Development of YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings Using Axial Suspension Plasma Spraying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Mirror polishing: Ra = 0.06 μm, Rz = 0.27 μm;
- Grinding: Ra = 0.26 μm, Rz = 1.89 μm;
- Mirror polishing and grit blasting: Ra = 2.82 μm, Rz = 21.6 μm;
- As sprayed HVOF bond coat: Ra = 10.4 μm, Rz = 67.4 μm;
- As sprayed rough HVOF bond coat: Ra = 14.4 μm, Rz = 87.5 μm.
2.2. Plasma Spraying Conditions
2.3. Microstructure and Porosity Characterization
2.4. Mechanical Property Tests
2.5. Thermal Shock Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Substrate Roughness on Coating Microstructure
3.2. Effect of Stand-Off Distance on the Coating Microstructure
3.3. Effect of the Input Power on the Coating Microstructures
3.4. Effect of Solid Content on the Coating Microstructures
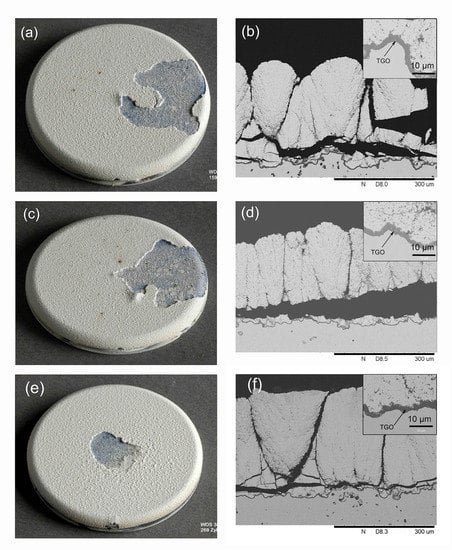
3.5. Thermal Cycling Performance of the Coatings
4. Conclusions
- Among the spraying parameters, bond coat roughness and stand-off distance played a dominant role on the microstructure formation of the top coats. Both increasing stand-off distance and reducing bond coat roughness increased the column density. Lowering the solid content in the suspension promotes the growth of columns. Also bond coat roughness, stand-off distance, and input power also had a significant influence on the microstructure and porosity of the top coats. Increasing bond coat roughness and stand-off distance, lowering input power, as well as the solid content in the suspension could enhance the porosity level of the coatings.
- The SPS process with axial injection had a high deposition efficiency of up to 60.7%. The deposition efficiency was mainly influenced by the stand-off distance. With increase of it, the deposition efficiency dropped greatly.
- Columnar-structured SPS TBCs exhibited a moderate thermal cycling performance. An evaluation of the major influencing factors of the lifetime showed that the relatively low fracture toughness is probably the main reason for the premature failure of the SPS TBCs.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaßen, R.; Giesen, S.; Stöver, D. Lifetime of plasma-sprayed thermal barrier coatings: Comparison of numerical and experimental results. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2009, 18, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassen, R.; Stuke, A.; Stöver, D. Recent developments in the field of thermal barrier coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2009, 18, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberlein, J.V.; Fauchais, P.; Boulos, M.I. Thermal Spray Fundamental; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.Q.; Vassen, R.; Stoever, D. Ceramic materials for thermal barrier coatings. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, S.; Schulz, U.; Jarligo, M.O.; Kuroda, S. Processing science of advanced thermal-barrier systems. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, U.; Saruhan, B.; Fritscher, K.; Leyens, C. Review on advanced EB-PVD ceramic topcoats for TBC applications. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2004, 1, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauer, G.; Schlegel, N.; Guignard, A.; Jarligo, M.; Rezanka, S.; Hospach, A.; Vassen, R. Plasma spraying of ceramics with particular difficulties in processing. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2015, 24, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhorn, C.; Mücke, R.; Mack, D.E.; Vassen, R. Probabilistic lifetime model for atmospherically plasma sprayed thermal barrier coating systems. Mech. Mater. 2016, 93, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, B.; Bianchi, L.; Malié, A.; Joulia, A.; Rémy, B. Columnar suspension plasma sprayed coating microstructural control for thermal barrier coating application. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 36, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padture, N.P.; Gell, M.; Jordan, E.H. Materials science—Thermal barrier coatings for gas-turbine engine applications. Science 2002, 296, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, N.; Ebert, S.; Mauer, G.; Vassen, R. Columnar-structured mg-al-spinel thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) by suspension plasma spraying (SPS). J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2015, 24, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, N.; Sebold, D.; Sohn, Y.; Mauer, G.; Vassen, R. Cycling performance of a columnar-structured complex perovskite in a temperature gradient test. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2015, 24, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganvir, A.; Curry, N.; Markocsan, N.; Nylén, P.; Toma, F.L. Comparative study of suspension plasma sprayed and suspension high velocity oxy-fuel sprayed YSZ thermal barrier coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 268, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanEvery, K.; Krane, M.J.; Trice, R.W.; Wang, H.; Porter, W.; Besser, M.; Sordelet, D.; Ilavsky, J.; Almer, J. Column formation in suspension plasma-sprayed coatings and resultant thermal properties. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2011, 20, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbos, C.; Fazilleau, J.; Rat, V.; Coudert, J.F.; Fauchais, P.; Pateyron, B. Phenomena involved in suspension plasma spraying part 2: Zirconia particle treatment and coating formation. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2006, 26, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganvir, A.; Curry, N.; Markocsan, N.; Nylén, P.; Joshi, S.; Vilemova, M.; Pala, Z. Influence of microstructure on thermal properties of axial suspension plasma-sprayed YSZ thermal barrier coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2016, 25, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, N.; Tang, Z.; Markocsan, N.; Nylén, P. Influence of bond coat surface roughness on the structure of axial suspension plasma spray thermal barrier coatings—Thermal and lifetime performance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 268, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Kim, H.; Yaroslavski, I.; Masindo, G.; Celler, Z.; Ellsworth, D. Novel Thermal Barrier Coatings Produced by Axial Suspension Plasma Spray. In Proceedings of the International Thermal Spray Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 27–29 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Berghaus, J.O.; Legoux, J.-G.; Moreau, C.; Tarasi, F.; Chraska, T. Mechanical and thermal transport properties of suspension thermal-sprayed alumina-zirconia composite coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2008, 17, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guignard, A.; Mauer, G.; Vaßen, R.; Stöver, D. Deposition and characteristics of submicrometer-structured thermal barrier coatings by suspension plasma spraying. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2012, 21, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowski, P.; Kozerski, S.; Pawłowski, L.; Ambroziak, A. The key process parameters influencing formation of columnar microstructure in suspension plasma sprayed zirconia coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 260, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joulia, A.; Duarte, W.; Goutier, S.; Vardelle, M.; Vardelle, A.; Rossignol, S. Tailoring the spray conditions for suspension plasma spraying. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2015, 24, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, B.; Mauer, G.; Vassen, R. Enhanced characteristics of hvof-sprayed mcraly bond coats for tbc applications. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2011, 20, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guignard, A. Development of Thermal Spray Processes with Liquid Feedstocks; Forschungszentrum Jülich: Jülich, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, N. Untersuchungen Zu Suspensionsplasmagespritzten Wärmedämmschichtsystemen; Forschungszentrum, Zentralbibliothek: Jülich, Germany, 2016. (In Germany) [Google Scholar]
- Andreola, F.; Leonelli, C.; Romagnoli, M.; Miselli, P. Techniques used to determine porosity. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 2000, 79, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, M.; Bhattacharya, R.N.; James, C.; Basu, A. A statistical approach to estimate the 3d size distribution of spheres from 2d size distributions. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2005, 117, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.S.; Sachais, B.S.; Jefferies, L.C. The Rietveld Method; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.R.; Zhu, D.; Miller, R.A. Mechanical properties/database of plasma-sprayed ZrO2-8wt % Y2O3 thermal barrier coatings. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2004, 1, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niihara, K.; Morena, R.; Hasselman, D. Evaluation of k lc of brittle solids by the indentation method with low crack-to-indent ratios. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1982, 1, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergejev, F.; Antonov, M. Comparative study on indentation fracture toughness measurements of cemented carbides. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Eng. 2006, 12, 388–398. [Google Scholar]
- Traeger, F.; Vaßen, R.; Rauwald, K.H.; Stöver, D. Thermal cycling setup for testing thermal barrier coatings. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, M.; Vaßen, R.; Stöver, D. Atmospheric plasma sprayed thermal barrier coatings with high segmentation crack densities: Spraying process, microstructure and thermal cycling behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Vaßen, R.; Stöver, D. Atmospheric plasma sprayed thick thermal barrier coatings with high segmentation crack density. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 186, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchais, P.; Montavon, G. Thermal and Cold Spray: Recent Developments. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Zürich, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- Moign, A.; Vardelle, A.; Themelis, N.; Legoux, J. Life cycle assessment of using powder and liquid precursors in plasma spraying: The case of yttria-stabilized zirconia. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassen, R.; Cao, X.Q.; Tietz, F.; Basu, D.; Stover, D. Zirconates as new materials for thermal barrier coatings. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viazzi, C.; Bonino, J.P.; Ansart, F.; Barnabé, A. Structural study of metastable tetragonal ysz powders produced via a sol–gel route. J. Alloy. Compd. 2008, 452, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beshish, G.; Florey, C.; Worzala, F.; Lenling, W. Fracture toughness of thermal spray ceramic coatings determined by the indentation technique. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 1993, 2, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, G.W.; Erdogan, F. Periodic cracking of elastic coatings. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1998, 35, 3615–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaßen, R.; Kerkhoff, G.; Stöver, D. Development of a micromechanical life prediction model for plasma sprayed thermal barrier coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 303, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munz, D.; Fett, T. Ceramics: Mechanical Properties, Failure Behaviour, Materials Selection; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]










| No. | D (mm) | P (kW) | S (wt %) | I (A) | Surface Preparation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 70 | 105 | 10 | 750 | Mirror polishing |
| B | 70 | 105 | 10 | 750 | Grinding |
| C | 70 | 105 | 10 | 750 | Grit blasting |
| D | 70 | 105 | 10 | 750 | As sprayed |
| E | 100 | 105 | 10 | 750 | Mirror polishing |
| F | 100 | 105 | 10 | 750 | Grinding |
| G | 100 | 105 | 10 | 750 | Grit blasting |
| H | 100 | 105 | 10 | 750 | As sprayed |
| I | 100 | 105 | 10 | 750 | As sprayed (rough) |
| J | 70 | 84 | 10 | 600 | As sprayed |
| K | 70 | 105 | 5 | 750 | As sprayed |
| L | 100 | 105 | 5 | 750 | As sprayed |
| M | 70 | 105 | 5 | 750 | As sprayed |
| N | 100 | 105 | 5 | 750 | As sprayed |
| O | 70 | 105 | 5 | 750 | As sprayed * |
| Sample | No. | Thickness (μm) | Bond Coat/Top Coat Interface Temperature (°C) | Top Coat Surface Temperature (°C) | Top Coat Temperature Gradient (°C/μm) | Lifetime (Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 1 | ~255 | 1119 | 1346 | 1.10 | 193 |
| 2 | ~257 | 1098 | 1284 | 0.78 | 160 | |
| N | 1 | ~257 | 1118 | 1384 | 1.10 | 81 |
| 2 | ~245 | 1121 | 1362 | 1.14 | 71 | |
| O | 1 | ~289 | 1094 | 1277 | 0.63 | 218 |
| 2 | ~317 | 1089 | 1283 | 0.61 | 269 |
| Sample | Condition | Hardness (GPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | As sprayed | 9.6 ± 1.1 | 113.7 ± 10.4 | 1.5 ± 0.3 |
| Thermal cycled | 10.2 ± 1.4 | 159.5 ± 16.8 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | |
| N | As sprayed | 6.2 ± 0.9 | 81.9 ± 8.5 | 1.0 ± 0.2 |
| Thermal cycled | 8.4 ± 1.4 | 127.9 ± 15.3 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | |
| O | As sprayed | 8.3 ± 0.6 | 100.7 ± 7.0 | 1.7 ± 0.4 |
| Thermal cycled | 10.5 ± 1.0 | 167.5 ± 13.2 | 2.5 ± 0.3 |
| Sample | Strain | Defect Size (μm) | Average Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Average Fracture Toughness (MPa·m1/2) | Lifetime (Cycles) | Lifetime/Pore Size (Cycles/μm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 0.0025 | 0.93 | 134 | 1.8 | 5.06 | 177 | 189.2 |
| N | 0.0025 | 1.38 | 105 | 1.4 | 4.05 | 76 | 55.1 |
| O | 0.0025 | 0.67 | 134 | 2.1 | 6.87 | 244 | 362.4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, D.; Guillon, O.; Vaßen, R. Development of YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings Using Axial Suspension Plasma Spraying. Coatings 2017, 7, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7080120
Zhou D, Guillon O, Vaßen R. Development of YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings Using Axial Suspension Plasma Spraying. Coatings. 2017; 7(8):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7080120
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Dapeng, Olivier Guillon, and Robert Vaßen. 2017. "Development of YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings Using Axial Suspension Plasma Spraying" Coatings 7, no. 8: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7080120
APA StyleZhou, D., Guillon, O., & Vaßen, R. (2017). Development of YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings Using Axial Suspension Plasma Spraying. Coatings, 7(8), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings7080120