The Fluorescent Quenching Mechanism of N and S Co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Fe3+ and Hg2+ Ions and Their Application as a Novel Fluorescent Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Details
2.2. Materials
2.3. Synthesis of N-GQDs
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Detection of Metal Ions
2.6. Detection of Fe3+ and Hg2+ in Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fluorescent Quenching Mechanisms of N, S-GQDs with Fe3+ or Hg2+
3.2. Characterization of N, S-GQDS
3.3. Optical Analyses of N, S-GQDS
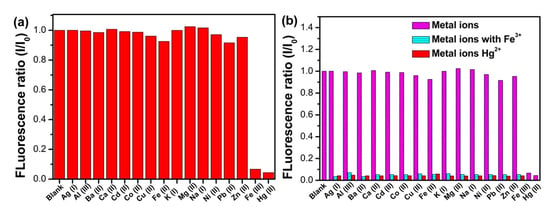
3.4. Selectivity of N, S-GQDs for Fe3+ and Hg2+ Detection
3.5. The Fluorescence Properties of N, S-GQDs under Acidity and Alkalinity Situations
3.6. Detection of Fe3+ and Hg2+ Using N, S-GQDs as a Sensor
3.7. Real Sample Detection Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, R.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Voelcker, N.H. Rhodamine-functionalized graphene quantum dots for detection of Fe3+ in cancer stem cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23958–23966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, H. Graphene quantum dots and their possible energy applications: A review. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2016, 16, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Shi, H.; He, X.; Wang, K.; He, D.; Yan, L.; Ye, X.; Tang, J.; Shangguan, J.; Luo, L. Masking agent-free and channel-switch-mode simultaneous sensing of Fe3+ and Hg2+ using dual-excitation graphene quantum dots. Analyst 2015, 140, 3925–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Pacheco, M.; Rojo, J.; Escarpa, A. Magnetocatalytic graphene quantum dots janus micromotors for bacterial endotoxin detection. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 7061–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Shen, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, J.; Xi, F.; Dong, X. Facile synthesis of sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots as fluorescent sensing probes for Ag+ ions detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.V. Photochemistry on nonreactive and reactive (semiconductor) surfaces. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 267–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, F.; Yan, F.; Bai, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X. The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: A review on mechanisms and applications. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, M. Static quenching of bovine serum albumin conjugated with small size CdS nanocrystalline quantum dots. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.-T.; Yang, J.-X.; Song, J.-M.; Chen, J.-S.; Niu, H.-L.; Mao, C.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Shen, Y.-H. Synthesis of high fluorescence graphene quantum dots and their selective detection for Fe3+ in aqueous solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Zhang, L.; Lan, C.; Zhao, J.; Su, Y.; Zhao, S. One-pot green synthesis of oxygen-rich nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and their potential application in pH-sensitive photoluminescence and detection of mercury(II) ions. Talanta 2015, 142, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisostomo, C.P.; Yao, L.-Z.; Huang, Z.-Q.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chuang, F.-C.; Lin, H.; Albao, M.A.; Bansil, A. Robust large gap two-dimensional topological insulators in hydrogenated III–V buckled honeycombs. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6568–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Ni, J. Strain induced phase transitions in silicene bilayers: A first principles and tight-binding study. AIP Adv. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhorge, Y.R.; Tsai, H.-T.; Huang, K.-F.; Pape, A.J.; Janaki, S.N.; Yen, Y.-P. A new pyrene-based Schiff-base: A selective colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensor for detection of Cu(II) and Fe(III). Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 130, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Tong, Y.; Guo, M. Iron chelators as potential therapeutic agents for Parkinsons disease. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2008, 4, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, N.; Govindaraju, T. Aldazine-based colorimetric sensors for Cu2+ and Fe3+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabner, B.J.; Turnbull, S.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A.; Allsop, D. Formation of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals from Aβ and α-synuclein as a possible mechanism of cell death in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajioka, R.S. Clinical consequences of iron overload in hemochromatosis homozygotes. Blood 2003, 101, 3351–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Hurrell, R.F. Nutritional iron deficiency. Lancet 2007, 370, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, F.; Majorani, C.; Amine, A.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. Hg2+ detection by measuring thiol groups with a highly sensitive screen-printed electrode modified with a nanostructured carbon black film. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 4209–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gou, X.; Blecha, J.; Cao, H. A highly selective pyrene based fluorescent sensor toward Hg2+ detection. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 3422–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchetti, R.; Zuurbier, M.; Jesenak, M.; Koppe, J.; Farah Ahmed, U.; Ceccatelli, S.; Pia Villa, M. Children’s health and mercury exposure. Acta Paediatr. 2006, 95, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wu, H.; Ding, J.; Fu, W.; Gan, L.; Li, Y. Mercury pollution in vegetables, grains and soils from areas surrounding coal-fired power plants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Yang, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, K. Facile synthesis of sulfur-doped carbon quantum dots from vitamin B1 for highly selective detection of Fe3+ ion. Opt. Mater. 2018, 77, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, M.D.; Lindan, P.J.D.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2717–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.H.; Almlof, J. General methods for geometry and wave function optimization. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 9768–9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Du, P.; Feng, X.; Wu, P.; Cai, C. Electrolyzing synthesis of boron-doped graphene quantum dots for fluorescence determination of Fe3+ ions in water samples. Talanta 2017, 164, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liao, L.; Xu, X.; Zou, M.; Liu, F.; Li, N. The electron-transfer based interaction between transition metal ions and photoluminescent graphene quantum dots (GQDs): A platform for metal ion sensing. Talanta 2013, 117, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, G.; Tan, X.; Qian, X.; Zhang, T.; Gui, J.; Yang, L.; Xie, X. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots with high quantum yield for colorimetric and fluorometric detection of ferric ions and in a fluorescent ink. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Peng, J.; Li, F.; Su, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, X. Phosphorus and chlorine co-doped carbon dots with strong photoluminescence as a fluorescent probe for ferric ions. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Tong, D.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, M. Red emitting and highly stable carbon dots with dual response to pH values and ferric ions. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Lv, J.; Wang, H.; Choi, M.M.F.; Bian, W. Graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots as an “off-on” fluorescent switch for determination of mercury(II) and sulfide. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, T.K.; Dinda, D.; Saha, S.K. Nitrogen, sulphur co-doped graphene quantum dot: An excellent sensor for nitroexplosives. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Secor, J.; Bandosz, T.J. Highly luminescent S-doped carbon dots for the selective detection of ammonia. Carbon 2017, 114, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta Chowdhury, A.; Doong, R. Highly sensitive and selective detection of nanomolar ferric ions using dopamine functionalized graphene quantum dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21002–21010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Du, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Tan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Sun, Z. Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-X.; Gao, H.; Li, X.-L. Synthesis and optical properties of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4615–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhu, J.; Fan, L.; Li, X. Sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots as a novel fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe3+. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10201–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangam, S.; Gupta, A.; Shakeel, A.; Bhattacharya, R.; Sharma, A.K.; Suhag, D.; Chakrabarti, S.; Garg, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Basu, B.; et al. Sustainable synthesis of single crystalline sulphur-doped graphene quantum dots for bioimaging and beyond. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4245–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Hai, X.; Chen, X.-W.; Wang, J.-H. Simultaneously fabrication of free and solidified N, S-doped graphene quantum dots via a facile solvent-free synthesis route for fluorescent detection. Talanta 2017, 168, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liang, M.; Xu, L.; Qi, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Solid-phase synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for sensitive and selective probing ferric ions in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9846–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Guo, Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Xu, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, G. Facile and highly effective synthesis of controllable lattice sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots via hydrothermal treatment of durian. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5750–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Huang, C.; Shan, Y.; Liu, C.; Qin, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, T. Understanding the selective detection of Fe3+ based on graphene quantum dots as fluorescent probes: The Ksp of a metal hydroxide-assisted mechanism. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12054–12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.T.N.; Chowdhury, A.D.; Doong, R. Highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions using N, S-codoped graphene quantum dots and its paper strip based sensing application in wastewater. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.H.; Faridbod, F.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P. Functionalized graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent “off–on” nanosensor for detection of mercury and ethyl xanthate. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 7457–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. One-step synthesis of self-doped carbon dots with highly photoluminescence as multifunctional biosensors for detection of iron ions and pH. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Choi, M.M.F. Low temperature synthesis of phosphorous and nitrogen co-doped yellow fluorescent carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6813–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standards for Drinking Water Quality. China National Standers. (No. GB5749-2006). Available online: http://www.gb688.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=73D81F4F3615DDB2C5B1DD6BFC9DEC86 (accessed on 8 May 2019).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Ground Water and Drinking Water; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Qi, P.; Zhang, D.; Wan, Y. Morphology-tunable polydopamine nanoparticles and their application in Fe3+ detection. Talanta 2017, 170, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Xin, X.; Ding, P.; Song, A.; Xie, Z.; Shen, J.; Xu, G. Fluorescent oligomer as a chemosensor for the label-free detection of Fe3+ and dopamine with selectivity and sensitivity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 926, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Jiang, C.; Guan, G.; Zhang, K.; Liu, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z. Fluorescent graphene oxide logic gates for discrimination of iron (3+) and iron (2+) in living cells by imaging. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G. Dual functional N- and S-co-doped carbon dots as the sensor for temperature and Fe3+ ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gan, J. Synthesis of blue-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots/polystyrenic anion-exchange resin for Fe(III) detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 372, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Gao, H.-W.; Uvdal, K. A logic gate-based fluorogenic probe for Hg2+ detection and its applications in cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 919, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wu, T.; Lv, L.; Yan, Z. A turn-on fluorescent probe for Hg2+ detection by using gold nanoparticle-based hybrid microgels. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wei, C. Highly sensitive and selective fluorescence detection of Hg2+ based on turn-on aptamer DNA silver nanoclusters. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56289–56295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Carbon nanodots as fluorescence probes for rapid, sensitive, and label-free detection of Hg2+ and biothiols in complex matrices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, P.; Zhang, F.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X. Fluorescent probes for “off–on” highly sensitive detection of Hg2+ and L-cysteine based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Talanta 2016, 152, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Kokot, S. A rapid and label-free dual detection of Hg(II) and cysteine with the use of fluorescence switching of graphene quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tam, T.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, W.M. Facile synthesis of cysteine–functionalized graphene quantum dots for a fluorescence probe for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 97598–97603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gong, Y.; Fan, Z. Cysteine detection using a high-fluorescence sensor based on a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot–mercury(II) system. J. Lumin. 2016, 175, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Materials | Atomic Populations (Mulliken) | Bond Population | d (Å) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | p | Total | Charge (e) | |||||
| Pure graphene | C | 1.05 | 2.95 | 4.00 | 0 | C-C | 1.02 | 1.42 |
| N, S-GQDs | C1 | 1.13 | 2.86 | 3.99 | 0.01 | C1-O | 0.64 | 1.37 |
| C2 | 1.07 | 2.99 | 4.07 | −0.07 | C1-S | 0.48 | 1.78 | |
| C3 | 1.27 | 2.82 | 4.09 | −0.09 | C2-S | 0.65 | 1.71 | |
| N | 1.39 | 3.84 | 5.23 | −0.23 | C2-N | 0.85 | 1.39 | |
| O | 1.76 | 4.61 | 6.37 | −0.37 | C3-N | 0.92 | 1.37 | |
| S | 1.67 | 3.56 | 5.24 | 0.76 | C3-O | −0.06 | 2.40 | |
| Probe | Dynamic Range | LOD | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polydopamine dots | 10–1000 μM | 4.6 μM | [54] |
| Tyloxapol | 0–100 μM | 2.2 μM | [55] |
| Graphene oxide | 5–50 μM | 0.64 μM | [56] |
| Dopamine-functionalized GQDs | 0.02–20 μM | 7.6 nM | [39] |
| Rhodamine-functionalized GQDs | 0–1.0 μM | 0.02 μM | [1] |
| N, S-CQDs | 1.5–200 μM | 1.02 nM | [57] |
| GQDs/PS-AER | 1–7 μM | 0.65 μM | [58] |
| GQDs | 10–200 μM | 10 μM | [3] |
| GQDs | 0–60 μM | 0.45 μM | [47] |
| N, S-GQDs | 1–90 nM | 2.88 nM | This work |
| 0.1–30 μM | 55.49 nM | This work |
| Probe | Dynamic Range | LOD | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhodamine derivative | 4–15 μM | 60.7 nM | [59] |
| Gold nanoparticle | 0.16–1.6 μM | 31 nM | [60] |
| DNA-Ag NCs | 2–18 nM | 0.25 nM | [61] |
| CDs | 0–3 μM | 4.2 nM | [62] |
| N-CQDs | 0–10 μM | 1.48 nM | [63] |
| GQDs | 1–50 nM | 0.43 nM | [64] |
| Cysteine-functionalized GQDs | 0–10 μM | 20 nM | [65] |
| N-GQDs | 0.05–30 μM | 1.3 nM | [66] |
| N, S-GQDs | 1–50 nM | 0.14 nM | [48] |
| N, S-GQDs | 1–30 nM | 0.27 nM | This work |
| 100–1000 nM | 36.85 nM | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zou, T.; Wang, Z.; Xing, X.; Peng, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. The Fluorescent Quenching Mechanism of N and S Co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Fe3+ and Hg2+ Ions and Their Application as a Novel Fluorescent Sensor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050738
Yang Y, Zou T, Wang Z, Xing X, Peng S, Zhao R, Zhang X, Wang Y. The Fluorescent Quenching Mechanism of N and S Co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Fe3+ and Hg2+ Ions and Their Application as a Novel Fluorescent Sensor. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(5):738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050738
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yue, Tong Zou, Zhezhe Wang, Xinxin Xing, Sijia Peng, Rongjun Zhao, Xu Zhang, and Yude Wang. 2019. "The Fluorescent Quenching Mechanism of N and S Co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Fe3+ and Hg2+ Ions and Their Application as a Novel Fluorescent Sensor" Nanomaterials 9, no. 5: 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050738
APA StyleYang, Y., Zou, T., Wang, Z., Xing, X., Peng, S., Zhao, R., Zhang, X., & Wang, Y. (2019). The Fluorescent Quenching Mechanism of N and S Co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Fe3+ and Hg2+ Ions and Their Application as a Novel Fluorescent Sensor. Nanomaterials, 9(5), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050738