A Fast Response Ammonia Sensor Based on Coaxial PPy–PAN Nanofiber Yarn
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of the Coaxial PPy–PAN Nanofiber Yarns
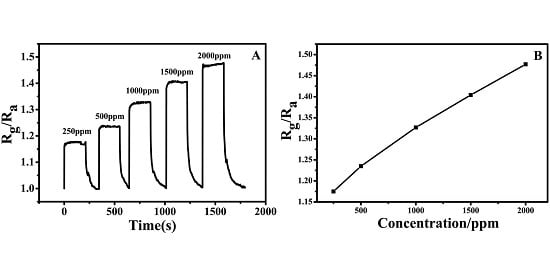
2.2. NH3 Sensing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. The Fabrication of the PAN Nanofiber Yarns
4.3. Polymerization of PPy on the Surface of the PAN Nanofiber Yarn
4.4. Characterization
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPy | polypyrrole |
| PAN | polyacrylonitrile |
| p-TSA | p-toluenesulfonic acid |
| PANI | polyaniline |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| ESEM | environment scanning electron microscopy |
| FESEM | field emission scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| FTIR | fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
References
- Martinelli, G.; Carotta, M.C.; Ferroni, M.; Sadaoka, Y.; Traversa, E. Screen-printed perovskite-type thick films as gas sensors for environmental monitoring. Sens. Actuators B 1999, 55, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshak, K.; Velusamy, V.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa-Stasiak, K.; Adley, C. Conducting polymers and their applications to biosensors: Emphasizing on foodborne pathogen detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 1942–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Bashur, C.A.; Goldstein, A.S.; Schmidt, C.E. Polypyrrole-coated electrospun plga nanofibers for neural tissue applications. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.D. Diverse applications of electronic-nose technologies in agriculture and forestry. Sensors 2013, 13, 2295–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Sridevi, S.; Pitchiah, R. Indoor air quality monitoring using wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the 2012 Sixth International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Kolkata, India, 18–21 December 2012; pp. 422–427.
- Yedavalli, R.K.; Belapurkar, R.K. Application of wireless sensor networks to aircraft control and health management systems. J. Control. Theory Appl. 2011, 9, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M.; Nicole, L. Applications of advanced hybrid organic–inorganic nanomaterials: From laboratory to market. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 696–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.R.; Menegazzo, N.; Riley, A.E.; Brons, C.H.; DiSanzo, F.P.; Givens, J.L.; Martin, J.L.; Disko, M.M.; Mizaikoff, B. Infrared hollow waveguide sensors for simultaneous gas phase detection of benzene, toluene, and xylenes in field environments. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6141–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshak, K.; Moore, E.; Lyons, G.; Harris, J.; Clifford, S. A review of gas sensors employed in electronic nose applications. Sens. Rev. 2004, 24, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janata, J.; Josowicz, M. Conducting polymers in electronic chemical sensors. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotcenkov, G. Metal oxides for solid-state gas sensors: What determines our choice? Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 139, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas sensors based on conducting polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, E.; Kim, T.; Park, H.-W.; You, S.A.; Yoon, H.; Jang, J. Multidimensional conducting polymer nanotubes for ultrasensitive chemical nerve agent sensing. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2797–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, P.; Lee, H.B.; Hong, S.; Lee, I.; Yeo, J.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, D.; Ko, S.H. Room-temperature nanosoldering of a very long metal nanowire network by conducting-polymer-assisted joining for a flexible touch-panel application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4171–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeger, A.J. Semiconducting and metallic polymers: The fourth generation of polymeric materials (nobel lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2591–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Oh, J.H.; Stucky, G.D. Fabrication of ultrafine conducting polymer and graphite nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4016–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, M.; Alizadeh, N. Methanol selective gas sensor based on nano-structured conducting polypyrrole prepared by electrochemically on interdigital electrodes for biodiesel analysis. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 183, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Wu, S. Polypyrrole-coated SnO2 hollow spheres and their application for ammonia sensor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 1662–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carquigny, S.; Sanchez, J.-B.; Berger, F.; Lakard, B.; Lallemand, F. Ammonia gas sensor based on electrosynthesized polypyrrole films. Talanta 2009, 78, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josowicz, M.; Janata, J. Suspended gate field effect transistors modified with polypyrrole as alcohol sensor. Anal. Chem. 1986, 58, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.; Yang, J.; Lin, C. Recognition of alcohol vapor molecules by simultaneous measurements of resistance changes on polypyrrole-based composite thin films and mass changes on a piezoelectric crystal. Sens. Actuators B 2001, 75, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Bae, J. Carbon nanofiber/polypyrrole nanocable as toxic gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 122, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.-S.; Wang, S.-H. On the sensitivity of conductimetric acetone gas sensor based on polypyrrole and polyaniline conducting polymers. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 185, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Luo, T.; Li, M.; Liu, J. A novel ammonia sensor based on high density, small diameter polypyrrole nanowire arrays. Sens. Actuators B 2009, 142, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ban, H.; Yang, M. Highly sensitive NH3 gas sensors based on novel polypyrrole-coated SnO2 nanosheet nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 224, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milella, E.; Musio, F.; Alba, M. Polypyrrole LB multilayer sensitive films for odorants. Thin Solid Films 1996, 284, 908–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachhav, S.G.; Patil, D.R. Study of polypyrrole-coated mwcnt nanocomposites for ammonia sensing at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Qin, X.-H. Uniaxially aligned polyacrylonitrile nanofiber yarns prepared by a novel modified electrospinning method. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-S.; Kim, W.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Hong, S.-H.; Yu, W.-R. Fabrication of SnO2 nanotube microyarn and its gas sensing behavior. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Song, W.; Burugapalli, K.; Moussy, F.; Li, Y.-L.; Zhong, X.-H. Nano-yarn carbon nanotube fiber based enzymatic glucose biosensor. Nanotechnology 2010, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Bradford, P.D.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, Q.; Yuan, F.-G.; Zhu, Y. Carbon nanotube yarn strain sensors. Nanotechnology 2010, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randeniya, L.K.; Martin, P.J.; Bendavid, A.; McDonnell, J. Ammonia sensing characteristics of carbon-nanotube yarns decorated with nanocrystalline gold. Carbon 2011, 49, 5265–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Yoon, H. Formation mechanism of conducting polypyrrole nanotubes in reverse micelle systems. Langmuir 2005, 21, 11484–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Lim, B. Facile fabrication of inorganic-polymer core–shell nanostructures by a one-step vapor deposition polymerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5600–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, K.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Hwang, H.R.; Lee, Y.H. Enhanced sensitivity of a gas sensor incorporating single-walled carbon nanotube–polypyrrole nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Yoon, H. Facile fabrication of polypyrrole nanotubes using reverse microemulsion polymerization. Chem. Commun. 2003, 720–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetiner, S.; Karakas, H.; Ciobanu, R.; Olariu, M.; Kaya, N.U.; Unsal, C.; Kalaoglu, F.; Sarac, A.S. Polymerization of pyrrole derivatives on polyacrylonitrile matrix, FTIR–ATR and dielectric spectroscopic characterization of composite thin films. Synth. Metals 2010, 160, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Zheng, W.; Wang, C. Fabrication of semiconductor nanostructures on the outer surfaces of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers by in-situ electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 2556–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, G.; Küçükyavuz, Z.; Küçükyavuz, S. Conductive copolymers of polyaniline, polypyrrole and poly(dimethylsiloxane). Synth. Metals 2005, 151, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Chemical synthesis of coral-like nanowires and nanowire networks of conducting polypyrrole. Synth. Metals 2003, 139, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Deng, S. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of CO2, CH4, N2O, and NH3 on ordered mesoporous carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, G.; Lundström, I.; Liedberg, B.; Wu, C.; Inganäs, O.; Wennerström, O. The interaction between ammonia and poly(pyrrole). Synth. Metals 1989, 31, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwood, D.; Josowicz, M. Work function and spectroscopic studies of interactions between conducting polymers and organic vapors. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. A Fast Response Ammonia Sensor Based on Coaxial PPy–PAN Nanofiber Yarn. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6070121
Liu P, Wu S, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Qin X. A Fast Response Ammonia Sensor Based on Coaxial PPy–PAN Nanofiber Yarn. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(7):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6070121
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Penghong, Shaohua Wu, Yue Zhang, Hongnan Zhang, and Xiaohong Qin. 2016. "A Fast Response Ammonia Sensor Based on Coaxial PPy–PAN Nanofiber Yarn" Nanomaterials 6, no. 7: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6070121
APA StyleLiu, P., Wu, S., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., & Qin, X. (2016). A Fast Response Ammonia Sensor Based on Coaxial PPy–PAN Nanofiber Yarn. Nanomaterials, 6(7), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6070121