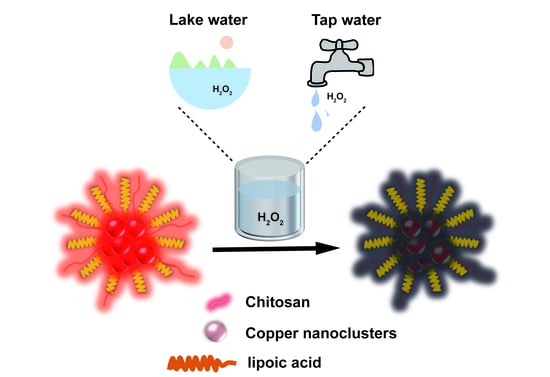
Preparation of a Red−Emitting, Chitosan−Stabilized Copper Nanocluster Composite and Its Application as a Hydrogen Peroxide Detection Probe in the Analysis of Water Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Synthesis of Nanocomposites
2.3.1. Preparation of LA−Cu NCs
2.3.2. Preparation of LA−Cu NCs@CS
2.4. Construction of Fluorescent Probe Based on LA−Cu NCs@CS
2.5. Detection of H2O2 Using LA−Cu NCs@CS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology of LA−Cu NCs and LA−Cu NCs@CS
3.2. Optical Performance Analysis
3.3. Optimization of Conditions
3.4. Fluorescence Response of LA−Cu NCs@CS in the Presence of H2O2
3.5. Stability and Selectivity
3.6. Actual Detection of H2O2
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benavides, J.; Quijada-Garrido, I.; García, O. The synthesis of switch-off fluorescent waterstable copper nanocluster Hg2+ sensors via a simple one-pot approach by an in situ metal reduction strategy in the presence of a thiolated polymer ligand template. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.G.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.M.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, B.K.; Lai, W.F.; Rogach, A.L. Water-soluble biocompatible copolymer hypromellose grafted chitosan able to load exogenous agents and copper nanoclusters with aggregation-induced emission. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Astruc, D. Atomically precise copper nanoclusters and their applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 359, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, X.D.; Zhang, X.D.; Chai, H.X.; Huang, Y.M. One-pot synthesis of the CuNCs/ZIF−8 nanocomposites for sensitively detecting H2O2 and screening of oxidase activity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Hu, J.; Yang, X.Y.; Wu, Y.X.; Su, W.M.; Zhang, C.Y. Target-initiated synthesis of fluorescent copper nanoparticles for the sensitive and label-free detection of bleomycin. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11134–11142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.F.; Wong, W.T.; Rogach, A.L. Development of copper nanoclusters for in vitro and in vivo theranostic applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.T.; Lu, Y.Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.W. One-pot synthesis, photoluminescence, and electrocatalytic properties of subnanometer-sized copper clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2060–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Li, C.Y.; Su, C.; Ji, X.H.; Zheng, J.; Tinnefeld, P.; He, Z.K. Enzymatic polymerization of poly(thymine) for the synthesis of copper nanoparticles with tunable size and their application in enzyme sensing. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8644–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar−Vidal, N.; Blanco, M.C.; López-Quintela, M.A.; Rivas, J.; Serra, C. Electrochemical synthesis of very stable photoluminescent copper clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 15924–15930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.M.; Cao, F.P.; Lei, X.L.; Mang, L.H.; Cheng, S.J.; Song, J.T. Fluorescent copper nanoparticles: Recent advances in synthesis and applications for sensing metal ions. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4852–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Transferrin−directed preparation of red−emitting copper nanoclusters for targeted imaging of transferrin receptor over-expressed cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2388–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparna, R.S.; Anjali Devi, J.S.; Anjana, R.R.; Nebu, J.; George, S. Zn(II) ion modulated red emitting copper nanocluster probe for the fluorescence turn on sensing of RDX. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 291, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahariah, P.; Másson, M. Antimicrobial chitosan and chitosan derivatives: A review of the structure-activity relationship. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3846–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoushab, F.; Yamabhai, M. Chitin research revisited. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1988–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.N.; Muzzarelli, R.A.; Muzzarelli, C.; Sashiwa, H.; Domb, A.J. Chitosan chemistry and pharmaceutical perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6017–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafari, J.; Barzanouni, H.; Mazloomi, S.; Farahani, N.A.A.; Sharafi, K.; Soleimani, P.; Haghighat, G.A. Effective adsorptive removal of reactive dyes by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles: Kinetic, isothermal studies and response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Qain, J.; Ding, F.Y. Emerging chitosan-based films for food packaging applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Guo, D.S.; Liu, Y.P. Supramolecular architectures of β-cyclodextrin-modified chitosan and pyrene derivatives mediated by carbon nanotubes and their DNA condensation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10431–10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, A.K.; Maiti, P. Injectable hydrogel through hydrophobic grafting on chitosan for controlled drug delivery. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2019, 2, 5415–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajomsang, W. Synthetic methods and applications of chitosan containing pyridylmethyl moiety and its quaternized derivatives: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, M.B.; Kumar, R.; Keibler, M.A.; Hess, J.R.; Bochicchio, G.V.; Raghavan, S.R. A self-assembling hydrophobically modified chitosan capable of reversible hemostatic action. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3351–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, P.S.; Selvakumar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kumar, N.S. Comparative study on antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of N−selective chitosan derivatives. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 124, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.P.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.L.; Han, Y.; Guo, B.L. Mussel−inspired, antibacterial, conductive, antioxidant, injectable composite hydrogel wound dressing to promote the regeneration of infected skin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, Z.Y.; Xiong, Y.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Cao, K.Y.; Chen, Y.J. In situ generation of silver nanoparticles and nanocomposite films based on electrodeposition of carboxylated chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Huang, X.Y.; Huang, S.; Dong, J.; Yuan, K.; Feng, X.P.; Liu, T.T.; Yu, K.Q.; Zeng, W.B. Sensitive water-soluble fluorescent probe based on umpolung and aggregation-induced emission strategies for selective detection of Hg2+ in living cells and zebrafish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2377–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.X.; Li, H.X.; Song, N.; Wang, D.; Tang, B.Z. Supramolecular materials based on AIE luminogens (AIEgens): Construction and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1144–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Together we shine, united we soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.N.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goswami, N.; Yao, Q.; Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Luminescent Metal Nanoclusters with Aggregation-Induced Emission. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 6, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Zou, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Assembly-Induced Enhancement of Cu Nanoclusters Luminescence with Mechanochromic Property. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12906–12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Mao, X.X.; Zhang, X.D.; Huang, Y.M. One-step synthesis of orange fluorescent copper nanoclusters forsensitive and selective sensing of Al3+ ions in food samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 247, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Y.; Hu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, S.L. Photoluminescence light-up detection of zinc ion and imaging in living cells based on the aggregation induced emission enhancement of glutathionecapped copper nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.J.; Chen, W.B.; Guo, X.Q. Facile one-pot synthesis of near-infrared luminescent gold nanoparticles for sensing copper (II). Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 095701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Yang, X.J.; Gao, Z.Q. In situ polymerization of aniline on carbon quantum dots: A new platform for ultrasensitive detection of glucose and hydrogen peroxide. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 21675–21680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaabasi, F.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Shamsipur, M. Hydrogen peroxide sensitive hemoglobin-capped gold nanoclusters as a fluorescence enhancing sensor for the label-free detection of glucose. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 33123–33135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Z.; He, S.J.; Zhang, C.M.; Chen, W. Three-dimensional Fe− and N-incorporated carbon structures as peroxidase mimics for fluorescence detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 4146–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhou, L.Y.; Liu, H.W. A novel two-photon fluorescent probe for the selective detection of hydrogen peroxide based on a naphthalene derivative. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4558–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.F.; Fei, Q.; Shan, H.Y.; Wang, B.J.; Hu, H.; Feng, G.D. A novel water-soluble sulfonated porphyrin fluorescence sensor for sensitive assays of H2O2 and glucose. Analyst 2015, 140, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Nanomaterial | Linear Range/μM | Detection Limit/μM | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| carbon quantum dots | 0.5~50 | 0.2 | [35] |
| gold nanoclusters capped by hemoglobin | 0.5~700 | 0.21 | [36] |
| Fe, N−incorporated carbon nanotubes | 0.1~100 | 0.068 | [37] |
| naphthalene backbone and a boric acid ester | 1~250 | 0.7 | [38] |
| sulfonated porphyrin | 1~8 | 0.32 | [39] |
| LA−Cu NCs@CS | 0.2~128 | 0.047 | This work |
| Samples | Added (µM) | Found (µM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 0.80 | 0.767 | 95.88 | 3.6 | |
| 8.00 | 7.860 | 98.25 | 4.5 | |
| 32.0 | 31.50 | 98.44 | 3.7 | |
| Lake water | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 0.80 | 0.755 | 94.38 | 2.9 | |
| 8.00 | 7.650 | 95.62 | 3.5 | |
| 32.0 | 32.80 | 102.5 | 3.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Guo, W.; Tian, C.; Luan, F.; Zhuang, X. Preparation of a Red−Emitting, Chitosan−Stabilized Copper Nanocluster Composite and Its Application as a Hydrogen Peroxide Detection Probe in the Analysis of Water Samples. Biosensors 2023, 13, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030361
Lu J, Wang D, Li X, Guo W, Tian C, Luan F, Zhuang X. Preparation of a Red−Emitting, Chitosan−Stabilized Copper Nanocluster Composite and Its Application as a Hydrogen Peroxide Detection Probe in the Analysis of Water Samples. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030361
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jiaojiao, Dawei Wang, Xin Li, Wei Guo, Chunyuan Tian, Feng Luan, and Xuming Zhuang. 2023. "Preparation of a Red−Emitting, Chitosan−Stabilized Copper Nanocluster Composite and Its Application as a Hydrogen Peroxide Detection Probe in the Analysis of Water Samples" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030361
APA StyleLu, J., Wang, D., Li, X., Guo, W., Tian, C., Luan, F., & Zhuang, X. (2023). Preparation of a Red−Emitting, Chitosan−Stabilized Copper Nanocluster Composite and Its Application as a Hydrogen Peroxide Detection Probe in the Analysis of Water Samples. Biosensors, 13(3), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030361