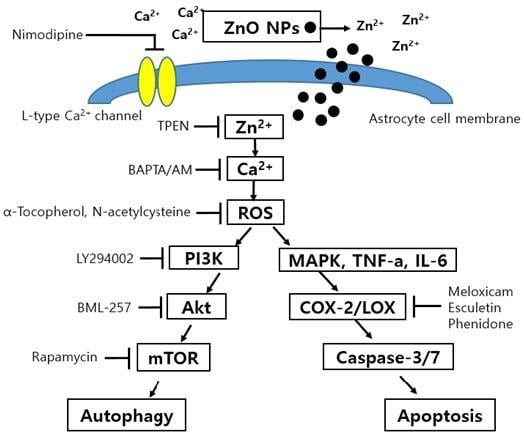
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and ZnO NP Suspension
2.2. Astrocyte Cultures and ZnO NP Treatment
2.3. Measurement of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Activity
2.4. MTT Assay
2.5. LC3-Antibody Detection
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. ELISA Assay
2.8. Protein Assay
2.9. PI3K/MAPK Dual Pathway Activation Assay
2.10. Caspase-3/7 Assay
2.11. DAPI Staining
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
3.2. Dose-Dependent ZnO NP-Induced Toxicity in Neocortical Astrocyte Cultures
3.3. TEM Analyses of Astrocyte Morphology Following Exposure to ZnO NPs
3.4. ZnO NP-Mediated Enhancement of Autophagy of Cultured Astrocytes
3.5. Effects of ZnO NPs on Caspase-3/7 Activity and DAPI Staining
3.6. Effects of ZnO NPs on IL-6, TNF-α, SOD, and GPx Levels in Cultured Astrocyte Cells
3.7. Effect of ZnO NPs on PI3K/MAPK Activation in Cultured Astrocytes
3.8. Effects of Meloxicam, Esculetin, and Phenidone on ZnO NP-Induced Toxicity
3.9. Effects of BML-257 and Rapamycin on ZnO NP-Induced Toxicity
3.10. Effects of Calcium Modulators, Antioxidants, and Metal Chelators on ZnO NP-Induced Toxicity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ancona, A.; Dumontel, B.; Garino, N.; Demarco, B.; Chatzitheodoridou, D.; Fazzini, W.; Engelke, H.; Cauda, V. Lipid-Coated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as Innovative ROS-Generators for Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Webster, T.J. The Investigation of ZnO/Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Nanocomposites with Improved Mechanical, Piezoelectric, and Antimicrobial Properties for Orthopedic Applications. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Genchi, G.G.; Mattoli, V.; Ciofani, G. Piezoelectric nanotransducers: The future of neural stimulation. Nanotoday 2017, 14, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Genchi, G.G.; Sinibaldi, E.; Ciofani, G. Piezoelectric Effects of Materials on Bio-Interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17663–17680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Choy, J.H. Biokinetics of zinc oxide nanoparticels: Toxicokinetics, biological fates, and protein interaction. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Kim, R.O.; Yoon, S.; Kim, W.K. Developmental toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles (Danio rerio): A transcriptomic analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, V.D.; Prasad, S.V.; Banerjee, A.; Gopinath, M.; Murugesan, R.; Marotta, F.; Sun, X.F.; Pathak, S. Health hazard of nanoparticles: Understanding the toxicity mechanism of nanosized ZnO in cosmetic products. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 42, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, U.; Siddique, S.; Ahmed, R.; Noreen, Z.; Bokhari, H.; Ahmad, I. Antibacterial, Structural and Optical Characterization of Mechano-Chemically Prepared ZnO Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; Wei, L. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce toxicity in CAL 27 oral cancer cell lines by activating PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3441–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-L.; Gao, J.-Q. Potential neurotoxicity of nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 394, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-Y.; Cheng, T.-J.; Yang, D.-M.; Wang, C.-T.; Chiung, Y.-M.; Liu, P.-S. Demonstration of an Olfactory Bulb–Brain Translocation Pathway for ZnO Nanoparticles in Rodent Cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 48, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Lin, B.; Wu, L.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Yan, J.; Liu, X.; Xi, Z. Neurotoxicity induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles: Age-related differences and interaction. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, D.; Ding, W. ZnO nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress triggers apoptosis by activating JNK signaling pathway in cultured primary astrocytes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakaran, S.; Athira, S.; Mohanan, P. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced neurotoxic potential upon interaction with primary astrocytes. NeuroToxicology 2019, 73, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barceloux, D.G. Zinc. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, T. Zinc ion as modulator effects on excitability and synaptic transmission in hippocampal CA1 neurons in Wistar rats. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 68, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, M.; Jeng, J.-M.; Malavolta, M.; Mocchegiani, E.; Sensi, S.L. Zinc dyshomeostasis: A key modulator of neuronal injury. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2005, 8, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Mizuno, D.; Koyama, H.; Konoha, K.; Ohkawara, S.; Sadakane, Y. Disruption of zinc homeostasis and the pathogenesis of senile dementia. Metallomics 2014, 6, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, M.S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Her, S.; Wie, M.-B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce lipoxygenase-mediated apoptosis and necrosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 90, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Chen, A.; Lai, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Kang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shao, L. Neuroinflammation is induced by tongue-instilled ZnO nanoparticles via the Ca2+-dependent NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Koh, J.-Y. Roles of zinc and metallothionein-3 in oxidative stress-induced lysosomal dysfunction, cell death, and autophagy in neurons and astrocytes. Mol. Brain 2010, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Timmins, G.S.; Liu, W.; Liu, K.J. Autophagy Mediates Astrocyte Death during Zinc-Potentiated Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Boil. Trace Element Res. 2015, 166, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sruthi, S.; Mohanan, P. Investigation on cellular interactions of astrocytes with zinc oxide nanoparticles using rat C6 cell lines. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.G.; Karam, A.R. Morphological and Biochemical Features of Cerebellar Cortex after Exposure to Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Possible Protective Role of Curcumin. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Boil. 2018, 301, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermanizadeh, A.; Jantzen, K.; Ward, M.B.; Durhuus, J.A.; Rasmussen, L.J.; Loft, S.; Møller, P. Nanomaterial-induced cell death in pulmonary and hepatic cells following exposure to three different metallic materials: The role of autophagy and apoptosis. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.-L.; Pei, J.-J.; Nishimura, T.; Winblad, B.; Cowburn, R.F. Zinc-induced anti-apoptotic effects in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 135, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-C.; Won, M.-H.; Yang, S.-R.; Kim, H.-C.; Wie, M.-B. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Exhibit Both Cyclooxygenase- and Lipoxygenase-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 35, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, M.; Choi, D. Combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 3510–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensi, S.L.; Rockabrand, E.; Canzoniero, L.M. Acidosis enhances toxicity induced by kainite and zinc exposure in aged cultured astrocyte. Biogerontology 2006, 7, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.Y.; Choi, D.W. Quantitative determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell culture by lactate dehydrogenase efflux assay. J. Neurosci. Methods 1987, 20, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-N.; Yoon, T.-J.; Minai-Tehrani, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Park, S.J.; Jeong, M.S.; Ha, S.-W.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, M.-H. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced autophagic cell death and mitochondrial damage via reactive oxygen species generation. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Najafzadeh, M.; Jacob, B.K.; Dhawan, A.; Anderson, D. Zinc oxide nanoparticles affect the expression of p53, Ras p21 and JNKs: An ex vivo/in vitro exposure study in respiratory disease patients. Mutagenesis 2015, 30, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinta-Ferreira, M.; Matias, C.; Arif, M.; Dionísio, J.; Matias, C. Measurement of presynaptic zinc changes in hippocampal mossy fibers. Brain Res. 2004, 1026, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, F.; Yin, J.; Pan, R.; Shi, W.; Qi, Z.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; et al. Synergistic Interaction Between Zinc and Reactive Oxygen Species Amplifies Ischemic Brain Injury in Rats. Stroke 2018, 49, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.B.; Wang, Z.Y. Disruption of brain zinc homeostasis promotes the pathophysiological progress of Alzheimer’s disease. Histol. Histopathol. 2016, 31, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Singh, V.; Gera, R.; Purohit, M.P.; Ghosh, D. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induces microglial death by NADPH oxidase-independent reactive oxygen species as well as energy depletion. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6273–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineley, K.E.; Scanlon, J.M.; Kress, G.J.; Stout, A.K.; Reynolds, I.J. Astrocyte are more resistant than neurons to the cytotoxic effects of increased [Zn2+]i. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxakis, A.; Ploumi, C.; Tavernarakis, N. Autophagy in Age-Associated Neurodegeneration. Cells 2018, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.-P.; Zhang, X.-F.; Huang, Y.-F.; Gurunathan, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6521–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Singh, S.K.; Chauhan, L.; Das, M.; Tripathi, A.; Dwivedi, P.D. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibition. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 227, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Cho, K.S.; Koh, J.-Y. Oxidative injury triggers autophagy in astrocytes: The role of endogenous zinc. Glia 2009, 57, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liang, H.; Liu, L.; Gong, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liao, G.; Cao, Y. Influence of pristine and hydrophobic ZnO nanoparticles on cytotoxicity and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-autophagy-apoptosis gene expression in A549-macrophage co-culture. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Parashar, V.; Chauhan, L.K.; Shanker, R.; Das, M.; Tripathi, A.; Qwivedi, P.D. Mechanism of uptake of ZnO nanoparticles and inflammatory response in macropahges require PI3K mediated MAPKs signaling. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wu, X.; Lei, M.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wen, L.; Xu, P.; Li, S.; Qu, S. Rapamycin upregulates glutamate transporter and IL-6 expression in astrocytes in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Zou, J.; Wong, M. Rapamycin Attenuates Acute Seizure-induced Astrocyte Injury in Mice in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshmit, Y.; Kanner, S.; Zacs, M.; Frisca, F.; Pinto, A.R.; Currie, P.D.; Pinkas-Kramarski, R. Rapamycin increases neuronal survival, reduces inflammation and astrocyte proliferation after spinal cord injury. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 68, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Aronstam, R.S.; Chen, D.-R.; Huang, Y.-W. Oxidative stress, calcium homeostasis, and altered gene expression in human lung epithelial cells exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouraqui, E.; Leon, A.; Repessé, Y.; Prigent-Tessier, A.; Bouhallab, S.; Bouglé, D.; Marie, C.; Duval, D. Deferoxamine blocks death induced by glutathione depletion in PC 12 cells. NeuroToxicology 2013, 37, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.M.Y. Antioxidative Effect of Vitamin D3 on Zinc-Induced Oxidative Stress in CNS. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1053, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, W.-J.; Jeong, M.-S.; Choi, D.-M.; Kim, K.-N.; Wie, M.-B. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071043
Song W-J, Jeong M-S, Choi D-M, Kim K-N, Wie M-B. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(7):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071043
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Woo-Ju, Myung-Seon Jeong, Dong-Min Choi, Kil-Nam Kim, and Myung-Bok Wie. 2019. "Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures" Nanomaterials 9, no. 7: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071043
APA StyleSong, W. -J., Jeong, M. -S., Choi, D. -M., Kim, K. -N., & Wie, M. -B. (2019). Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures. Nanomaterials, 9(7), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071043