Solvent-Free Reactive Vapor Deposition for Functional Fabrics: Separating Oil–Water Mixtures with Fabrics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
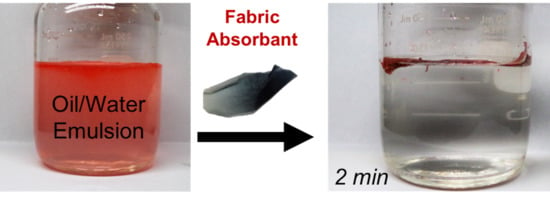
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kintisch, E. An Audacious Decision in Crisis Gets Cautious Praise. Science 2010, 329, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbatly, R.; Krishnaiah, D.; Kamin, Z. A review of polymer nanofibres by electrospinning and their application in oil–water separation for cleaning up marine oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, C. Slick death: Oil-spill treatment kills coral. Sci. News 2007, 172, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Si, Y.; Ge, J.; Ding, B.; Liu, L.; Zheng, G.; Luo, W.; Yu, J. In situ polymerized superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes for gravity driven oil-water separation. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11657–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A Super-Hydrophobic and Super-Oleophilic Coating Mesh Film for the Separation of Oil and Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2012–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.B.; Shi, Z.; Wang, D.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Nanowire-Haired Inorganic Membranes with Superhydrophilicity and Underwater Ultralow Adhesive Superoleophobicity for High-Efficiency Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4192–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Huang, S.; Lu, Y.; Bu, X.; Mates, J.E.; Ghosh, A.; Ganguly, R.; Carmalt, C.J.; Parkin, I.P.; Xu, W.; et al. Self-Driven One-Step Oil Removal from Oil Spill on Water via Selective-Wettability Steel Mesh. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19858–19865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Electrospun Porous Structure Fibrous Film with High Oil Adsorption Capacity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Seeger, S. Polyester Materials with Superwetting Silicone Nanofilaments for Oil/Water Separation and Selective Oil Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Wu, L.; Wang, A. Facile preparation of durable and robust superhydrophobic textiles by dip coating in nanocomposite solution of organosilanes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11509–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Geng, T.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P. Facile fabrication of stable superhydrophobic SiO2/polystyrene coating and separation of liquids with different surface tension. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Fabrication of superhydrophobic cotton textiles for water–oil separation based on drop-coating route. Carb. Polym. 2013, 97, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, F.; Niu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z. Superhydrophobic surfaces: From structural control to functional application. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Hou, L.; He, J.; Feng, J.; Liu, S.; Yao, Y. Facile process for the fabrication of durable superhydrophobic fabric with oil/water separation property. Fiber Polym. 2016, 17, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Cai, R.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Yu, M.; Li, J.; Xie, L.; et al. Laundering Durability of Superhydrophobic Cotton Fabric. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5473–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y.; You, J.B.; Choi, W.; Im, S.G. A stacked polymer film for robust superhydrophobic fabrics. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A. Cutting out textile pollution. Chemical & Engineering News, 19 October 2015; 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bystrzejewska-Piotrowska, G.; Golimowski, J.; Urban, P.L. Nanoparticles: Their potential toxicity, waste and environmental management. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, V.L. The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Andrew, T.L. Reactive Vapor Deposition of Conjugated Polymer Films on Arbitrary Substrates. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, e56775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fairbanks, M.; Andrew, T.L. Rugged Textile Electrodes for Wearable Devices Obtained by Vapor Coating Off-the-Shelf, Plain-Woven Fabrics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Zhang, L.; Joon Kim, J.; Andrew, T.L. Vapor phase organic chemistry to deposit conjugated polymer films on arbitrary substrates. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 5787–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Howden, R.M.; Borrelli, D.C.; Gleason, K.K. Vapor phase oxidative synthesis of conjugated polymers and applications. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 1329–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adebajo, M.O.; Frost, R.L.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Carmody, O.; Kokot, S. Porous Materials for Oil Spill Cleanup: A Review of Synthesis and Absorbing Properties. J. Porous Mater. 2003, 10, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genzer, J.; Efimenko, K. Creating Long-Lived Superhydrophobic Polymer Surfaces Through Mechanically Assembled Monolayers. Science 2000, 290, 2130–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alf, M.E.; Asatekin, A.; Barr, M.C.; Baxamusa, S.H.; Chelawat, H.; Ozaydin-Ince, G.; Petruczok, C.D.; Sreenivasan, R.; Tenhaeff, W.E.; Trujillo, N.J.; et al. Chemical Vapor Deposition of Conformal, Functional, and Responsive Polymer Films. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1993–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Baima, M.; Andrew, T.L. Transforming Commercial Textiles and Threads into Sewable and Weavable Electric Heaters. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32299–32307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Xiao, P.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, T. Janus Polymer/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Membranes for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16204–16209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Khan, F.A.; Baik, S. Janus Graphene Oxide Sponges for High-Purity Fast Separation of Both Water-in-Oil and Oil-in-Water Emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16694–16703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, L.; Hoxie, S.; Andrew, T.L. Towards Seamlessly-Integrated Textile Electronics: Methods to Coat Fabrics and Fibers with Conducting Polymers for Electronic Applications. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7182–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacik, P.; del Hierro, G.; Livernois, W.; Gleason, K.K. Scale-up of oCVD: large-area conductive polymer thin films for next-generation electronics. Mater. Horiz. 2015, 2, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, N.; Park, K.-W.; Andrew, T.L. Solvent-Free Reactive Vapor Deposition for Functional Fabrics: Separating Oil–Water Mixtures with Fabrics. Fibers 2019, 7, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib7010002
Cheng N, Park K-W, Andrew TL. Solvent-Free Reactive Vapor Deposition for Functional Fabrics: Separating Oil–Water Mixtures with Fabrics. Fibers. 2019; 7(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib7010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Nongyi, Kwang-Won Park, and Trisha L. Andrew. 2019. "Solvent-Free Reactive Vapor Deposition for Functional Fabrics: Separating Oil–Water Mixtures with Fabrics" Fibers 7, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib7010002
APA StyleCheng, N., Park, K.-W., & Andrew, T. L. (2019). Solvent-Free Reactive Vapor Deposition for Functional Fabrics: Separating Oil–Water Mixtures with Fabrics. Fibers, 7(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib7010002