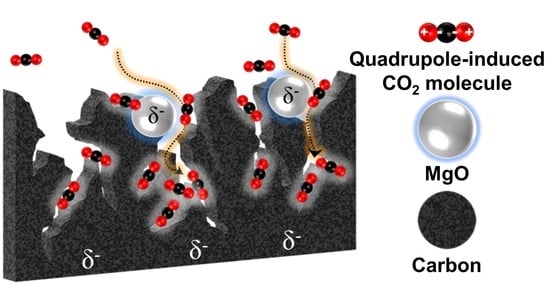
Roles of London Dispersive and Polar Components of Nano-Metal-Coated Activated Carbons for Improving Carbon Dioxide Uptake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Properties
3.2. Surface Properties
3.3. Structural Properties
3.4. Textural Properties
3.5. CO2 Uptake Behaviors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamson, A. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 784. [Google Scholar]
- Saint Flour, C.; Papirer, E. Gas-solid chromatography. A method of measuring surface free energy characteristics of short glass fibers. 1. Through adsorption isotherms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1982, 21, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Brendle, M. London dispersive component of the surface free energy and surface enthalpy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 188, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.M. Attractive forces at interfaces. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1964, 56, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D. Physical adsorption on low energy solids. II. Adsorption of nitrogen, argon, carbon tetrafluoride, and ethane on polypropylene1. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 2788–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, V. The Donor-Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Coriani, S.; Halkier, A.; Rizzo, A.; Ruud, K. On the molecular electric quadrupole moment and the electric-field-gradient-induced birefringence of CO2 and CS2. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 326, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-S.; Suh, M.P. Highly selective CO2 capture in flexible 3d coordination polymer networks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6865–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, A.D.; Disch, R.L.; Pople, J.A. The quadrupole moment of the carbon dioxide molecule. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1963, 273, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonenfant, D.; Kharoune, M.; Niquette, P.; Mimeault, M.; Hausler, R. Advances in principal factors influencing carbon dioxide adsorption on zeolites. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 013007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashof, D.A.; Ahuja, D.R. Relative contributions of greenhouse gas emissions to global warming. Nature 1990, 344, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Lee, J.; Karakoti, A.; Bahadur, R.; Yi, J.B.; Zhao, D.Y.; AlBahily, K.; Vinu, A. Emerging trends in porous materials for CO2 capture and conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4360–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetti, R.K.; Karunathilake, H.; Chhipi-Shrestha, G.; Sadiq, R.; Hewage, K. Prospects of integrating carbon capturing into community scale energy systems. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2020, 133, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, C. Carbon capture from flue gas and the atmosphere: A perspective. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 560849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegelman, R.L.; Milner, P.J.; Kim, E.J.; Weston, S.C.; Long, J.R. Challenges and opportunities for adsorption-based CO2 capture from natural gas combined cycle emissions. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2161–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Park, S.-J. A review on solid adsorbents for carbon dioxide capture. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardakhti, M.; Jafari, T.; Tobin, Z.; Dutta, B.; Moharreri, E.; Shemshaki, N.S.; Suib, S.; Srivastava, R. Trends in solid adsorbent materials development for CO2 capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34533–34559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.-Y.; Park, S.-J. Effect of ZnCl2 activation on CO2 adsorption of N-doped nanoporous carbons from polypyrrole. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 218, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Park, S.-J. Microporous carbons derived from melamine and isophthalaldehyde: One-pot condensation and activation in a molten salt medium for efficient gas adsorption. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehman, A.; Heo, Y.-J.; Nazir, G.; Park, S.-J. Solvent-free, one-pot synthesis of nitrogen-tailored alkali-activated microporous carbons with an efficient CO2 adsorption. Carbon 2021, 172, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Park, S.-J. Influence of nitrogen moieties on CO2 capture by polyaminal-based porous carbon. Macromol. Res. 2017, 25, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Contrino, D.; Mazyck, D.W. Role of activated carbon precursor in mercury removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 17740–17747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Park, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, S.-J. Effects of microporosity and surface chemistry on separation performances of N-containing pitch-based activated carbons for CO2/N2 binary mixture. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnalagadda, M.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Shair, O.H.M.; Mutyala, S. Porous carbon supported calcium oxide for CO2 adsorption and separation of CO2/CH4. Environ. Technol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, U.; Park, S.-J. Tuning ratios of KOH and NaOH on acetic acid-mediated chitosan-based porous carbons for improving their textural features and CO2 uptakes. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 40, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreńscek-Nazzal, J.; Kiełbasa, K. Advances in modification of commercial activated carbon for enhancement of CO2 capture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 494, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnen, K.P.; Ho, K.M. Structure and dynamics at metal surfaces. Surf. Sci. Rep. 1993, 19, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutch, G.A.; Shulda, S.; McCue, A.J.; Menart, M.J.; Ciobanu, C.V.; Ngo, C.; Anderson, J.A.; Richards, R.M.; Vega-Maza, D. Carbon capture by metal oxides: Unleashing the potential of the (111) facet. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4736–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawool, S.A.; Belgamwar, R.; Jana, R.; Maity, A.; Bhumla, A.; Yigit, N.; Datta, A.; Rupprechter, G.; Polshettiwar, V. Direct CO2 capture and conversion to fuels on magnesium nanoparticles under ambient conditions simply using water. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5774–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerabhadrappa, M.G.; Maroto-Valer, M.M.; Chen, Y.; Garcia, S. Layered double hydroxides-based mixed metal oxides: Development of novel structured sorbents for CO2 capture applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11805–11813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhaimi, A.H.; Aziz, M.A.A.; Jalil, A.A. Magnesium oxide-based adsorbents for carbon dioxide capture: Current progress and future opportunities. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 43, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, L.K.G.; Bhatta, U.M.; Venkatesh, K. Metal oxides for carbon dioxide capture. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 38: Carbon Sequestration Vol. 2 Materials and Chemical Methods; Inamuddin, Asiri, A.M., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 63–83. [Google Scholar]
- Taifan, W.; Boily, J.-F.; Baltrusaitis, J. Surface chemistry of carbon dioxide revisited. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2016, 71, 595–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, S.Y. Hydrogen storage behaviors of platinum-supported multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 13048–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, M.F.; Grant, J.T. Deconvolution in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1984, 33, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, L.G.; Barrett, E.P.; Skold, R. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. II. Comparison between nitrogen isotherm and mercury porosimeter methods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 3155–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinheimer, V.; Unluer, C.; Liu, J.; Ruan, S.; Pan, J.; Monteiro, P.J.M. XPS study on the stability and transformation of hydrate and carbonate phases within MgO systems. Materials 2017, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santamaria, M.; Di Quarto, F.; Zanna, S.; Marcus, P. Initial surface film on magnesium metal: A characterization by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and photocurrent spectroscopy (PCS). Electrochim. Acta 2007, 53, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ardizzone, S.; Bianchi, C.L.; Fadoni, M.; Vercelli, B. Magnesium salts and oxide: An XPS overview. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 119, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Matthes, F.; Schneider, C.M. Photoemission study of the Fe(001)/MgO interface for varying oxidation conditions of magnesium oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 09G519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Wen, X.; Fu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhao, N.; Xiao, F.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. MgO/Al2O3 sorbent for CO2 Capture. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 5773–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukal, A.; Pastva, J.; Čejka, J. MgO-modified mesoporous silicas impregnated by potassium carbonate for carbon dioxide adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 167, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.-J.; Park, S.-J. Facile synthesis of MgO-modified carbon adsorbents with microwave—assisted methods: Effect of MgO particles and porosities on CO2 capture. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Li, X.; Lu, G.; Zhang, T. The humidity-sensitive property of MgO-SBA-15 composites in one-pot synthesis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Liu, Y. Electroless deposition of Cu on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Rare Met. 2006, 25, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.J.; Park, S.J. A role of steam activation on CO2 capture and separation of narrow microporous carbons produced from cellulose fibers. Energy 2015, 91, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Q.; Lou, X. Investigation of pore structure characteristics and adsorption characteristics of coals with different destruction types. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 623–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Specimens | Atomic Percentage (at.%) | Textural Properties | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Mg | SBET1 | Vtotal2 | Vmicro3 | Vmeso4 | |
| AC | 85.4 | 12.2 | - | 1608 | 1.57 | 0.20 | 1.37 |
| 1-MgO-AC | 81.2 | 15.8 | 0.87 | 1203 | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.81 |
| 2-MgO-AC | 78.9 | 15.7 | 2.55 | 1123 | 0.96 | 0.16 | 0.75 |
| 5-MgO-AC | 63.8 | 22.9 | 6.72 | 1096 | 0.74 | 0.13 | 0.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Rhee, K.-Y.; Park, S.-J. Roles of London Dispersive and Polar Components of Nano-Metal-Coated Activated Carbons for Improving Carbon Dioxide Uptake. Coatings 2021, 11, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11060691
Lee S-Y, Lee J-H, Kim Y-H, Rhee K-Y, Park S-J. Roles of London Dispersive and Polar Components of Nano-Metal-Coated Activated Carbons for Improving Carbon Dioxide Uptake. Coatings. 2021; 11(6):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11060691
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seul-Yi, Jong-Hoon Lee, Yeong-Hun Kim, Kyong-Yop Rhee, and Soo-Jin Park. 2021. "Roles of London Dispersive and Polar Components of Nano-Metal-Coated Activated Carbons for Improving Carbon Dioxide Uptake" Coatings 11, no. 6: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11060691
APA StyleLee, S. -Y., Lee, J. -H., Kim, Y. -H., Rhee, K. -Y., & Park, S. -J. (2021). Roles of London Dispersive and Polar Components of Nano-Metal-Coated Activated Carbons for Improving Carbon Dioxide Uptake. Coatings, 11(6), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11060691