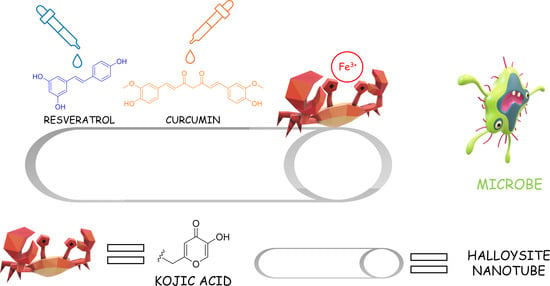
Total Bio-Based Material for Drug Delivery and Iron Chelation to Fight Cancer through Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of HNTs
2.2.1. Synthesis of Chlorokojic Acid (2)
2.2.2. Synthesis of HNTs/Kojic Acid Derivative
2.3. IR and UV–vis
2.4. Resveratrol and Curcumin Uptake
2.5. ICP/MS
2.6. SEM, EDX, and TGA
2.7. Antibacterial Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Drug Loading and Release
3.3. Microbiological Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.; Yang, Y.; Pan Bei, H.; Tang, C.-Y.; Zhao, X. Antibacterial nanosystems for cancer therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 6814–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y. The effect of periodontal bacteria infection on incidence and prognosis of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e19698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, V.C.; Patel, S.K.S.; Cho, B.-K.; Wood, T.K.; Lee, J.-K. Emerging applications of bacteria as antitumor agents. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadegarynia, D.; Tarrand, J.; Raad, I.; Rolston, K. Current spectrum of bacterial infections in patients with cancer. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 1144–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, D.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Mendonça, A.G.; Correia, I.J. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascelles, B.D.; Dernell, W.S.; Correa, M.T.; Lafferty, M.; Devitt, C.M.; Kuntz, C.A.; Straw, R.C.; Withrow, S.J. Improved survival associated with postoperative wound infection in dogs treated with limb-salvage surgery for osteosarcoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2005, 12, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Sarkar, A. Review on Multiple Facets of Drug Resistance: A Rising Challenge in the 21st Century. J. Xenobiot. 2021, 11, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repac Antić, D.; Parčina, M.; Gobin, I.; Petković Didović, M. Chelation in Antibacterial Drugs: From Nitroxoline to Cefiderocol and Beyond. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, N.K.; Teng, C.; Frei, C.R. Brief Overview of Approaches and Challenges in New Antibiotic Development: A Focus On Drug Repurposing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 684515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.L.; Sodre, C.L.; Valle, R.S.; Silva, B.A.; Abi-Chacra, E.A.; Silva, L.V.; Souza-Goncalves, A.L.; Sangenito, L.S.; Goncalves, D.S.; Souza, L.O.; et al. Antimicrobial action of chelating agents: Repercussions on the microorganism development, virulence and pathogenesis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2715–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, S.; Kim, C.J.; Dutta, D.; Salifu, M.; Lim, S.H. Antimicrobial therapy during cancer treatment: Beyond antibacterial effects. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Lim, C.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Lin, T.-W.; Muir, B.W.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Shen, H.-H. Recent Advances in the Development of Lipid-, Metal-, Carbon-, and Polymer-Based Nanomaterials for Antibacterial Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yougbaré, S.; Mutalik, C.; Okoro, G.; Lin, I.H.; Krisnawati, D.I.; Jazidie, A.; Nuh, M.; Chang, C.C.; Kuo, T.R. Emerging Trends in Nanomaterials for Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5831–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Floresta, G.; Abbate, V. Recent progress in the imaging of c-Met aberrant cancers with positron emission tomography. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1588–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floresta, G.; Memdouh, S.; Pham, T.; Ma, M.T.; Blower, P.J.; Hider, R.C.; Abbate, V.; Cilibrizzi, A. Targeting integrin αvβ6 with gallium-68 tris (hydroxypyridinone) based PET probes. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 12796–12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failla, M.; Floresta, G.; Abbate, V. Peptide-based positron emission tomography probes: Current strategies for synthesis and radiolabelling. RSC Med. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floresta, G.; Keeling, G.P.; Memdouh, S.; Meszaros, L.K.; de Rosales, R.T.M.; Abbate, V. NHS-Functionalized THP Derivative for Efficient Synthesis of Kit-Based Precursors for 68Ga Labeled PET Probes. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilibrizzi, A.; Pourzand, C.; Abbate, V.; Reelfs, O.; Versari, L.; Floresta, G.; Hider, R. The synthesis and properties of mitochondrial targeted iron chelators. Biometals 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, S.; Cui, P.; Hu, H.; Ni, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, J. Hydrogels for Antitumor and Antibacterial Therapy. Gels 2022, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagni, C.; Coco, A.; Patamia, V.; Floresta, G.; Curcuruto, G.; Mangano, K.; Mecca, T.; Rescifina, A.; Carroccio, S. Cyclodextrin-Based Cryogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. Med. Sci. Forum 2022, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagni, C.; Dattilo, S.; Mecca, T.; Gugliuzzo, C.; Scamporrino, A.A.; Privitera, V.; Puglisi, R.; Carola Carroccio, S. Single and dual polymeric sponges for emerging pollutants removal. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 179, 111556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagni, C.; Scamporrino, A.A.; Riccobene, P.M.; Floresta, G.; Patamia, V.; Rescifina, A.; Carroccio, S.C. Portable Nanocomposite System for Wound Healing in Space. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, R.R.; Gaber, B.P.; Lvov, Y. In-vitro release characteristics of tetracycline HCl, khellin and nicotinamide adenine dineculeotide from halloysite; a cylindrical mineral. J. Microencapsul. 2001, 18, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.M.; Shchukin, D.G.; Möhwald, H.; Price, R.R. Halloysite clay nanotubes for controlled release of protective agents. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, M.; Abdouss, M.; Shojaei, S. Nanocontainers for drug delivery systems: A review of Halloysite nanotubes and their properties. Int. J. Artif. Organs. 2021, 44, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Singh, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Fuloria, N.K. Smart carbon nanotubes for drug delivery system: A comprehensive study. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddeci, G.; Spinelli, G.; Colomba, P.; Di Blasi, F. Nanomaterials: A Review about Halloysite Nanotubes, Properties, and Application in the Biological Field. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, V.; Lvov, Y.M.; Leporatti, S. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Resveratrol Delivery to Cancer Cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Tommonaro, G. Curcumin and Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brisdelli, F.; D’Andrea, G.; Bozzi, A. Resveratrol: A natural polyphenol with multiple chemopreventive properties. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant properties of resveratrol: A structure–activity insight. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Luo, W.; Quinn, P.J.; Liu, Z.; Hider, R.C. Design, Synthesis, Physicochemical Properties, and Evaluation of Novel Iron Chelators with Fluorescent Sensors. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6349–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patamia, V.; Fiorenza, R.; Brullo, I.; Zambito Marsala, M.; Balsamo, S.A.; Distefano, A.; Furneri, P.M.; Barbera, V.; Scirè, S.; Rescifina, A. A sustainable porous composite material based on loofah-halloysite for gas adsorption and drug delivery. Mater. Chem. Front. 2022, 6, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisi, C.; Hanafy, N.; Nobile, C.; Giorgi, M.L.D.; Rinaldi, R.; Casciaro, S.; Lvov, Y.M.; Leporatti, S. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes as Carriers for Curcumin: Characterization and Application. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2016, 15, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. M100: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 32nd. ed.; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard, M.; Ingmer, H. Antibacterial and antifungal properties of resveratrol. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Hassandarvish, P.; Tajik, H.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 186864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munir, Z.; Banche, G.; Cavallo, L.; Mandras, N.; Roana, J.; Pertusio, R.; Ficiarà, E.; Cavalli, R.; Guiot, C. Exploitation of the Antibacterial Properties of Photoactivated Curcumin as ‘Green’ Tool for Food Preservation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patamia, V.; Tomarchio, R.; Fiorenza, R.; Zagni, C.; Scirè, S.; Floresta, G.; Rescifina, A. Carbamoyl-Decorated Cyclodextrins for Carbon Dioxide Adsorption. Catalysts 2023, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharfar, R.; Alinezhad, H.; Azimi, R. Use of DABCO-functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 as catalyst for efficient synthesis of kojic acid derivatives, potential antioxidants. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 8637–8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.F.; Lima, G.d.S.; Gastelois, P.L.; Assis Gomes, D.; Macedo, W.A.d.A.; de Sousa, E.M.B. Surface modification and biological evaluation of kojic acid/silica nanoparticles as platforms for biomedical systems. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2020, 17, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, Z.; Kent, M.; Freeman, C.; Landge, S.; Koricho, E. Halloysite nanotubes functionalized with epoxy and thiol organosilane groups to improve fracture toughness in nanocomposites. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cai, C.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Han, J. Drug-binding albumins forming stabilized nanoparticles for co-delivery of paclitaxel and resveratrol: In vitro/in vivo evaluation and binding properties investigation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chang, Y.; Yang, J.; You, Y.; He, R.; Chen, T.; Zhou, C. Functionalized halloysite nanotube by chitosan grafting for drug delivery of curcumin to achieve enhanced anticancer efficacy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.M.; Kumar, A.; Suneetha, M.; Han, S.S. pH and near-infrared active; chitosan-coated halloysite nanotubes loaded with curcumin-Au hybrid nanoparticles for cancer drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanphai, P.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Encapsulation of micronutrients resveratrol, genistein, and curcumin by folic acid-PAMAM nanoparticles. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 449, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokh, A.; Pourmadadi, M.; Rashedi, H.; Yazdian, F.; Navaei-Nigjeh, M. Assessment of synthesized chitosan/halloysite nanocarrier modified by carbon nanotube for pH-sensitive delivery of curcumin to cancerous media. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 237, 123937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyankson, E.; Awuzah, D.; Tiburu, E.K.; Efavi, J.K.; Agyei-Tuffour, B.; Paemka, L. Curcumin loaded Ag–TiO2-halloysite nanotubes platform for combined chemo-photodynamic therapy treatment of cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 33108–33123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Juneja, S.; Ghosal, A.; Bandara, N.; Khan, R.; Wallen, S.L.; Ramakrishna, S.; Kaushik, A. Antibacterial and antiviral high-performance nanosystems to mitigate new SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 21, 100363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermini, M.L.; Voliani, V. Antimicrobial Nano-Agents: The Copper Age. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6008–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Element Symbol | Atomic Conc. % | Weight Conc. % |
|---|---|---|
| O | 45.27 | 45.06 |
| C | 40.70 | 30.41 |
| Al | 6.76 | 11.35 |
| Si | 6.22 | 10.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patamia, V.; Zagni, C.; Fiorenza, R.; Fuochi, V.; Dattilo, S.; Riccobene, P.M.; Furneri, P.M.; Floresta, G.; Rescifina, A. Total Bio-Based Material for Drug Delivery and Iron Chelation to Fight Cancer through Antimicrobial Activity. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142036
Patamia V, Zagni C, Fiorenza R, Fuochi V, Dattilo S, Riccobene PM, Furneri PM, Floresta G, Rescifina A. Total Bio-Based Material for Drug Delivery and Iron Chelation to Fight Cancer through Antimicrobial Activity. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(14):2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142036
Chicago/Turabian StylePatamia, Vincenzo, Chiara Zagni, Roberto Fiorenza, Virginia Fuochi, Sandro Dattilo, Paolo Maria Riccobene, Pio Maria Furneri, Giuseppe Floresta, and Antonio Rescifina. 2023. "Total Bio-Based Material for Drug Delivery and Iron Chelation to Fight Cancer through Antimicrobial Activity" Nanomaterials 13, no. 14: 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142036
APA StylePatamia, V., Zagni, C., Fiorenza, R., Fuochi, V., Dattilo, S., Riccobene, P. M., Furneri, P. M., Floresta, G., & Rescifina, A. (2023). Total Bio-Based Material for Drug Delivery and Iron Chelation to Fight Cancer through Antimicrobial Activity. Nanomaterials, 13(14), 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142036