Silica-Supported Assemblage of CuII Ions with Carbon Dots for Self-Boosting and Glutathione-Induced ROS Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
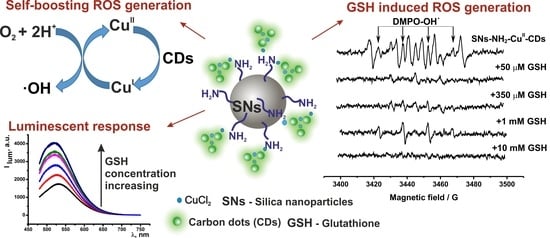
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Hybrid SNs
3.2. Sensing of GSH by the Fluorescent Response of SNs-NH2-CuII-CDs
3.3. ROS Generation
3.4. Cell Internalization of SNs-NH2-CuII-CDs and Its Effect on Cell Viability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lucena, R.; Simonet, B.M.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Potential of nanoparticles in sample preparation. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 620–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, C.; Parola, V.L.; Testa, M.L.; Liotta, L.F. Antifouling and antimicrobial activity of Ag, Cu and Fe nanoparticles supported on silica and titania. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 529, 120636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibu, E.S.; Hamada, M.; Murase, N.; Biju, V. Nanomaterials formulations for photothermal and photodynamic therapy of cancer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2013, 15, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W. Nanomaterials in fluorescence-based biosensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Meziani, M.J.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.; Luo, P.G.; Lin, Y.; Harruff, B.A.; Veca, L.M.; Murray, D.; et al. carbon dots for multiphoton bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11318–11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Rehman, S.; Fu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Bi, H.; Morais, P.C. Room-temperature multiferroicity in magnetic field-poled polyaniline and its enhancement via Cu2+-complexation. Synth. Met. 2019, 253, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieszczycka, K.; Staszak, K.; Wozniak-Budych, M.J.; Litowczenko, J.; Maciejewska, B.M.; Jurga, S. Surface functionalization—The way for advanced applications of smartmaterials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 436, 2138462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.; Saha, B.; De, P. Recent progress in polymer-based optical chemosensors for Cu2+ and Hg2+ Ions: A comprehensive review. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 145, 110233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaferi, M.; Esfahani, M.K.M.; Raza, A.; Harthi, S.A.; Shahmabadi, H.E.; Alavi, S.E. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis methods and their therapeutic use-recent advances. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M.; Minami, H.; Suzuki, T.; Hossain, M.K.; Ahmad, H. Mesoporous amine functionalized SiO2 supported Cu nanocatalyst and a kinetic-mechanistic degradation study of azo dyes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 617, 126403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Fan, H.; Zhang, H.; He, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, W. Carbon dot doped silica nanoparticles as fluorescent probe for determination of bromate in drinking water samples. Can. J. Chem. 2018, 96, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Sun, S.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Shu, Q.; Lin, H. In Situ Synthesis of Fluorescent Mesoporous Silica–Carbon Dot Nanohybrids Featuring Folate Receptor-Overexpressing Cancer Cell Targeting and Drug Delivery. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aliaga, M.E.; López Alarcón, C.; Bridi, R.; Speisky Cosoy, H. Redox-implications associated with the formation of complexes between copper ions and reduced or oxidized glutathione. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 154, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, Q.; Tang, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Tumor microenvironment stimuli-responsive fluorescence imaging and synergistic cancer therapy by carbon-dot–Cu2+ nanoassemblies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połeć-Pawlak, K.; Ruzik, R.; Lipiec, E. Investigation of Cd(II), Pb(II) and Cu(I) complexation by glutathione and its component amino acids by ESI-MS and size exclusion chromatography coupled to ICP-MS and ESI-MS. Talanta 2007, 72, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, G.; Bi, H.; Xu, J.; Feng, L.; Yang, D.; Sun, Q.; Gai, S.; He, F.; Dai, Y.; et al. Combination of CuS and g-C3N4 QDs on upconversion nanoparticles for targeted photothermal and photodynamic cancer therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Duan, J.; Li, Z.; Kong, Y.; Sang, Y.; Liu, H.; Bu, W.; et al. Self-Assembled Copper–Amino Acid Nanoparticles for in Situ Glutathione “AND” H2O2 Sequentially Triggered Chemodynamic Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Li, K.; Cao, X.; Dai, Y.; Mao, L.; Wang, S.; Tai, X. A simultaneously GSH-depleted bimetallic Cu(ii) complex for enhanced chemodynamic cancer therapy. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 11851–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, F.; Gu, D.; You, C.; Sun, B. A pH-activated autocatalytic nanoreactor for self-boosting Fenton-like chemodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17319–17331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, A.N.; Pandey, A.; Fernandes, G.; Kulkarni, S.; Mutalik, S.P.; Padya, B.S.; George, S.D.; Mutalik, S. Copper sulphide based heterogeneous nanoplatforms for multimodal therapy and imaging of cancer: Recent advances and toxicological perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 419, 213356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, L. Recent progress of chemodynamic therapy-induced combination cancer therapy. Nano Today 2020, 35, 100946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Based Nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4881–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, L.; Fang, L.; Kumar, A.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, J. Recent advances in MOF-based nanoplatforms generating reactive species for chemodynamic therapy. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 11045–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, S. Modulating intracellular oxidative stress via engineered nanotherapeutics. J. Control. Release 2020, 319, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhou, N.; Lua, X.; Zhao, C. Multifunctional red carbon dots: A theranostic platform for magnetic resonance imaging and fluorescence imaging-guided chemodynamic therapy. Analyst 2020, 145, 3592–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholobak, N.M.; Popov, A.L.; Shcherbakov, A.B.; Popova, N.R.; Guzyk, M.M.; Antonovich, V.P.; Yegorova, A.V.; Scrypynets, Y.V.; Leonenko, I.I.; Baranchikov, A.Y.; et al. Facile fabrication of luminescent organic dots by thermolysis of citric acid in urea melt, and their use for cell staining and polyelectrolyte microcapsule labelling. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.-L.; Liu, T.-C.; Liu, B.; Cao, Y.-C.; Huang, Z.-L.; Zhao, Y.-D.; Luo, Q.-M. Optimization of methods for intoduction of amine groups onto the silica nanoparticle surface. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2007, 80A, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafina, A.R.; Fedorenko, S.V.; Konovalova, O.D.; Menshikova, A.Y.; Shevchenko, N.N.; Soloveva, S.E.; Konovalov, A.I.; Antipin, I.S. Novel Highly Charged Silica-Coated Tb(III) Nanoparticles with Fluorescent Properties Sensitive to Ion Exchange and Energy Transfer Processes in Aqueous Dispersions. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3146–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Fluorescent quantification of amino groups on silica nanoparticle surfaces. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 2503–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharipova, R.R.; Belenok, M.G.; Garifullin, B.F.; Sapunova, A.S.; Voloshina, A.D.; Andreeva, O.V.; Strobykina, I.Y.; Skvortsova, P.V.; Zuev, Y.F.; Kataev, V.E. Synthesis and anti-cancer activities of glycosides and glycoconjugates of diterpenoid isosteviol. Med. Chem. Comm. 2019, 10, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon, F.H.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Villegas-Lelovsky, L.; Silva, S.W.; Cesar, D.F.; Nagamine, L.C.C.M.; Cohen, R.; Menéndez-Proupin, E.; Morais, P.C. Evolution of the doping regimes in the Al-doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by a polymer precursor method. J. Phys. Cond. Matter 2015, 27, 095301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhishvili, S.A.; Kharlampieva, E.; Izumrudov, V. Where polyelectrolyte multilayers and polyelectrolyte complexes meet. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 8873–8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Guo, X.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y. A fluorescent “on-off-on” assay for selective recognition of Cu(II) and glutathione based on modified carbon nanodots, and its application to cellular imaging. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Shang, Y.; Li, B. Carbon dots doped with nitrogen and sulfur and loaded with copper(II) as a “turn-on” fluorescent probe for cystein, glutathione and homocysteine. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elistratova, J.; Mukhametshina, A.; Kholin, K.; Nizameev, I.; Mikhailov, M.; Sokolov, M.; Khairullin, R.; Miftakhova, R.; Shammas, G.; Kadirov, M.; et al. Interfacial uploading of luminescent hexamolybdenum cluster unitsonto amino-decorated silica nanoparticles as new design ofnanomaterial for cellular imaging and photodynamic therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 538, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorenko, S.; Elistratova, J.; Stepanov, A.; Khazieva, A.; Mikhailov, M.; Sokolov, M.; Kholin, K.; Nizameev, I.; Mendes, R.; Rümmeli, M.; et al. ROS-generation and cellular uptake behavior of amino-silica nanoparticles arisen from their uploading by both iron-oxides and hexamolybdenum clusters. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 1113052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, K.; Babić, N.; Peyrot, F. Use of spin traps to detect superoxide production in living cells by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy. Methods 2016, 109, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carini, M.; Aldini, G.; Orioli, M.; Facino, R. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy: A versatile and powerful tool in pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2006, 2, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelé-Martínez, C.; Nguyen, K.V.T.; Ameer, F.S.; Anker, J.N.; Brumaghim, J.L. Reactive oxygen species generation by copper(II) oxide nanoparticles determined by DNA damage assays and EPR spectroscopy. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedrick, W.R.; Webb, M.D.; Zimbrick, J.D. Spin trapping of reactive uracilyl radicals produced by ionizing radiation in aqueous solutions. Inter. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1982, 41, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirino, Y.; Ohkuma, T.; Kwan, T. Spin trapping with 5,5-dimethylpyrroline-N-oxide in aqueous solution. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, T.J.; Cui, K.; Dong, Y.D. Reduction of copper oxide with graphite by mechanical alloying. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 4062–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, C.; Song, J.; Ji, X.; Wang, W. Cytidine-gold nanoclusters as peroxidase mimetic for colorimetric detection of glutathione (GSH), glutathione disulfide (GSSG) and glutathione reductase (GR). Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 250, 119316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. Engineering nanomedicine for glutathione depletion-augmented cancer therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, S.; Treccani, L.; Dringen, R.; Rezwan, K. Modulation of Silica Nanoparticle Uptake into Human Osteoblast Cells by Variation of the Ratio of Amino and Sulfonate Surface Groups: Effects of Serum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13821–13833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fedorenko, S.V.; Mustafina, A.R.; Mukhametshina, A.R.; Jilkin, M.E.; Mukhametzyanov, T.A.; Solovieva, A.O.; Pozmogova, T.N.; Shestopalova, L.V.; Shestopalov, M.A.; Kholin, K.V.; et al. Cellular imaging by green luminescence of Tb(III)-doped aminomodified silica nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of Surface Properties on Nanoparticle–Cell Interactions. Small 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Liu, R.; Koynov, K.; Wu, D.; Best, A.; Kumar, R.; Bonoiu, A.; Prasad, P.N. Photoluminescent carbon dots as biocompatible nanoprobes for targeting cancer cells in vitro. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 12062–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; et al. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Wu, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L. Carbon dots: A booming material for biomedical applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harush-Frenkel, O.; Debotton, N.; Benita, S.; Altschuler, Y. Targeting of nanoparticles to the clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Liao, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, P.; Guo, K.; Kong, J.; Ji, C.; Liu, B. Size-dependent cellular uptake efficiency, mechanism, and cytotoxicity of silica nanoparticles toward HeLa cells. Talanta 2013, 107, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| System | dTEM, nm | dDLS, nm | PDI | ζ, mV | Mean Peaks, nm | Si:Cu | Content of Cu, mol·L−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNs-NH2 | 55 ± 5 | * | 0.437 | 22 | 220 and 1496 | - | - |
| SNs-NH2-CuII | - | * | 0.428 | −33 | 231 and 1289 | 1:0.026 | 1.7 × 10−5 |
| SNs-NH2-CuII-CDs | - | 266 ± 9 | 0.334 | −31 | - | 1:0.005 | 1.8 × 10−6 |
| SNs | 50 ± 5 | 128 ± 1 | 0.352 | −36 | - | - | - |
| SNs-CuII | - | 113 ± 2 | 0.248 | −23 | - | 1:0.007 | 5 × 10−6 |
| SNs-CuII-CDs | - | 207 ± 2 | 0.184 | −24 | - | 1:0 ** | ** |
| CDs (C = 0.005 gL−1) | - | * | 0.558 | −24 | 467; 4962 | - | - |
| CDs + 30 μM CuCl2 | - | * | 0.628 | −19 | 3; 602; 3615 | - | 3 × 10−5 |
| CDs + 300 μM CuCl2 | - | * | 0.627 | −15 | 175; 886; 5203 | - | 3 × 10−4 |
| Compound | Concentration, gL−1 | M-HeLa | Chang Liver | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Viability,% | IC50 | Cell Viability,% | IC50 | ||
| SNs-NH2-CuII-CDs | 1 | 71.3 | >1 gL−1 | 62.2 | >1 gL−1 |
| 0.5 | 79.3 | 64.4 | |||
| 0.25 | 82.5 | 74.5 | |||
| 0.125 | 100 | 79.4 | |||
| 0.0625 | 100 | 83.8 | |||
| 0.0313 | 100 | 87.9 | |||
| SNs-NH2-CuII | 1 | 69.3 | >1 gL−1 | 63.8 | >1 gL−1 |
| 0.5 | 75.13 | 67.4 | |||
| 0.25 | 76.3 | 78.9 | |||
| 0.125 | 79.1 | 79.1 | |||
| 0.0625 | 100 | 82.3 | |||
| 0.0313 | 100 | 89.8 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochkova, O.; Dovjenko, A.; Zairov, R.; Kholin, K.; Biktimirova, R.; Fedorenko, S.; Nizameev, I.; Laskin, A.; Voloshina, A.; Lyubina, A.; et al. Silica-Supported Assemblage of CuII Ions with Carbon Dots for Self-Boosting and Glutathione-Induced ROS Generation. Coatings 2022, 12, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010097
Bochkova O, Dovjenko A, Zairov R, Kholin K, Biktimirova R, Fedorenko S, Nizameev I, Laskin A, Voloshina A, Lyubina A, et al. Silica-Supported Assemblage of CuII Ions with Carbon Dots for Self-Boosting and Glutathione-Induced ROS Generation. Coatings. 2022; 12(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010097
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochkova, Olga, Alexey Dovjenko, Rustem Zairov, Kirill Kholin, Rinata Biktimirova, Svetlana Fedorenko, Irek Nizameev, Artem Laskin, Alexandra Voloshina, Anna Lyubina, and et al. 2022. "Silica-Supported Assemblage of CuII Ions with Carbon Dots for Self-Boosting and Glutathione-Induced ROS Generation" Coatings 12, no. 1: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010097
APA StyleBochkova, O., Dovjenko, A., Zairov, R., Kholin, K., Biktimirova, R., Fedorenko, S., Nizameev, I., Laskin, A., Voloshina, A., Lyubina, A., Amerhanova, S., Daminova, A., Evtugyn, V., Gerasimova, T., & Mustafina, A. (2022). Silica-Supported Assemblage of CuII Ions with Carbon Dots for Self-Boosting and Glutathione-Induced ROS Generation. Coatings, 12(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010097