Functional Conducting Polymers via Thiol-ene Chemistry
Abstract
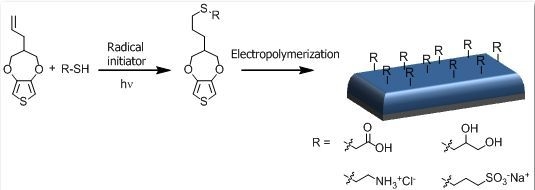
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. General Procedures and Materials
2.2. Synthesis of ProDOT-CO2H
2.3. Synthesis of ProDOT-NH2
2.4. Synthesis of ProDOT-SO3Na
2.5. Synthesis of ProDOT-Glycerol
2.6. Synthesis of Ethylhexyl-ProDOT (EH-ProDOT)
2.7. Poly(EH-ProDOT)
2.8. Poly(ProDOT-SO3Na)
2.9. Electropolymerization Procedure
3. Results and Discussion

3.1. Electrochemical Polymerization of Functional Monomers

3.2. Morphology of Deposited Films

3.3. Electrochemical Behavior of Functional Films

3.4. Synthesis of Soluble Conducting Polymers

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Brabec, C.J.; Sariciftci, N.S.; Hummelen, J.C. Plastic solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2001, 11, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, R.H.; Gymer, R.W.; Holmes, A.B.; Burroughes, J.H.; Marks, R.N.; Taliani, C.; Bradley, D.D.C.; Santos, D.A.D.; Bredas, J.L.; Logdlund, M.; et al. Electroluminescence in conjugated polymers. Nature 1999, 397, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchmeyer, S.; Reuter, K. Scientific importance, properties and growing applications of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Chen, G.Z.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Fray, D.J.; Windle, A.H. Electrochemical capacitance of a nanoporous composite of carbon nanotubes and polypyrrole. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, M. Application of conducting polymers to biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Wiler, J.A.; Anderson, D.J.; Kipke, D.R.; Martin, D.C. Conducting polymers on hydrogel-coated neural electrode provide sensitive neural recordings in auditory cortex. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson-Burns, S.M.; Hendricks, J.L.; Martin, D.C. Electrochemical polymerization of conducting polymers in living neural tissue. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, L6–L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Lee, V.A.; Raphael, Y.; Wiler, J.A.; Hetke, J.F.; Anderson, D.J.; Martin, D.C. Surface modification of neural recording electrodes with conducting polymer/biomolecule blends. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2001, 56, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Kushto, G.P.; Kim, H.; Kafafi, Z.H. Effect of annealing on the electrical properties and morphology of a conducting polymer used as an anode in organic light-emitting devices. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 2522–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, T.-F.; Yang, Y. Effects of thermal annealing on the performance of polymer light emitting diodes. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 1595:1–1595:6. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.-Q.; Martini, I.B.; Liu, J.; Schwartz, B.J. Controlling interchain interactions in conjugated polymers: The effects of chain morphology on exciton-exciton annihilation and aggregation in MEH-PPV films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-Y.; Yen, H.-B.; Hung, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Lin, S.-C.; Huang, W.-Y.; Han, Y.-K. Effect of solvent-assisted thermal treatment on the performance of polyfluorene-based polymer light emitting diodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, J116–J119. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.E.; Lee, K.S.; Garcia, A.; Tarver, J.; Gomez, E.D.; Baldwin, K.; Sun, Y.; Meng, H.; Nguyen, T.-Q.; Loo, Y.-L. Directly patternable, highly conducting polymers for broad applications in organic electronics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5712–5717. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.; Chan, M.; Fung, M.; Lee, C.; Lee, S. Concentration effect of glycerol on the conductivity of PEDOT film and the device performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2003, 104, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peet, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Coates, N.E.; Ma, W.L.; Moses, D.; Heeger, A.J.; Bazan, G.C. Efficiency enhancement in low-bandgap polymer solar cells by processing with alkane dithiols. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, D.; Menon, R. Conformational modification of conducting polymer chains by solvents: Small-angle X-ray scattering study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 425, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.; Davis, F.; Legge, C. The effect of dopant molecules on the molecular order of electrically-conducting films of polypyrrole. Synth. Met. 1988, 26, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.W.; Travaš-Sejdić, J.; Cooney, R.P.; Bowmaker, G.A. Studies of dopant effects in poly(3,4-ethylenedi-oxythiophene) using Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2006, 37, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.A; Lovell, N.H.; Poole-Warren, L.A. Impact of co-incorporating laminin peptide dopants and neurotrophic growth factors on conducting polymer properties. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernaut, J.-M.; Reynolds, J.R. Use of conducting electroactive polymers for drug delivery and sensing of bioactive molecules. A redox chemistry approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 4080–4090. [Google Scholar]
- Wadhwa, R.; Lagenaur, C.F.; Cui, X.T. Electrochemically controlled release of dexamethasone from conducting polymer polypyrrole coated electrode. J. Control. Release 2006, 110, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, C.E.; Lee, T.Y.; Roper, T. Thiol-enes: Chemistry of the past with promise for the future. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 5301–5338. [Google Scholar]
- Kade, M.J.; Burke, D.J.; Hawker, C.J. The power of thiol-ene chemistry. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 743–750. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, H.-B.; Götz, G.; Reinold, E.; Vogt, A.; Schmid, S.; Blanco, R.; Segura, J.L.; Bäuerle, P. Click-functionalization of conducting poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT). Chem. Commun. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugaard, A.E.; Hvilsted, S.; Hansen, T.S.; Larsen, N.B. Conductive polymer functionalization by click chemistry. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 4321–4327. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, H.-B.; Götz, G.; Reinold, E.; Vogt, A.; Azumi, R.; Segura, J.L.; Bäuerle, P. "Click”-modification of a functionalized poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) soluble in organic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2677–2679. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, J.; Sahoo, R.; Kumar, A. Processable, regioregular, and “Click”able monomer and polymers based on 3,4-Propylenedioxythiophene with tunable solubility. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2015–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killops, K.L.; Campos, L.M.; Hawker, C.J. Robust, efficient, and orthogonal synthesis of dendrimers via thiol-ene “click” chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5062–5064. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, S.B.; Lin, C.-C.; Kuntzler, D.V.; Anseth, K.S. The performance of human mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in cell-degradable polymer-peptide hydrogels. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3564–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, B.D.; Schwartz, M.P.; Halevi, A.E.; Nuttelman, C.R.; Bowman, C.N.; Anseth, K.S.A. Versatile synthetic extracellular matrix mimic via thiol-norbornene photopolymerization. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 5005–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.M.; Killops, K.L.; Sakai, R.; Paulusse, J.M.J.; Damiron, D.; Drockenmuller, E.; Messmore, B.W.; Hawker, C.J. Development of thermal and photochemical strategies for thiolene click polymer functionalization. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 7063–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, B.; Hanks, T.W. Spectroscopic, microscopic, and surface analysis of alkanethiol- and fluoroalkanethiol-modified conducting polymer thin films. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8035–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, P.J.; Wallace, G.G.; Hanks, T.W. Hydrophobic conducting polymer films from post deposition thiol exposure. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, A.; Sindhu, S.; Narasimharao, K.; Gopal, E. Novel high contrast electrochromic polymer materials based on 3,4-propylenedioxythiophene. Opt. Mater. 2007, 30, 143–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Mishra, S. Novel 3,4-Propylenedioxythiophene Derivatives with Pendant Functional Groups. WO Patent WO/2006/117800, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Lee, V.A.; Raphael, Y.; Wiler, J.A.; Hetke, J.F.; Anderson, D.J.; Martin, D.C. Surface modification of neural recording electrodes with conducting polymer/biomolecule blends. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 56, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y. Adhesion of neural cells on silicon wafer with nano-topographic surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 187, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, V.; Maiorano, G.; Rizzello, L.; Sorce, B.; Sabella, S.; Cingolani, R.; Pompa, P.P. Neurons sense nanoscale roughness with nanometer sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6264–6269. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Feldman, K.E.; Martin, D.C. Functional Conducting Polymers via Thiol-ene Chemistry. Biosensors 2012, 2, 305-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2030305
Feldman KE, Martin DC. Functional Conducting Polymers via Thiol-ene Chemistry. Biosensors. 2012; 2(3):305-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2030305
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeldman, Kathleen E., and David C. Martin. 2012. "Functional Conducting Polymers via Thiol-ene Chemistry" Biosensors 2, no. 3: 305-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2030305
APA StyleFeldman, K. E., & Martin, D. C. (2012). Functional Conducting Polymers via Thiol-ene Chemistry. Biosensors, 2(3), 305-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2030305