Eu2O3@Cr2O3 Nanoparticles-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Efficient Electrochemical Sensing of Neurotransmitters Precursor L-DOPA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Instrumentation
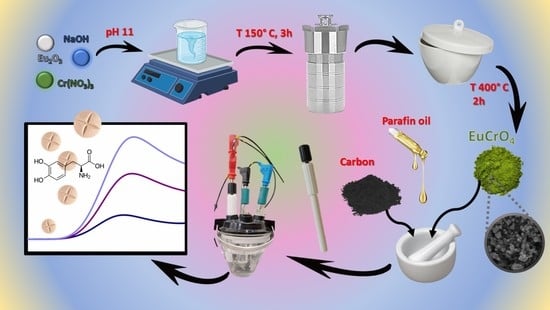
2.2. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Eu2O3@Cr2O3
2.3. Fabrication of Eu2O3@Cr2O3/CPE
2.4. Preparation of the Real Sample
3. Results
3.1. Morphological and Microstructural Characterisation of Eu2O3@Cr2O3 Nanocomposite
3.2. Electrochemical Characterisation of Eu2O3@Cr2O3 Nanocomposite
3.3. Electrochemical Performance of Eu2O3@Cr2O3/CPE toward L-DOPA Detection
3.4. Effect of Supporting Electrolyte
3.5. Analytical Procedure for L-DOPA Detection
3.6. Interferences
3.7. Real Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Allen, C.; Arora, M.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brown, A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015: GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Lancet 2016, 388, 1545–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Naghavi, M.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; Coates, M.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015: GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samii, A.; Nutt, J.G.; Ransom, B.R. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2004, 363, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, K.R.; Saadabadi, A. Levodopa (L-Dopa). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482140/ (accessed on 29 November 2022).
- Atta, N.F.; Galal, A.; El-Gohary, A.R. Crown ether modified poly(hydroquinone)/carbon nanotubes based electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of levodopa, uric acid, tyrosine and ascorbic acid in biological fluids. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 863, 114032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, B.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, L.; Havakeshian, E.; Ensafi, A.A. An electrochemical biosensor based on nanoporous stainless steel modified by gold and palladium nanoparticles for simultaneous determination of levodopa and uric acid. Talanta 2016, 158, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennickent, S.; Nail, M.; Vega, M.; Diego, M.d. Quantitative determination of L-DOPA in tablets by high performance thin layer chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska, I.; Płonka, J. Determination of levodopa and biogenic amines in urine samples using high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2008, 46, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbarbry, F.; van Nguyen; Mirka, A.; Zwickey, H.; Rosenbaum, R. A new validated HPLC method for the determination of levodopa: Application to study the impact of ketogenic diet on the pharmacokinetics of levodopa in Parkinson’s participants. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Rossi, D.T.; Fountain, S.T. Development and validation of a semi-automated method for L-dopa and dopamine in rat plasma using electrospray LC/MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 24, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- César, I.C.; Byrro, R.M.D.; Cardoso, F.F.S.E.S.; Mundim, I.M.; Souza Teixeira, L.; Gomes, S.A.; Bonfim, R.R.; Pianetti, G.A. Development and validation of a high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantitation of levodopa and carbidopa in human plasma. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 46, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-W.; Zhou, X.-W.; Lu, J.-Q. Simultaneous determination of benserazide and levodopa by capillary electrophoresis-chemiluminescence using an improved interface. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1131, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.-C.; Shih, C.-I.; Chiang, C.-C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Yeh, Y.-C. Reagent-free DOPA-dioxygenase colorimetric biosensor for selective detection of L-DOPA. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helaleh, M.I.H.; Rahman, N.; Abu-Nameh, E.S.M. Use of Cerium(IV) Nitrate in the Spectrophotometric Determination of Levodopa and Methyldopa in the Pure Form and Pharmaceutical Preparations. Anal. Sci. 1997, 13, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Su, D.; Berry, S.N.; Lee, J.; Chang, Y.-T. A new approach for turn-on fluorescence sensing of l-DOPA. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 12465–12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- State, R.G.; van Staden, J.F. Review. Electrochemical sensors used in the determination of L-Dopa. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2022, 2, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaji, U.; Govindasamy, M.; Sha, R.; Alshgari, R.A.; Juang, R.-S.; Liu, T.-Y. Surface engineering of 3D spinel Zn3V2O8 wrapped on sulfur doped graphitic nitride composites: Investigation on the dual role of electrocatalyst for simultaneous detection of antibiotic drugs in biological fluids. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 242, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pu, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Z.; Luo, H.; et al. Single-atom nanozymes Co–N–C as an electrochemical sensor for detection of bioactive molecules. Talanta 2023, 254, 124171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemčeková, K.; Labuda, J. Advanced materials-integrated electrochemical sensors as promising medical diagnostics tools: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 120, 111751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognjanović, M.; Nikolić, K.; Bošković, M.; Pastor, F.; Popov, N.; Marciuš, M.; Krehula, S.; Antić, B.; Stanković, D.M. Electrochemical Determination of Morphine in Urine Samples by Tailoring FeWO4/CPE Sensor. Biosensors 2022, 12, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Chen, T.-W.; Chen, S.-M.; Baskar, T.; Kannan, R.; Elumalai, P.; Raja, P.; Jeyapragasam, T.; Dinakaran, K.; Gnana Kumar, G.P. A review of the advanced developments of electrochemical sensors for the detection of toxic and bioactive molecules. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 3418–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojević, V.; Djurdjić, S.; Ognjanović, M.; Antić, B.; Kalcher, K.; Mutić, J.; Stanković, D.M. RuO2/graphene nanoribbon composite supported on screen printed electrode with enhanced electrocatalytic performances toward ethanol and NADH biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q. Advanced Nanomaterials for Pollutant Sensing and Environmental Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128147979. [Google Scholar]
- Sawkar, R.R.; Shanbhag, M.M.; Tuwar, S.M.; Veerapur, R.S.; Shetti, N.P. Glucose Incorporated Graphite Matrix for Electroanalysis of Trimethoprim. Biosensors 2022, 12, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmeti, E.; Stanković, D.M.; Chaiyo, S.; Švorc, Ľ.; Kalcher, K. Manganese dioxide-modified carbon paste electrode for voltammetric determination of riboflavin. Mikrochim. Acta 2016, 183, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tajik, S.; Beitollahi, H.; Nejad, F.G.; Safaei, M.; Zhang, K.; van Le, Q.; Varma, R.S.; Jang, H.W.; Shokouhimehr, M. Developments and applications of nanomaterial-based carbon paste electrodes. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21561–21581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalcher, K. Chemically modified carbon paste electrodes in voltammetric analysis. Electroanalysis 1990, 2, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhu, J.-J. The electrochemical applications of rare earth-based nanomaterials. Analyst 2019, 144, 6789–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, W.; Liu, L.; Gao, F.; Li, M. The electrochemical determination of l-cysteine at a Ce-doped Mg–Al layered double hydroxide modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 70, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Sakthivel, K.; Gandhi, S.; Huy, B.T.; Lee, Y.-I. An improved non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on europium functionalized inorganic hybrid material—Evaluation of optical and electrochemical properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xue, Q.; Jiao, C.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, H.; Yang, Q. A non-enzymatic nanoceria electrode for non-invasive glucose monitoring. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh Jahani, P.; Akbari Javar, H.; Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H. A new electrochemical sensor based on Europium-doped NiO nanocomposite for detection of venlafaxine. Measurement 2021, 173, 108616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ning, G.; Lin, Y. Preparation of Eu(OH)3 and Eu2O3 Nanorods through a Simple Method. Chem. Lett. 2007, 36, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Structural analysis of perovskite LaCr 1 − x Ni x O3 by Rietveld refinement of X-ray powder diffraction data. Acta Cryst. B Struct. Sci. 2008, 64, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knežević, S.; Ognjanović, M.; Stanković, V.; Zlatanova, M.; Nešić, A.; Gavrović-Jankulović, M.; Stanković, D. La(OH)3 Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Carbon Paste-Based Sensing Approach for the Detection of Uric Acid-A Product of Environmentally Stressed Cells. Biosensors 2022, 12, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Fan, C.; Xu, T.; Su, L.; Zhang, X. An electrochemical wearable sensor for levodopa quantification in sweat based on a metal–Organic framework/graphene oxide composite with integrated enzymes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 359, 131586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đurđić, S.; Stanković, V.; Vlahović, F.; Ognjanović, M.; Kalcher, K.; Manojlović, D.; Mutić, J.; Stanković, D.M. Carboxylated single-wall carbon nanotubes decorated with SiO2 coated-Nd2O3 nanoparticles as an electrochemical sensor for L-DOPA detection. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.H.S.; Gogola, J.L.; Bergamini, M.F.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Janegitz, B.C. Disposable and low-cost lab-made screen-printed electrodes for voltammetric determination of L-dopa. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2021, 3, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu State, R.; Stefanov, C.; Staden, J.F.; Staden, R.-I.S. Application of a Tetraamino Cobalt(II) Phthalocyanine Modified Screen Printed Carbon Electrode for the Sensitive Electrochemical Determination of L-Dopa in Pharmaceutical and Biological Samples. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 1778–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorle, G.; Bathinapatla, A.; Kanchi, S.; Ling, Y.C.; Rezakazemi, M. Low dimensional Bi2Se3 NPs/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for simultaneous detection of L-Dopa and acetaminophen in presence of ascorbic acid in biological samples and pharmaceuticals. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2022, 12, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, A.; Radhakrishnan, S. Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles functionalized polypyrrole nanotubes for the highly sensitive detection of l-dopa. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooraj, M.P.; Nair, A.S.; Pillai, S.C.; Hinder, S.J.; Mathew, B. CuNPs decorated molecular imprinted polymer on MWCNT for the electrochemical detection of l-DOPA. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2483–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanvand, Z.; Jalali, F. Simultaneous determination of l-DOPA, l-tyrosine and uric acid by cysteic acid—Modified glassy carbon electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 98, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghian, E.; Shahdost-fard, F.; Sohouli, E.; Safarifard, V.; Najafi, M.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.; Sobhani-Nasab, A. Electrochemical determination of levodopa on a reduced graphene oxide paste electrode modified with a metal-organic framework. Microchem. J. 2020, 156, 104888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, D.M.; Jović, M.; Ognjanović, M.; Lesch, A.; Fabián, M.; Girault, H.H.; Antić, B. Point-of-care amperometric determination of L-dopa using an inkjet-printed carbon nanotube electrode modified with dandelion-like MnO2 microspheres. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyam Sunder, G.S.; Rohanifar, A.; Devasurendra, A.M.; Kirchhoff, J.R. Selective determination of -DOPA at a graphene oxide/yttrium oxide modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 301, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Electrode | Method | Linear Range (µM) | LOD (µM) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu2O3@Cr2O3/CPE | DPV | 1–100 | 0.72 | This work |
| GC/CNT/PHQ/CE | DPV | 0.005–20 | 0.000221 | [5] |
| tyrosinase@ZIF-8/GO/Au | Amperometry | 1–95 | 0.45 | [36] |
| SWCNT-COOH@Nd2O3-SiO2 | Amperometry | 2–52 | 0.7 | [37] |
| GP-CAc/PVC | SWV | 8–100 | 0.06 | [38] |
| pCoTAPc/SPCE | DPV | 0.1–1000 | 0.03 | [39] |
| Bi2Se3 NPs/rGO/Pt-E | DPV | 6–250 | 0.23 | [40] |
| AuNP/PPy/GCE | Amperometry | 0.1–6 | 0.075 | [41] |
| CuNPs/MWCNT-MIP | CV | 0.01–1 | 0.009 | [42] |
| Cysteic acid/GCE | DPV | 0.35–4 | 0.11 | [43] |
| RGO/TMU-22PE | SWV | 0.1–85 | 0.02 | [44] |
| MnO2@ IJPCNT | Amperometry | 0.1–10 | 0.054 | [45] |
| GO-Y2O3/GCE | SWV | 0.5–350 | 0.05 | [46] |
| Added (µM) | Found (µM) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 4.96 | 98.6 |
| 10 | 9.73 | 97.3 |
| 20 | 19.24 | 96.2 |
| 40 | 38.28 | 95.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mijajlović, A.; Ognjanović, M.; Manojlović, D.; Vlahović, F.; Đurđić, S.; Stanković, V.; Stanković, D. Eu2O3@Cr2O3 Nanoparticles-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Efficient Electrochemical Sensing of Neurotransmitters Precursor L-DOPA. Biosensors 2023, 13, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020201
Mijajlović A, Ognjanović M, Manojlović D, Vlahović F, Đurđić S, Stanković V, Stanković D. Eu2O3@Cr2O3 Nanoparticles-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Efficient Electrochemical Sensing of Neurotransmitters Precursor L-DOPA. Biosensors. 2023; 13(2):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020201
Chicago/Turabian StyleMijajlović, Aleksandar, Miloš Ognjanović, Dragan Manojlović, Filip Vlahović, Slađana Đurđić, Vesna Stanković, and Dalibor Stanković. 2023. "Eu2O3@Cr2O3 Nanoparticles-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Efficient Electrochemical Sensing of Neurotransmitters Precursor L-DOPA" Biosensors 13, no. 2: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020201
APA StyleMijajlović, A., Ognjanović, M., Manojlović, D., Vlahović, F., Đurđić, S., Stanković, V., & Stanković, D. (2023). Eu2O3@Cr2O3 Nanoparticles-Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Efficient Electrochemical Sensing of Neurotransmitters Precursor L-DOPA. Biosensors, 13(2), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020201