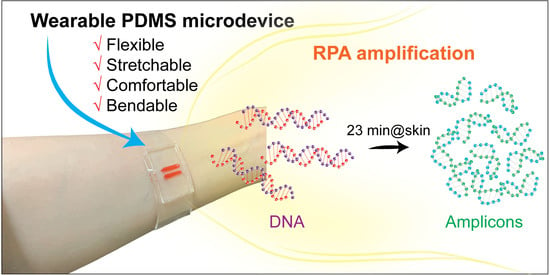
Fabrication of Wearable PDMS Device for Rapid Detection of Nucleic Acids via Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Operated by Human Body Heat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production of the Flexible PDMS with Different Mixing Ratios
2.3. Design and Fabrication of Wearable Microdevice
2.4. Sample Preparation and DNA Extraction
2.5. Temperature Measurement
2.6. Nucleic Acid Amplification by RPA
3. Results
3.1. Water Contact Angle Measurement
3.2. Characterization of the PDMS Substrates with Different Mixing Ratios
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of the RPA Assays Using Human Body Heat for the Detection of E. coli O157:H7
3.4. Results of on-Chip RPA Performed Using Human Body Heat for the Detection of E. coli O157:H7
3.5. Amplification of Plasmid DNA of COVID-19 Using the Wearable RPA Device
3.6. On-Site Detection of Amplicons Using SYBR Green I-Based Fluorescence Signal
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louie, M.; Louie, L.; Simor, A.E. The role of DNA amplification technology in the diagnosis of infectious diseases. CMAJ 2000, 163, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- LaBarre, P.; Boyle, D.; Hawkins, K.; Weigl, B. Instrument-free nucleic acid amplification assays for global health settings. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2011, 16, 802920. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrberg, C.D.; Manz, A.; Chung, B.G. Polymerase chain reaction in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3866–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, N.Y.; Ahn, J.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, J.-H.; Song, C.-S.; Hwang, S.Y. Rapid subtyping and pathotyping of avian influenza virus using chip-based RT-PCR. BioChip J. 2019, 13, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Stabler, R.A.; Lee, N.Y. Fabrication of a foldable all-in-one point-of-care molecular diagnostic microdevice for the facile identification of multiple pathogens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 314, 128057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahamtan, A.; Ardebili, A. Real-time RT-PCR in COVID-19 detection: Issues affecting the results. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, J.; AL-maskri, A.A.A.; Kang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Cai, S. Recent advances and perspectives of nucleic acid detection for coronavirus. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymouri, M.; Mollazadeh, S.; Mortazavi, H.; Ghale-noie, Z.N.; Keyvani, V.; Aghababaei, F.; Hamblin, M.R.; Abbeszadeh-Goudarzi, G.; Pourghadamyari, H.; Hashemian, S.M.R.; et al. Recent advances and challenges of RT-PCR tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 221, 153443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgannezhad, L.; Stratton, H.; Nguyen, N.-T. Microfluidic-based nucleic acid amplification systems in microbiology. Micromachines 2019, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trinh, T.N.D.; Lee, N.Y. A rapid and eco-friendly isothermal amplification microdevice for multiplex detection of foodborne pathogens. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 2369–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Trinh, T.N.D.; Lee, N.Y. Fully integrated and slidable paper-embedded plastic microdevice for point-of-care testing of multiple foodborne pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Chow, W.H.; Li, Y.; Kong, H.; Tang, Y.W.; Lemieux, B. Nucleic acid assay system for tier II laboratories and moderately complex clinics to detect HIV in low-resource settings. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahalanabis, M.; Do, J.; ALMuayad, H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Klapperich, C.M. An integrated disposable device for DNA extraction and helicase dependent amplification. Biomed. Microdevices 2010, 12, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, D.; Zhu, M.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. A microfluidic-integrated lateral flow recombinase polymerase amplification (MI-IF-RPA) assay for rapid COVID-19 detection. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Davydova, E.K.; Du, W.; Kreutz, J.E.; Piepenburg, O.; Ismagilov, R.F. Digital isothermal quantification of nucleic acids via simultaneous chemical initiation of recombinase polymerase amplification reactions on SlipChip. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3533–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohrman, B.; Richards-Kortum, R. Inhibition of recombinase polymerase amplification by background DNA: A lateral flow-based method for enriching target DNA. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase polymerase amplification for diagnostic applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Macdonald, J.; von Stetten, F. Review: A comprehensive summary of a decade development of the recombinase polymerase amplification. Analyst 2019, 144, 31–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Kong, J.; Fang, X. Bandage-like wearable flexible microfluidic recombinase polymerase amplification sensor for the rapid visual detection of nucleic acids. Talanta 2019, 204, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Hu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, D.; Lin, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. A wearable microfluidic device for rapid detection of HIV-1 DNA using recombinase polymerase amplification. Talanta 2019, 205, 120155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; You, H. Efficient bond of PDMS and printed circuit board with an application on continuous-flow polymerase chain reaction. BioChip J. 2020, 14, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Duan, S.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Li, C. Kirigami-patterned highly stretchable conductors from flexible carbon nanotube-embedded polymer films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 8714–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-W.; Jeon, S.; Maria, J.; Zaumseil, J.; Hsu, J.W.P.; Rogers, J.A. Soft-contact optical lithography using transparent elastomeric stamps and application to nanopatterned organic light-emitting devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.-H.; Thelen, J.; Qusba, A.; Hayes, G.J.; Lazzi, G.; Dickey, M.D. Reversibly deformable and mechanically tunable fluidic antennas. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3632–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Hjort, K.; Hilborn, J.; Wu, Z. PDMS-based elastomer tuned soft, stretchable, and sticky for epidermal electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5830–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.C.; Liao, E.; Ong, W.L.; Wong, J.D.S.; Agarwal, A.; Nagarajan, R.; Yobas, L. Evaluation of bonding between oxygen plasma treated polydimethyl siloxane and passivated silicon. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 34, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Effenhauser, C.S.; Bruin, G.J.M.; Paulus, A.; Ehrat, M. Integrated capillary electrophoresis on flexible silicone microdevices: analysis of dna restriction fragments and detection of single DNA molecules on microchips. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 3451–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademhosseini, A.; Yeh, J.; Eng, G.; Karp, J.; Kaji, H.; Borenstein, J.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R. Cell docking inside microwells within reversibly sealed microfluidic channels for fabricating multiphenotype cell arrays. Lab Chip 2005, 12, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Wolf, F.; Baier, S.K. Effect of varying mixing ratio of PDMS on the consistency of the soft-contact Stribeck curve for glycerol solutions. Tribol. Int. 2015, 89, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Zhang, H.; Kang, D.-J.; Kahng, S.-H.; Tall, B.D.; Lee, N.Y. Fabrication of polymerase chain reaction plastic lab-on-a-chip device for rapid molecular diagnoses. Int. Neurourol. J. 2016, 20, S38–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, X.Q.; Ookawa, K.; Wong, J.Y. Evaluation of polydimethylsiloxane scaffolds with physiologically-relevant elastic moduli: Interplay of substrate mechanics and surface chemistry effects on vascular smooth muscle cell response. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3123–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeShields, J.B.; Moroz, N.; Braley, L.E.; Mora-Romero, G.A.; Tanaka, K. Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) for the rapid isothermal detection of Spongospora subterranean f. sp. subterranea and potato mop-top virus. Am. J. Potato Res. 2019, 96, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trinh, K.T.L.; Lee, N.Y. Fabrication of Wearable PDMS Device for Rapid Detection of Nucleic Acids via Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Operated by Human Body Heat. Biosensors 2022, 12, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020072
Trinh KTL, Lee NY. Fabrication of Wearable PDMS Device for Rapid Detection of Nucleic Acids via Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Operated by Human Body Heat. Biosensors. 2022; 12(2):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020072
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrinh, Kieu The Loan, and Nae Yoon Lee. 2022. "Fabrication of Wearable PDMS Device for Rapid Detection of Nucleic Acids via Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Operated by Human Body Heat" Biosensors 12, no. 2: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020072
APA StyleTrinh, K. T. L., & Lee, N. Y. (2022). Fabrication of Wearable PDMS Device for Rapid Detection of Nucleic Acids via Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Operated by Human Body Heat. Biosensors, 12(2), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020072