On the Beneficial Effect of MgCl2 as Electrolyte Additive to Improve the Electrochemical Performance of Li4Ti5O12 as Cathode in Mg Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Li4Ti5O12
3.2. Cyclic Voltammetry with the MgCl2-Electrolyte and Control Experiments
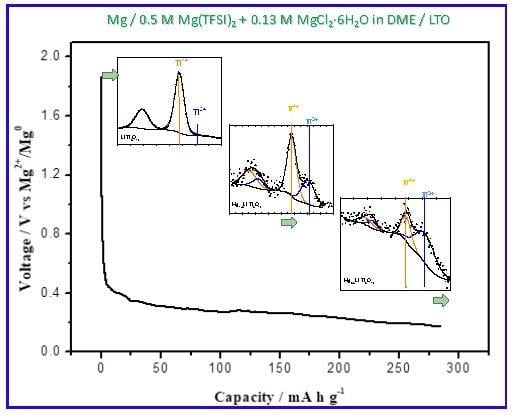
3.3. Extended Discharge and Capacity Retention
3.4. Effect of MgCl2 in Electrolytes on Charge-Discharge Properties (with Capacity Cut-Off)
3.5. Change in the Li4Ti5O12 Lattice by the Charge-Discharge
3.6. Changes in the Oxidation State by XPS
3.7. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gregory, T.D.; Hoffman, R.J.; Winterton, R.C. Nonaqueous electrochemistry of magnesium—Applications to energy-storage. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Desilvestro, J. Electrochemical insertion of magnesium in metal-oxides and sulfides from aprotic electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.D.; Shterenberg, I.; Gofer, Y.; Gershinsky, G.; Pour, N.; Aurbach, D. Mg rechargeable batteries: An on-going challenge. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtadi, R.; Mizuno Beilstein, F. Magnesium batteries: Current state of the art, issues and future perspectives. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1291–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccolo, M.; Giffin, G.A.; Vezzu, K.; Bertasi, F.; Alotto, P.; Guarnieri, M.; Di Noto, V. Molecular Relaxations in Magnesium Polymer Electrolytes via GHz Broadband Electrical Spectroscopy. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 2157–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebenow, C.; Yang, Z.; Lobitz, P. The electrodeposition of magnesium using solutions of organomagnesium halides, amidomagnesium halides and magnesium organoborates. Electrochem. Commun. 2000, 2, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Weissman, I.; Gofer, Y.; Levi, E. Nonaqueous magnesium electrochemistry and its application in secondary batteries. Chem. Rec. 2003, 3, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muldoon, J.; Bucur, C.B.; Gregory, T. Quest for Nonaqueous Multivalent Secondary Batteries: Magnesium and Beyond. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11683–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spahr, M.E.; Novak, P.; Haas, O.; Nesper, R. Electrochemical insertion of lithium, sodium, and magnesium in molybdenum(vi) oxide. J. Power Sources 1995, 54, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, R.E.; Han, R.; Hwang, J.; Gmitter, A.J.; Shterenberg, I.; Yoo, H.D.; Pour, N.; Aurbach, D. Novel electrolyte solutions comprising fully inorganic salts with high anodic stability for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.T.; Yamabuki, K.; Morita, M.; Tsutsumi, H.; Yoshimoto, N. Effects of alkoxide addition on the electrochemical deposition and dissolution in triglyme-based solution dissolving magnesium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide. J. Power Sources 2015, 278, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vittadello, M.; Stallworth, P.E.; Alamgir, F.M.; Suarez, S.; Abbrent, S.; Drain, C.M.; Di Noto, V.; Greenbaum, S.G. Polymeric delta-MgCl2 nanoribbons. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2006, 359, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Noto, V.; Lavina, S.; Longo, D.; Vidali, M. A novel electrolytic complex based on delta-MgCl2 and poly(ethylene glycol) 400. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffin, G.A. Ionic liquid-based electrolytes for “beyond lithium” battery technologies. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13378–13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, N.; Pan, B.; Saha-Shah, A.; Hubaud, A.A.; Vaughey, J.T.; Baker, L.A.; Liao, C.; Burrell, A.K. Role of Chloride for a Simple, Non-Grignard Mg Electrolyte in Ether-Based Solvents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16002–16008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebié, S.; Ngo, H.P.K.; Leprêtre, J.C.; Iojoiu, C.; Cointeaux, L.; Berthelot, R.; Alloin, F. Electrolyte Based on Easily Synthesized, Low Cost Triphenolate−Borohydride Salt for High Performance, Mg(TFSI)2-Glyme Rechargeable Magnesium Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28377–28385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebié, S.; Alloin, F.; Iojoiu, C.; Berthelot, R.; Leprêtre, J.C. Magnesium Anthracene System-Based Electrolyte as a Promoter of High Electrochemical Performance Rechargeable Magnesium Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5527–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shterenberg, I.; Salama, M.; Gofer, Y.; Aurbach, D. Hexafluorophosphate-Based Solutions for Mg Batteries and the Importance of Chlorides. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9472–9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Stolley, R.M.; Han, K.S.; Shao, Y.; Arey, B.W.; Washton, N.M.; Mueller, K.T.; Helm, M.L.; Sprenkle, V.L.; Liu, J.; et al. Highly active electrolytes for rechargeable Mg batteries based on a [Mg2(μ-Cl)2]2+ cation complex in dimethoxyethane. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 13307–13314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shterenberg, I.; Salama, M.; Yoo, H.D.; Gofer, Y.; Park, J.-B.; Sun, Y.-K.; Aurbach, D. Evaluation of (CF3SO2)2N−(TFSI) based electrolyte solutions for Mg batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A7118–A7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkening, M.; Iwaniak, W.; Heine, J.; Epp, V.; Kleinert, A.; Behrens, M.; Nuspl, G.; Bensch, W.; Heitjans, P. Microscopic Li Self-Diffusion Parameters in the Lithiated Anode Material Li4+xTi5O12 (0 ≤ x ≤ 3) Measured by 7Li Solid State NMR. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 6199–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T.; Liao, C.; Wang, Z.; Sun, K. Facile Preparation of Nanocrystalline Li4Ti5O12 and Its High Electrochemical Performance as Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 654–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zou, H.; Xiang, H.; Guo, X.; Zhou, T.; Wu, Y.; Xu, W.; Yan, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.G.; et al. Ultrathin Li4Ti5O12 Nanosheets as Anode Materials for Lithium and Sodium Storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16718–16726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Pan, H.; Lu, X.; Gu, L.; Hu, Y.S.; Li, H.; Armand, M.; Ikuhara, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Direct Atomic-Scale Confirmation of Three-Phase Storage Mechanism in Li4Ti5O12 Anodes for Room-Temperature Sodium-Ion Batteries. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1870–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Yin, Y.X.; Guo, Y.G. Size-dependent electrochemical magnesium storage performance of spinel lithium titanate. Chem. Asian. J. 2014, 9, 2099–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Lyu, Y.C.; Xiao, R.J.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y.X.; Yang, X.Q.; Li, H.; Gu, L.; Guo, Y.G. A highly reversible, low-strain Mg-ion insertion anode material for rechargeable Mg-ion batteries. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; NuLi, Y.; Wang, N.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Hirano, S. Effect of Mg2+/Li+ mixed electrolytes on a rechargeable hybrid battery with Li4Ti5O12 cathode and Mg anode. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3231–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Yao, H.-R.; Yin, Y.-X.; Gu, L.; Guo, Y.-G. Improving the Electrochemical Performance of the Li4Ti5O12 Electrode in a Rechargeable Magnesium Battery by Lithium-Magnesium Co-Intercalation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5757–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello, M.; Nacimiento, F.; Alcántara, R.; Lavela, P.; Ortiz, G.F.; Tirado, J.L. Nanobelts of Beta-Sodium Vanadate as Electrode for Magnesium and Dual Magnesium-Sodium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A2781–A2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohzuku, T.; Ueda, A.; Yamamoto, N. Zero-strain insertion material of Li[Li1/3Ti5/3]O4 for rechargeable lithium cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.J.; Lai, Q.Y.; Liu, D.Q.; Xu, Z.U.; Ji, X.Y. Synthesis by citric acid sol-gel method and electrochemical properties of Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium-ion battery. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 94, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muldoon, J.; Bucur, C.B.; Gregory, T. Fervent Hype behind Magnesium Batteries: An Open Call to Synthetic Chemists-Electrolytes and Cathodes Needed. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12064–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; He, Y.B.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Du, H.; Qin, X.; Lin, Z.; Li, B.; Kang, F. Large Polarization of Li4Ti5O12 Lithiated to 0 V at Large Charge/Discharge Rates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 18788–18796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchitchekova, D.; Ponrouch, A.; Verrelli, R.; Broux, T.; Frontera, C.; Sorrentino, A.; Barde, F.; Biskup, N.; Arroyo-de Dompablo, M.E.; Palacin, M.R. Electrochemical Intercalation of Calcium and Magnesium in TiS2: Fundamental Studies Related to Multivalent Battery Applications. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.W.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Salama, M.; Shterenberg, I.; Gofer, Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Yang, E.; Park, C.S.; Kim, J.S.; et al. The High Performance of Crystal Water Containing Manganese Birnessite Cathodes for Magnesium Batteries. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 4071–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, Y.; Okubo, M.; Hosono, E.; Kudo, T.; Zhou, H.; Ohishi, K. Suppressed Activation Energy for Interfacial Charge Transfer of a Prussian Blue Analog Thin Film Electrode with Hydrated Ions (Li+, Na+, and Mg2+). J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 10877–10882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Okubo, M.; Hosono, E.; Kudo, T.; Ohishi, K.; Okazawa, A.; Kojima, N.; Kurono, R.; Nishimura, S.-I.; Yamada, A. Electrochemical Mg2+ intercalation into a bimetallic CuFe Prussian blue analog in aqueous electrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 13055–13059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.-Y.; Lee, Y.-W.; Woo, S.W.; Koo, B.; Kim, J.-S.; Cho, J.; Lee, K.T.; Choi, N.-S. Magnesium (II) bis (trifluoromethane sulfonyl) imide-based electrolytes with wide electrochemical windows forrechargeable magnesium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 4063–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldon, L.; Kubiak, P.; Womes, M.; Jumas, J.C.; Olivier-Fourcade, J.; Tirado, J.L.; Corredor, J.I.; Pérez Vicente, C. Chemical and electrochemical Li-insertion into the Li4Ti5O12 spinel. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 5721–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, P.; Li, H.; Zhou, H. An unsymmetrical lithium-ion pathway between charge and discharge processes in a two-phase stage of Li4Ti5O12. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 9086–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, D.J.; Zheng, J.P.; Roy, D. Electrochemical examination of core–shell mediated Li+ transport in Li4Ti5O12 anodes of lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 2013, 240, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.R.; Yin, L.C.; Yi, T.F.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, R.S. Electrochemical performance and lithium-ion intercalation kinetics of submicron-sized Li4Ti5O12 anode material. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 547, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.S.; Benayad, A.; Choi, Y.M.; Park, K.S. Does Li4Ti5O12 need carbon in lithium ion batteries? Carbon-free electrode with exceptionally high electrode capacity. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.S.; Kim, R.H.; Baek, S.W.; Lee, K.S.; Park, K.; Benayad, A. Is Li4Ti5O12 a solid-electrolyte-interphase-free electrode material in Li-ion batteries? Reactivity between the Li4Ti5O12 electrode and electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, M.G.; Baggetto, L.; Balke, N.; Veith, G.M.; Seo, J.K.; Wang, Z.; Meng, Y.S. Elucidating the Phase Transformation of Li4Ti5O12 Lithiation at the Nanoscale. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4312–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucur, C.B.; Gregory, T.; Oliver, A.G.; Muldoon, J. Confession of a Magnesium Battery. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 3578–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Li4Ti5O12 | Mg0.85Li4Ti5O12 | Mg1.5Li4Ti5O12 | Mg2Li4Ti5O12 | Mg2.5Li4Ti5O12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IB-LVol(111)/nm | 82.5 | 70.8 | 57.9 | 74.8 | 60.1 |
| IB-LVol(311)/nm | 98.5 | 78.1 | 58.4 | 69.7 | 66.6 |
| IB-LVol(400)/nm | 98.0 | 67.7 | 63.7 | 76.0 | 64.3 |
| a/Å | 8.325(2) | 8.387(1) | 8.387(2) | 8.389(2) | 8.398(2) |
| V/Å3 | 577.02(1) | 590.16(1) | 570.09(2) | 590.40(1) | 592.47(1) |
| Ti4+/% | 100 | 78.7 | 64.4 | - | 33.6 |
| Ti3+/% | 0 | 21.3 | 35.6 | - | 66.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabello, M.; Ortiz, G.F.; Lavela, P.; Tirado, J.L. On the Beneficial Effect of MgCl2 as Electrolyte Additive to Improve the Electrochemical Performance of Li4Ti5O12 as Cathode in Mg Batteries. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030484
Cabello M, Ortiz GF, Lavela P, Tirado JL. On the Beneficial Effect of MgCl2 as Electrolyte Additive to Improve the Electrochemical Performance of Li4Ti5O12 as Cathode in Mg Batteries. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(3):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030484
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabello, Marta, Gregorio F. Ortiz, Pedro Lavela, and José L. Tirado. 2019. "On the Beneficial Effect of MgCl2 as Electrolyte Additive to Improve the Electrochemical Performance of Li4Ti5O12 as Cathode in Mg Batteries" Nanomaterials 9, no. 3: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030484
APA StyleCabello, M., Ortiz, G. F., Lavela, P., & Tirado, J. L. (2019). On the Beneficial Effect of MgCl2 as Electrolyte Additive to Improve the Electrochemical Performance of Li4Ti5O12 as Cathode in Mg Batteries. Nanomaterials, 9(3), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030484