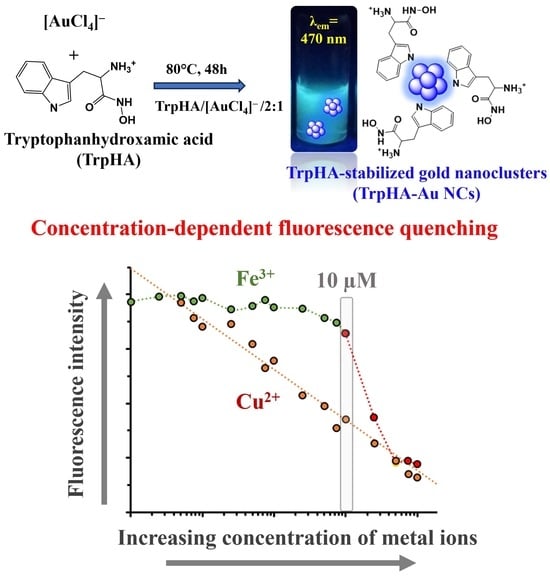
Tryptophanhydroxamic Acid-Stabilized Ultrasmall Gold Nanoclusters: Tuning the Selectivity for Metal Ion Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of TrpHA
2.3. Synthesis of TrpHA-Directed Au NCs
2.4. Instruments for Characterization
2.5. Interactions between TrpHA-Au NCs with Mono-, Di- and Trivalent Metal Ions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Preparation Protocol
3.2. Structural and Optical Features of the Fluorescent NCs
3.3. Interaction of the NCs with Different Metal Ions
3.4. Proposed Mechanism for Interaction of TrpHA-Au NCs with Cu2+
3.5. Proposed Mechanism for Interaction of TrpHA-Au NCs with Fe3+
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sardar, R.; Funston, A.M.; Mulvaney, P.; Murray, R.W. Gold Nanoparticles: Past, Present, and Future†. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13840–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Dong, S.; Nienhaus, G.U. Ultra-small fluorescent metal nanoclusters: Synthesis and biological applications. Nano Today 2011, 6, 6401–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R. Quantum sized, thiolate-protected gold nanoclusters. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liang, Y.; Jin, L.; Shi, J.; Shang, L. Weak Interaction-Tailored Catalytic Interface of Ultrasmall Gold Nanoclusters as Enzyme Mimics for Enhanced Colorimetric Biosensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 13, 58209–58219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Wang, C.W.; Yuan, Z.; Chang, H.T. Fluorescent gold nanoclusters: Recent advances in sensing and imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Xia, F.; Alfranca, G.; Yan, H.; Zhi, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhang, C.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Cui, D. Nanoparticles for multi-modality cancer diagnosis: Simple protocol for self-assembly of gold nanoclusters mediated by gadolinium ions. Biomaterials 2017, 120, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharov, V.P.; Galitovskaya, E.N.; Johnson, C.; Kelly, T. Photothermal nanotherapeutics and nanodiagnostics for selective killing of bacteria targeted with gold nanoparticles. Lasers Surg. Med. 2005, 37, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, D.M. Properties and applications of protein-stabilized fluorescent gold nanoclusters: Short review. J. Nanophotonics 2012, 6, 064504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungor, D.; Horváth, K.; Dékány, I.; Csapó, E. Red-emitting gold nanoclusters for rapid fluorescence sensing of tryptophan metabolites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.D.; Cong, V.T.; Baek, C.; Min, J. Fabrication of peptide stabilized fluorescent gold nanocluster/graphene oxide nanocomplex and its application in turn-on detection of metalloproteinase-9. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csapó, E.; Ungor, D.; Juhász, Á.; Tóth, G.K.; Dékány, I. Gold nanohybrid systems with tunable fluorescent feature: Interaction of cysteine and cysteine-containing peptides with gold in two- and three-dimensional systems. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 511, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csapó, E.; Ungor, D.; Kele, Z.; Baranyai, P.; Deák, A.; Juhász, Á.; Janovák, L.; Dékány, I. Influence of pH and aurate/amino acid ratios on the tuneable optical features of gold nanoparticles and nanoclusters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 532, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungor, D.; Dékány, I.; Csapó, E. Reduction of tetrachloroaurate (III) ions with bioligands: Role of the thiol and amine functional groups on the structure and optical features of gold nanohybrid systems. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; El-sayed, W.A.; El-manawaty, M.A.; Gassoumi, M.; Ali, R. Microwave-Assisted Rapid Synthesis of Luminescent Tryptophan-Stabilized Silver Nanoclusters for Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Fe(III), and Their Application in a Test Strip. Biosensors 2022, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiao, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Qi, L.J. Ligand-modulated synthesis of gold nanoclusters for sensitive and selective detection of folic acid. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Cai, Z. Gold Nanoclusters as a Fluorescent Probe for the Sensitive Determination of Morin and Sensing of Temperature. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202203005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swathy, S.; Pallam, G.S.; Kumar, K.G. Tryptophan capped gold–silver bimetallic nanoclusters-based turn-off fluorescence sensor for the determination of histamine. Talanta 2023, 256, 124321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardar, Z.S.; Shemirani, F.; Zadmard, R. Determination of iron(II) and iron(III) via static quenching of the fluorescence of tryptophan-protected copper nanoclusters. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, G.; Shi, H.; Yang, M.; Tan, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, W. A fluorescent probe based on tryptophan-coated silver nanoclusters for copper (II) ions detection and bioimaging in cells. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yin, H.; Li, Y.; Bi, F.; Gan, F. One–step synthesis of L-tryptophan-stabilized dual-emission fluorescent gold nanoclusters and its application for Fe3+ sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungor, D.; Bélteki, R.; Horváth, K.; Dömötör, O.; Csapó, E. Fluorescence Quenching of Tyrosine-Ag Nanoclusters by Metal Ions: Analytical and Physicochemical Assessment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, S. Novel synthesis of gold nanoclusters templated with l-tyrosine for selective analyzing tyrosinase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 840, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezhhan, H.; Akhond, M.; Shamsipur, M.; Lumin, J. Histidine capped-gold nanoclusters mediated fluorescence detection of glucose and hydrogen peroxide based on glucose oxidase-mimicking property of gold nanoparticles via an inner filter effect mechanism. J. Lumin. 2020, 228, 117604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélteki, R.; Kuklis, L.; Gombár, G.; Ungor, D.; Csapó, E. The Role of the Amino Acid Molecular Characteristics on the Formation of Fluorescent Gold- and Silver-Based Nanoclusters. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202300720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakannan, P.R.; Mandal, S.; Phadtare, S.; Gole, A.; Pasricha, R.; Adyanthaya, S.D.; Sastry, M. Water-dispersible tryptophan-protected gold nanoparticles prepared by the spontaneous reduction of aqueous chloroaurate ions by the amino acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 269, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombár, G.; Simon, P.; Ungor, D.; Szatmári, I.; Csapó, E. Histidinehydroxamic acid as new biomolecule to produce molecular-like fluorescent gold nanoclusters: Possible mechanisms for metal ion sensing. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 387, 122597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlford, K.; Adolfsson, H. Amino acid derived amides and hydroxamic acids as ligands for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation in aqueous media. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AZur, A.; Chien, H.C.; Augustyn, E.; Flint, A.; Heeren, N.; Finke, K.; Hernandez, C.; Hansen, L.; Miller, S.; Lin, L.; et al. LAT1 activity of carboxylic acid bioisosteres: Evaluation of hydroxamic acids as substrates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5000–5006. [Google Scholar]
- Kurzak, B.; Kroczewska, D.; Jezierska, J.; Huza-Koralewicz, M. Stability and Structure of Copper (II)-LHistidinehydroxamic Acid Complexes. Transit. Met. Chem. 1988, 13, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.Q.; Peng, B.; Shan, B.Q.; Zong, Y.X.; Jiang, J.G.; Wu, P.; Zhang, K. Origin of the Photoluminescence of Metal Nanoclusters: From Metal-Centered Emission to Ligand-Centered Emission. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leporati, E. Thermodynamic and spectrophotometric investigation of complex formation between hydrogen, cobalt(II), nickel(II), and copper(II) ions and 2-amino-N-hydroxypropanamide in aqueous solution. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1989, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallavalle, F.; Folesani, G.; Sabatini, A.; Tegoni, M.; Vacca, A. Formation equilibria of ternary complexes of copper(II) with (S)-tryptophanhydroxamic acid and both D- and L-amino acids in aqueous solution. Polyhedron 2001, 20, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loock, H.P.; Wentzell, P.D. Detection limits of chemical sensors: Applications and misapplications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.D.; Subramanian, S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: Forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| T (K) | Kb (M−1) | n | ΔH0 (kJ∙mol−1) | ΔS0 (kJ∙mol−1∙K−1) | ΔCp (kJ∙mol−1∙K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283 | 2.39 × 102 ± 9.09 × 10−1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | −29.69 ± 3.40 | −0.11 ± 0.01 | −7.19 ± 0.31 |
| 293 | 6.11 × 101 ± 8.72 × 10−1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | |||
| 303 | 4.56 × 101 ± 8.72 × 10−1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | |||
| 313 | 1.24 × 102 ± 8.72 × 10−1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | |||
| 318 | 3.34 × 102 ± 8.99 × 10−1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gombár, G.; Ungor, D.; Szatmári, I.; Juhász, Á.; Csapó, E. Tryptophanhydroxamic Acid-Stabilized Ultrasmall Gold Nanoclusters: Tuning the Selectivity for Metal Ion Sensing. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14050434
Gombár G, Ungor D, Szatmári I, Juhász Á, Csapó E. Tryptophanhydroxamic Acid-Stabilized Ultrasmall Gold Nanoclusters: Tuning the Selectivity for Metal Ion Sensing. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(5):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14050434
Chicago/Turabian StyleGombár, Gyöngyi, Ditta Ungor, István Szatmári, Ádám Juhász, and Edit Csapó. 2024. "Tryptophanhydroxamic Acid-Stabilized Ultrasmall Gold Nanoclusters: Tuning the Selectivity for Metal Ion Sensing" Nanomaterials 14, no. 5: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14050434
APA StyleGombár, G., Ungor, D., Szatmári, I., Juhász, Á., & Csapó, E. (2024). Tryptophanhydroxamic Acid-Stabilized Ultrasmall Gold Nanoclusters: Tuning the Selectivity for Metal Ion Sensing. Nanomaterials, 14(5), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14050434