Acquisition of Colistin Resistance Links Cell Membrane Thickness Alteration with a Point Mutation in the lpxD Gene in Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
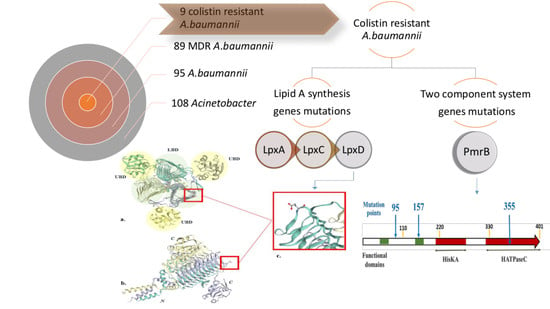
2.1. Testing the Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Identified A. baumannii Isolates
2.2. Colistin Resistance Induction
2.3. Susceptibility Profile and Colistin Resistance Acquisition
2.4. Colistin Resistance Acquisition and Cell Morphology
2.5. Mutation Analysis of PmrB and LpxACD Based on Nucleotide Sequences
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Bacterial Strains
5.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
5.3. Colistin Resistance Induction
5.4. Cell Morphological Examination Using Thin-Section Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
5.5. Nucleotide Sequencing of pmrB and lpx lipid A Biosynthesis Genes
5.6. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
5.7. Protein 3D Model Prediction
Abbreviation
| Col-R | Colistin-resistant |
| Col-S | Colistin-sensitive |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| CA-MHB | Cation adjustment Muller–Hinton Broth |
| CFU | Colony-Forming Unit |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Rayner, C.R.; Nation, R.L.; Owen, R.J.; Spelman, D.; Tan, K.E.; Liolios, L. Heteroresistance to colistin in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antunes, L.; Imperi, F.; Carattoli, A.; Visca, P. Deciphering the multifactorial nature of Acinetobacter baumannii pathogenicity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, D.; Nielsen, T.; Bonomo, R.; Pantapalangkoor, P.; Luna, B.; Spellberg, B. Clinical and Pathophysiological Overview of Acinetobacter Infections: A Century of Challenges. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 409–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikaido, H. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2003, 67, 593–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dahdouh, E.; Gómez-Gil, R.; Sanz, S.; González-Zorn, B.; Daoud, Z.; Mingorance, J.; Suárez, M. A novel mutation in pmrB mediates colistin resistance during therapy of Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pournaras, S.; Poulou, A.; Dafopoulou, K.; Chabane, Y.N.; Kristo, I.; Makris, D.; Hardouin, J.; Cosette, P.; Tsakris, A.; Dé, E. Growth retardation, reduced invasiveness, and impaired colistin-mediated cell death associated with colistin resistance development in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Napier, B.A.; Burd, E.M.; Satola, S.W.; Cagle, S.M.; Ray, S.M.; Mcgann, P.; Pohl, J.; Lesho, E.P.; Weiss, D.S. Clinical use of colistin induces cross-resistance to host antimicrobials in Acinetobacter baumannii. MBio 2013, 4, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Halfawy, O.M.; Valvano, M.A. Antimicrobial heteroresistance: An Emerging Field in Need of Clarity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Halfawy, O.; Valvano, M. Chemical Communication of Antibiotic Resistance by a highly Resistant subpopulation of bacterial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moffatt, J.; Harper, M.; Harrison, P.; Hale, J.D.F.; Vinogradov, E.; Seemann, T.; Henry, R.; Crane, B.; St. Michael, F.; Cox, A.D.; et al. Colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii is mediated by complete loss of lipopolysaccharide production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4971–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Zeng, X.; Hinenoya, A.; Lina, J. MCR-1 Confers Cross-Resistance to Bacitracin, a Widely Used In-Feed Antibiotic. mSphere 2018, 3, e00411–e00418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adam, M.; Murali, B.; Glenn, N.O.; Potter, S. Epigenetic Inheritance Based Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Lesho, E.; Yoon, E.J.; Mcgann, P.; Snesrud, E.; Kwak, Y.; Milillo, M.; Onmus-Leone, F.; Preston, L.; St. Clair, K.; Nikolich, M.; et al. Emergence of colistin-resistance in extremely drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii containing a novel pmrCAB operon during colistin therapy of wound infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arroyo, L.A.; Herrera, C.M.; Fernandez, L.; Hankins, J.V.; Trent, M.S.; Hancock, R.E.W. The pmrCAB Operon Mediates Polymyxin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 and Clinical Isolates through Phosphoethanolamine Modification of Lipid A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3743–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trent, M.; Ribeiro, A.; Lin, S.; Cotter, R.; Raetz, C. An inner membrane enzyme in Salmonella and Escherichia coli that transfers 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose to lipid A: Induction on polymyxin-resistant mutants and role of a novel lipid-linked donor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43122–43131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Hsu, F.F.; Turk, J.; Groisman, E.A. The PmrA-regulated pmrC gene mediates phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A and polymyxin resistance in Salmonella enterica. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 4124–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunn, J.S. The Salmonella PmrAB regulon: Lipopolysaccharide modifications, antimicrobial peptide resistance and more. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro, A.; Llobet, E.; Aranda, J.; Bengoechea, J.A.; Doumith, M.; Hornsey, M.; Dhanji, H.; Chart, H.; Bou, G.; Livermore, D.M.; et al. Phosphoethanolamine Modification of Lipid A in Colistin-Resistant Variants of Acinetobacter baumannii Mediated by the pmrAB Two-Component Regulatory System. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3370–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, M.D.; Nickel, G.C.; Bajaksouzian, S.; Lavender, H.; Murthy, A.R.; Jacobs, M.R.; Bonomo, R.A. Resistance to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii associated with mutations in the PmrAB two-component system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3628–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soon, R.; Nation, R.; Hartley, P.; Larson, I.; Li, J. Atomic force microscopy investigation of the morphology and topography of colistin-heteroresistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains as a function of growth phase and in response to colistin treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4979–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo’pez-Rojas, R.; Domínguez-Herrera, J.; McConnell, M.; Docobo-Peréz, F.; Smani, Y.; Fernández-Reyes, M.; Rivas, L.; Pachón, J. Impaired Virulence and in Vivo Fitness of Colistin Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hesham, M.; Saleh, N.M.; Ahmed, R.S.; Amin, M.A. Colistin Resistance Induction Effect on Multi-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter Baeumannii. In Proceedings of the Poster AAR LB11 abstr Antimicrobial Resistance American Society of Microbiology, Atlanta, Gorgia, 15 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, X.; Liu, L.; Fang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Shi, K.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yu, Y. Colistin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii MDR-ZJ06 Revealed by a Multiomics Approach. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdulzahra, A.T.; Khalil, M.A.F.; Elkhatib, W.F. First report of colistin resistance among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates recovered from hospitalized patients in. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 26, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Mechanisms and epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 15, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Agamy, M.H.; Khalaf, N.G.; Tawfick, M.M.; Shibl, A.M.; El Kholy, A. Molecular characterization of carbapenem-insensitive Acinetobacter baumannii in Egypt. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 22, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Hassan, L.; Zafer, M.M.; El-Mahallawy, H. Multiple sequence types responsible for healthcare-associated Acinetobacter baumannii dissemination in a single centre in Egypt. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benmahmod, A.B.; Said, H.S.; Ibrahim, R.H. Prevalence and Mechanisms of Carbapenem Resistance Among Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates in Egypt. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Servat, S.; Yero, D.; Huedo, P.; Marquez, R.; Molina, G.; Daura, X.; Gibert, I. Heterogeneous colistin-resistance phenotypes coexisting in stenotrophomonas maltophiliaisolates influence colistin susceptibility testing. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournaras, S.; Ikonomidis, A.; Markogiannakis, A.; Maniatis, A.N.; Tsakris, A. Heteroresistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 1055–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, C.H.; Li, J.; Nation, R.L. Activity of colistin against heteroresistant Acinetobacter baumannii and emergence of resistance in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3413–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezadi, F.; Jamali, A.; Heidari, A.; Javid, N.; Ardebili, A. Heteroresistance to colistin in oxacillinases-producing carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Gorgan, Northern Iran. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, J.S.; Murray, C.K.; Jorgensen, J.H. Colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter and its association with previous colistin therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moosavian, M.; Shoja, S.; Nashibi, R.; Ebrahimi, N.; Tabatabaiefar, M.A.; Rostami, S.; Peymani, A. Post neurosurgical meningitis due to colistin heteroresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.J.; Ko, K.S. Mutant prevention concentrations of colistin for Acinetobacter baumannii, pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charretier, Y.; Diene, S.M.; Baud, D.; Chatellier, S.; Santiago-Allexant, E.; Van Belkum, A.; Guigon, G.; Schrenzel, J. Colistin heteroresistance and involvement of the PmrAB regulatory system in acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pachón, J.; Vila, J. Treatment of multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 10, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Owen, R.J.; Wong, S.; Spelman, D.; Franklin, C. Antibiograms of Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Acinetobacter baumannii: Promising Therapeutic Options for Treatment of Infection with Colistin-Resistant Strains. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Y.; Hua, X. The effect of colistin resistance-associated mutations on the fitness of Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bojkovic, J.; Richie, D.L.; Six, D.A.; Rath, C.M.; Sawyer, W.S.; Hu, Q.; Dean, C.R. Characterization of an Acinetobacter baumannii lptD Deletion Strain: Permeability Defects and Response to Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide and Fatty Acid Biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurtop, E.; Bayındır, B.F.; Menekse, S.; Kurt, A.O.; Gönen, M.; Ergonul, O.; Can, F. Promoters of Colistin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Infections. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badger, J.; Chie-Leon, B.; Logan, C.; Sridhar, V.; Sankaran, B.; Zwart, P.; Nienabera, V. Structure determination of LpxD from the lipopolysaccharide-synthesis pathway of Acinetobacter baumannii. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2013, 69, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheah, S.E.; Johnson, M.D.; Zhu, Y.; Tsuji, B.T.; Forrest, A.; Bulitta, J.B.; Boyce, J.D.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Polymyxin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Genetic Mutations and Transcriptomic Changes in Response to Clinically Relevant Dosage Regimens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moskowitz, S.; Brannon, M.; Dasgupta, N.; Pier, M.; Sgambati, N.; Miller, A.; Denton, M.; Conway, P.; Johansen, H.; Høiby, N. PmrB mutations promote polymyxin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from colistin-treated cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filloux, A. Secretion signal and protein targeting in bacteria: A biological puzzle. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3847–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cannatelli, A.; Giani, T.; Aiezza, N.; Pilato, V.D.; Principe, L.; Luzzaro, F.; Galeotti, C.L.; Rossolini, G.M. An allelic variant of the PmrB sensor kinase responsible for colistin resistance in an Escherichia coli strain of clinical origin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, N.; Ellington, M.J.; Coelho, J.M.; Turton, J.F.; Ward, M.E.; Brown, S.; Amyes, S.G.B.; Livermore, D.M. Multiplex PCR for genes encoding prevalent OXA carbapenemases in Acinetobacter spp. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 27, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Fourth Informational Supplement M100-S24; CLSI Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Thi Khanh Nhu, N.; Riordan, D.W.; Do Hoang Nhu, T.; Thanh, D.P.; Thwaites, G.; Huong Lan, N.P.; Wren, B.W.; Baker, S.; Stabler, R.A. The induction and identification of novel Colistin resistance mutations in Acinetobacter baumannii and their implications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 14, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Antibiotic Name | Resistance Level in Clinical A. baumannii Isolates | Level of Co-Resistance to Antibiotic and Colistin * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | I | S | No. | % | |||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | ||||
| Ampicillin/sulbactam | 85 | 90 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 100 | |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 66 | 70 | 23 | 24 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 88.8 | |
| 3rd generation | Ceftazidime | 88 | 93 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 100 |
| 4th generation | Cefepime | 89 | 94 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 100 |
| Amikacin | 68 | 72 | 19 | 20 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 77.7 | |
| Ciprofloxacin | 78 | 82 | 12 | 13 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 88.8 | |
| Imipenem | 66 | 70 | 2 | 2 | 27 | 28 | 8 | 88.8 | |
| Tigecycline | 21 | 22 | 35 | 37 | 39 | 41 | 4 | 44.4 | |
| Trimethoprim/ Sulfamethoxazole | 81 | 85 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 100 | |
| Clinical A. baumannii Isolates Antibiotics | Resistance Pattern | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS48D | MS50 | MS64 | MS48D | MS050 | MS64 | |
| Col-S Before Induction | Col-R After Induction | |||||
| Colistin MIC (μg/mL) | 0.125 | <0.06 | 0.06 | 14 | 16 | 32 |
| CT | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| TZP | R | S | S | R | R | R |
| FEP | R | I | S | R | R | R |
| CIP | R | S | S | R | R | R |
| IMP | S | S | S | S | S | I |
| TGC | I | S | S | I | I | I |
| CAZ | R | R | S | R | R | R |
| SAM | R | S | S | R | R | R |
| SXT | R | S | S | R | R | R |
| AK | R | S | S | R | R | R |
| Strains | Colistin (Col) a MIC (g/mL) | Amino Acid Change(s) in b: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pmrB (444 aa) | ||||||
| lpxD (aa356) | TM1 (aa 10–29) | TM2 (142–164) | HisKA (aa 218–280) | HATPaseC (aa 326–437) | ||
| MS64Col-S | 32 | |||||
| MS64Col-R | 14 | K117E | ||||
| MS34Col-R | 16 | K117E | A95T | P157R | 355 frameshift | |
| Gene Name | Use | Sequence (5′-3′) | bp | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaOXA-51-like | A. baumannii Identification | F | 5′TAATGCTTTGAT CGGCCTTG3′ | 353 | [47] |
| R | 5′TGGATTGCACTTCATCTTGG3′ | ||||
| lpxA | Lipid A synthesis | F | 5′TGAAGCATTA GCTCAAGTTT3′ | 1181 | [10] |
| R | 5′GTCAGCAAATCAATACAAGA3′ | ||||
| lpxD | F | 5′CAAAGTATGAATACAACTTTTGAG3′ | 1164 | ||
| R | 5′GTCAATGGCACATCTGCTAAT3′ | ||||
| lpxC | F | 5′TGAAGATGACGTTCCTGCAA3′ | 1502 | ||
| R | 5′TGGTGAAAATCAGGCAATGA3′ | ||||
| pmrB1 | Two-Component System | F | 5′GTGCATTATTCATTAAAAAAAC 3′ | 1335 | [18] |
| R | 5′TCACGCTCTTGTTTCATGTA 3′ | ||||
| pmrB2 | F | 5′GGTTCGTGAAGCTTTCG 3′ | 599 | ||
| R | 5′CCTAAATCGATTTCTTTTTG 3′ | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, N.M.; Hesham, M.S.; Amin, M.A.; Samir Mohamed, R. Acquisition of Colistin Resistance Links Cell Membrane Thickness Alteration with a Point Mutation in the lpxD Gene in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040164
Saleh NM, Hesham MS, Amin MA, Samir Mohamed R. Acquisition of Colistin Resistance Links Cell Membrane Thickness Alteration with a Point Mutation in the lpxD Gene in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(4):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040164
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Neveen M., Marwa S. Hesham, Magdy A. Amin, and Reham Samir Mohamed. 2020. "Acquisition of Colistin Resistance Links Cell Membrane Thickness Alteration with a Point Mutation in the lpxD Gene in Acinetobacter baumannii" Antibiotics 9, no. 4: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040164
APA StyleSaleh, N. M., Hesham, M. S., Amin, M. A., & Samir Mohamed, R. (2020). Acquisition of Colistin Resistance Links Cell Membrane Thickness Alteration with a Point Mutation in the lpxD Gene in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics, 9(4), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040164