Cationic Biomimetic Particles of Polystyrene/Cationic Bilayer/Gramicidin for Optimal Bactericidal Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
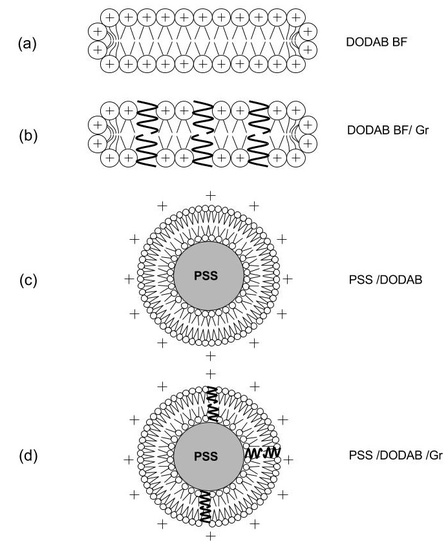
2.1. Physical Properties of the Dispersions
2.2. Microbicidal Activity of the Cationic Biomimetic NPs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of the Lipid Dispersions
4.3. Preparation of DODAB/Gr Dispersions
4.4. Preparation of PSS/DODAB and PSS/DODAB/Gr Dispersions
4.5. Physical Characterization of the Dispersions by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
4.6. Bacterial Growth and Cell Viability from Plating and CFU Counting
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biomimetic Systems in Nanomedicine. In Handbook of Nanobiomedical Research: Fundamentals, Applications and Recent Developments; Torchilin, V., Ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 401–456. ISBN 978-981-4520-70-6. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Barbassa, L.; de Melo, L.D. Antimicrobial Biomimetics. In Biomimetics Based Applications; George, A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 227–284. ISBN 978-953-307-195-4. [Google Scholar]
- Campanhã, M.T.N.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between cationic liposomes and bacteria: the physical-chemistry of the bactericidal action. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melo, L.D.; Palombo, R.R.; Petri, D.F.S.; Bruns, M.; Pereira, E.M.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Structure-Activity Relationship for Quaternary Ammonium Compounds Hybridized with Poly(methyl methacrylate). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. The Versatile Dioctadecyldimethylammonium Bromide. In Application and Characterization of Surfactants; Najjar, R., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 157–181. ISBN 978-953-51-3325-4. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; de Melo Carrasco, L.D. Cationic Antimicrobial Polymers and Their Assemblies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9906–9946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; de Melo Carrasco, L.D. Novel Formulations for Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18040–18083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, D.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic nanoparticles for delivery of amphotericin B: preparation, characterization and activity in vitro. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2008, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanches, L.M.; Petri, D.F.S.; de Melo Carrasco, L.D.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. The antimicrobial activity of free and immobilized poly (diallyldimethylammonium) chloride in nanoparticles of poly (methylmethacrylate). J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Midmore, B.R. Synthetic bilayer adsorption onto polystyrene microspheres. Langmuir 1992, 8, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, H.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interactions between Bacteriophage DNA and Cationic Biomimetic Particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16422–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo Carrasco, L.D.; Sampaio, J.L.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Supramolecular Cationic Assemblies against Multidrug-Resistant Microorganisms: Activity and Mechanism of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6337–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbassa, L.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Supramolecular assemblies of rifampicin and cationic bilayers: Preparation, characterization and micobactericidal activity. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, D.B.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Synthetic Bilayer Fragments for Solubilization of Amphotericin B. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 244, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Fernández, L.; Hancock, R.E. Bacterial biofilm development as a multicellular adaptation: Antibiotic resistance and new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, L.D.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Antimicrobial Particles from Cationic Lipid and Polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12300–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Biomimetic nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raemdonck, K.; Braeckmans, K.; Demeester, J.; Smedt, S.C.D. Merging the best of both worlds: Hybrid lipid-enveloped matrix nanocomposites in drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 43, 444–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadinoto, K.; Sundaresan, A.; Cheow, W.S. Lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Bilayer vesicles and liposomes as interface agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2001, 30, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincopan, N.; Espíndola, N.M.; Vaz, A.J.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic supported lipid bilayers for antigen presentation. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 340, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincopan, N.; Espíndola, N.M.; Vaz, A.J.; da Costa, M.H.B.; Faquim-Mauro, E.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Novel immunoadjuvants based on cationic lipid: Preparation, characterization and activity in vivo. Vaccine 2009, 27, 5760–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Lipid Bilayer Fragments and Disks in Drug Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo Carrasco, L.D.; Bertolucci, R.J.; Ribeiro, R.T.; Sampaio, J.L.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Nanostructures against Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragioto, D.A.; Carrasco, L.D.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Novel gramicidin formulations in cationic lipid as broad-spectrum microbicidal agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, C.A.; Olivares-Ortega, C.; Soto-Arriaza, M.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Interaction of gramicidin with DPPC/DODAB bilayer fragments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 3064–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Chaimovich, H. Preparation and characterization of large dioctadecyldimethylammonium chloride liposomes and comparison with small sonicated vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 733, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, P.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Kurihara, K. Dihexadecyl phosphate monolayers: intralayer and interlayer interactions. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riool, M.; de Breij, A.; de Boer, L.; Kwakman, P.H.S.; Cordfunke, R.A.; Cohen, O.; Malanovic, N.; Emanuel, N.; Lohner, K.; Drijfhout, J.W.; et al. Controlled Release of LL-37-Derived Synthetic Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Peptides SAAP-145 and SAAP-276 Prevents Experimental Biomaterial-Associated Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondaveeti, S.; Damato, T.C.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Sierakowski, M.R.; Petri, D.F.S. Sustainable hydroxypropyl methylcellulose/xyloglucan/gentamicin films with antimicrobial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Koh, J.-J.; Liu, S.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Verma, C.S.; Beuerman, R.W. Membrane Active Antimicrobial Peptides: Translating Mechanistic Insights to Design. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Tao, J.; Zheng, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, F.; Wang, X. RGD conjugated liposome-hollow silica hybrid nanovehicles for targeted and controlled delivery of arsenic trioxide against hepatic carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Ortis, F.; Schumacher, R.I.; Armelin, M.C.S. Interactions between Cationic Vesicles and Cultured Mammalian Cells. Langmuir 1997, 13, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.M.A.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Adsorption of Cationic Lipid Bilayer onto Flat Silicon Wafers: Effect of Ion Nature and Concentration. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 10070–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Haney, E.F.; Straus, S.K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Broad-Spectrum Anti-biofilm Peptide That Targets a Cellular Stress Response. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.M.A.; Kosaka, P.M.; Rosa, H.; Vieira, D.B.; Kawano, Y.; Petri, D.F.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Hybrid Materials from Intermolecular Associations between Cationic Lipid and Polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 9301–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, D.B.; Rapuano, R.; Lessa, M.M.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Counterion Effects on Properties of Cationic Vesicles. Langmuir 1998, 14, 7387–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schales, O.; Schales, S. A simple and accurate method for the determination of chloride in biological fluids. J. Biol. Chem. 1941, 140, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Sobral, C.N.C.; Soto, M.A.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Characterization of DODAB/DPPC vesicles. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2008, 152, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, E.; Morrison, I. Particle size distribution from analysis of quasi-elastic light scattering data. In Measurement of Suspended Particles by Quasi-Elastic Light Scattering; Dahneke, B.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 21, pp. 199–236. [Google Scholar]
- Chapin, K.; Lauderdale, T.L. Comparison of Bactec 9240 and Difco ESP blood culture systems for detection of organisms from vials whose entry was delayed. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






| Assembly | Dz (nm) | ζ (mV) | P | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DODAB BF | 59 ± 1 | 43 ± 2 | 0.215 ± 0.006 | [24] |
| DODAB BF | 55 ± 1 | 36 ± 2 | 0.248 ± 0.004 | This work |
| DODAB BF/Gr | 54 ± 1 | 72 ± 4 | 0.277 ± 0.004 | [24] |
| DODAB BF/Gr | 71 ± 1 | 58 ± 2 | 0.261 ± 0.003 | This work |
| PSS | 137 ± 2 * | - | - | - |
| PSS | 140 ± 2 | -43 ± 3 | 0.038 ± 0.013 | This work |
| PSS/DODAB | 149 ± 1 | 30 ± 2 | 0.049 ± 0.014 | [11] |
| PSS/DODAB/Gr | 150 ± 1 | 42 ± 2 | 0.039 ± 0.015 | This work |
| Assembly | MBC (mM)/log (CFU/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli | S. aureus | |
| DODAB BF | 0.063/7.6 | 0.063/3.4 |
| DODAB BF/Gr | 0.031/7.5 | 0.015/3.8 |
| PSS/DODAB | 0.059/7.5 | 0.471/4.6 |
| PSS/DODAB/Gr | 0.300/6.0 | 0.057/5.7 |
| Gr | 0.010/0.3 * | 0.010/2.1 * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xavier, G.R.S.; Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M. Cationic Biomimetic Particles of Polystyrene/Cationic Bilayer/Gramicidin for Optimal Bactericidal Activity. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120422
Xavier GRS, Carmona-Ribeiro AM. Cationic Biomimetic Particles of Polystyrene/Cationic Bilayer/Gramicidin for Optimal Bactericidal Activity. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(12):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120422
Chicago/Turabian StyleXavier, Gabriel R. S., and Ana M. Carmona-Ribeiro. 2017. "Cationic Biomimetic Particles of Polystyrene/Cationic Bilayer/Gramicidin for Optimal Bactericidal Activity" Nanomaterials 7, no. 12: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120422
APA StyleXavier, G. R. S., & Carmona-Ribeiro, A. M. (2017). Cationic Biomimetic Particles of Polystyrene/Cationic Bilayer/Gramicidin for Optimal Bactericidal Activity. Nanomaterials, 7(12), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120422