in molten salt combined with Ni/Al2O3 catalyst. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 158, 105243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhao, M.; Feng, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Zha, M.; Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. PO43− Coordinated Robust Single-Atom Platinum Catalyst for Selective Polyol Oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, e202116059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Luo, S.; Guo, R.; Xu, D. Synthesis of Furanic Ethers from Furfuryl Alcohol for Biofuel Production. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 12725–12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, H.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Xia, C. Selective hydrogenolysis of furfuryl alcohol to 1,5- and 1,2-pentanediol over Cu-LaCoO3 catalysts with balanced Cu0-CoO sites. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Brentzel, Z.J.; Barnett, K.J.; Dumesic, J.A.; Huber, G.W.; Maravelias, C.T. Conversion of Furfural to 1,5-Pentanediol: Process Synthesis and Analysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4699–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Cui, Y.-T.; Lang, R.; Li, L.; Su, Y.; Miao, S.; Sun, H.; et al. Catalytic cascade conversion of furfural to 1,4-pentanediol in a single reactor. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Amada, Y.; Tamura, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tomishige, K. One-pot selective conversion of furfural into 1,5-pentanediol over a Pd-added Ir–ReOx/SiO2 bifunctional catalyst. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, M.Y.; Lee, M.S. Effect of carboxylate stabilizers on the performance of Pt/C catalysts for furfural hydrogenation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, J.; Rapado, P.; Faba, L.; Díaz, E.; Ordóñez, S. From biomass to diesel additives: Hydrogenation of cyclopentanone-furfural aldol condensation adducts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Hao, F.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Xiong, W.; Luo, H. MOF-derived well-structured bimetallic catalyst for highly selective conversion of furfural. Fuel 2021, 289, 119910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.-G.; Hu, T.-L. Incorporation of Active Metal Species in Crystalline Porous Materials for Highly Efficient Synergetic Catalysis. Small 2021, 17, 2003971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pei, Y.; Maligal-Ganesh, R.V.; Li, X.; Cruz, A.; Spurling, R.J.; Chen, M.; Yu, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, W. Influence of Sn on Stability and Selectivity of Pt–Sn@UiO-66-NH2 in Furfural Hydrogenation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 17495–17501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Luo, J.; Liang, C. Construction of Cu-M-Ox (M = Zn or Al) Interface in Cu Catalysts for Hydrogenation Rearrangement of Furfural. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 16939–16950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalong, M.; Srifa, A.; Hongmanorom, P.; Cholsuk, C.; Klysubun, W.; Ratchahat, S.; Koo-amornpattana, W.; Khemthong, P.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Kawi, S. Catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol and 2-methylfuran over CuFe catalysts: Ex situ observation of simultaneous structural phase transformation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 231, 107256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fan, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhuang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Z. Selective Hydrogenation of Furfural over the Co-Based Catalyst: A Subtle Synergy with Ni and Zn Dopants. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 8507–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, T.W.; Tsung, C.-K.; Huang, W. Spectroscopy Identification of the Bimetallic Surface of Metal–Organic Framework-Confined Pt–Sn Nanoclusters with Enhanced Chemoselectivity in Furfural Hydrogenation. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 23254–23260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Peng, F.; Huang, Q.; Xiong, L.; Huang, C.; Ouyang, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Selective Hydrogenation of Furfural to Furfuryl Alcohol over Acid-Activated Attapulgite-Supported NiCoB Amorphous Alloy Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Z.; Weng, M.; Zhou, W.; Fan, H.; Fu, J. Facile Preparation of Oxygen-Vacancy-Mediated Mn3O4 for Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Furfural. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 9706–9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolek, W.; Nanthasanti, N.; Pongthawornsakun, B.; Praserthdam, P.; Panpranot, J. Effects of TiO2 structure and Co addition as a second metal on Ru-based catalysts supported on TiO2 for selective hydrogenation of furfural to FA. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Guo, X.; Mu, X. Highly selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over Pt nanoparticles supported on g-C3N4 nanosheets catalysts in water. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitthisa, S.; An, W.; Resasco, D.E. Selective conversion of furfural to methylfuran over silica-supported NiFe bimetallic catalysts. J. Catal. 2011, 284, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, M.G.; Mahalakshmy, R.; Krishnamurthy, K.R.; Viswanathan, B. Studies on Ni–M (M=Cu, Ag, Au) bimetallic catalysts for selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde. Catal. Today 2016, 263, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lin, W.; Song, W.; Li, S. High efficient conversion of furfural to 2-methylfuran over Ni-Cu/Al2O3 catalyst with formic acid as a hydrogen donor. Appl. Catal. A 2017, 547, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Yan, P.; Li, K.; Yang, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Zhou, S. Hollow Mesoporous Nanoreactors with Encaged PtSn Alloy Nanoparticles for Selective Hydrogenation of Furfural to Furfuryl Alcohol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 6078–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Lin, L.; Qi, H.; Chen, R.; Wu, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, T.; Luo, W. Zeolite-Encapsulated Cu Nanoparticles for the Selective Hydrogenation of Furfural to Furfuryl Alcohol. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 10246–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wojcieszak, R.; Dumeignil, F.; Marceau, E.; Royer, S. How Catalysts and Experimental Conditions Determine the Selective Hydroconversion of Furfural and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11023–11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutchings, G.S.; Luc, W.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Vlachos, D.G.; Jiao, F. Nanoporous Cu–Al–Co Alloys for Selective Furfural Hydrodeoxygenation to 2-Methylfuran. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 3866–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qiu, M.; Yang, J.; Shen, F.; Wang, X.; Qi, X. One-pot self-assembly synthesis of Ni-doped ordered mesoporous carbon for quantitative hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.-D. Engineering Bimetallic Centers in Porous Metal Silicate Materials for Hydrogenation of Furfural at Lower Temperature. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Huy, C.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Kwak, J.H.; An, K. Mesoporous mixed CuCo oxides as robust catalysts for liquid-phase furfural hydrogenation. Appl. Catal. A 2019, 571, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Sheng, M.; Nakata, A.; Nakajima, K.; Yamazoe, S.; Yamasaki, J.; Yamaguchi, S.; Mizugaki, T.; Mitsudome, T. Air-Stable and Reusable Cobalt Phosphide Nanoalloy Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Furfural Derivatives. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, D. Aqueous phase catalytic hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over in-situ synthesized Cu–Zn/SiO2 catalysts. Mater. Chem. Phy. 2021, 260, 124152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongratkaew, S.; Luadthong, C.; Kiatphuengporn, S.; Khemthong, P.; Hirunsit, P.; Faungnawakij, K. Cu-Al spinel-oxide catalysts for selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Catal. Today 2021, 367, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Ma, L. In Situ Synthesis of Cu Nanoparticles on Carbon for Highly Selective Hydrogenation of Furfural to Furfuryl Alcohol by Using Pomelo Peel as the Carbon Source. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12944–12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Huy, C.; Lee, J.; Seo, J.H.; Yang, E.; Lee, J.; Choi, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.S.; Joo, S.H.; et al. Structure-dependent catalytic properties of mesoporous cobalt oxides in furfural hydrogenation. Appl. Catal. A 2019, 583, 117125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-F.; Shen, Y.; Cui, W.-G.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, T.-L. MOF derived non-noble metal catalysts to control the distribution of furfural selective hydrogenation products. Mol. Catal. 2021, 513, 111824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, P.; Seelam, P.K.; Balaga, R.; Rajesh, R.; Perupogu, V.; Liang, T.X. Immobilized highly dispersed Ni nanoparticles over porous carbon as an efficient catalyst for selective hydrogenation of furfural and levulinic acid. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Gómez, C.P.; Cecilia, J.A.; García-Sancho, C.; Moreno-Tost, R.; Maireles-Torres, P. Gas phase hydrogenation of furfural to obtain valuable products using commercial Cr-free catalysts as an environmentally sustainable alternative to copper chromite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, Z.; Li, Q.; Feng, X.; Song, Z.; Cai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, D.; et al. Reversing Titanium Oligomer Formation towards High-Efficiency and Green Synthesis of Titanium-Containing Molecular Sieves. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3443–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Jadeja, G.C.; Parikh, J. A versatile bi-metallic copper–cobalt catalyst for liquid phase hydrogenation of furfural to 2-methylfuran. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, L.; Xiao, G. Metal-organic frameworks derived bimetallic Cu-Co catalyst for efficient and selective hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Mol. Catal. 2017, 436, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalong, M.; Hongmanorom, P.; Ratchahat, S.; Koo-amornpattana, W.; Faungnawakij, K.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Srifa, A.; Kawi, S. Hydrogen-free hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol and 2-methylfuran over Ni and Co-promoted Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 214, 106721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyngazova, M.S.; Grazia, L.; Lolli, A.; Innocenti, G.; Tabanelli, T.; Mella, M.; Albonetti, S.; Cavani, F. Mechanistic insights into the catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural with methanol and alkaline earth oxides. J. Catal. 2019, 372, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafriz, R.S.R.M.; Shafizah, I.N.; Arifin, N.A.; Salmiaton, A.; Yunus, R.; Yap, Y.H.T.; Shamsuddin, A.H. Effect of Ni/Malaysian dolomite catalyst synthesis technique on deoxygenation reaction activity of waste cooking oil. Renew. Energy 2021, 178, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azri, N.; Ramli, I.; Nda-Umar, U.I.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Saiman, M.I.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Copper-dolomite as effective catalyst for glycerol hydrogenolysis to 1,2-propanediol. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 112, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, X. Synergistic effect for selective hydrodeoxygenation of anisole over Cu-ReOx/SiO2. Catal. Today 2021, 365, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Mou, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, C.; Zhu, H.; Lin, R.; et al. Bifunctional rhenium–copper nanostructures for intensified and stable ethanol synthesis via hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 3175–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, N.; García, R.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Wheeler, C.; Austin, R.N.; Gallagher, J.R.; Miller, J.T.; Krause, T.R.; Escalona, N.; Sepúlveda, C. Effect of Cu addition as a promoter on Re/SiO2 catalysts in the hydrodeoxygenation of 2-methoxyphenol as a model bio oil compound. Fuel 2016, 186, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.J.; Park, G.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jun, K.-W.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.T.; Kwak, G. Higher alcohol synthesis from syngas over xerogel-derived Co-Cu-Al2O3 catalyst with an enhanced metal proximity. Mol. Catal. 2019, 475, 110481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastella, M.A.; Gislon, E.S.; Pelisser, F.; Ricken, C.; Silva, L.d.; Angioletto, E.; Montedo, O.R.K. Mechanical and toxicological evaluation of concrete artifacts containing waste foundry sand. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.; Liu, L.; Yang, G.; Cai, W.; Long, J.; Yu, H. Mg-promoted Ni-CaO microsphere as bi-functional catalyst for hydrogen production from sorption-enhanced steam reforming of glycerol. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Shen, B.; Shi, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, C. Dual functional catalytic materials of Ni over Ce-modified CaO sorbents for integrated CO2 capture and conversion. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 244, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naeem, M.A.; Armutlulu, A.; Imtiaz, Q.; Donat, F.; Schäublin, R.; Kierzkowska, A.; Müller, C.R. Optimization of the structural characteristics of CaO and its effective stabilization yield high-capacity CO2 sorbents. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Yang, H.; Gao, P.; Li, X.; Zhong, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. Direct conversion of CO2 to long-chain hydrocarbon fuels over K–promoted CoCu/TiO2 catalysts. Catal. Today 2018, 311, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Hu, Z.; Duan, W.; Cheng, F.; Chen, J. Porous CuO nanowires as the anode of rechargeable Na-ion batteries. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srifa, A.; Viriya-empikul, N.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Faungnawakij, K. Catalytic behaviors of Ni/γ-Al2O3 and Co/γ-Al2O3 during the hydrodeoxygenation of palm oil. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 3693–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, G.; Chen, T.; Zeng, Z.; Guo, S.; Lv, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X. Bimetallic CoCu catalyst derived from in-situ grown Cu-ZIF-67 encapsulated inside KIT-6 for higher alcohol synthesis from syngas. Fuel 2020, 278, 118292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Yao, D.; Fan, S.; Guo, S.; Lv, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X. High-Performance CoCu Catalyst Encapsulated in KIT-6 for Higher Alcohol Synthesis from Syngas. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, K.B. Mass transfer enhanced CaO pellets for CO2 sorption: Utilization of CO2 emitted from CaCO3 pellets during calcination. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.S.; Garcia, L.C.F.; Assaf, J.M. The enhanced activity of Ca/MgAl mixed oxide for transesterification. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 125, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.-H.; Li, N.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.-T.; Liu, Z.-T. Selective hydrogenation of quinolines over a CoCu bimetallic catalyst at low temperature. Mol. Catal. 2019, 470, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Core–shell Cu@(CuCo-alloy)/Al2O3 catalysts for the synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chernavskii, P.A.; Khodakov, A.Y.; Wang, Y. Structure and catalytic performance of alumina-supported copper–cobalt catalysts for carbon monoxide hydrogenation. J. Catal. 2012, 286, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, D.; Liu, D.; Xu, X.-C.; Shi, B.; Wang, X.; Si, R.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Higher alcohols synthesis from syngas over CoCu/SiO2 catalysts: Dynamic structure and the role of Cu. J. Catal. 2016, 336, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Tao, Y.; Ling, H.; Chen, Z.; Ding, J.; Zeng, X.; Liao, X.; Stampfl, C.; Huang, J. Cooperation of Ni and CaO at Interface for CO2 Reforming of CH4: A Combined Theoretical and Experimental Study. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10060–10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamoori, A.; Lawson, S.; Rownaghi, A.A.; Rezaei, F. Improving Adsorptive Performance of CaO for High-Temperature CO2 Capture through Fe and Ga Doping. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yu, H.; Dong, F.; Zhu, B.; Huang, W.; Zhang, S. High efficiency and stability of Au–Cu/hydroxyapatite catalyst for the oxidation of carbon monoxide. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 45420–45431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Tian, X.; Garg, S.; Rufford, T.E.; Zhao, P.; Wu, Y.; Yago, A.J.; Ge, L.; Rudolph, V.; Wang, G. Modulated Sn Oxidation States over a Cu2O-Derived Substrate for Selective Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 22760–22770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewangan, N.; Ashok, J.; Sethia, M.; Das, S.; Pati, S.; Kus, H.; Kawi, S. Cobalt-Based Catalyst Supported on Different Morphologies of Alumina for Non-oxidative Propane Dehydrogenation: Effect of Metal Support Interaction and Lewis Acidic Sites. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 4923–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaniš, G.; Fele Žilnik, L.; Likozar, B.; Grilc, M. Hydrogen solubility in bio-based furfural and furfuryl alcohol at elevated temperatures and pressures relevant for hydrodeoxygenation. Fuel 2021, 290, 120021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhuang, C.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zou, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhu, G. Efficient single-atom Ni for catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Entry | Catalyst | FAL Conversion (%) | FOL Yield <break/>(%) | FOL Selectivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cu/CaO | 38.0 ± 1.3 | 38.0 ± 1.3 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| 2 | Co0.49Cu1/CaO | 74.2 ± 4.1 | 74.2 ± 4.1 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| 3 | Co0.96Cu1/CaO | 91.8 ± 2.6 | 89.4 ± 3.4 | 97.3 ± 1.0 |
| 4 | Co1.40Cu1/CaO | 100 | >99 | >99 |
| 5 | Co1.94Cu1/CaO | 100 | >99 | >99 |
| 6 | Co/CaO | 9.5 ± 2.1 | 9.4 ± 1.9 | 98.7 ± 1.6 |
| 7 b | Bulk Co1.40Cu1 | 33.5 ± 3.3 | 33.3± 3.4 | 99.5 ± 0.4 |
| 8 c | Bare CaO | 1.6 ± 0.0 | 1.6 ± 0.0 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| 9 d | Bulk Co1.40Cu1 + bare CaO | 15.7 ± 0.9 | 15.7 ± 0.9 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Mass Ratio of FAL to Catalyst | Solvent | T | Time | P | FAL Conversion | FOL Yield | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| °C | h | bar | % | % | |||||
| 1 | NiCoZn@CN-600 a | 9.6 | THF | 160 | 4 | 20 | 100 | 99 | [21] |
| 2 | Ni0.5@OMC-600 b | 2.9 | 1-Propanol | 180 | 4 | 30 | 99 | 98 | [34] |
| 3 | PMS-2-CuCo c | 9.6 | Methanol | 110 | 1 | 10 | 99 | 98 | [35] |
| 4 | Cu1Co5 d | 100 | 2-Propanol | 180 | 5 | 10 | 100 | 38.1 | [36] |
| 5 | CuCo0.4/C-873 | 12.9 | Ethanol | 140 | N/A | 30 | 98.7 | 96.4 | [47] |
| 6 | Cu–Co/γ-Al2O3 | 4.3 | 2-Propanol | 200 | 4 | 40 | 98.8 | 25.3 | [46] |
| 7 | Nano-Co2P/Al2O3 | – | Methanol | 130 | 2 | 40 | 85 | 84.2 | [37] |
| 8 | Na−Cu@TS-1 e | 1 | 2-Propanol | 110 | 2 | 10 | 93 | 91.2 | [31] |
| 9 | Cu2Zn/SiO2 | 7.7 | H2O | 120 | 4 | 25 | 81.9 | 77.6 | [38] |
| 10 | CuAl2O4 | – | 2-Propanol | 170 | 1 | 30 | 100 | >95 | [39] |
| 11 | Cu/C | 6 | 2-Propanol | 170 | 3 | 20 | 99.6 | 98.9 | [40] |
| 12 | m-Co3O4(p6 mm)-350 f | 50 | 2-Propanol | 180 | 3 | 20 | 100 | 65 | [41] |
| 13 | ZnCo-US@NC-700 g | 0.48 | Ethanol | 120 | 4 | 20 | 100 | 91.5 | [42] |
| 14 | Co1.40Cu1/CaO | 3.3 | 2-Propanol | 100 | 4 | 20 | 100 | 98.9 | This work |
| 15 | Co1.40Cu1/CaO | 5 | 2-Propanol | 120 | 2 | 20 | 100 | >99 | This work |
| Sample | Elemental Composition (%) a | SBET b | Vp c | Dp d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Cu | Ca | Si | Mg | O | (m2 g–1) | (cm3 g–1) | (nm) | |
| Cu/CaO | – | 28.5 | 40.0 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 28.0 | 3 | 0.031 | 59.0 |
| Co0.49Cu1/CaO | 5.4 | 12.0 | 47.3 | 3.7 | 0.6 | 31.0 | 6 | 0.048 | 44.1 |
| Co0.96Cu1/CaO | 10.7 | 12.0 | 42.4 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 30.9 | 6 | 0.059 | 44.1 |
| Co1.40Cu1/CaO | 15.3 | 11.8 | 38.8 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 30.9 | 10 | 0.096 | 37.9 |
| Co1.94Cu1/CaO | 19.8 | 11.0 | 35.5 | 2.3 | 0.5 | 30.9 | 7 | 0.068 | 37.9 |
| Co/CaO | 25.2 | – | 39.0 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 32.7 | 6 | 0.045 | 51.1 |
| CaO | – | – | 62.2 | 4.1 | 1.1 | 32.6 | 7 | 0.097 | 143.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalong, M.; Ratchahat, S.; Khemthong, P.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Srifa, A. Effect of Co-Doping on Cu/CaO Catalysts for Selective Furfural Hydrogenation into Furfuryl Alcohol. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091578
Kalong M, Ratchahat S, Khemthong P, Assabumrungrat S, Srifa A. Effect of Co-Doping on Cu/CaO Catalysts for Selective Furfural Hydrogenation into Furfuryl Alcohol. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(9):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091578
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalong, Munsuree, Sakhon Ratchahat, Pongtanawat Khemthong, Suttichai Assabumrungrat, and Atthapon Srifa. 2022. "Effect of Co-Doping on Cu/CaO Catalysts for Selective Furfural Hydrogenation into Furfuryl Alcohol" Nanomaterials 12, no. 9: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091578
APA StyleKalong, M., Ratchahat, S., Khemthong, P., Assabumrungrat, S., & Srifa, A. (2022). Effect of Co-Doping on Cu/CaO Catalysts for Selective Furfural Hydrogenation into Furfuryl Alcohol. Nanomaterials, 12(9), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091578