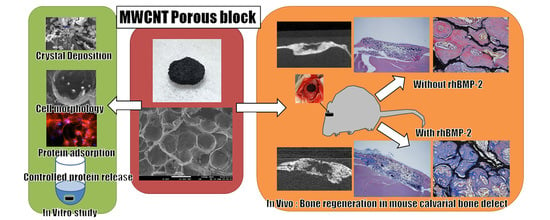
In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a Three-Dimensional Porous Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Scaffold for Bone Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Surface Observation by a Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.2. Mechanical Strength
2.3. Crystal Deposition Analysis
2.4. Qualitative Protein Adsorption Profiles
2.5. In Vitro Protein Releasing Assay
2.6. Degradation Assay
2.7. Cell Morphology
2.8. Cytotoxicity Determination
2.9. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Assay
2.10. Bone Regeneration of Mouse Critical-Sized Calvarial Defects
2.11. Bone Regeneration of Mouse Critical-Sized Calvarial Defects in Combination with Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (rhBMP-2)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Surface Observation by a Scanning Electron Microscopy
4.3. Mechanical Strength
4.4. Crystal Deposition Analysis
4.5. Qualitative Protein Adsorption Profiles
4.6. In Vitro Protein Releasing Assay
4.7. Degradation Assay
4.8. Cell Culture
4.9. Cell Morphology
4.10. Cytotoxicity Determination
4.11. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Assay
4.12. Bone Regeneration of Mouse Critical-Sized Calvarial Defects
4.13. Bone Regeneration of Mouse Critical-Sized Calvarial Defects in Combination with Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (rhBMP-2)
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oryan, A.; Alidadi, S.; Moshiri, A.; Maffulli, N. Bone regenerative medicine: Classic options, novel strategies, and future directions. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2014, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannoudis, P.V.; Dinopoulos, H.; Tsiridis, E. Bone substitutes: An update. Injury 2005, 36, S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Roy, M.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.F. On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krampera, M.; Pizzolo, G.; Aprili, G.; Franchini, M. Mesenchymal stem cells for bone, cartilage, tendon and skeletal muscle repair. Bone 2006, 39, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-david, D.; Srouji, S.; Shapira-Schweitzer, K.; Kossover, O.; Ivanir, E.; Kuhn, G.; Müller, R.; Seliktar, D.; Livne, E. Low dose BMP-2 treatment for bone repair using a PEGylated fibrinogen hydrogel matrix. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Kuboyama, N. A biodegradable porous composite scaffold of PGA/β-TCP for bone tissue engineering. Bone 2010, 46, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Katagiri, T.; Ikeda, T.; Wozney, J.M.; Rosen, V.; Wang, E.A.; Kahn, A.J.; Suda, T.; Yoshiki, S. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates osteoblastic maturation and inhibits myogenic differentiation in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, I.; Hwang, M.P.; Du, P.; Ko, J.; Ha, C.W.; Hee, S.; Park, K. Bioactive cell-derived matrices combined with polymer mesh scaffold for osteogenesis and bone healing. Biomaterials 2015, 50, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Katagiri, T.; Toyoda, H.; Takada, T.; Yanai, T.; Fukuda, T.; Chung, U.I.; Koike, T.; Takaoka, K.; Kamijo, R. Heparin potentiates the in Vivo ectopic bone formation induced by bone morphogenetic protein-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 23246–23253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Feng, Q.; Wang, M.; Guo, X.; Zheng, Q. Porous nano-HA/collagen/PLLA scaffold containing chitosan microspheres for controlled delivery of synthetic peptide derived from BMP-2. J. Control Release 2009, 134, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasaka, T.; Watari, F.; Sato, Y.; Tohji, K. Apatite formation on carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.L.; Church, J.S.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A.M. Tubular micro-scale multiwalled carbon nanotube-based scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Mizoguchi, T.; Nakamura, H.; Kawahara, I.; Narita, N.; Usui, Y.; Aoki, K.; Hara, K.; Haniu, H.; et al. Carbon nanotubes induce bone calcification by bidirectional interaction with osteoblasts. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, K.; Ishihara, A.; Mizoguchi, T.; Usui, Y.; Aoki, K.; Simizu, M.; Kato, H.; et al. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes specifically inhibit osteoclast differentiation and function. Nano. Lett. 2009, 9, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, J.; Pallela, R.; Kim, S. Applications of Carbon Nanomaterials in Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 3105–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K. Carbon Nanotube for Bone Repair. In Handbook of Polymer Nanocomposites. Processing, Performance and Application; Springer-Verlag New York, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, N.; Haniu, H.; Usui, Y.; Aoki, K.; Hara, K.; Takanashi, S.; Shimizu, M.; Narita, N.; Okamoto, M.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Safe Clinical Use of Carbon Nanotubes as Innovative Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6040–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, Y.; Aoki, K.; Narita, N.; Murakami, N.; Nakamura, I.; Nakamura, K.; Ishigaki, N.; Yamazaki, H.; Horiuchi, H.; Kato, H.; et al. Carbon nanotubes with high bone-tissue compatibility and bone-formation acceleration effects. Small 2008, 4, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, E.; Uo, M.; Takita, H.; Akasaka, T.; Watari, F.; Yokoyama, A. Multiwalled carbon nanotube-coating of 3D collagen scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Carbon 2011, 49, 3284–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Yang, W.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, H.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Q. Incorporation of carboxylation multiwalled carbon nanotubes into biodegradable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balani, K.; Anderson, R.; Laha, T.; Andara, M.; Tercero, J.; Crumpler, E.; Agarwal, A. Plasma-sprayed carbon nanotube reinforced hydroxyapatite coatings and their interaction with human osteoblasts in vitro. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felício-Fernandes, G.; Laranjeira, M.C.M. Calcium phosphate biomaterials from marine algae. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterisation. Quim. Nova 2000, 23, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joschek, S.; Nies, B.; Krotz, R.; Göpferich, A. Chemical and physicochemical characterization of porous hydroxyapatite ceramics made of natural bone. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haniu, H.; Saito, N.; Matsuda, Y.; Kim, Y.-A.; Park, K.C.; Tsukahara, T.; Usui, Y.; Aoki, K.; Shimizu, M.; Ogihara, N.; et al. Effect of dispersants of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on cellular uptake and biological responses. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 3295–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haniu, H.; Saito, N.; Matsuda, Y.; Tsukahara, T.; Maruyama, K.; Usui, Y.; Aoki, K.; Takanashi, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Nomura, H.; et al. Culture medium type affects endocytosis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in BEAS-2B cells and subsequent biological response. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgrabli, D.; Dachraoui, W.; Menard-Moyon, C.; Liu, X.J.; Begin, D.; Begin-Colin, S.; Bianco, A.; Gazeau, F.; Alloyeau, D. Carbon Nanotube Degradation in Macrophages: Live Nanoscale Monitoring and Understanding of Biological Pathway. ACS Nano. 2015, 9, 10113–10124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Aoki, K.; Usui, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Narita, N.; Ogihara, N.; Nakamura, K.; Ishigaki, N.; Sano, K.; Haniu, H.; et al. Evaluation of CNT toxicity by comparison to tattoo ink. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, H.; Takanashi, S.; Tanaka, M.; Haniu, H.; Aoki, K.; Okamoto, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Takizawa, T.; Usui, Y.; Oishi, A.; et al. Specific biological responses of the synovial membrane to carbon nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Gawronski, D.; Blum, J.; Goldberg, J.; Gronowicz, G. Differential response of human osteoblast-like cells to commercially pure (cp) titanium grades 1 and 4. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 46, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Feng, Q.; Cui, F.; Watari, F. The effect of calcium phosphate microstructure on bone-related cells in vitro. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degasne, I.; Basle, M.; Demais, V. Effects of roughness, fibronectin and vitronectin on attachment, spreading, and proliferation of human osteoblast-like cells (Saos-2) on titanium surfaces. Calcif. Tissue. Int. 1999, 64, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalfas, I.H. Principles of bone healing. Neurosurg. Focus 2001, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuls, R.G.M.; Jiya, T.U.; Smit, T.H. Scaffold stiffness influences cell behavior: Opportunities for skeletal tissue engineering. Open Orthop. J. 2008, 2, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X. Controlling Bovine Serum Albumin Release From Biomimetic Calcium Phosphate Coatings. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 2, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Meinel, L.; Hofmann, S.; Malhotra, A.; Volloch, V.; Kaplan, D. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 decorated silk fibroin films induce osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2004, 71, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Taylor, S.; Fu, K.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hanks, T.W.; Rao, A.M.; Sun, Y.P. Attaching Proteins to Carbon Nanotubes via Diimide-Activated Amidation. Nano. Lett. 2002, 2, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, M. Cross-links in carbon nanotube assembly introduced by using polyacrylonitrile as precursor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2013, 5, 8173–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, M. Fabrication of Cross-Linked Carbon Nanotube Foam Using Polymethylmethacrylate Microsphere as Template. J. Mater. Chem A. 2013, 1, 13984–13988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Woods, M.D.; Illingworth, K.D.; Niemeier, R.; Schafer, I.; Cady, C.; Filip, P.; El-Amin, S.F. Single walled carbon nanotube composites for bone tissue engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.H.; Yun, Y.P.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K.; Kim, S.E.; Song, H.R. Bone formation in a rat tibial defect model using carboxymethyl cellulose/BioC/bone morphogenic protein-2 hybrid materials. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Hospitals, I.; Magalhães, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004, 11, 36–43. [Google Scholar]











© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, M.; Sato, Y.; Zhang, M.; Haniu, H.; Okamoto, M.; Aoki, K.; Takizawa, T.; Yoshida, K.; Sobajima, A.; Kamanaka, T.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a Three-Dimensional Porous Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Scaffold for Bone Regeneration. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7020046
Tanaka M, Sato Y, Zhang M, Haniu H, Okamoto M, Aoki K, Takizawa T, Yoshida K, Sobajima A, Kamanaka T, et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a Three-Dimensional Porous Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Scaffold for Bone Regeneration. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(2):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7020046
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Manabu, Yoshinori Sato, Mei Zhang, Hisao Haniu, Masanori Okamoto, Kaoru Aoki, Takashi Takizawa, Kazushige Yoshida, Atsushi Sobajima, Takayuki Kamanaka, and et al. 2017. "In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a Three-Dimensional Porous Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Scaffold for Bone Regeneration" Nanomaterials 7, no. 2: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7020046
APA StyleTanaka, M., Sato, Y., Zhang, M., Haniu, H., Okamoto, M., Aoki, K., Takizawa, T., Yoshida, K., Sobajima, A., Kamanaka, T., Kato, H., & Saito, N. (2017). In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of a Three-Dimensional Porous Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Scaffold for Bone Regeneration. Nanomaterials, 7(2), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7020046