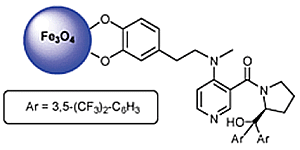
Recent Advances in the Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Support for Homogeneous Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Immobilisation of Inorganic Catalysts on Magnetic Nanoparticles




3. Immobilisation of Organic Catalysts onto Magnetic Nanostructures






4. Immobilisation of Enzyme Catalysts onto Magnetic Nanoparticles

5. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Philipse, A.P. Heterogeneous catalysis: On bathroom mirrors and boiling stones. J. Chem. Educ. 2011, 88, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Downing, R.S. Heterogeneous catalytic transformations for environmentally friendly production. Appl. Catal. A 1999, 189, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole-Hamilton, D.J. Homogeneous catalysis—New approaches to catalyst separation, recovery, and recycling. Science 2003, 299, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornils, B.; Herrmann, W.A. Concepts in homogeneous catalysis: The industrial view. J. Catal. 2003, 216, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.G. Nanoparticles in catalysis. Top. Catal. 2003, 24, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.L.; Erathodiyil, N.; Ying, J.Y. Nanostructured catalysts for organic transformations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 46, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X.; Tryk, D.A. TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2008, 63, 515–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Vander Elst, L.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.H. Magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S.J.; Corr, S.A.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Kelly, J.M.; Brougham, D.F.; Ghosh, S. Magnetic nanoparticle assemblies on denatured DNA show unusual magnetic relaxivity and potential applications for MRI. Chem. Commun. 2004, 22, 2560–2561. [Google Scholar]
- Nasongkla, N.; Bey, E.; Ren, J.; Ai, H.; Khemtong, C.; Guthi, J.S.; Chin, S.-F.; Sherry, A.D.; Boothman, D.A.; Gao, J. Multifunctional polymeric micelles as cancer-targeted, MRI-ultrasensitive drug delivery systems. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Drug Dev. Res. 2006, 67, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherine, C.B.; Adam, S.G.C. Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D 2003, 36, R198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Carlesso, N.; Tung, C.-H.; Tang, X.-W.; Cory, D.; Scadden, D.T.; Weissleder, R. Tat peptide-derivatized magnetic nanoparticles allow in vivo tracking and recovery of progenitor cells. Nat. Biotechol. 2000, 18, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Starz-Gaiano, M.; Bridges, T.; Montell, D. Purification of specific cell populations from Drosophila tissues by magnetic bead sorting, for use in gene expression profiling. Protoc. Exch. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, R.B.N.; Varma, R.S. Magnetically retrievable catalysts for organic synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 752–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Sun, L.; Lin, H.; Guo, Z. Multifunctional composite core-shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4474–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.-J.; Lee, W.; Oh, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-K. Magnetic nanoparticles as a catalyst vehicle for simple and easy recycling. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Li, M.; Yang, N.; Zou, G. Anatase TiO2 nanolayer coating on cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic photocatalyst. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3530–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Reziq, R.; Wang, D.; Post, M.; Alper, H. Platinum nanoparticles supported on ionic liquid-modified magnetic nanoparticles: Selective hydrogenation catalysts. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 2145–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir Baig, R.B.; Varma, R.S. Magnetic silica-supported ruthenium nanoparticles: An efficient catalyst for transfer hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 805–809. [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig, J.; Ceylan, S.; Kupracz, L.; Coutable, L.; Kirschning, A. Heating under high-frequency inductive conditions: Application to the continuous synthesis of the neurolepticum olanzapine (zyprexa). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9813–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dalaigh, C.; Corr, S.A.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Connon, S.J. A magnetic-nanoparticle-supported 4-N,N-dialkylaminopyridine catalyst: Excellent reactivity combined with facile catalyst recovery and recyclability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4329–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, O.; Tekoriute, R.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Connon, S.J. The first magnetic nanoparticle-supported chiral dmap analogue: Highly enantioselective acylation and excellent recyclability. Chemisty 2009, 15, 5669–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Yamashita, H. Design of colloidal and supported metal nanoparticles: Their synthesis, characterization, and catalytic application. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2011, 54, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shylesh, S.; Schunemann, V.; Thiel, W.R. Magnetically separable nanocatalysts: Bridges between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3428–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Pericas, M.A. Functionalized nanoparticles as catalysts for enantioselective processes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2669–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno, C.S.; Sayalero, S.; Pericàs, M.A. Covalent Heterogenization of Asymmetric Catalysts on Polymers and Nanoparticles. In Heterogenized Homogeneous Catalysts for Fine Chemicals Production, Catalysis by Metal Complexes; Pierluigi, B., Francesca, L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 33, pp. 123–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Stubbs, L.P.; Ho, F.; Liu, R.; Ship, C.P.; Maguire, J.A.; Hosmane, N.S. Magnetic nanocomposites: A new perspective in catalysis. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, Q.M.; Reiser, O. Polymer- and dendrimer-coated magnetic nanoparticles as versatile supports for catalysts, scavengers, and reagents. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 667–677. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Salmon, L.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. A recyclable Ruthenium(II) complex supported on magnetic nanoparticles: A regioselective catalyst for alkyne-azide cycloaddition. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6956–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, F.; Lagunas, A.; Jimeno, C.; Pericas, M.A. Synthesis of functional cobalt nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Use in asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of ketones. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4692–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Liu, S.; Lin, W. Immobilization of chiral catalysts on magnetite nanoparticles for highly enantioselective asymmetric hydrogenation of aromatic ketones. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2576–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Garrido, S.E.; Francos, J.; Cadierno, V.; Basset, J.-M.; Polshettiwar, V. Chemistry by nanocatalysis: First example of a solid-supported rapta complex for organic reactions in aqueous medium. ChemSusChem 2010, 4, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghani, F.; Sardarian, A.R.; Esmaeilpour, M. Salen complex of Cu(II) supported on superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles: An efficient and recyclable catalyst for synthesis of 1-and 5-substituted 1h-tetrazoles. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 743, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilpour, M.; Sardarian, A.R.; Javidi, J. Schiff base complex of metal ions supported on superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles: An efficient, selective and recyclable catalyst for synthesis of 1,1-diacetates from aldehydes under solvent-free conditions. Appl. Catal. A 2012, 445–446, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfigol, M.A.; Khakyzadeh, V.; Moosavi-Zare, A.R.; Rostami, A.; Zare, A.; Iranpoor, N.; Beyzavi, M.H.; Luque, R. A highly stable and active magnetically separable pd nanocatalyst in aqueous phase heterogeneously catalyzed couplings. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.P.; Kim, D.-P. A microchemical system with continuous recovery and recirculation of catalyst-immobilized magnetic particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6825–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.T.; Dang, T.B.; Le, H.V.; Phan, N.T.S. Suzuki reaction of aryl bromides using a phosphine-free magnetic nanoparticle-supported palladium catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2011, 32, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.T.S.; Le, H.V. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles-supported phosphine-free palladium catalyst for the Sonogashira coupling reaction. J. Mol. Catal. A 2011, 334, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, S.H.; Stein, B.D.; Nikoshvili, L.Z.; Matveeva, V.G.; Sulman, M.G.; Sulman, E.M.; Morgan, D.G.; Yuzik-Klimova, E.Y.; Mahmoud, W.E.; Bronstein, L.M. Functionalization of monodisperse iron oxide nps and their properties as magnetically recoverable catalysts. Langmuir 2013, 29, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, H.; Nazifi, Z. A highly efficient nano-Fe3O4 encapsulated-silica particles bearing sulfonic acid groups as a solid acid catalyst for synthesis of 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthene derivatives. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucoski, G.M.; Nunes, F.S.; DeFreitas-Silva, G.; Idemori, Y.M.; Nakagaki, S. Metalloporphyrins immobilized on silica-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Magnetically recoverable catalysts for the oxidation of organic substrates. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 459, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeifard, A.; Jafarpour, M.; Farshid, P.; Naeimi, A. Nanomagnet-supported partially brominated manganese–porphyrin as a promising catalyst for the selective heterogeneous oxidation of hydrocarbons and sulfides in water. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5515–5524. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.-J.; Choi, J.-W.; Kang, H.; Kang, T.; Lee, S.-M.; Jun, B.-H.; Lee, Y.-S. Recyclable NHC-Ni complex immobilized on magnetite/silica nanoparticles for C-S cross-coupling of aryl halides with thiols. Synlett 2010, 16, 2518–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Arruebo, M.; Yeung, K.L. Flow-synthesis of mesoporous silicas and their use in the preparation of magnetic catalysts for knoevenagel condensation reactions. Catal. Today 2013, 204, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayati, S.; Abdolalian, P. Heterogenization of a molybdenum schiff base complex as a magnetic nanocatalyst: An eco-friendly, efficient, selective and recyclable nanocatalyst for the oxidation of alkenes. C. R. Chim. 2013, 16, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Water-tolerant heteropolyacid on magnetic nanoparticles as efficient catalysts for esterification of free fatty acid. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 13748–13755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidale, L.C.; Nikolajski, M.; Rudolph, T.; Dutz, S.; Schacher, F.H.; Heinze, T. Hybrid Fe3O4@amino cellulose nanoparticles in organic media—Heterogeneous ligands for atom transfer radical polymerizations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 390, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Shentu, B.; Gu, C.; Weng, Z. Immobilization of Copper(II)-poly (N-vinylimidazole) complex on magnetic nanoparticles and its catalysis of oxidative polymerization of 2,6-dimethylphenol in water. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3730–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeltner, M.; Schatz, A.; Hefti, M.L.; Stark, W.J. Magnetothermally responsive C/Co@pnipam-nanoparticles enable preparation of self-separating phase-switching palladium catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2991–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Kawasaki, N.; Kanoh, H. Magnetically separable Cu-carboxylate MOF catalyst for the henry reaction. Synlett 2012, 23, 1549–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Kong, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H.; Qiu, J.; Yeung, K.L. Synthesis of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 magnetic core-shell microspheres and their potential application in a capillary microreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, S.; Schaetz, A.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J.; Reiser, O. A recyclable nanoparticle-supported palladium catalyst for the hydroxycarbonylation of aryl halides in water. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1867–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, M.; Collière, V.; Reiser, O.; Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.-P.; Ouali, A. Pyrene-tagged dendritic catalysts noncovalently grafted onto magnetic Co/C nanoparticles: An efficient and recyclable system for drug synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3626–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaetz, A.; Long, T.R.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J.; Hanson, P.R.; Reiser, O. Immobilization on a nanomagnetic Co/C surface using rom polymerization: Generation of a hybrid material as support for a recyclable palladium catalyst. Adv.Func. Mater. 2010, 20, 4323–4328. [Google Scholar]
- Linhardt, R.; Kainz, Q.M.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J.; Reiser, O. Palladium nanoparticles supported on ionic liquid modified, magnetic nanobeads—Recyclable, high-capacity catalysts for alkene hydrogenation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 8541–8549. [Google Scholar]
- Kainz, Q.M.; Linhardt, R.; Grass, R.N.; Vilé, G.; Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Stark, W.J.; Reiser, O. Palladium nanoparticles supported on magnetic carbon-coated cobalt nanobeads: Highly active and recyclable catalysts for alkene hydrogenation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2020–2027. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, G.-L.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Preparation of multifunctional nanoparticles and their assemblies. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1677–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghzadeh, S.M.; Nasseri, M.A. Methylene dipyridine nanoparticles stabilized on Fe3O4 as catalysts for efficient, green, and one-pot synthesis of pyrazolophthalazinyl spirooxindoles. Catal. Today 2013, 217, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, S.; Puglisi, A.; Benaglia, M.; Ramella, D.; Drago, C.; Ferretti, A.; Ponti, A. Magnetic nanoparticles conjugated to chiral imidazolidinone as recoverable catalyst. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.; Tan, R.; Zhao, L.; Yin, D. L-proline supported on ionic liquid-modified magnetic nanoparticles as a highly efficient and reusable organocatalyst for direct asymmetric aldol reaction in water. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2422–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, S.; Bazrafshan, M.; Delluei, A.A.; Parizi, Z.P. Phospha-michael addition of diethyl phosphite to α, β-unsaturated malonates catalyzed by nano γ-Fe2O3-pyridine based catalyst as a new magnetically recyclable heterogeneous organic base. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 454, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, A.; Atashkar, B.; Moradi, D. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of magnetic nanoparticle supported guanidine in base catalyzed synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates and α-acetoxyphosphonates. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 467, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Farhangi, E. A highly recyclable magnetic core-shell nanoparticle-supported TEMPO catalyst for efficient metal- and halogen-free aerobic oxidation of alcohols in water. Chemistry 2011, 17, 6056–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, J.; Kiasat, A.R. Nanomagnetic double-charged diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane dichloride silica as a novel nanomagnetic phase-transfer catalyst for the aqueous synthesis of benzyl acetates and thiocyanates. Catal. Commun. 2013, 42, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riente, P.; Yadav, J.; Pericàs, M.A. A click strategy for the immobilization of macmillan organocatalysts onto polymers and magnetic nanoparticles. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3668–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riente, P.; Mendoza, C.; Pericas, M.A. Functionalization of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for organocatalytic michael reactions. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7350–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, Q.M.; Zeltner, M.; Rossier, M.; Stark, W.J.; Reiser, O. Synthesis of trisubstituted ureas by a multistep sequence utilizing recyclable magnetic reagents and scavengers. Chemistry 2013, 19, 10038–10045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Perrier, A.; Linhardt, R.; Travers, L.; Wittmann, S.; Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.-P.; Reiser, O.; Ouali, A. Dendrimers or nanoparticles as supports for the design of efficient and recoverable organocatalysts? Adv. Synth. Cat. 2013, 355, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Hosseini, S.H.; Doulabi, M.; Fakoorpoor, S.M.; Seidi, F. Multi-layer functionalized poly (ionic liquid) coated magnetic nanoparticles: Highly recoverable and magnetically separable brønsted acid catalyst. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoğlu, E.; Baykal, A.; Șenel, M.; Sözeri, H.; Toprak, M.S. Synthesis and characterization of piperidine-4-carboxylic acid functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a magnetic catalyst for knoevenagel reaction. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 2480–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaetz, A.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J.; Reiser, O. TEMPO supported on magnetic C/Co-nanoparticles: A highly active and recyclable organocatalyst. Chemistry 2008, 14, 8262–8266. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker-Schwartz, A.K.; Garrell, R.L. Simple preparation and application of tempo-coated Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticles for selective oxidation of alcohols. Chemistry 2010, 16, 12718–12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, O.; Davies, G.L.; Peschiulli, A.; Tekoriute, R.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Connon, S.J. The immobilisation of chiral organocatalysts on magnetic nanoparticles: The support particle cannot always be considered inert. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 7929–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, H.H.P.; Keane, M.A. Enzyme–magnetic nanoparticle hybrids: New effective catalysts for the production of high value chemicals. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horák, D.; Kučerová, J.; Korecká, L.; Jankovičová, B.; Palarčík, J.; Mikulášek, P.; Bílková, Z. New monodisperse magnetic polymer microspheres biofunctionalized for enzyme catalysis and bioaffinity separations. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.A.; Husain, Q. Potential applications of enzymes immobilized on/in nano materials: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, C. Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for sample preparation in proteomics and peptidomics analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8517–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, I.; Ahmad, I.; Chen, G.; Huizhou, L. A surfactant-coated lipase immobilized in magnetic nanoparticles for multicycle ethyl isovalerate enzymatic production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 73, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-C.; Sheu, D.-C.; Duan, K.-J. Production of fructooligosaccharides using β-fructofuranosidase immobilized onto chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.10.003.
- Ashtari, K.; Khajeh, K.; Fasihi, J.; Ashtari, P.; Ramazani, A.; Vali, H. Silica-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles: Enzyme immobilization and cytotoxic study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Lee, I.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, O.K.; Shim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, E.Y. Enhanced stability and reusability of marine epoxide hydrolase using ship-in-a-bottle approach with magnetically-separable mesoporous silica. J. Mol. Catal. B 2013, 89, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, W.J.; Makam, V.S.; Hu, J.; Kang, L.; Zheng, M.; Yoong, S.L.; Udalagama, C.N.B.; Pastorin, G. Iron oxide filled magnetic carbon nanotube-enzyme conjugates for recycling of amyloglucosidase: Toward useful applications in biofuel production process. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16864–16873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Feng, W.; Ji, P. Lipase immobilized on magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 115, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Govan, J.; Gun'ko, Y.K. Recent Advances in the Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Support for Homogeneous Catalysts. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 222-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4020222
Govan J, Gun'ko YK. Recent Advances in the Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Support for Homogeneous Catalysts. Nanomaterials. 2014; 4(2):222-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4020222
Chicago/Turabian StyleGovan, Joseph, and Yurii K. Gun'ko. 2014. "Recent Advances in the Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Support for Homogeneous Catalysts" Nanomaterials 4, no. 2: 222-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4020222
APA StyleGovan, J., & Gun'ko, Y. K. (2014). Recent Advances in the Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Support for Homogeneous Catalysts. Nanomaterials, 4(2), 222-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4020222