Room Temperature Synthesis of Branched ZnO Nanowires Array with Tunable Morphology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
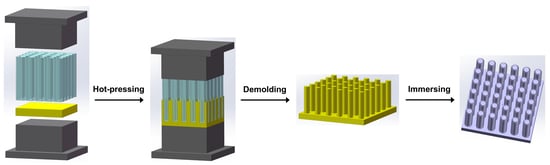
2.2. Preparation of Zn NWA
2.3. Preparation of B-ZnO NWA
2.4. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Controlled Synthesis of Zn NWA
3.2. The Effect of NaOH Concentration on the Growth of B-ZnO NWA
3.3. The Effect of Solution Temperature on the Growth of B-ZnO NWA
3.4. The Effect of Immersion Time on the Growth of B-ZnO NWA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kegel, J.; Povey, I.M.; Pemble, M.E. Zinc oxide for solar water splitting: A brief review of the material’s challenges and associated opportunities. Nano Energy 2018, 54, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Look, D.C. Recent advances in ZnO materials and devices. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2001, 80, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Z.L. One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: Solution growth and functional properties. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 1013–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Pan, F.; Deng, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, W. Mace-like carbon fiber/ZnO nanorod composite derived from Typha orientalis for lightweight and high-efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Yousefzadeh, S.; Samadi, M.; Dong, C.; Zhang, J.; Moshfegh, A.Z. Facile preparation of branched hierarchical ZnO nanowire arrays with enhanced photocatalytic activity: A photodegradation kinetic model. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, M.; Zhang, W.; Deng, Y. High Efficiency Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells Based on Three-Dimensional Multilayered ZnO Nanowire Arrays with “Caterpillar-like” Structure. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3656–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H.; Lee, D.; Kang, H.W.; Nam, K.H.; Yeo, J.Y.; Hong, S.J.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; Sung, H.J. Nanoforest of Hydrothermally Grown Hierarchical ZnO Nanowires for a High Efficiency Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Kang, Z.; Cao, S.; Zhang, Y. 3D-Branched ZnO/CdS Nanowire Arrays for Solar Water Splitting and the Service Safety Research. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Sangle, A.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, L.; Hoye, R.L.Z.; Cho, S.; Li, D.; MacManus-Driscoll, J.L. Photoelectrochemical water splitting strongly enhanced in fast-grown ZnO nanotree and nanocluster structures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10203–10211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiang, Q.; Li, H.; Pan, Q.; Xu, P. Brush-Like Hierarchical ZnO Nanostructures: Synthesis, Photoluminescence and Gas Sensor Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 3430–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Park, S.; Ko, H.; Jin, C.; Lee, W.I.; Lee, C. Enhanced gas sensing properties of branched ZnO nanowires. Thin Solid Film 2013, 547, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zheng, J.-G.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Wong, K.S.; Liang, C.; Wu, M. Complex ZnO nanotree arrays with tunable top, stem and branch structures. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Ji, H.; Tambunan, O.T.; Hwang, I.-S.; Woo, H.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, B.W.; Liu, C.; Rhee, S.J.; Jung, C.U.; et al. Brush-Shaped ZnO Heteronanorods Synthesized Using Thermal-Assisted Pulsed Laser Deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4682–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Mao, Y. Morphology-tunable synthesis of ZnO nanoforest and its photoelectrochemical performance. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8769–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielinski, A.R.; Boban, M.; He, Y.; Kazyak, E.; Lee, D.H.; Wang, C.; Tuteja, A.; Dasgupta, N.P. Rational Design of Hyperbranched Nanowire Systems for Tunable Superomniphobic Surfaces Enabled by Atomic Layer Deposition. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, C.; Shao, Y.; Lu, Q.; Gao, S.; Huang, K.; Wu, H.; Yao, K. High-Performance Carbon Dioxide Electrocatalytic Reduction by Easily Fabricated Large-Scale Silver Nanowire Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17950–17956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Amorphous Germanium. Phys. Status Solidi B 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, N.; Nandhakumar, E.; Priya, P.; Selvakumar, M.; Potheher, I.V. Green and sustainable preparation of flower-like ZnO nanostructures via soft bio-template approach for the enhancement of biomedical applications. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 128, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobbs, J.H. Kubelka—Munk Theory and the Prediction of Reflectance. Rev. Prog. Color. Relat. Top. 1985, 15, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Pang, Q.; Wen, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. Synthesis of Ultrathin ZnO Nanofibers Aligned on a Zinc Substrate. Small 2006, 2, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Jang, J.-W.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, K.-H. Room temperature synthesis and optical properties of small diameter (5 nm) ZnO nanorod arrays. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, W.K.; Razak, K.A.; Lockman, Z.; Kawamura, G.; Muto, H.; Matsuda, A. Formation of highly crystallized ZnO nanostructures by hot-water treatment of etched Zn foils. Mater. Lett. 2013, 91, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Dev, A.; Chaudhuri, S. Simple Solvothermal Route to Synthesize ZnO Nanosheets, Nanonails, and Well-Aligned Nanorod Arrays. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 17848–17853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, G. Growth and comparison of different morphologic ZnO nanorod arrays by a simple aqueous solution route. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4362–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.B.; Fields, C.L.; Gregg, B.A. Epitaxial Chemical Deposition of ZnO Nanocolumns from NaOH Solutions. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5114–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Huang, G.; Fu, F.; Cheng, H.; Guo, W.; Li, J.; Wu, H. Synthesis of bilayer ZnO nanowire arrays: Morphology evolution, optical properties and photocatalytic performance. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 11710–11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Ai, H. Single-crystalline ZnO nanowires on zinc substrate by a simple hydrothermal synthesis method. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2507–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Shen, D.; Fan, X. Growth of ZnO Nanostructures with Different Morphologies by Using Hydrothermal Technique. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 20263–20267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hatzoglou, C.; Sneed, B.; Fan, Z.; Guo, W.; Jin, K.; Chen, D.; Bei, H.; Wang, Y.; Weber, W.J.; et al. Interpreting nanovoids in atom probe tomography data for accurate local compositional measurements. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega, Y.; Dieker, C.; Jäger, W.; Piqueras, J.; Fernández, P. Voids, nanochannels and formation of nanotubes with mobile Sn fillings in Sn doped ZnO nanorods. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 225604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.; Hao, X.; Zhu, F. A General Low-Temperature Route for Large-Scale Fabrication of Highly Oriented ZnO Nanorod/Nanotube Arrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2378–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.-Y.; Kuo, S.-Y.; Han, H.-V.; Yang, J.-F.; Liao, Y.-K.; Lai, F.-I.; Kuo, H.-C. Enhanced broadband and omnidirectional performance of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells with ZnO functional nanotree arrays. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3841–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Chang, H.-S.; Yao, K.; Shao, Y. Room Temperature Synthesis of Branched ZnO Nanowires Array with Tunable Morphology. Coatings 2023, 13, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020275
Zhao W, Chang H-S, Yao K, Shao Y. Room Temperature Synthesis of Branched ZnO Nanowires Array with Tunable Morphology. Coatings. 2023; 13(2):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020275
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wei, Hsiang-Shun Chang, Kefu Yao, and Yang Shao. 2023. "Room Temperature Synthesis of Branched ZnO Nanowires Array with Tunable Morphology" Coatings 13, no. 2: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020275
APA StyleZhao, W., Chang, H.-S., Yao, K., & Shao, Y. (2023). Room Temperature Synthesis of Branched ZnO Nanowires Array with Tunable Morphology. Coatings, 13(2), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13020275