Nano-Assemblies of Modified Cyclodextrins and Their Complexes with Guest Molecules: Incorporation in Nanostructured Membranes and Amphiphile Nanoarchitectonics Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins
- (i)
- Cyclodextrins with hydrophobic anchors on the primary face: “Medusa-like” molecules;
- (ii)
- Cyclodextrins with hydrophobic anchors on the secondary face: “Skirt-shaped” molecules;
- (iii)
- Cyclodextrins with hydrophobic or hydrophilic anchors on the both faces: “Bouquet-like” molecules.

2.1. Cyclodextrins Modified by Large Moieties on the Primary Face
2.1.1. Monosubstituted Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins
2.1.2. Polysubstituted Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins
2.2. Cyclodextrins Modified on the Secondary Face
2.3. Cyclodextrins Modified on Both Faces
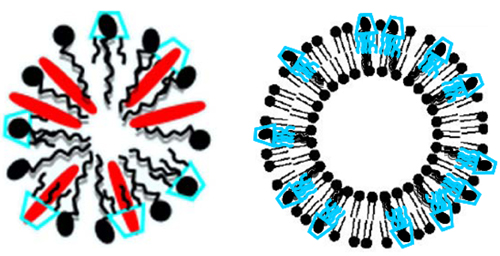
3. Supramolecular Assemblies of Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins

| Amphiphilic cyclodextrins | Organized systems | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| 2,3-diacyl-O-β-cyclodextrin | Nanocapsules | [21] |
| Heptakis(2-ω-amino-O-oligo(ethylene oxide)-6-hexylthio)-β-CD (SC6CDNH2) | Nanoparticles | [29] |
| Heptakis(2-O-oligo(ethylene oxide)-6-hexylthio)-β-CD (SC6OH) | Nanoparticles | [30] |
| 2,3-di-O-hexanoyl cyclomaltoheptaose (βCD-C6) | Nanocapsules | [31] |
| SC6NH2@SC6Dns | Nanoparticles | [32] |
| 2,6-di-O-methyl-β-CD | Micelles | [33] |
| βCD-C6 | Nanospheres/Nanocapsules | [34] |
| βCD-C6/6-N-CAPRO-β-CD | Nanospheres | [35] |
| βCD-C6/6-N-MYRISTO-β-CD | Nanocapsules | [36] |
| βCD-C6/βCD-C12/ βCD-C14 | Nanospheres | [37] |
| N-Octadecylperylene 3,4:9,10 tetra-caboxylic-3,4-permethyl-β-cyclodextrin-9,10-imide | Nanorods, Micelles,Vesicles | [38] |
| 6I-(Cholest-5-en-3α-ylamido)succinylamido-6I-deoxy-per(2,6-di-O-methyl)cyclomaltoheptaose | Micelles | [39] |
| Mono [6-(2-aminohexylamino)-6-deoxy]-β –cyclodextrin | Nanorods, vesicles | [40] |
| Hexakis[6-deoxy-6-(3-perfluorohexylpropanethio)-2,3-di-O-methyl]-α-cyclodextrin (α-C6F13) or β-C6F13 | Nanospheres | [41] |
| N-dodecyl-Nα-(6I-amidosuccinyl-6I-deoxy-2I,3I-di-O-methyl-hexakis-(2II-VII,3II-VII,6II-VIItri- O-methyl)-cyclomaltoheptaose)-L-leucine | Micelles/Colloidal aggregates | [42] |
| Folate-polycationic amphiphilic CD | Nanocomplexes with DNA | [43] |
| Polycationic amphiphilic CD | Nanocomplexes with siRNA | [44] |
| Polycationic glyco-amphiphilic CDs | Nanocomplexes with DNA | [45] |
| Polycationic amphiphilic CD | Nanocomplexes with DNA | [45,46] |
| Poly-6-cationic amphiphilic CD | Nanocomplexes with DNA | [46] |
| Cationic amphiphilic β-cyclodextrins (hydrophobic n-alkylthio chains (C16) at the primary hydroxyl face and hydrophilic ω-amino-oligo(ethylene glycol) units at the secondary face) | Bilayer vesicles | [47] |
| SC8CDcysteamine (lipophilic group on the secondary face) | Nanocomplexes with siRNA | [48] |
| SC8CDcysteamine (lipophilicgroup on the primary face) | Nanocomplexes with siRNA | [48] |
3.1. Colloidal Systems Involving Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins



3.2. Organized Nanosystems of Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins as Non-Viral Gene Carriers

4. Nanosystems of Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins Mixed with Membrane-Forming Molecules and Lipids
| Amphiphilic cyclodextrins | Co-Lipid(s) | Organized systems | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Per-(6-amino-2,3-di-O-hexyl) β-CD hydrochloride salt (NH3- β-CD-OC6) | 1,2-dipalmitoyl,3-sn-phosphatidyl choline or 1,2-dipalmitoyl,3-sn-phosphatidic acid | Monolayers | [49] |
| Per-(6-dodecanoylamino-6-deoxy) β-CD (C11CONH- β-CD) | 1,2-dipalmitoyl,3-phosphatidyl-choline (DPPC) | Monolayers | [49] |
| 6I-(cholest-5-en-3α-ylamido)succinylamido-6I-deoxy-per(2,6-di-O-methyl) cyclomaltoheptaose (chol-DIMEB) | Dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) | Newtons black films | [50] |
| Heptakis (2,3-di-O-hexanoyl)-β-CD (βCD-C6) | Dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) | Monolayers and hydrated multibilayers | [51] |
| Trimethyl-α-CD-Succinyl-Cholesterol (TASC) | Dipalmitoyl-L-α-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) | Monolayers and bilayers | [52] |
| Trimethyl-β-CD-Succinyl-Cholesterol (TBSC) | Dipalmitoyl-L-α-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) | Monolayers and bilayers | [52] |
| Trimethyl- Β-CD-diSuccinyl-Cholesterol (TBdSC) | Dipalmitoyl-L-α-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) | Monolayers and bilayers | [52] |
| Dilauryl-β-CD Dilauryl-di-2,6-O-methyl β-CD Dilauryl-tri-2,3,6-O-methyl β-CD | Dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) | Lamellar-phase bilayers | [53,54] |
| 2,3-di-O-hexanoyl cyclomaltooctaose (γCDC6) | n-octyl-β-D-glucopyranoside | Spheres | [55] |
| Amphiphilic β-CD (modified on the primary face) | Dioleyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine (DOPE), dioleyl phosphatidylcholine (DOPC) and cholesterol | Three-dimensional multilayered structures | [56] |
| Amphiphilic β-CD (substituted with seven hydrophobic n-dodecyl chains on the primary face and seven hydrophilic oligo(ethylene glycol) groups on the secondary face) | Dioleyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine (DOPE), dioleyl phosphatidylcholine (DOPC) and cholesterol | Giant unilamellar vesicles (GUV), liposomes, Mixed vesicles | [28] |
| Mono-(N-n-alkyl,N,N-dimethylamino)-β-CD | Cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidyl choline mixture | Three-dimensional multilayered structures of liposome type | [57] |



5. Potential Application of Supramolecular Assemblies of Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins
| Amphiphilic CDs | Systems | Potential applications | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heptakis (2-O-oligo(ethyleneoxide)-6-hexadecylthio-)-β-CD (SC16OH) | Nanoparticles | Drug carriers (docetaxel) | [58] |
| 6-O-CAPRO-β-CD | Nanoparticles (nanospheres, nanocapsules, vesicles) | Drug carriers (paclitaxel, camptothecin) | [59,60] |
| βCD-C6/6-N-CAPRO-β-CD 6-N-MYRISTO-β-CD | Nanospheres Nanocapsules | Drug carriers (progesterone, camptothecin) | [35,36,60] |
| Oligoethyleneimine-βCD | CDplexes | Gene delivery | [61] |
| Heptakis[6-(2-amino-ethylthio)-6-deoxy-2-O-octylsulfanylpropyl]-β-cyclodextrin hepta-N-trifluoroacetate | CDplexes | Gene delivery | [62] |
| Heptakis[6-diBoc-guanidinoethylthio-2-O-(N-(ω-(p-methoxybenzamido)-PEG440-yl)-1′H-triazole-4’-yl-methyl)]-β-cyclodextrin | CDplexes | Gene delivery | [63] |
| Heptakis[6-deoxy-6-(2-(N’-(2-(N,N-di-(2-aminoethyl)amino)ethyl)thioureido)ethylthio)-2,3-di-O-hexanoyl] cyclomaltoheptaose | CDplexes | Gene delivery | [64] |
| Heptakis(6-dodecylthio-2-oligo(ethylenoxide)-β-cyclodextrin-2-(4-(phenyldiazenyl)phenoxy) acetate | Vesicles | Phototherapy | [65] |
| Heptakis(2-O-oligo(ethylene oxide)-6-hexylthio)-β-CD (SC6OH) | Nanoparticles | Phototherapy | [30] |
| SC6NH3-β-CD; SC16NH3-β-CD | Multilayer films | Photoresponsive multilayer films | [66] |
| Peptidyl-β-cyclodextrins | Assemblies with biological membranes | Artificial receptors | [67] |
| Amphiphilic β-cyclodextrins with n-dodecyl groups and n-hexadecyl chains on both faces | Assemblies with biological membranes | Artificial receptors | [28] |
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angelova, A.; Angelov, B.; Mutafchieva, R.; Lesieur, S.; Couvreur, P. Self-assembled multicompartment liquid crystalline lipid carriers for protein, peptide, and nucleic acid drug delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, C.; Le, T.; Drummond, C.J. Lyotropic liquid crystal engineering-ordered nanostructured small molecule amphiphile self-Assembly materials by design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1297–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelov, B.; Angelova, A.; Filippov, S.; Drechsler, M.; Štěpánek, P.; Lesieur, S. Multicompartment lipid cubic nanoparticles with high protein upload: Millisecond dynamics of formation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5216–5226. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, C.E.; Drummond, C.J. Nanostructured bicontinuous cubic lipid self-assembly materials as matrices for protein encapsulation. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3449–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, B.; Angelova, A.; Filippov, S.K.; Narayanan, T.; Drechsler, M.; Štěpánek, P.; Couvreur, P.; Lesieur, S. DNA/fusogenic lipid nanocarrier assembly: Millisecond structural dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Angelov, B.; Angelova, A.; Garamus, V.M.; Drechsler, M.; Willumeit, R.; Mutafchieva, R.; Štěpánek, P.; Lesieur, S. Earliest stage of the tetrahedral nanochannel formation in cubosome particles from unilamellar nanovesicles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16647–16655. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, M.; Shrestha, L.K.; Mori, T.; Ji, Q.; Hill, J.P.; Ariga, K. Amphiphile nanoarchitectonics: From basic physical chemistry to advanced applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10580–10611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angelov, B.; Angelova, A.; Mutafchieva, R.; Lesieur, S.; Vainio, U.; Garamus, V.M.; Jensen, G.V.; Pedersen, J.S. SAXS Investigation of a cubic to a sponge (L3) phase transition in self-assembled lipid nanocarriers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3073–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelov, B.; Angelova, A.; Filippov, S.; Karlsson, G.; Terrill, N.; Lesieur, S.; Štěpánek, P. Topology and internal structure of PEGylated lipid nanocarriers for neuronal transfection: Synchrotron radiation SAXS and cryo-TEM studies. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9714–9720. [Google Scholar]
- Angelova, A.; Angelov, B.; Garamus, V.M.; Couvreur, P.; Lesieur, S. Small-angle X-ray scattering investigations of biomolecular confinement, loading, and release from liquid crystalline nanochannel assemblies. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 445–457. [Google Scholar]
- Auzély-Velty, R.; Perly, B.; Taché, O.; Zemb, T.; Jéhan, P.; Guenot, P.; Dalbiez, J.-P.; Djedaı̈ni-Pilard, F. Cholesteryl-cyclodextrins: Synthesis and insertion into phospholipid membranes. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 318, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gervaise, C.; Bonnet, V.; Wattraint, O.; Aubry, F.; Sarazin, C.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F. Synthesis of lipophosphoramidyl-cyclodextrins and their supramolecular properties. Biochimie 2012, 94, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Nakamura, T.; Tanaka, M.; Manda, E.; Takahashi, H.; Tamura, S.; Tagaki, W.; Nakahara, H.; Fukuda, K. Langmuir-Blodgett films of amphiphilic cyclodextrins. Thin Solid Films 1988, 159, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Azumi, R.; Tachibana, H.; Nakamura, T.; Kawabata, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Miyasaka, T.; Tagaki, W.; Nakahara, H.; Fukuda, K. Recognition properties of amphiphilic cyclodextrin monolayers at the air-water interface. Thin Solid Films 1994, 244, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Noguchi, S.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M.; Matsumoto, M. Hybrid Langmuir and Langmuir-Blodgett films composed of amphiphilic cyclodextrins and hydrophobic azobenzene derivative. Thin Solid Films 2006, 510, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, A.; Fajolles, C.; Bauer, M.; Collot, M.; Mallet, J.-M.; Daillant, J. Amphiphilic behavior and membrane solubility of a dicholesteryl-cyclodextrin. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7580–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choisnard, L.; Gèze, A.; Putaux, J.-L.; Wong, Y.-S.; Wouessidjewe, D. Nanoparticles of β-cyclodextrin esters obtained by self-assembling of biotransesterified β-cyclodextrins. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memisoglu, E.; Bochot, A.; Özalp, M.; Sen, M.; Duchêne, D.; Hincal, A.A. Direct formation of nanospheres from amphiphilic-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Skiba, M.; Duchêne, D.; Puisieux, F.; Wouessidjewe, D. Development of a new colloidal carrier from chemically-modified cyclodextrins nanospheres and influence of physicochemical and technological factors on particle size. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 129, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Choisnard, L.; Gèze, A.; Vanhaverbeke, C.; Yaméogo, J.B.G.; Putaux, J.-L.; Brasme, B.; Jullien, L.; Boullanger, S.; Elfakir, C.; Wouessidjewe, D. Physicochemical characterization of α-, β-, and γ-cyclodextrins bioesterified with decanoate chains used as building blocks of colloidal nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba, M.; Nemati, F.; Puisieux, F.; Duchêne, D. Spontaneous formation of drug-containing β-cyclodextrin nanocapsules. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 145, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Choisnard, L.; Gèze, A.; Yaméogo, B.G.J.; Putaux, J.-L.; Wouessidjewe, D. Miscellaneous nanoaggregates made of β-CD esters synthesised by an enzymatic pathway. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 344, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gèze, A.; Aous, S.; Baussanne, I.; Putaux, J.; Defaye, J.; Wouessidjewe, D. Influence of chemical structure of amphiphilic β-cyclodextrins on their ability to form stable nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Yaméogo, J.B.G.; Gèze, A.; Choisnard, L.; Putaux, J.-L.; Gansané, A.; Sirima, S.B.; Semdé, R.; Wouessidjewe, D. Self-assembled biotransesterified cyclodextrins as Artemisinin nanocarriers—I: Formulation, lyoavailability and in vitro antimalarial activity assessment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 508–517. [Google Scholar]
- Gèze, A.; Chau, L.T.; Choisnard, L.; Mathieu, J.-P.; Marti-Batlle, D.; Riou, L.; Putaux, J.-L.; Wouessidjewe, D. Biodistribution of intravenously administered amphiphilic β-cyclodextrin nanospheres. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 344, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Gèze, A.; Choisnard, L.; Putaux, J.-L.; Wouessidjewe, D. Colloidal systems made of biotransesterified α, β and γ cyclodextrins grafted with C10 alkyl chains. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, D.; Longo, A.; Darcy, R.; Mazzaglia, A. Structural properties of nonionic cyclodextrin colloids in water. Langmuir 2004, 20, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauscher, U.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Drücker, P.; Galla, H.-J.; Ravoo, B.J. Incorporation of amphiphilic cyclodextrins into liposomes as artificial receptor units. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7377–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sortino, S.; Mazzaglia, A.; Monsù Scolaro, L.; Marino Merlo, F.; Valveri, V.; Sciortino, M.T. Nanoparticles of cationic amphiphilic cyclodextrins entangling anionic porphyrins as carrier-sensitizer system in photodynamic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4256–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaglia, A.; Bondì, M.L.; Scala, A.; Zito, F.; Barbieri, G.; Crea, F.; Vianelli, G.; Mineo, P.; Fiore, T.; Pellerito, C.; et al. Supramolecular assemblies based on complexes of nonionic amphiphilic cyclodextrins and a meso-tetra(4-sulfonatophenyl)porphine tributyltin(IV) derivative: Potential nanotherapeutics against melanoma. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3820–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skiba, M.; Morvan, C.; Duchêne, D.; Puisieux, F.; Wouessidjewe, D. Evaluation of gastrointestinal behaviour in the rat of amphiphilic β-cyclodextrin nanocapsules, loaded with indomethacin. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 126, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaglia, A.; Valerio, A.; Micali, N.; Villari, V.; Quaglia, F.; Castriciano, M.A.; Scolaro, L.M.; Giuffrè, M.; Siracusano, G.; Sciortino, M.T. Effective cell uptake of nanoassemblies of a fluorescent amphiphilic cyclodextrin and an anionic porphyrin. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9140–9142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chipot, C.; Shao, X.; Cai, W. Structural characterization of micelles formed of cholesteryl-functionalized cyclodextrins. Langmuir 2011, 27, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memisoglu-Bilensoy, E.; Vural, I.; Bochot, A.; Renoir, J.M.; Duchene, D.; Hıncal, A.A. Tamoxifen citrate loaded amphiphilic β-cyclodextrin nanoparticles: In vitro characterization and cytotoxicity. J. Controll. Release 2005, 104, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Memişoğlu, E.; Bochot, A.; Şen, M.; Duchêne, D.; Hıncal, A.A. Non-surfactant nanospheres of progesterone inclusion complexes with amphiphilic β-cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 251, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Ringard-Lefebvre, C.; Bochot, A.; Memisoğlu, E.; Charon, D.; Duchêne, D.; Baszkin, A. Effect of spread amphiphilic β-cyclodextrins on interfacial properties of the oil/water system. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2002, 25, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Skiba, M.; Wouessidjewe, D.; Puisieux, F.; Duchêne, D.; Gulik, A. Characterization of amphiphilic β-cyclodextrin nanosphères. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 142, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.-P.; Guo, D.-S.; Liu, Y. Self-assembly of amphiphilic perylene-cyclodextrin conjugate and vapor sensing for organic amines. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 7258–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auzély-Velty, R.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F.; Désert, S.; Perly, B.; Zemb, T.H. Micellization of hydrophobically modified cyclodextrins.1. Micellar structure. Langmuir 2000, 16, 3727–3734. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, H.; Kong, L.; Qiao, H.; Li, Y.; Xin, F.; Hao, A. Controlled transformation from nanorods to vesicles induced by cyclomaltoheptaoses (β-cyclodextrins). Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perret, F.; Marminon, C.; Zeinyeh, W.; Nebois, P.; Bollacke, A.; Jose, J.; Parrot-Lopez, H.; Le Borgne, M. Preparation and characterization of CK2 inhibitor-loaded cyclodextrin nanoparticles for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angelova, A.; Fajolles, C.; Hocquelet, C.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F.; Lesieur, S.; Bonnet, V.; Perly, B.; Lebas, G.; Mauclaire, L. Physico-chemical investigation of asymmetrical peptidolipidyl-cyclodextrins. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranda, C.; Urbiola, K.; Méndez Ardoy, A.; García Fernández, J.M.; Ortiz Mellet, C.; de Ilarduya, C.T. Targeted gene delivery by new folate–polycationic amphiphilic cyclodextrin-DNA nanocomplexes in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Godinho, B.M.D.C.; Ogier, J.R.; Darcy, R.; O’Driscoll, C.M.; Cryan, J.F. Self-assembling modified β-cyclodextrin nanoparticles as neuronal siRNA delivery vectors: Focus on Huntington’s disease. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Moscoso, A.; Guilloteau, N.; Bienvenu, C.; Méndez-Ardoy, A.; Jiménez Blanco, J.L.; Benito, J.M.; Le Gourriérec, L.; Di Giorgio, C.; Vierling, P.; Defaye, J.; et al. Mannosyl-coated nanocomplexes from amphiphilic cyclodextrins and pDNA for site-specific gene delivery. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7263–7273. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, M.J.; Guo, J.; Byrne, C.; Darcy, R.; O’ Driscoll, C.M. Mechanistic studies on the uptake and intracellular trafficking of novel cyclodextrin transfection complexes by intestinal epithelial cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 413, 174–183. [Google Scholar]
- Donohue, R.; Mazzaglia, A.; Ravoo, B.J.; Darcy, R. Cationic β-cyclodextrin bilayer vesicles. Chem. Commun. 2002, 2002, 2864–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, A.M.; Doyle, D.; Darcy, R.; Cryan, J.F.; O’Driscoll, C.M. Characterisation of cationic amphiphilic cyclodextrins for neuronal delivery of siRNA: Effect of reversing primary and secondary face modifications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 896–903. [Google Scholar]
- Kasselouri, A.; Coleman, A.W.; Baszkin, A. Mixed monolayers of amphiphilic cyclodextrins and phospholipids: I. Miscibility under dynamic conditions of compression. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 180, 384–397. [Google Scholar]
- Javierre, I.; Nedyalkov, M.; Petkova, V.; Benattar, J.-J.; Weisse, W.; Auzély-Velty, R.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F.; Perly, B. Direct investigation of the vectorization properties of amphiphilic cyclodextrins in phospholipid films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 254, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesieur, S.; Charon, D.; Lesieur, P.; Ringard-Lefebvre, C.; Muguet, V.; Duchêne, D.; Wouessidjewe, D. Phase behavior of fully hydrated DMPC-amphiphilic cyclodextrin systems. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2000, 106, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Charitat, T.; Fajolles, C.; Fragneto, G.; Daillant, J. Insertion properties of cholesteryl cyclodextrins in phospholipid membranes: A molecular study. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, M.; Moutard, S.; Perly, B.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F. Lipid lateral segregation driven by diacyl cyclodextrin interactions at the membrane surface. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, M.; Sternin, E.; Bonnet, V.; Fajolles, C.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F. Dynamic lipid lateral segregation driven by lauryl cyclodextrin interactions at the membrane surface. Langmuir 2013, 29, 3677–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos-Senna, E.; Wouessidjewe, D.; Duchêne, D.; Lesieur, S. Amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanospheres: Particle solubilization and reconstitution by the action of a non-ionic detergent. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 1998, 10, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Roling, O.; Wendeln, C.; Kauscher, U.; Seelheim, P.; Galla, H.-J.; Ravoo, B.J. Layer-by-layer deposition of vesicles mediated by supramolecular interactions. Langmuir 2013, 29, 10174–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machut-Binkowski, C.; Hapiot, F.; Cecchelli, R.; Martin, P.; Monflier, E. A versatile liposome/cyclodextrin supramolecular carrier for drug delivery through the blood-brain barrier. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 57, 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Quaglia, F.; Ostacolo, L.; Mazzaglia, A.; Villari, V.; Zaccaria, D.; Sciortino, M.T. The intracellular effects of non-ionic amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles in the delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilensoy, E.; Gürkaynak, O.; Doğan, A.L.; Hıncal, A.A. Safety and efficacy of amphiphilic ß-cyclodextrin nanoparticles for paclitaxel delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 347, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Çirpanli, Y.; Bilensoy, E.; Lale Doğan, A.; Çaliş, S. Comparative evaluation of polymeric and amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles for effective camptothecin delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 73, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, Á.; Bienvenu, C.; Jiménez Blanco, J.L.; Vierling, P.; Mellet, C.O.; García Fernández, J.M.; Di Giorgio, C. Amphiphilic oligoethyleneimine-β-cyclodextrin “click” clusters for enhanced DNA delivery. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 8143–8148. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, M.J.; O’Mahony, A.M.; Byrne, C.; Darcy, R.; O’Driscoll, C.M. Gastrointestinal gene delivery by cyclodextrins—In vitro quantification of extracellular barriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 390–399. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Ogier, J.R.; Desgranges, S.; Darcy, R.; O’Driscoll, C. Anisamide-targeted cyclodextrin nanoparticles for siRNA delivery to prostate tumours in mice. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7775–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Moscoso, A.; Vercauteren, D.; Rejman, J.; Benito, J.M.; Ortiz Mellet, C.; De Smedt, S.C.; Fernández, J.M.G. Insights in cellular uptake mechanisms of pDNA-polycationic amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles (CDplexes). J. Controll. Release 2010, 143, 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Kauscher, U.; Samanta, A.; Ravoo, B.J. Photoresponsive vesicle permeability based on intramolecular host-guest inclusion. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valli, L.; Giancane, G.; Mazzaglia, A.; Scolaro, L.M.; Conoci, S.; Sortino, S. Photoresponsive multilayer films by assembling cationic amphiphilic cyclodextrins and anionic porphyrins at the air/water interface. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1660–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Seyedi, S.M.; Sadeghian, H.; Jabbari, A.; Assadi, A.; Momeni, H. Design and synthesis of a new series of amphiphilic peptide-β-cyclodextrins as phase transfer carriers for glucosamine. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 6754–6760. [Google Scholar]
- Angelova, A.; Ringard-Lefebvre, C.; Baszkin, A. Drug-cyclodextrin association constants determined by surface tension and surface pressure measurements. I. Host-guest complexation of water soluble drugs by cyclodextrins: Polymyxin B-beta-cyclodextrin system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 212, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Angelova, A.; Ringard-Lefebvre, C.; Baszkin, A. Drug-cyclodextrin association constants determined by surface tension and surface pressure measurements. II. Sequestration of water insoluble drugs from the air/water interface: Retinol-beta-cyclodextrin system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 212, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Yaméogo, J.B.G.; Gèze, A.; Choisnard, L.; Putaux, J.-L.; Semdé, R.; Wouessidjewe, D. Progress in developing amphiphilic cyclodextrin-based nanodevices for drug delivery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 526–541. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, P.X. Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular systems for drug delivery: Recent progress and future perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, M.; Kurkov, S.V.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Self-assembled cyclodextrin aggregates and nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roux, M.; Perly, B.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F. Self-assemblies of amphiphilic cyclodextrins. Eur. Biophys. J. 2007, 36, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Yan, Y.; Huang, J. Versatility of cyclodextrins in self-assembly systems of amphiphiles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Fu, P.; Shen, X.; Gao, H. Cyclodextrin-based aggregates and characterization by microscopy. Micron 2008, 39, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Loh, X.J. Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular architectures: Synthesis, structures, and applications for drug and delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1000–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallas, F.; Darcy, R. Amphiphilic cyclodextrins—Advances in synthesis and supramolecular chemistry. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 2008, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Polysaccharides-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Si, J.; Tang, J.; Sui, M.; Shen, Y. Jellyfish-shaped amphiphilic dendrimers: Synthesis and formation of extremely uniform aggregates. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Ardoy, A.; Guilloteau, N.; Di Giorgio, C.; Vierling, P.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F.; Ortiz Mellet, C.; García Fernandez, J.-M. β-Cyclodextrin-based polycationic amphiphilic “click” clusters: Effect of structural modifications in their DNA complexing and delivery properties. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 5882–5894. [Google Scholar]
- Ghera, B.B.; Perret, F.; Chevalier, Y.; Parrot-Lopez, H. Novel nanoparticles made from amphiphilic perfluoroalkyl alpha-cyclodextrin derivatives: Preparation, characterization and application to the transport of acyclovir. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 375, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.-D.; Tang, G.-P.; Chu, P.K. Cyclodextrin-based host-guest supramolecular nanoparticles for delivery: From design to applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 7, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zerkoune, L.; Angelova, A.; Lesieur, S. Nano-Assemblies of Modified Cyclodextrins and Their Complexes with Guest Molecules: Incorporation in Nanostructured Membranes and Amphiphile Nanoarchitectonics Design. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 741-765. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030741
Zerkoune L, Angelova A, Lesieur S. Nano-Assemblies of Modified Cyclodextrins and Their Complexes with Guest Molecules: Incorporation in Nanostructured Membranes and Amphiphile Nanoarchitectonics Design. Nanomaterials. 2014; 4(3):741-765. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030741
Chicago/Turabian StyleZerkoune, Leïla, Angelina Angelova, and Sylviane Lesieur. 2014. "Nano-Assemblies of Modified Cyclodextrins and Their Complexes with Guest Molecules: Incorporation in Nanostructured Membranes and Amphiphile Nanoarchitectonics Design" Nanomaterials 4, no. 3: 741-765. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030741
APA StyleZerkoune, L., Angelova, A., & Lesieur, S. (2014). Nano-Assemblies of Modified Cyclodextrins and Their Complexes with Guest Molecules: Incorporation in Nanostructured Membranes and Amphiphile Nanoarchitectonics Design. Nanomaterials, 4(3), 741-765. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030741