Dielectric Nanoparticles Coated upon Silver Hollow Nanosphere as an Integrated Design to Reinforce SERS Detection of Trace Ampicillin in Milk Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Fabrications of PS, Ag HNS, and Di NPs/Ag HNS
2.2. Structural and Morphological Characterization
2.3. SERS Property of Ag HNS and Di NPs/Ag HNS
2.4. Trace Detection of Ampicillin in Water and in Milk Solution
2.5. Enhancement Factor Evaluation and Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Size and Dimension of Ag HNS
3.2. Di NPs upon Ag HNS
3.3. SERS Property of Di NPs/Ag HNS
3.4. Di NPs/Ag HNS for Trace Detection of Antibiotic Residue in Water
3.5. Di NPs/Ag HNS for Trace Detection of Ampicillin in Milk Solution
3.6. Schematic Description of Ampicillin Detection in Water and in Milk Solution
4. Conclusions
5. Highlights
- Ag HNS is prepared by a template-assisted method, followed by e-beam evaporated Di NPs, and formed as Di NPs/Ag HNS.
- Al2O3/Ag HNS with low dielectric constant and smaller diameter of HNS obtains higher SERS enhancement factor.
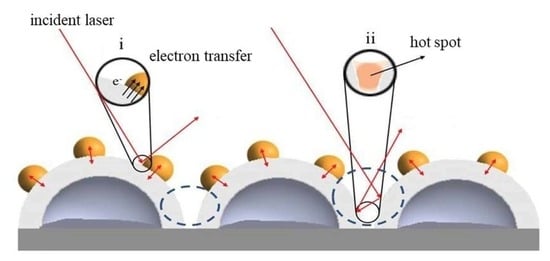
- The main electromagnetic effect of Di NPs/Ag HNS occurs at the interfaces of Di NPs, the surface of Ag shell, and the space of cavity.
- For all Di NPs/Ag HNS, trace detection of ampicillin in water is efficient, SERS intensities increase with the addition of ampicillin.
- Ampicillin in milk solution is influenced by non-specific binding molecules that lengthen the distance of ampicillin with SERS-active sites.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pu, H.; Xiao, W.; Sun, D. SERS-microfluidic systems: A potential platform for rapid analysis of food contaminants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T.; Merkoçi, A.; Manz, A.; Urban, G.A.; Güder, F. Disposable Sensors in Diagnostics, Food, and Environmental Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E. Environmental transformations of silver nanoparticles: Impact on stability and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Sun, D.W.; Pu, H.; Chen, L.; Lin, L. Applications of Raman spectroscopic techniques for quality and safety evaluation of milk: A review of recent developments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 770–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Sun, Z.; Gong, B. Preparation of ampicillin surface molecularly imprinted polymers for its selective recognition of ampicillin in eggs samples. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 2018, 5897381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, C.; Kiefl, J.; Reichenbach, S.E.; Bicchi, C. Characterization of odorant patterns by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography: A challenge in omic studies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, B.; Echeverria, A.; Gonzalez, F.; Castillo, O.; Eubanks, T.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Phytochemical investigation of Magnolia grandiflora green seed cones: Analytical and phytoceutical studies. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faraji, M. Determination of some red dyes in food samples using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent-based vortex assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1591, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banholzer, M.J.; Millstone, J.E.; Qin, L.; Mirkin, C.A. Rationally designed nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Cao, P.; Liu, R. A multi-residue method for fast determination of pesticides in tea by ultra performance liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry combined with modified QuEChERS sample preparation procedure. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.A.; Zhao, Y.; Sivashanmugan, K.; Alan, X. Quantitative TLC-SERS detection of histamine in seafood with support vector machine analysis. Food Control 2019, 103, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaseen, T.; Sun, D.W.; Cheng, J.H. Raman imaging for food quality and safety evaluation: Fundamentals and applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Li, X. Optimal Size of Gold Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy under Different Conditions. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 790323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Liao, J.-D.; Sivashanmugan, K.; Liu, B.; Fu, W.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, G.; Juang, Y.-D. Gold Nanoparticle-Coated ZrO2-Nanofiber Surface as a SERS-Active Substrate for Trace Detection of Pesticide Residue. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.Y.; Yi, J.; Li, J.F.; Ren, B.; Wu, D.Y.; Panneerselvam, R.; Tian, Z.Q. Nanostructure-based plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for surface analysis of materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Han, G.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, R.; Jiang, C.; Wang, S.; Han, M.Y. Shell thickness-dependent Raman enhancement for rapid identification and detection of pesticide residues at fruit peels. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivashanmugan, K.; Liao, J.; Der Liu, B.H.; Yao, C.K. Focused-ion-beam-fabricated Au nanorods coupled with Ag nanoparticles used as surface-enhanced Raman scattering-active substrate for analyzing trace melamine constituents in solution. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 800, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrini, L.; Graham, D. Molecularly-mediated assemblies of plasmonic nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7085–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Andrade, G.F.S.; Ahmed, A.; Souza, M.L.; Coombs, N.; Tumarkin, E.; Liu, K.; Gordon, R.; Brolo, A.G.; Kumacheva, E. Probing dynamic generation of hot-spots in self-assembled chains of gold nanorods by surface-enhanced raman scattering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7563–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivashanmugan, K.; Liao, J.; Der Liu, B.H.; Yao, C.K.; Luo, S.C. Ag nanoclusters on ZnO nanodome array as hybrid SERS-active substrate for trace detection of malachite green. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.C.; Luong, T.Q.N.; Cao, T.A.; Kieu, N.M. High-sensitive SERS detection of thiram with silver nanodendrites substrate. Nat. Sci.-Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.N.; Larmour, I.A.; Smith, W.E.; Faulds, K.; Graham, D. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering investigation of hollow gold nanospheres. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8338–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Cheng, L.; Lee, S.T.; Liu, Z. Noble metal coated single-walled carbon nanotubes for applications in surface enhanced raman scattering imaging and photothermal therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7414–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolosiuk, A.; Tognalli, N.G.; Martínez, E.D.; Granada, M.; Fuertes, M.C.; Troiani, H.; Bilmes, S.A.; Fainstein, A.; Soler-Illia, G.J.A.A. Silver nanoparticle-mesoporous oxide nanocomposite thin films: A platform for spatially homogeneous SERS-active substrates with enhanced stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5263–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Hassan, M.M.; Ahmad, W.; Jiao, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Q. A highly structured hollow ZnO@Ag nanosphere SERS substrate for sensing traces of nitrate and nitrite species in pickled food. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, K.B.; Xu, C.; Xu, S.C.; Li, G.H. Large-scale solvothermal synthesis of Ag nanocubes with high SERS activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 772, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Song, X.; Bu, Y. A green and general strategy for the synthesis of hollow Ag/CdS nanocomposites for superior SERS performance. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 3709–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zang, Y.; Yue, C.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Wu, Z. Ag nanoparticle/ZnO hollow nanosphere arrays: Large scale synthesis and surface plasmon resonance effect induced Raman scattering enhancement. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7902–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Ji, X. A facile approach for the fabrication of Au/ZnO-hollow-sphere-monolayer thin films and their photocatalytic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 412, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.; Oveys, H.; Fan, X. Increasing the enhancement of SERS with dielectric microsphere resonators. Spectrosc. Springf. Eugene Duluth 2006, 21, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Anandan, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Pugazhenthiran, N.; Madhavan, J.; Maruthamuthu, P. Effect of loaded silver nanoparticles on TiO2 for photocatalytic degradation of Acid Red 88. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Fan, Y. Simultaneous Thermal Stability and Ultrahigh Sensitivity of Heterojunction SERS Substrates. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleinman, S.L.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.I.; Dieringer, J.A.; Van Duyne, R.P. Creating, characterizing, and controlling chemistry with SERS hot spots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; Zou, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. High-Performance Real-Time SERS Detection with Recyclable Ag Nanorods@HfO2 Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27162–27168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.Y.; de Albuquerque, C.D.L.; Poppi, R.J.; Brolo, A.G. Determination of aqueous antibiotic solutions using SERS nanogratings. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 982, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Hassan, M.M.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Synthesized Au NPs@silica composite as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrate for fast sensing trace contaminant in milk. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 206, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.H.; Lim, Y.T.; Suh, D.J.; Park, O.O. Three-Dimensional Self-Assembly of Colloids at a Water-Air Interface: A Novel Technique for the Fabrication of Photonic Bandgap Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1367–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.P.; Franca, A.S.; Irudayaraj, J. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Applied to Food Safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, C.; Mirsafavi, R.; Moskovits, M.; Meinhart, C.D. Detection of low concentrations of ampicillin in milk. Analyst 2015, 140, 5003–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, A.I.; Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Brongersma, M.L.; Kivshar, Y.S.; Luk’yanchuk, B. Optically resonant dielectric nanostructures. Science 2016, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yesilkoy, F.; Arvelo, E.R.; Jahani, Y.; Liu, M.; Tittl, A.; Cevher, V.; Kivshar, Y.; Altug, H. Ultrasensitive hyperspectral imaging and biodetection enabled by dielectric metasurfaces. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Sun, D.W.; Pu, H.; Wei, Q. Shell thickness-dependent Au@Ag nanoparticles aggregates for high-performance SERS applications. Talanta 2019, 195, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Zhang, A.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, D. Monodisperse Au@Ag core-shell nanoprobes with ultrasensitive SERS-activity for rapid identification and Raman imaging of living cancer cells. Talanta 2019, 198, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitjar, J.; Liao, J.-D.; Lee, H.; Liu, B.H.; Fu, W. SERS-Active Substrate with Collective Amplification Design for Trace Analysis of Pesticides. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.X.; Fan, H.J. Highly ordered arrays of particle-in-bowl plasmonic nanostructures for surface-enhanced raman scattering. Small 2012, 8, 2548–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarek, M.; Roguska, A.; Kudelski, A.; Andrzejczuk, M.; Janik-Czachor, M.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. The role of Ag particles deposited on TiO2 or Al2O3 self-organized nanoporous layers in their behavior as SERS-active and biomedical substrates. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, M.T.; Chau, R.S.; Ghani, T.; Mistry, K. The high-k solution. IEEE Spectr. 2007, 44, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ru, E.C.; Blackie, E.; Meyer, M.; Etchegoint, P.G. Surface enhanced raman scattering enhancement factors: A comprehensive study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13794–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zahry, M.R.; Refaat, I.H.; Mohamed, H.A.; Rosenberg, E.; Lendl, B. Utility of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) for elucidation and simultaneous determination of some penicillins and penicilloic acid using hydroxylamine silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2015, 144, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivashanmugan, K.; Lee, H.; Syu, C.; Liu, B.H.; Liao, J. Nanoplasmonic Au/Ag/Au nanorod arrays as SERS-active substrate for the detection of pesticides residue. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 75, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Lock, A.L.; Garnsworthy, P.C. Technical Note: A Rapid Lipid Separation Method for Determining Fatty Acid Composition of Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3785–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Xhibo, F.; Yücel, N.; Turan, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Nanomaterials for SERS Biomedical/Environmental Application Project Supervisors. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336498006_Synthesis_and_Characterization_of_Novel_Nanomaterials_for_SERS_BiomedicalEnvironmental_Application_Project_Supervisors (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Aguilar-Hernández, I.; Afseth, N.K.; López-Luke, T.; Contreras-Torres, F.F.; Wold, J.P.; Ornelas-Soto, N. Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy of phenolic antioxidants: A systematic evaluation of ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid and sinapic acid. Vib. Spectrosc. 2017, 89, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Substrates | Raman Laser Wavelength of 633 nm at the Characteristic Peak of 1361 cm−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ISERS (× 104) | NSERS (× 106) | EF (× 107) | |
| Ag HNS_130 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 1.6 |
| HfO2/Ag HNS | 8.9 | 2.6 | 5.4 |
| TiO2/Ag HNS | 8.7 | 2.6 | 5.2 |
| Al2O3/Ag HNS | 10.3 | 2.6 | 6.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Yang, J.-W.; Liao, J.-D.; Sitjar, J.; Liu, B.H.; Sivashanmugan, K.; Fu, W.-E.; Chen, G.D. Dielectric Nanoparticles Coated upon Silver Hollow Nanosphere as an Integrated Design to Reinforce SERS Detection of Trace Ampicillin in Milk Solution. Coatings 2020, 10, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10040390
Lee H, Yang J-W, Liao J-D, Sitjar J, Liu BH, Sivashanmugan K, Fu W-E, Chen GD. Dielectric Nanoparticles Coated upon Silver Hollow Nanosphere as an Integrated Design to Reinforce SERS Detection of Trace Ampicillin in Milk Solution. Coatings. 2020; 10(4):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10040390
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Han, Jia-Wei Yang, Jiunn-Der Liao, Jaya Sitjar, Bernard Haochih Liu, Kundan Sivashanmugan, Wei-En Fu, and Guo Dung Chen. 2020. "Dielectric Nanoparticles Coated upon Silver Hollow Nanosphere as an Integrated Design to Reinforce SERS Detection of Trace Ampicillin in Milk Solution" Coatings 10, no. 4: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10040390
APA StyleLee, H., Yang, J. -W., Liao, J. -D., Sitjar, J., Liu, B. H., Sivashanmugan, K., Fu, W. -E., & Chen, G. D. (2020). Dielectric Nanoparticles Coated upon Silver Hollow Nanosphere as an Integrated Design to Reinforce SERS Detection of Trace Ampicillin in Milk Solution. Coatings, 10(4), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10040390