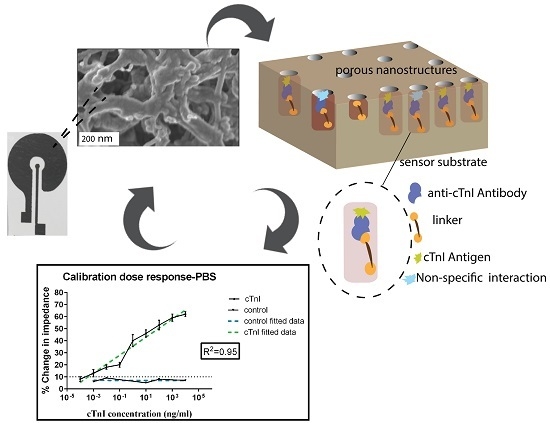
Flexible Molybdenum Electrodes towards Designing Affinity Based Protein Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sensor Fabrication and Characterization
2.2. Surface Functionalization of Sensor
2.3. Calibration Dose Response Analysis for cTnI Detection
2.4. EIS Technique for Label-Free Biosensing
3. Results
3.1. Material Characterization of Mo Deposition
3.2. Baseline Electrical Characterization
3.3. Antibody Saturation Study
3.4. Calibration Dose Response Study
3.5. Optical Readout for cTnI Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Chinnasamy, T.; Lifson, M.A.; Inci, F.; Demirci, U. Flexible substrate-based devices for point-of-care diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Advances in paper-based point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, G.; Fan, C. Development of electrochemical immunosensors towards point of care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panpradist, N.; Lai, J.J. 4.1—Point-of-Care Diagnostics A2—Ebara, Mitsuhiro. In Biomaterials Nanoarchitectonics; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Gan, N.; Hu, F.; Li, T.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, L. A single antibody sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on protein magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers mimicking capture probes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminati, M.; Vergani, M.; Ferrari, G.; Caranzi, L.; Caironi, M.; Sampietro, M. Accuracy and resolution limits in quartz and silicon substrates with microelectrodes for electrochemical biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, H.; Asghar, W.; Inci, F.; Yuksekkaya, M.; Jahangir, M.; Zhang, M.H.; Durmus, N.G.; Gurkan, U.A.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Demirci, U. Paper and flexible substrates as materials for biosensing platforms to detect multiple biotargets. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M.; Carrilho, E. Diagnostics for the developing world: Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, S.H.; Nam, H.; Cha, G.S.; Paeng, K.-J. A disposable amperometric sensor screen printed on a nitrocellulose strip: A glucose biosensor employing lead oxide as an interference-removing agent. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.T.T.; Peh, A.E.K.; Chee, C.Y.L.; Fink, K.; Chow, V.T.K.; Ng, M.M.L.; Toh, C.-S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy characterization of nanoporous alumina dengue virus biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2012, 88, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiga, S.P.; Jin, C.; Curtiss, L.A.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Narayan, R.J. Nanoporous membranes for medical and biological applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 1, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scampicchio, M.; Arecchi, A.; Lawrence, N.S.; Mannino, S. Nylon nanofibrous membrane for mediated glucose biosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assolant-vinet, C.H.; Coulet, P.R. New immobilized enzyme membranes for tailor-made biosensors. Anal. Lett. 1986, 19, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquette, C.A.; Leca, B.D.; Blum, L.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol for oxidase-based fibre-optic biosensors. Luminescence 2001, 16, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munje, R.D.; Muthukumar, S.; Panneer Selvam, A.; Prasad, S. Flexible nanoporous tunable electrical double layer biosensors for sweat diagnostics. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panneer Selvam, A.; Prasad, S.; Barrett, T.W.; Kazmierczak, S.C. Electrical nanowell diagnostics sensors for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, H.; Kakiage, M.; Sekiya, M.; Sakuma, D.; Yamonobe, T.; Takano, N.; Barraud, A.; Meurville, E.; Ryser, P. Size-selective diffusion in nanoporous but flexible membranes for glucose sensors. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattipalli, K.; Feikert, P.; Brandigampala, S.; Prasad, S. Study of nanoporous membranes with applications in the enhanced detection of cadiovascular biomarker proteins. Nano Life 2010, 01, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Yu, H.; Niu, Y.; Sun, C. Covalent attachment of glucose oxidase to an Au electrode modified with gold nanoparticles for use as glucose biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2005, 67, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogomolova, A.; Komarova, E.; Reber, K.; Gerasimov, T.; Yavuz, O.; Bhatt, S.; Aldissi, M. Challenges of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in protein biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3944–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.; Liu, W.; Xie, X.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S.; Banerjee, K. MoS2 field-effect transistor for next-generation label-free biosensors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3992–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Ou, J.Z. Biosensors based on two-dimensional MoS2. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, L.; Santagata, F.; Iervolino, E.; Mihailovic, M.; Rossi, T.; Tran, A.T.; Schellevis, H.; Creemer, J.F.; Sarro, P.M. A molybdenum MEMS microhotplate for high-temperature operation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 188, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Han, J.; Jang, A.; Bishop, P.L.; Ahn, C.H. A disposable on-chip phosphate sensor with planar cobalt microelectrodes on polymer substrate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1902–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, X.-Y.; Fu, H.-Y.; Hou, C.; Han, G.-F.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.-B.; Jiang, Q. Nanoporous gold supported cobalt oxide microelectrodes as high-performance electrochemical biosensors. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Radhakrishnan, L.; Zhao, B.; Uppalapati, B.; Daniels, R.C.; Ward, K.R.; Collinson, M.M. Electrochemical properties of nanostructured porous gold electrodes in biofouling solutions. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11610–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherng, J.; Chen, T.; Lin, C. Pulsed-DC sputtering of molybdenum bottom electrode and piezoelectric aluminum nitride films for bulk acoustic resonator applications. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 6797–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilha, J.C.; Martini, E.M.A.; Brum, C.; de Souza, M.O.; de Souza, R.F. Study of molybdenum electrodes for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-W.; Li, F.; Wu, Z.-S.; Ren, W.; Cheng, H.-M. Electrochemical interfacial capacitance in multilayer graphene sheets: Dependence on number of stacking layers. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikstrom, L.; Nobe, K. The electrochemical behavior of molybdenum. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1969, 116, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byskov, L.S.; Hammer, B.; Nørskov, J.K.; Clausen, B.S.; Topsøe, H. Sulfur bonding in MoS2 and Co-Mo-S structures. Catal. Lett. 1997, 47, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, B.; Auckland, M.L.; Cummins, P. Cardiac-specific troponin-l radioimmunoassay in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 1987, 113, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, G.S.; Porter, S.; Landt, Y.; Ladenson, J.H. Development of monoclonal antibodies for an assay of cardiac troponin-I and preliminary results in suspected cases of myocardial infarction. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 2203–2214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- hen, W.; Tian, D.; Cui, H.; Yang, D.; Bian, Z. Nanoparticle-based electrochemiluminescence immunosensor with enhanced sensitivity for cardiac troponin I using N-(aminobutyl)-N-(ethylisoluminol)-functionalized gold nanoparticles as labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 27, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Singal, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Biradar, A.M.; Mulchandani, A.; Rajesh. Pt nanoparticles-chemical vapor deposited graphene composite based immunosensor for the detection of human cardiac troponin I. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 205, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Biosensors for cardiac biomarkers detection: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittmer, W.U.; Evers, T.H.; Hardeman, W.M.; Huijnen, W.; Kamps, R.; de Kievit, P.; Neijzen, J.H.M.; Nieuwenhuis, J.H.; Sijbers, M.J.J.; Dekkers, D.W.C.; et al. Rapid, high sensitivity, point-of-care test for cardiac troponin based on optomagnetic biosensor. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-Y.; Bian, Z.-P.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhu, J.-J. PDMS gold nanoparticle composite film-based silver enhanced colorimetric detection of cardiac troponin I. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-C.; Kim, M.-G.; Kim, E.-M.; Shin, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-K.; Lee, S.D.; Cho, M.-J.; Ro, H.-S. Development of a surface plasmon resonance-based immunosensor for the rapid detection of cardiac troponin I. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Oncescu, V.; Lee, S.; Choi, I.; Erickson, D. Label-free electrochemical monitoring of vasopressin in aptamer-based microfluidic biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 759, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, J.S.; Pourmand, N. Label-free impedance biosensors: Opportunities and challenges. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 1239–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randviir, E.P.; Banks, C.E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: An overview of bioanalytical applications. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1098–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Davis, J.J. Electrical biosensors and the label free detection of protein disease biomarkers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5944–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.; Muthukumar, S.; Panneer Selvam, A.; Engel Craven, J.; Prasad, S. Ultra-sensitive electrical immunoassay biosensors using nanotextured zinc oxide thin films on printed circuit board platforms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisdat, F.; Schäfer, D. The use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for biosensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Evers, T.H.; Prins, M.W.J. How Antibody Surface Coverage on Nanoparticles Determines the Activity and Kinetics of Antigen Capturing for Biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8158–8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Qu, F.; Lu, Y.; He, Y.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Platinum nanowire nanoelectrode array for the fabrication of biosensors. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5944–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Xi, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, E. Three-dimensional electrochemical immunosensor for sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen based on monolithic and macroporous graphene foam. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Technique | LoD | Dynamic Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemiluminescence | 0.0025 ng/mL | 0.0025–10 ng/mL | [34] |
| Faradaic Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) | 4.2 pg/mL | 0.01–10 ng/mL | [35] |
| Optomagnetic biosensor | 0.03 ng/mL | 0.03–6.5 ng/mL | [37] |
| Colorimetric | 0.01 ng/mL | 0.01–5 ng/mL | [38] |
| Surface plasmon resonance | 68 ng/L | 68 ng/L–660 μg/L | [39] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamakoti, V.; Panneer Selvam, A.; Radha Shanmugam, N.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Flexible Molybdenum Electrodes towards Designing Affinity Based Protein Biosensors. Biosensors 2016, 6, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030036
Kamakoti V, Panneer Selvam A, Radha Shanmugam N, Muthukumar S, Prasad S. Flexible Molybdenum Electrodes towards Designing Affinity Based Protein Biosensors. Biosensors. 2016; 6(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamakoti, Vikramshankar, Anjan Panneer Selvam, Nandhinee Radha Shanmugam, Sriram Muthukumar, and Shalini Prasad. 2016. "Flexible Molybdenum Electrodes towards Designing Affinity Based Protein Biosensors" Biosensors 6, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030036
APA StyleKamakoti, V., Panneer Selvam, A., Radha Shanmugam, N., Muthukumar, S., & Prasad, S. (2016). Flexible Molybdenum Electrodes towards Designing Affinity Based Protein Biosensors. Biosensors, 6(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6030036