Mimicking the Annulus Fibrosus Using Electrospun Polyester Blended Scaffolds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterizing IVD and AF Tissue
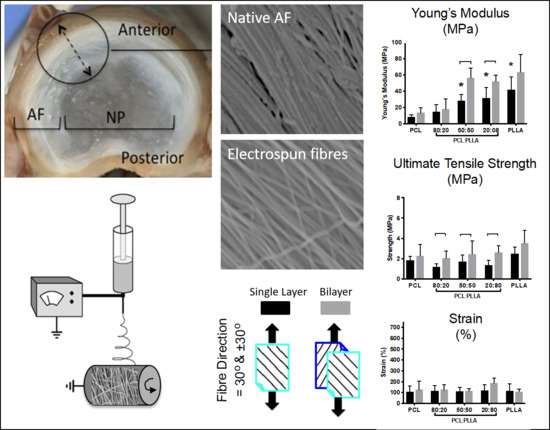
2.1.1. Lumbar Disc Dissection
2.1.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.1.3. Histology
2.2. Mimicking the AF Tissue Using Electrospinning
Scaffold Fabrication
2.3. Material Characterization of AF Electrospun Biomimics
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.3. Tensile Testing
2.3.4. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
2.4. In Vitro Cell Response to AF Electrospun Biomimics
2.4.1. Cell Culture
2.4.2. Cell Metabolic Activity
2.4.3. Cell Morphology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterizing the IVD and AF Tissue
3.2. Mimicking the AF Tissue
3.3. Material Characterization of AF Electrospun Biomimics
3.3.1. Fiber Properties
3.3.2. DSC
3.3.3. Tensile Testing
3.3.4. WCA
3.4. In Vitro Cell Response to AF Electrospun Biomimics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Weiner, B.K. Treatment of lumbar disc herniation: Evidence-based practice. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2010, 3, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Shimmer, A.L.; Li, X. The challenge and advancement of annulus fibrosus tissue engineering. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schollum, M.L.; Robertson, P.A.; Broom, N.D. A microstructural investigation of intervertebral disc lamellar connectivity: Detailed analysis of the translamellar bridges. J. Anat. 2009, 214, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, F.; Ahmed, A.M. Investigation of the laminate structure of lumbar disc anulus fibrosus. Spine 1990, 15, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosworth, L.A.; Rathbone, S.R.; Bradley, R.S.; Cartmell, S.H. Dynamic loading of electrospun yarns guides mesenchymal stem cells towards a tendon lineage. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 39, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shanti, R.M.; Tuan, R.S. Electrospinning Technology for Nanofibrous Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering. In Nanotechnologies for the Life Sciences; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen LBai, Y.; Liao, G.; Peng, E.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xie, X. Electrospun Poly(L-lactide)/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Blend Nanofibrous Scaffold: Characterization and Biocompatibility with Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Todo, M.; Harada, A.; Tsuji, H. Fracture Characterization of Biodegradableplla Polymer Blends. In Proceedings of the 16 th International Conference on Composite Materials Fracture Characterization of Biodegradable PLLA Polymer Blends, Kyoto, Japan, 8–13 July 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Boldt, J. Synthetic Biopolymers; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 308–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P. Effect of Collector on Electrospinning To Fabricate Aligned Nanofiber Effect of Collector on Electrospinning To Fabricate Aligned Nanofiber; National Institutes of Technology: Calicut (Kerela), Indian, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Doergens, A.; Roether, J.A.; Dippold, D.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Schubert, D.W. Identifying key processing parameters for the electrospinning of aligned polymer nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 2015, 140, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, I.; Ploegmakers, J.J.W.; Verkerke, G.J.; Veldhuizen, A.G. Comparative anatomical dimensions of the complete human and porcine spine. Eur. Spine J. 2010, 19, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yingling, V.R.; Callaghan, J.P.; McGill, S.M. The porcine cervical spine as a model of the human lumbar spine: An anatomical, geometric, and functional comparison. J. Spinal Disord. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, L.A.; Dewitte-Orr, S.J.; Gregory, D.E. A comparison between porcine, ovine, and bovine intervertebral disc anatomy and single lamella annulus fibrosus tensile properties. J. Morphol. 2016, 277, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Ghosh, P.; Jenkin, G.; Oehme, D.; Goldschlager, T. A Review of Animal Models of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Pathophysiology, Regeneration, and Translation to the Clinic. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5952165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, L.; Whittaker, P. Collagen and Picrosirius Red Staining: A Polarized Light Assessment of Fibrillar Hue and Spatial Distribution. Braz. J. Morphol. Sci. 2005, 22, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Montes, G.S.; Junqueira, L.C. The use of the Picrosirius-polarization method for the study of the biopathology of collagen. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 1991, 86 (Suppl. 3), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, D.S.; Hukins, D.W. Collagen fibril diameters and elastic fibres in the annulus fibrosus of human fetal intervertebral disc. J. Anat. 1981, 133, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Malašauskiene, J.; Milašius, R. Mathematical analysis of the diameter distribution of Electrospun nanofibres. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2010, 83, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, H.; Takeda, T. Three-dimensional observation of collagen framework of lumbar intervertebral discs. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1975, 46, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D.A.; Barnes, G.R.; Craig, A.S. A comparison of the size distribution of collagen fibrils in connective tissues as a function of age and a possible relation between fibril size distribution and mechanical properties. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1978, 203, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gentsch, R.; Boysen, B.; Lankenau, A.; Börner, H.G. Single-step electrospinning of bimodal fiber meshes for ease of cellular infiltration. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Gevelber, M. Investigation of electrospun fiber diameter distribution and process variations. J. Electrostat. 2010, 68, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, C. Solution Electrospinning of Nanofibers. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khajavi, R.; Abbasipour, M. Controlling Nanofiber Morphology by the Electrospinning Process. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y. Improving fiber alignment during electrospinning. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, P.; Chen, M.; Yang, H.; Li, B. The effect of the fibre orientation of electrospun scaffolds on the matrix production of rabbit annulus fibrosus-derived stem cells. Bone Res. 2015, 3, 15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsah, A.H.; Richardson, S.M.; Cartmell, S.H.; Bosworth, L.A. Mimicking the annulus fibrosus with electrospun nanofibre scaffolds. Eur. Cells Mater. 2016, 32, 2262. [Google Scholar]
- Bosworth, L.A.; Alam, N.; Wong, J.K.; Downes, S. Investigation of 2D and 3D electrospun scaffolds intended for tendon repair. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosworth, L.A. Fibrous Scaffolds Made by Electrospinning for Tendon Repair. Available online: https://www.britishsocietynanomedicine.org/assets/files/BSNanomedicine_Bosworth_AO1FINAL.pdf (accessed on 21 August 2017).
- Zhang, C.; Zhai, T.; Turng, L.S.; Dan, Y. Morphological, Mechanical, and Crystallization Behavior of Polylactide/Polycaprolactone Blends Compatibilized by l -Lactide/Caprolactone Copolymer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 9505–9511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakova, E.K.; Meszaros, L.; Maskova, G.; Blazkova, L.; Turcsan, T.; Lukas, D. Crystallinity of Electrospun and Centrifugal Spun Polycaprolactone Fibers: A Comparative Study. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, L.A.; Downes, S. Physicochemical characterisation of degrading polycaprolactone scaffolds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hadi, A.M.; Mohan, S.D.; Davis, F.J.; Mitchell, G.R. Enhancing the crystallization and orientation of electrospinning poly (lactic acid) (PLLA) by combining with additives. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degradasi, P.; Vitro, I.; Perancah, B.; Nano, G.; Gelatin, P. Comparison on in Vitro Degradation of Polycaprolactone and Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Nanofibrous Scaffold. Malay. J. Anal. Sci. 2017, 21, 627–632. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.C.; Chueh, J.Y.; Tseng, H.; Huang, H.M.; Lee, S.Y. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable PLA polymeric blends. Biomaterials 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício, T.; Domingos, M.; Gloria, A.; Bártolo, P. Characterisation of PCL and PCL/PLA scaffolds for tissue engineering. Procedia CIRP 2013, 5, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, D.L.; Weidenbaum, M.; Iatridis, J.C.; Ratcliffe, A.; Mow, V.C. Regional variation in tensile properties and biochemical composition of the human lumbar anulus fibrosus. Spine 1994, 19, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerurkar, N.L.; Elliott, D.M.; Mauck, R.L. Mechanics of oriented electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for annulus fibrosus tissue engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, T.P.; Nakasone, R.H.; Szczesny, S.E.; Elliott, D.M.; Mauck, R.L. Biaxial mechanics and inter-lamellar shearing of stem-cell seeded electrospun angle-ply laminates for annulus fibrosus tissue engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, T.P.; Nerurkar, N.L.; Jacobs, N.T.; Elliott, D.M.; Mauck, R.L. Fiber angle and aspect ratio influence the shear mechanics of oriented electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, D.M.; Setton, L.A. Anisotropic and inhomogeneous tensile behavior of the human anulus fibrosus: Experimental measurement and material model predictions. J. Biomech. Eng. 2001, 123, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebara SIatridis, J.C.; Setton, L.A.; Foster, R.J.; Mow, V.C.; Weidenbaum, M. Tensile properties of nondegenerate human lumbar anulus fibrosus. Spine 1996, 21, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, G.A.; Schulze-Bauer, C.A.J.; Feigl, G.; Regitnig, P. Single lamellar mechanics of the human lumbar anulus fibrosus. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2005, 3, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerurkar, N.L.; Baker, B.M.; Sen, S.; Wible, E.E.; Elliott, D.M.; Mauck, R.L. Nanofibrous biologic laminates replicate the form and function of the annulus fibrosus. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, C.O.; Murphy, J.G. Fiber orientation effects in simple shearing of fibrous soft tissues. J. Biomech. 2017, 64, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priest, C.; Albrecht, T.W.J.; Sedev, R.; Ralston, J. Asymmetric wetting hysteresis on hydrophobic microstructured surfaces. Langmuir 2009, 25, 5655–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šikalo, Š.; Tropea, C.; Ganić, E. Dynamic wetting angle of a spreading droplet. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2005, 29, 795–802. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, G.B.C.; Perea, G.N.R.; D’Avila, M.A.; Dias, C.G.B.T.; Zavaglia, C.A.C.; Arruda, A.C.F. Initial Study of Electrospinning PCL/PLLA Blends. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2011, 1, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadikhan, M.; Soleimani, M.; Parivar, K.; Yaghmaei, P. ADSCs on PLLA/PCL hybrid nanoscaffold and gelatin modification: Cytocompatibility and mechanical properties. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2015, 7, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oyama, H.T.T.; CortellaaIsabel, L.R.X.; Rosa, N.S.; Filho, L.E.R.; Hui, W.S.; Cestari, I.N.; Cestari, I.A. Assessment of the biocompatibility of the PLLA-PLCL scaffold obtained by electrospinning. Procedia Eng. 2015, 110, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruehlmann, S.B.; Rattner, J.B.; Matyas, J.R.; Duncan, N.A. Regional variations in the cellular matrix of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. J. Anat. 2002, 201, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu CLi, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, P.; Yang, H.; Li, B. Modulation of the gene expression of annulus fibrosus-derived stem cells using poly(ether carbonate urethane)urea scaffolds of tunable elasticity. Acta Biomater. 2016, 29, 228–238. [Google Scholar]







| PCL | PLLA | Total Crystallinity (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Ratio PCL:PLLA | Tm (°C) | ΔHf (J/g) | Crystallinity (%) | Tm (°C) | ΔHf (J/g) | Crystallinity (%) | |
| 100:0 | 56 | 50.67 | 36.32 | - | - | - | 36.32 |
| 80:20 | 55.23 | 35.81 | 26.71 | 160.2 | 5.98 | 6.43 | 32.10 |
| 50:50 | 56.24 | 19.2 | 13.76 | 164.6 | 13.9 | 14.93 | 28.69 |
| 20:80 | 55.33 | 8.63 | 6.42 | 163.2 | 27.28 | 22.87 | 29.29 |
| 0:100 | - | - | - | 161.1 | 36.22 | 38.95 | 38.95 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shamsah, A.H.; Cartmell, S.H.; Richardson, S.M.; Bosworth, L.A. Mimicking the Annulus Fibrosus Using Electrospun Polyester Blended Scaffolds. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040537
Shamsah AH, Cartmell SH, Richardson SM, Bosworth LA. Mimicking the Annulus Fibrosus Using Electrospun Polyester Blended Scaffolds. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(4):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040537
Chicago/Turabian StyleShamsah, Alyah H., Sarah H. Cartmell, Stephen M. Richardson, and Lucy A. Bosworth. 2019. "Mimicking the Annulus Fibrosus Using Electrospun Polyester Blended Scaffolds" Nanomaterials 9, no. 4: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040537
APA StyleShamsah, A. H., Cartmell, S. H., Richardson, S. M., & Bosworth, L. A. (2019). Mimicking the Annulus Fibrosus Using Electrospun Polyester Blended Scaffolds. Nanomaterials, 9(4), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040537