Inclusion of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles into Virus-Like Peptide Nanocapsules Self-Assembled from Viral β-Annulus Peptide
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Self-Assembly of ZnO-Binding β-Annulus Peptide

2.2. Preparation and UV-Vis Spectra of ZnO Nanoparticles

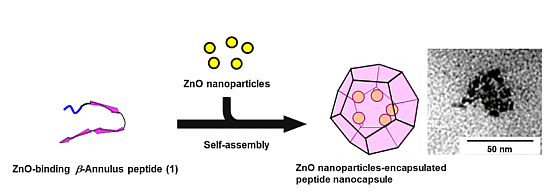
2.3. Inclusion of ZnO Nanoparticles into Peptide Nanocapsules



2.4. Fluorescence Spectra of ZnO Nanoparticles Included in Peptide Nanocapsule

3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Syntheses of Peptides
3.3. Syntheses of ZnO Nanoparticle
3.4. Inclusion of ZnO Nanoparticles into Peptide Nanocapsules
3.5. Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles in the Presence of Peptide 1
3.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements
3.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Alivisatos, A.P. Perspectives on the physical chemistry of semiconductor nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 13226–13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, T.; O’Brien, P.; Pickett, N.L. Nanocrystalline semiconductors: Synthesis, properties, and perspectives. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3843–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.H.; Cui, Y.Y.; Levenson, R.M.; Chung, L.W.K.; Nie, S.M. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biju, V.; Itoh, T.; Anas, A.; Sujith, A.; Ishikawa, M. Semiconductor quantum dots and metal nanoparticles: Syntheses, optical properties, and biological applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 2469–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.M.; Duan, H.W.; Mohs, A.M.; Nie, S.M. Bioconjugated quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1226–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zrazhevskiy, P.; Sena, M.; Gao, X.H. Designing multifunctional quantum dots for bioimaging, detection, and drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4326–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, T.; Bakhshi, R.; Petrova, D.; Pocock, R.; Imani, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4717–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijken, A.; Meulenkamp, E.A.; Vanmaekelbergh, D.; Meijerink, A. The kinetics of the radiative and nonradiative processes in nanocrystalline ZnO particles upon photoexcitation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Kitai, A.H.; Mascher, P. Point defects and luminescence centres in zinc oxide and zinc oxide doped with manganese. J. Lumin. 1992, 54, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.S.; Li, W.L.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO: Zn with green emission at low temperature with reduction process. Solid State Commun. 2005, 135, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Shibamoto, S.; Okuyama, K. Synthesis of ZnO/SiO2 nanocomposites emitting specific luminescence colors. Opt. Mater. 2004, 26, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.M.; Xu, Y.; Ren, O.G.; Xia, Y.Y. Stable aqueous ZnO@polymer core-shell nanoparticles with tunable photoluminescence and their application in cell imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7522–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, P.; Hines, D.A.; Kamat, P.V. Recent advances in quantum dot surface chemistry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3041–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.M.; Arosio, P. Ferritins: Molecular properties, iron storage function and cellular regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1275, 161–203. [Google Scholar]
- Massover, W.H. Ultrastructure of ferritin and apoferritin: A review. Micron 1993, 24, 389–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K.W.; Mann, S. Small-scale structures in biomineralisation and biomimetic materials chemistry. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 3, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Suzuki, M.; Goto, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Nagayama, K.; Watanabe, Y. Size-selective olefin hydrogenation by a Pd nanocluster provided in an apo-ferritin cage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2527–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez, N.; Sanchez, P.; Dominguez-Vera, J.M. Preparation of Cu and CuFe prussian blue derivative nanoparticles using the apoferritin cavity as nanoreactor. Dalton Trans. 2005, 15, 2492–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez, N.; Sanchez, P.; Dominguez-Vera, J.M.; Soriano-Portillo, A.; Clemente-Leon, M.; Coronado, E. Apoferritin-encapsulated Ni and Co superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 2757–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Swift, J.; Butts, C.A.; Yerubandi, V.; Dmochowski, I.J. Structure and activity of apoferritin-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 101, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.K.W.; Mann, S. Biomimetic synthesis of cadmium sulfide-ferritin nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 1996, 8, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, I.; Hayashi, J.; Hara, M. Bio-template synthesis of uniform CdSe nanoparticles using cage-shaped protein, apoferritin. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 1158–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahori, K.; Morioka, T.; Yamashita, I. The optimization of CdSe nanoparticles synthesis in the apoferritin cavity. Phys. Stat. Sol. 2006, 203, 2658–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahori, K.; Yoshizawa, K.; Muraoka, M.; Yamashita, I. Fabrication of ZnSe nanoparticles in the apoferritin cavity by designing a slow chemical reaction system. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6393–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, K.; Iwahori, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Yamashita, I. Fabrication of gold sulfide nanoparticles using the protein cage of apoferritin. Chem. Lett. 2006, 35, 1192–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennequin, B.; Turyanska, L.; Ben, T.; Beltran, A.M.; Molina, S.I.; Li, M.; Mann, S.; Patane, A.; Thomas, N.R. Aqueous near-infrared fluorescent composites based on apoferritin-encapsulated PbS quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3592–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzumoto, Y.; Okuda, M.; Yamashita, I. Fabrication of zinc oxide semiconductor nanoparticles in the apoferritin cavity. Cryst. Grow. Des. 2012, 12, 4130–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branden, C.; Tooze, J. Introduction to Protein Structure, 2nd ed.; Garland Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, T.; Young, M. Viruses: Making friends with old foes. Science 2006, 312, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, N.F.; Evans, D.J. Utilisation of plant viruses in bionanotechnology. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 2891–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, N.F.; Lin, T.; Lomonossoff, G.P.; Johnson, J.E. Structure-based engineering of an icosahedral virus for nanomedicine and nanotechnology. Viruses Nanotechnol. 2009, 327, 23–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bronstein, L.M. Virus-based nanoparticles with inorganic cargo: What does the future hold? Small 2011, 7, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillitzer, E.; Willits, D.; Young, M.; Douglas, T. Chemical modification of a viral cage for multivalent presentation. Chem. Commun. 2002, 20, 2390–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, L.; Guenther, R.H.; Lommel, S.A.; Franzen, S. Infusion of dye molecules into red clover necrotic mosaic virus. Chem. Commun. 2008, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wong, S.M.; Lim, L.-Y. Folic acid-conjugated protein cages of a plant virus: Anovel deliveryplatform for doxorubicin. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comellas-Aragonès, M.; Engelkamp, H.; Claessen, V.I.; Sommerdijik, N.A.J.M.; Rowan, A.E.; Christianen, P.C.M.; Maan, J.C.; Verduin, B.J.M.; Cornelissen, J.J.L.M.; Nolte, R.J.M. A virus-based single-enzyme nanoreactor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Minten, I.J.; Hendriks, L.J.A.; Nolte, R.J.M.; Cornelissen, J.J.L.M. Controlled encapsulation of multiple proteins in virus capsids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17771–17773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Comellas-Aragonès, M.; de la Escosura, A.; Dirks, A.T.J.; van der Ham, A.; Fusté-Cuñé, A.; Cornelissen, J.J.L.M.; Nolte, R.J.M. Controlled integration of polymers into viral capsids. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3141–3147. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Kwak, E.S.; Stein, B.; Kao, C.C.; Dragnea, B. Packaging of gold particles in viral capsids. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Daniel, M.C.; Quinkert, Z.T.; De, M.; Stein, B.; Bowman, V.D.; Chipman, P.R.; Rotello, V.M.; Kao, C.C.; Dragnea, B. Nanoparticle-templated assembly of viral protein cages. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, L.; Guenther, R.H.; Basnayake, V.R.; Lommel, S.A.; Franzen, S. Controlled encapsidation of gold nanoparticles by a viral protein shell. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4502–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.L.; Bronstein, L.M.; Retrum, J.; Dufort, C.; Tsvetkova, I.; Aniagyei, S.; Stein, B.; Stucky, G.; McKenna, B.; Remmes, N.; et al. Self-assembled virus-like particles with magnetic cores. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, Z.P.; Li, F.; Men, D.; Deng, J.Y.; Wei, H.P.; Zhang, X.E.; Cui, Z.Q. Quantum dot-induced viral capsid assembling in dissociation buffer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, S.K.; Goicochea, N.L.; Daniel, M.C.; Murali, A.; Bronstein, L.; De, M.; Stein, B.; Rotello, V.M.; Kao, C.C.; Dragnea, B. Quantum dot encapsulation in viral capsids. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuurua, K. Rational design of self-assembled proteins and peptides for nano- and micro-sized architectures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2942–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakers, B.E.I.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Lowik, D. Molecular tools for the construction of peptide-based materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2743–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, K.; Watanabe, K.; Matsuzaki, T.; Sakurai, K.; Kimizuka, N. Self-assembled synthetic viral capsids from a 24-mer viral peptide fragment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9662–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, K. Construction of spherical virus-inspired peptide nanoassemblies. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, K.; Watanabe, K.; Matsushita, Y.; Kimizuka, N. Guest-binding behavior of peptide nanocapsules self-assembled from viral peptide fragments. Polym. J. 2013, 45, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, C.K.; Dai, H.X.; Sastry, M.S.R.; Sarikaya, M.; Schwartz, D.T.; Baneyx, F. Identification and characterization of Cu2O- and ZnO-binding polypeptides by Escherichia coli cell surface display: Toward an understanding of metal oxide binding. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 87, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergaard, K.; Sorensen, J.K.; Schembri, M.A.; Klemm, P. Sequestration of zinc oxide by fimbrial designer chelators. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golec, P.; Karczewska-Golec, J.; Los, M.; Wegrzyn, G. Novel ZnO-binding peptides obtained by the screening of a phage display peptide library. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Umetsu, M.; Mizuta, M.; Tsumoto, K.; Ohara, S.; Takami, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kumagai, I.; Adschiri, T. Bioassisted room-temperature immobilization and mineralization of zinc oxide—The structural ordering of ZnO nanoparticles into a flower-type morphology. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2571–2575. [Google Scholar]
- Okochi, M.; Sugita, T.; Furusawa, S.; Umetsu, M.; Adschiri, T.; Honda, H. Peptide array-based characterization and design of ZnO-high affinity peptides. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 106, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HCVAHR sequence might be adsorbed on ZnO surface through coordination bonds with His and Cys residues.
- Uekawa, N.; Yamazaki, A.; Ishii, S.; Kojima, T.; Kakegawa, K. Synthesis of a stable sol of ZnO nanoparticles by low-temperature heating of Zn(OH)2 in ethylene glycol containing Zn2+ ions. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 118, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenkamp, E.A. Synthesis and growth of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 5566–5572. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.W.; Yu, X.A.; Lei, B.F.; Liu, P.Y.; Mai, W.J. Novel blue-violet photoluminescence from sputtered ZnO thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5437–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, H.J. Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline ZnO particles from a hydrothermal process. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Cao, X.L.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L. Enhancement of the ultraviolet emission of ZnO nanostructures by polyaniline modification. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 446, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujita, S.; Matsuura, K. Inclusion of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles into Virus-Like Peptide Nanocapsules Self-Assembled from Viral β-Annulus Peptide. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 778-791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030778
Fujita S, Matsuura K. Inclusion of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles into Virus-Like Peptide Nanocapsules Self-Assembled from Viral β-Annulus Peptide. Nanomaterials. 2014; 4(3):778-791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030778
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujita, Seiya, and Kazunori Matsuura. 2014. "Inclusion of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles into Virus-Like Peptide Nanocapsules Self-Assembled from Viral β-Annulus Peptide" Nanomaterials 4, no. 3: 778-791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030778
APA StyleFujita, S., & Matsuura, K. (2014). Inclusion of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles into Virus-Like Peptide Nanocapsules Self-Assembled from Viral β-Annulus Peptide. Nanomaterials, 4(3), 778-791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano4030778