Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Plasma and Plasma EVs of Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasma Sampling
2.2. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Isolation of Deiminated Proteins Using F95 Enrichment
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis
2.6. Silver Staining
2.7. Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) Analysis of Deiminated Protein Candidates
2.8. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
2.9. Neighbor-Joining Tree Construction for PADs from Deer
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
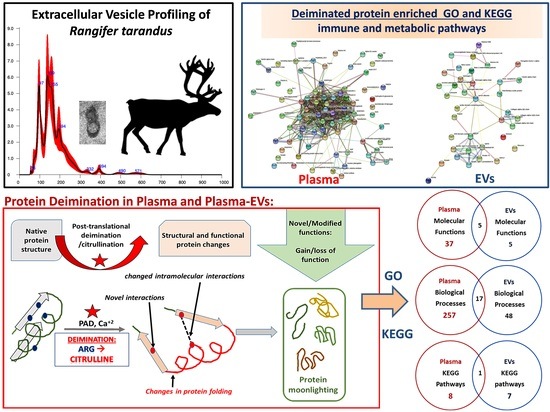
3.1. Characterization of Reindeer Plasma EVs
3.2. PAD Protein Homologue and Deiminated Proteins in Reindeer Plasma and Plasma EVs
3.3. LC–MS/MS Analysis of Deiminated Proteins in Reindeer Plasma and Plasma EVs
3.4. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Identification of Deiminated Proteins in Reindeer Plasma and Plasma EVs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weldenegodguad, M.; Pokharel, K.; Ming, Y.; Honkatukia, M.; Peippo, J.; Reilas, T.; Røed, K.H.; Kantanen, J. Genome sequence and comparative analysis of reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) in northern Eurasia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xia, W.; Liu, C.; Zhu, W.; Wang, H.; Yan, B.; et al. Biological adaptations in the Arctic cervid, the reindeer (Rangifer tarandus). Science 2019, 364, eaav6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.S.; Young, S. Chronic wasting disease of captive mule deer: A spongiform encephalopathy. J. Wildl. Dis. 1980, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, S.J.; Kunkle, R.; Greenlee, M.H.; Nicholson, E.; Richt, J.; Hamir, A.; Waters, W.R.; Greenlee, J. Horizontal Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease in Reindeer. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2142–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tryland, M.; Beckmen, K.B.; Burek-Huntington, K.A.; Breines, E.M.; Klein, J. Orf virus infection in Alaskan mountain goats, Dall’s sheep, muskoxen, caribou and Sitka black-tailed deer. Acta Vet. Scand. 2018, 60, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollard, C.A.; Burns, D.S.; Ho, B.; Johnston, A.M. Meningoencephalitis in a Royal Marine after skinning reindeer in Norway. J. R. Army Med. Corps 2018, 164, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, M.V.; Stoffregen, W.C.; Rogers, D.G.; Hamir, A.N.; Richt, J.A.; Pedersen, D.D.; Waters, W.R. West Nile virus infection in reindeer (Rangifer tarandus). J. Vet. Diagn Investig. 2004, 16, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez Romano, J.; Grund, L.; Obiegala, A.; Nymo, I.H.; Ancin-Murguzur, F.J.; Li, H.; Król, N.; Pfeffer, M.; Tryland, M. A Multi-Pathogen Screening of Captive Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) in Germany Based on Serological and Molecular Assays. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.V.; Martins, M.; Falkenberg, S.; Buckley, A.; Caserta, L.C.; Mitchell, P.K.; Cassmann, E.D.; Rollins, A.; Diel, D.G. Susceptibility of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) to SARS-CoV-2. J. Virol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.S.; Horn, R.L.; Zhang, X.; Golding, G.B.; Manseau, M.; Wilson, P.J. The Caribou (Rangifer tarandus) Genome. Genes 2019, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cronin, M.A.; Macneil, M.D.; Patton, J.C. Mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite DNA variation in domestic reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) and relationships with wild caribou (Rangifer tarandus granti, Rangifer tarandus groenlandicus, and Rangifer tarandus caribou). J. Hered. 2006, 97, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magnadottir, B.; Kraev, I.; Guđmundsdóttir, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Lange, S. Extracellular vesicles from cod (Gadus morhua L.) mucus contain innate immune factors and deiminated protein cargo. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 99, 103397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadottir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Dodds, A.W.; Gudmundsdottir, S.; Lange, S. Extracellular vesicles, deiminated protein cargo and microRNAs are novel serum biomarkers for environmental rearing temperature in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadottir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Svansson, V.; Hayes, P.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins and extracellular vesicles—Novel serum biomarkers in whales and orca. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 34, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadottir, B.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Svansson, V.; Skírnisson, K.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins and extracellular vesicles as novel biomarkers in pinnipeds: Grey seal (Halichoerus gryptus) and harbour seal (Phoca vitulina). Biochimie 2020, 171–172, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Kraev, I.; Dodds, A.W.; Lange, S. The Proteome and Citrullinome of Hippoglossus hippoglossus Extracellular Vesicles-Novel Insights into Roles of the Serum Secretome in Immune, Gene Regulatory and Metabolic Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins in extracellular vesicles and plasma of nurse shark (Ginglymostoma cirratum)—Novel insights into shark immunity. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Petersen, L.H.; Lange, S. Deimination Protein Profiles in Alligator mississippiensis Reveal Plasma and Extracellular Vesicle-Specific Signatures Relating to Immunity, Metabolic Function, and Gene Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Deiminated proteins in extracellular vesicles and serum of llama (Lama glama)-Novel insights into camelid immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 117, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, M.F.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Post-translational protein deimination signatures in serum and serum-extracellular vesicles of Bos taurus reveal immune, anti-pathogenic, anti-viral, metabolic and cancer-related pathways for deimination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, T.J.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Extracellular vesicles and post-translational protein deimination signatures in haemolymph of the American lobster (Homarus americanus). Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, T.J.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Post-translational protein deimination signatures and extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the Atlantic horseshoe crab (Limulus polyphemus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 110, 103714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, T.J.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Extracellular Vesicles and Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Mollusca—The Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis), Soft Shell Clam (Mya arenaria), Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) and Atlantic Jacknife Clam (Ensis leei). Biology 2020, 9, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamenter, M.E.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Huynh, K.W.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Post-translational deimination of immunological and metabolic protein markers in plasma and extracellular vesicles of naked mole-rat (Heterocephalus glaber). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, R.A.; Kraev, I.; Lange, S. Protein deimination and extracellular vesicle profiles in Antarctic seabirds. Biology. 2020, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Zendman, A.J.; Van Venrooij, W.J.; Pruijn, G.J. PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: Genes, features and involvement in disease. Bioessays 2003, 25, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- György, B.; Toth, E.; Tarcsa, E.; Falus, A.; Buzas, E.I. Citrullination: A posttranslational modification in health and disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1662–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadottir, B.; Hayes, P.; Hristova, M.; Bragason, B.Þ.; Nicholas, A.P.; Dodds, A.W.; Gudmundsdottir, S.; Lange, S. Post-translational Protein Deimination in Cod (Gadus morhua L.) Ontogeny—Novel Roles in Tissue Remodelling and Mucosal Immune Defences? Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 87, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Bragason, B.T.; Bricknell, I.R.; Bowden, T.; Nicholas, A.P.; Hristova, M.; Guðmundsdóttir, S.; Dodds, A.W.; Lange, S. Peptidylarginine deiminase and deiminated proteins are detected throughout early halibut ontogeny—Complement components C3 and C4 are post-translationally deiminated in halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 92, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M.; Alasmari, D.; Assiri, A.; Mattar, E.; Aljaddawi, A.A.; Alattas, S.G.; Redwan, E.M. An Overview of the Intrinsic Role of Citrullination in Autoimmune Disorders. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7592851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bicker, K.L.; Thompson, P.R. The protein arginine deiminases: Structure, function, inhibition, and disease. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Peptidylarginine deiminases in citrullination, gene regulation, health and pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witalison, E.E.; Thompson, P.R.; Hofseth, L.J. Protein Arginine Deiminases and Associated Citrullination: Physiological Functions and Diseases Associated with Dysregulation. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.; Gallagher, M.; Kholia, S.; Kosgodage, U.S.; Hristova, M.; Hardy, J.; Inal, J.M. Peptidylarginine Deiminases-Roles in Cancer and Neurodegeneration and Possible Avenues for Therapeutic Intervention via Modulation of Exosome and Microvesicle (EMV) Release? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Thompson, P.R. Protein Arginine Deiminases (PADs): Biochemistry and Chemical Biology of Protein Citrullination. Acc. Chem Res. 2019, 52, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, C.J. Protein moonlighting: What is it, and why is it important? Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebl, A.; Köllner, B.; Anders, E.; Wimmers, K.; Goldammer, T. Peptidylarginine deiminase gene is differentially expressed in freshwater and brackish water rainbow trout. Mol. Biol Rep. 2010, 37, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, L.; Zubáčová, Z.; Karnkowska, A.; Kolisko, M.; Hroudová, M.; Stairs, C.W.; Simpson, A.G.; Keeling, P.J.; Roger, A.J.; Čepička, I.; et al. Arginine deiminase pathway enzymes: Evolutionary history in metamonads and other eukaryotes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavinho, B.; Sabatke, B.; Feijoli, V.; Rossi, I.V.; Da Silva, J.M.; Evans-Osses, I.; Palmisano, G.; Lange, S.; Ramirez, M.I. Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibition abolishes the production of large extracellular vesicles from Giardia intestinalis, affecting host-pathogen interactions by hindering adhesion to host cells. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka, E.; Scavenius, C.; Kantyka, T.; Jusko, M.; Mizgalska, D.; Szmigielski, B.; Potempa, B.; Enghild, J.J.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Blom, A.M.; et al. Peptidyl arginine deiminase from Porphyromonas gingivalis abolishes anaphylatoxin C5a activity. J. Biol Chem. 2014, 289, 32481–32487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Matewele, P.; Mastroianni, G.; Kraev, I.; Brotherton, D.; Awamaria, B.; Nicholas, A.P.; Lange, S.; Inal, J.M. Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibitors reduce bacterial membrane vesicle release and sensitize bacteria to antibiotic treatment. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Sayed, A.S.A.; Shindia, A.A.; AbouZaid, A.A.; Yassin, A.M.; Ali, G.S.; Sitohy, M.Z. Biochemical characterization of peptidylarginine deiminase-like orthologs from thermotolerant Emericella dentata and Aspergillus nidulans. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2019, 124, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Kraev, I.; Magnadóttir, B.; Dodds, A.W. Complement component C4-like protein in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.)—Detection in ontogeny and identification of post-translational deimination in serum and extracellular vesicles. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 101, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadóttir, B.; Hayes, P.; Gísladóttir, B.; Bragason, B.Þ.; Hristova, M.; Nicholas, A.P.; Guðmundsdóttir, S.; Lange, S. Pentraxins CRP-I and CRP-II are post-translationally deiminated and differ in tissue specificity in cod (Gadus morhua L.) ontogeny. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 87, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraro, S.P.; De Souza, G.F.; Gallo, S.W.; Da Silva, B.K.; De Oliveira, S.D.; Vinolo, M.A.R.; Saraiva, E.M.; Porto, B.N. Respiratory Syncytial Virus induces the classical ROS-dependent NETosis through PAD-4 and necroptosis pathways activation. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 14166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, V.; Sousa, F.H.; Shakamuri, P.; Svoboda, P.; Buch, C.; D’Acremont, M.; Christophorou, M.A.; Pohl, J.; Stevens, C.; Barlow, P.G. Citrullination Alters the Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Activities of the Human Cathelicidin LL-37 During Rhinovirus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kholia, S.; Jorfi, S.; Thompson, P.R.; Causey, C.P.; Nicholas, A.P.; Inal, J.; Lange, S. A Novel Role for Peptidylarginine Deiminases (PADs) in Microvesicle Release: A Therapeutic Potential for PAD Inhibitors to Sensitize Prostate Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Trindade, R.P.; Thompson, P.R.; Inal, J.M.; Lange, S. Chloramidine/Bisindolylmaleimide -I-Mediated Inhibition of Exosome and Microvesicle Release and Enhanced Efficacy of Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; MacLatchy, A.; Kraev, I.; Chatterton, N.P.; Nicholas, A.P.; Inal, J.M.; Lange, S. Peptidylarginine Deiminases Post-Translationally Deiminate Prohibitin and Modulate Extracellular Vesicle Release and MicroRNAs in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uysal-Onganer, P.; MacLatchy, A.; Mahmoud, R.; Kraev, I.; Thompson, P.R.; Inal, J.M.; Lange, S. Peptidylarginine Deiminase Isozyme-Specific PAD2, PAD3 and PAD4 Inhibitors Differentially Modulate Extracellular Vesicle Signatures and Cell Invasion in Two Glioblastoma Multiforme Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inal, J.M.; Ansa-Addo, E.A.; Lange, S. Interplay of host-pathogen microvesicles and their role in infectious disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Drapkina, O.; Tonevitsky, A. Transcriptome of extracellular vesicles: State-of-the-art. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vagner, T.; Chin, A.; Mariscal, J.; Bannykh, S.; Engman, D.M.; Di Vizio, D. Protein composition reflects extracellular vesicle heterogeneity. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1800167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antwi-Baffour, S.; Malibha-Pinchbeck, M.; Stratton, D.; Jorfi, S.; Lange, S.; Inal, J. Plasma mEV levels in Ghanain malaria patients with low parasitaemia are higher than those of healthy controls, raising the potential for parasite markers in mEVs as diagnostic targets. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 9, 1697124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramirez, S.H.; Andrews, A.M.; Paul, D.; Pachter, J.S. Extracellular vesicles: Mediators and biomarkers of pathology along CNS barriers. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2018, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholas, A.P.; Whitaker, J.N. Preparation of a monoclonal antibody to citrullinated epitopes: Its characterization and some applications to immunohistochemistry in human brain. Glia 2002, 37, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Gögel, S.; Leung, K.Y.; Vernay, B.; Nicholas, A.P.; Causey, C.P.; Thompson, P.R.; Greene, N.D.; Ferretti, P. Protein deiminases: New players in the developmentally regulated loss of neural regenerative ability. Dev. Biol. 2011, 355, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lange, S.; Rocha-Ferreira, E.; Thei, L.; Mawjee, P.; Bennett, K.; Thompson, P.R.; Subramanian, V.; Nicholas, A.P.; Peebles, D.; Hristova, M.; et al. Peptidylarginine deiminases: Novel drug targets for prevention of neuronal damage following hypoxic ischemic insult (HI) in neonates. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.V.; Sim, R.B. Complement in health and disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, B.I.; Santiago, K.G.; Lee, D.; Ha, S.; Seo, K. RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) Based Transcriptome Analysis in Immune Response of Holstein Cattle to Killed Vaccine against Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Type I. Animals 2020, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, H.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Mao, Y.; Karrow, N.A.; Loor, J.J.; Moore, S.; Yang, Z. Transcriptomics and iTRAQ-Proteomics Analyses of Bovine Mammary Tissue with Streptococcus agalactiae-Induced Mastitis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11188–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Yun, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Ren, Y.; Jia, Y. Transcriptome profiling revealed multiple genes and ECM-receptor interaction pathways that may be associated with breast cancer. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenberger, N.J.; Somasundaram, A.; Stabile, L.P. The Role of the Estrogen Pathway in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanajou, D.; Ghorbani Haghjo, A.; Argani, H.; Aslani, S. AGE-RAGE axis blockade in diabetic nephropathy: Current status and future directions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 833, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senatus, L.M.; Schmidt, A.M. The AGE-RAGE Axis: Implications for Age-Associated Arterial Diseases. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.; Khan, H.; Siddiqui, Z.; Khan, M.Y.; Rehman, S.; Shahab, U.; Godovikova, T.; Silnikov, V.; Moinuddin. AGEs, RAGEs and s-RAGE; friend or foe for cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 49, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetuschi, A.; Pompili, S.; Di Marco, G.P.; Calvaruso, F.; Iacomino, E.; Angelosante, L.; Festuccia, C.; Colapietro, A.; Sferra, R. Can the AGE/RAGE/ERK signalling pathway and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition interact in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps? Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64, 3079. [Google Scholar]
- Waghela, B.N.; Vaidya, F.U.; Ranjan, K.; Chhipa, A.S.; Tiwari, B.S.; Pathak, C. AGE-RAGE synergy influences programmed cell death signaling to promote cancer. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkovic, A.L.; Bathgate, R.A.; Samuel, C.S.; Kocan, M. Understanding relaxin signalling at the cellular level. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2019, 487, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Xiao, J.X.; Li, S.; Liu, J.J.; Alugongo, G.M.; Cao, Z.J.; Yang, H.J.; Wang, S.X.; Swanson, K.C. Protein Metabolism and Signal Pathway Regulation in Rumen and Mammary Gland. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; He, D.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Li, B. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: Opportunities and challenges in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Cao, F.; Yin, H.L.; Huang, Z.J.; Lin, Z.T.; Mao, N.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, N.; Radic, M. Citrullination of autoantigens implicates NETosis in the induction of autoimmunity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Spek, A.H.; Fliers, E.; Boelen, A. The classic pathways of thyroid hormone metabolism. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 458, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, W.W.; Yen, P.M. Thermogenesis in Adipose Tissue Activated by Thyroid Hormone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucchi, R.; Rutigliano, G.; Saponaro, F. Novel thyroid hormones. Endocrine 2019, 66, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullur, R.; Liu, Y.Y.; Brent, G.A. Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 355–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morshed, S.A.; Ma, R.; Latif, R.; Davies, T.F. Cleavage Region Thyrotropin Receptor Antibodies Influence Thyroid Cell Survival In Vivo. Thyroid 2019, 29, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, B.; Ma, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X. Investigating the expression, effect and tumorigenic pathway of PADI2 in tumors. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozlowski, H.N.; Lai, E.T.; Havugimana, P.C.; White, C.; Emili, A.; Sakac, D.; Binnington, B.; Neschadim, A.; McCarthy, S.D.; Branch, D.R. Extracellular histones identified in crocodile blood inhibit in-vitro HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2016, 30, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrmann, J.; Thompson, P.R. Protein Arginine Methylation and Citrullination in Epigenetic Regulation. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Florin-Christensen, M.; Schnittger, L.; Dominguez, M.; Mesplet, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Ferreri, L.; Asenzo, G.; Wilkowsky, S.; Farber, M.; Echaide, I.; et al. Search for Babesia bovis vaccine candidates. Parassitologia 2007, 49 (Suppl. S1), 9–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ragg, H. The role of serpins in the surveillance of the secretory pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2763–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laporte, M.; Naesens, L. Airway proteases: An emerging drug target for influenza and other respiratory virus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 24, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barksdale, S.M.; Hrifko, E.J.; Chung, E.M.; Van Hoek, M.L. Peptides from American alligator plasma are antimicrobial against multi-drug resistant bacterial pathogens including Acinetobacter baumannii. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grenfell, B.T. Gastrointestinal nematode parasites and the stability and productivity of intensive ruminant grazing systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1988, 312, 541–563. [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsdottir, B.; Skirnisson, K. The third newly discovered Eimeria species (Protozoa: Eimeriidae) described from wild reindeer, Rangifer tarandus, in Iceland. Parasitol. Res. 2006, 99, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorsen, O. Epidemiology of reindeer parasites. Parasitol. Today 1986, 2, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoberg, E.P.; Kutz, S.J.; Galbreath, K.E.; Cook, J. Arctic biodiversity: From discovery to faunal baselines—Revealing the history of a dynamic ecosystem. J. Parasitol. 2003, 89, S84–S95. [Google Scholar]
- Hrabok, J.T.; Oksanen, A.; Nieminen, M.; Rydzik, A.; Uggla, A.; Waller, P.J. Reindeer as hosts for nematode parasites of sheep and cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 136, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josefsen, T.D.; Oksanen, A.; Gjerde, B. Parasites in reindeer in Fennoscandia—A Review. Norsk Veterinærtidskrift 2014, 2, 186–201. [Google Scholar]
- Skírnisson, K.; Cuyler, C. A new Eimeria species (Protozoa: Eimeriidae) from caribou in Ameralik, West Greenland. Para Res. 2016, 115, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamnes, I.S.; Gjerde, B.; Robertson, L.; Vikøren, T.; Handeland, K. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in free-ranging wild cervids in Norway. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 141, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Lebbad, M.; Clark, C.G. Genetic characterisation of uninucleated cyst-producing Entamoeba spp. from ruminants. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubey, J.P. Redescription of Besnoitia tarandi (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) from the reindeer (Rangifer tarandus). Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madubata, C.; Dunams-Morel, D.B.; Elkin, B.; Oksanen, A.; Rosenthal, B.M. Evidence for a recent population bottleneck in an Apicomplexan parasite of caribou and reindeer, Besnoitia tarandi. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, A.; Åsbakk, K.; Nieminen, M.; Norberg, H.; Näreaho, A. Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in Fennoscandian reindeer—Association with the degree of domestication. Parasitol. Int. 1997, 46, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikøren, T.; Tharaldsen, J.; Fredriksen, B.; Handeland, K. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in wild red deer, roe deer, moose, and reindeer from Norway. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 120, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lewis, B.; Beam, K.; Abbitt, B. Transplacental toxoplasmosis in a reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) fetus. Vet. Parasitol 2002, 110, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, S.J.; Elkin, B.T.; Panayi, D.; Dubey, J.P. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in barren-ground caribou (Rangifer tarandus groenlandicus) from the Canadian Arctic. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, B. Studies on the Sarcocyst Morphology and Life Cycle of Six Species of Sarcocystis from Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus). Ph.D. Thesis, Norges Veterinærhøgskole, Oslo, Norway, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlgren, S.S.; Gjerde, B.; Skirnisson, K.; Gudmundsdottir, B. Morphological and molecular identification of three species of Sarcocystis in reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in Iceland. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 149, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikander, S.; Saari, S. Notable seasonal variation observed in the morphology of the reindeer rumen fluke (Paramphistomum leydeni) in Finland. Rangifer 2007, 27, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tøllefsen, L. Endoparasitter hos Rein (Rangifer tarandus L.) med Særlig Vekt på Gastrointestinale Nematoda. Master’s Thesis, University of Tromsø, Tromsø, Norway, 1983; 83p. [Google Scholar]
- Bye, K. Cestodes of reindeer (Rangifer tarandus platyrhynchus Vrolik) on the Arctic islands of Svalbard. Can. J. Zool. 1985, 63, 2885–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, R.A. Current status of reindeer/caribou diseases in Alaska. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Reindeer/Caribou Symposium, Röros, Norway, 17–21 September 1979; Reimers, E., Gaare, E., Skjenneberg, S., Eds.; Direktoratet for vilt og Ferskvannsfisk: Trondheim, Norway, 1980; pp. 438–441. [Google Scholar]
- Kummenje, K. Diseases in reindeer in northern Norway. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Reindeer/Caribou Symposium, Röros, Norway, 17–21 September 1979; Reimers, E., Gaare, E., Skjenneberg, S., Eds.; Direktoratet for vilt og Ferskvannsfisk: Trondheim, Norway, 1980; pp. 456–458. [Google Scholar]
- Bye, K. Parasitter hos Svalbardrein Rangifer tarandus platyrhyncus. Fauna 1983, 36, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hoberg, E.P.; Kocan, A.A.; Rickard, L.G. Gastrointestinal strongyles in wild ruminants. In Parasitic Diseases of Wild Mammals, 2nd ed.; Samuel, W.M., Pybus, M.J., Kocan, A.A., Eds.; Manson Publishing Ltd.: London, UK, 2001; pp. 193–227. [Google Scholar]
- Fruetel, M.; Lankester, M.W. Gastrointestinal helminths of woodland and barren ground caribou (Rangifer tarandus) in Canada, with key to species. Can. J. Zool. 1989, 67, 2253–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenfels, J.R.; Hoberg, E.P. The systematics of nematodes that cause ostertagiasis in domestic and wild ruminants in North America: An update and a key to species. Vet. Parasitol. 1993, 46, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, A.; Irvine, R.J.; Ropstads, E.; Halvorsen, O.; Langvatn, R.; Albon, S.D. The impact of gastro-intestinal nematodes on wild reindeer: Experimental and cross-sectional studies. J. Anim. Ecol. 2002, 71, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, O.; Nikander, S. Un nématode ashasmidien dans les capillaires de l’oreille du renne, Lappnema auris. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1983, 58, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehbinder, C. Some vector borne parasites in Swedish reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus L). Rangifer 1990, 2, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikander, S.; Laaksonen, S.; Saari, S. Oksanen, A. The morphology of the filaroid nematode Setaria tundra, the cause of peritonitis in reindeer Rangifer tarandus. J. Helminthol. 2007, 81, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, R.K.; Mørk, T.; Holmgren, K.E.; Oksanen, A. Infection with brainworm (Elaphostrongylus rangiferi) in reindeer (Rangifer tarandus ssp.) in Fennoscandia. Acta Vet. Scand. 2020, 62, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummeneje, K. Dictyocaulus viviparus infestation in reindeer in northern Norway—A contribution to its epidemiology. Acta Vet. Scand. 1977, 18, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikander, S.; Rahko, T. Studies on the occurence of lung worm infection in the reindeer in Finnish Eastern Lapland. Rangifer 1990, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugerud, R.E.; Nilssen, A.C. Life history of the reindeer sinus worm, Linguatula arctica (Pentastomida), a prevalent parasite in reindeer calves. Rangifer 1990, 3, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helle, T.; Tavainen, L. Effects of insect harrassment on weight gain and survival in reindeer calves. Rangifer 1984, 4, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persen, E.; Jacobsen, E.; Lenvik, D.; Skjenneberg, S. Forsøk med behandling av reinkalver mot reinbremslarver (Oedomagena tarandi L og Cephenemyia trompe L). Effekt på kalvens kondisjon målt ved levende vekt og overlevinsevne. Rangifer 1982, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehbinder, C.; Nikander, S. Ren Och Rensjukdomar; Studentlitteratur: Lund, Norway, 1999; pp. 13–132. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Nie, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Liu, A.; Zhao, W.; Li, H. First detection and genotyping of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in reindeers (Rangifer tarandus): A zoonotic potential of ITS genotypes. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, A.L.; Das Neves, C.G.; Finstad, G.F.; Beckmen, K.B.; Skjerve, E.; Nymo, I.H.; Tryland, M. Evidence of alphaherpesvirus infections in Alaskan caribou and reindeer. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das Neves, C.G.; Ihlebæk, H.M.; Skjerve, E.; Hemmingsen, W.; Li, H.; Tryland, M. Gammaherpesvirus infection in semidomesticated reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus): A cross-sectional, serologic study in northern Norway. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das Neves, C.G.; Roth, S.; Rimstad, E.; Thiry, E.; Tryland, M. Cervid herpesvirus 2 infection in reindeer: A review. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, K.M.; Das Neves, C.G.; Granquist, E.G.; Madslien, K.; Stuen, S.; Pedersen, B.N.; Vikse, R.; Rocchi, M.; Laming, E.; Stiasny, K.; et al. Cervids as sentinel-species for tick-borne encephalitis virus in Norway—A serological study. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schürch, A.C.; Schipper, D.; Bijl, M.A.; Dau, J.; Beckmen, K.B.; Schapendonk, C.M.; Raj, V.S.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Haagmans, B.L.; Tryland, M.; et al. Metagenomic survey for viruses in Western Arctic caribou, Alaska, through iterative assembly of taxonomic units. PLoS ONE 2014, 20, e105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.; Tryland, M. Characterisation of parapoxviruses isolated from Norwegian semi-domesticated reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus). Virol. J. 2005, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oreshkova, N.; Molenaar, R.J.; Vreman, S.; Harders, F.; Oude Munnink, B.B.; Hakze-van der Honing, R.W.; Gerhards, N.; Tolsma, P.; Bouwstra, R.; Sikkema, R.S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in farmed minks, the Netherlands, April and May 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 2001005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oude Munnink, B.B.; Sikkema, R.S.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Molenaar, R.J.; Munger, E.; Molenkamp, R.; Van der Spek, A.; Tolsma, P.; Rietveld, A.; Brouwer, M.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on mink farms between humans and mink and back to humans. Science 2021, 371, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, A.S.; Quaade, M.L.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Fonager, J.; Rasmussen, M.; Mundbjerg, K.; Lohse, L.; Strandbygaard, B.; Jørgensen, C.S.; Alfaro-Núñez, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Transmission between Mink (Neovison vison) and Humans, Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, W.R.; Palmer, M.V.; Bannantine, J.P.; Greenwald, R.; Esfandiari, J.; Andersen, P.; McNair, J.; Pollock, J.M.; Lyashchenko, K.P. Antibody responses in reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) infected with Mycobacterium bovis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovani/, E.R.; Beckmen/, K.B.; Highland/, M.A. Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae Associated with Polymicrobial Pneumonia in a Free-Ranging Yearling Barren Ground Caribou (Rangifer tarandus granti) from Alaska, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdussalam, M.; Fein, D.A. Brucellosis as a world problem. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1976, 31, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Godfroid, J.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Saegerman, C.; Blasco, J.M. Brucellosis in terrestrial wildlife. Rev. Sci. Technol. 2013, 32, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stella, E.; Mari, L.; Gabrieli, J.; Barbante, C.; Bertuzzo, E. Permafrost dynamics and the risk of anthrax transmission: A modelling study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschfalk, A.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Müller, W.; Goethe, R. Toxin types of Clostridium perfringens isolated from free-ranging, semi-domesticated reindeer in Norway. Vet. Rec. 2002, 151, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummeneje, K.; Bakken, G. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxaemia in reindeer. Nord. Vet. Med. 1973, 25, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Embury-Hyatt, C.K.; Wobeser, G.; Simko, E.; Woodbury, M.R. Investigation of a syndrome of sudden death, splenomegaly, and small intestinal hemorrhage in farmed deer. Can. Vet. J. 2005, 46, 702–708. [Google Scholar]
- Sundset, M.A.; Kohn, A.; Mathiesen, S.D.; Praesteng, K.E. Eubacterium rangiferina, a novel usnic acid-resistant bacterium from the reindeer rumen. Naturwissenschaften 2008, 95, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondo, K.J.; Macbeth, B.; Schwantje, H.; Orsel, K.; Culling, D.; Culling, B.; Tryland, M.; Nymo, I.H.; Kutz, S. Health Survey of Boreal Caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou) in Northeastern British Columbia, Canada. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 544–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena, J.R.; Wille, H. The Structure of the Infectious Prion Protein and Its Propagation. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 150, 341–359. [Google Scholar]
- Osterholm, M.T.; Anderson, C.J.; Zabel, M.D.; Scheftel, J.M.; Moore, K.A.; Appleby, B.S. Chronic Wasting Disease in Cervids: Implications for Prion Transmission to Humans and Other Animal Species. mBio 2019, 10, e01091-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakudo, A. Chronic Wasting Disease: Current Assessment of Transmissibility. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2020, 36, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safar, J.G.; Lessard, P.; Tamgüney, G.; Freyman, Y.; Deering, C.; Letessier, F.; Dearmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Transmission and detection of prions in feces. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trone-Launer, E.K.; Wang, J.; Lu, G.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E.; Zick, P.R.; Lamer, J.T.; Shelton, P.A.; Jacques, C.N. Differential gene expression in chronic wasting disease-positive white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 12600–12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, B.; Kim, E.; Choi, J.K.; Jin, J.K.; Kim, J.I.; Ishigami, A.; Maruyama, N.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.K. Accumulation of citrullinated proteins by up-regulated peptidylarginine deiminase 2 in brains of scrapie-infected mice: A possible role in pathogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, D.S.; Meersman, F.; Oxley, D.; Webster, J.; Gill, A.C.; Bronstein, I.; Lowe, C.R.; Dear, D.V. Effect of enzymatic deimination on the conformation of recombinant prion protein. Biochim. Acta Biophys. 2009, 1794, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, B.; Ishigami, A.; Maruyama, N.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.K. Peptidylarginine deiminase and protein citrullination in prion diseases: Strong evidence of neurodegeneration. Prion 2013, 7, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, B.; Jin, J.K.; Jeon, Y.C.; Cho, H.J.; Ishigami, A.; Choi, K.C.; Carp, R.I.; Maruyama, N.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.K. Involvement of peptidylarginine deiminase-mediated post-translational citrullination in pathogenesis of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.; Jeon, Y.C.; Shin, H.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Kondo, Y.; Ishigami, A.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.K. Myelin Basic Protein Citrullination, a Hallmark of Central Nervous System Demyelination, Assessed by Novel Monoclonal Antibodies in Prion Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 3172–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancandi, M.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Kraev, I.; Mercer, A.; Lange, S. Protein Deimination Signatures in Plasma and Plasma-EVs and Protein Deimination in the Brain Vasculature in a Rat Model of Pre-Motor Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, U.; Almeida, L.M.; Dudas, S.; Graham, C.E.; Czub, S.; Moore, S.S.; Guan, L.L. Gene expression alterations in Rocky Mountain elk infected with chronic wasting disease. Prion 2012, 6, 282–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, S.J.; West Greenlee, M.H.; Kondru, N.; Manne, S.; Smith, J.D.; Kunkle, R.A.; Kanthasamy, A.; Greenlee, J.J. Experimental Transmission of the Chronic Wasting Disease Agent to Swine after Oral or Intracranial Inoculation. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00926-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waddell, L.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Otten, A.; Corrin, T.; Hierlihy, K. Current evidence on the transmissibility of chronic wasting disease prions to humans-A systematic review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benestad, S.L.; Telling, G.C. Chronic wasting disease: An evolving prion disease of cervids. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






| Protein ID Protein Name | Species Name Common Name | Matches (Sequences) | Total Score (p < 0.05) † |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0A140T897_BOVIN Albumin | Bos taurus Cow | 2 (39) | 2322 |
| L8ISP4_9CETA Serum albumin | Bos mutus Domestic Yak | 107 (37) | 2198 |
| A0A4W2GW83_BOBOX Uncharacterized protein (ALB protein) | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 105 (37) | 2072 |
| A0A5N3XZ04_MUNRE IF rod domain-containing protein | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 44 (25) | 1128 |
| *A0A212DF80_CEREH KRT5 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 44 (25) | 1275 |
| A0A6J0WT46_ODOVR Serum albumin | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 52 (22) | 1177 |
| A0A5N4DHW9_CAMDR Keratin | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 40 (21) | 1116 |
| A0A4W2C021_BOBOX Uncharacterized protein (collagen alpha-1(I) chain) | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 34 (20) | 1080 |
| A0A452FHU9_CAPHI Uncharacterized protein (collagen type I alpha 1 chain) | Capra hircus Goat | 34 (16) | 988 |
| A0A5N3WTF4_MUNMU Uncharacterized protein (collagen alpha-1(I) chain isoform X1) | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 23 (13) | 976 |
| A0A5N4D320_CAMDR Keratin | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 37 (15) | 832 |
| A0A6J0WBI9_ODOVR Histidine-rich glycoprotein isoform X1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 33 (14) | 806 |
| *A0A212D793_CEREH KRT19 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 32 (13) | 785 |
| A0A287B5W2_PIG Trypsinogen isoform X1 | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 185 (157) | 765 |
| A0A4W2D3K5_BOBOX Keratin 75 | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 33 (13) | 729 |
| A0A4W2DIS9_BOBOX Keratin 75 | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 31 (15) | 724 |
| A0A6B0R6W5_9CETA Uncharacterized protein (IF rod domain-containing; glial fibrillary acidic protein) | Bos mutus Domestic yak | 25 (14) | 704 |
| 9XAP9_CAMFR Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14-like protein | Camelus ferus Wild Bactrian camel | 24 (10) | 694 |
| A0A452FN18_CAPHI IF rod domain-containing protein | Capra hircus Goat | 13 (9) | 676 |
| A0A5N4DGN6_CAMDR Keratin | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 29 (14) | 670 |
| A0A4W2IN22_BOBOX IF rod domain-containing protein | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 25 (11) | 670 |
| A0A6I9IRH0_VICPA keratin, type I cytoskeletal | Vicugna pacos Alpaca | 10 (8) | 667 |
| A0A5G2QXD3_PIG IF rod domain-containing protein | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 27 (18) | 655 |
| *A0A3Q1LZN8_BOVIN Collagen alpha-2(I) chain | Bos taurus Cow | 26 (13) | 634 |
| A0A287BLD2_PIG Uncharacterized protein (collagen alpha-1(I) chain preproprotein; alpha 1 chain of type I collagen) | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 19 (9) | 628 |
| *A0A212D6S5_CEREH KRT17 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 16 (11) | 580 |
| A0A5N4DFY6_CAMDR Keratin | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 19 (12) | 550 |
| A0A212CMY9_CEREH Uncharacterized protein (immunoglobulin heavy constant; beta-2-microglobulin) | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 10 (8) | 539 |
| *A0A6J3QLJ4_TURTR Collagen alpha-1(I) chain | Tursiops truncates Common bottlenose dolphin | 9 (7) | 488 |
| A0A2Y9SJP9_PHYMC Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A | Physeter macrocephalus Sperm Whale | 26 (10) | 469 |
| A0A452EP10_CAPHI IF rod domain-containing protein | Capra hircus Goat | 9 (7) | 469 |
| A0A6B0R542_9CETA Uncharacterized protein (bradykinin; kininogen-1; kininogen-2) | Bos mutus Wild yak | 16 (8) | 466 |
| A0A5N4DG47_CAMDR Keratin | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 19 (9) | 463 |
| A0A5N3WDS4_MUNMU Bradykinin | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 10 (9) | 443 |
| *A0A1S7J1Y9_PIG Alpha2 chain of type I collagen | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 17 (10) | 442 |
| A0A5N4DFY1_CAMDR Keratin | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 13 (8) | 380 |
| A0A383ZWF6_BALAS Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6A-like isoform X2 | Balaenoptera acutorostrata scammoni Minke whale | 13 (8) | 360 |
| W5Q4S0_SHEEP Uncharacterized protein (collagen alpha-1(III) chain; collagen type III alpha 1 chain; fibrillar collagen NC1 domain-containing protein) | Ovis aries Sheep | 7 (5) | 340 |
| A0A2F0AVL6_ESCRO Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4 | Eschrichtius robustus Gray whale | 12 (7) | 339 |
| *A0A5N3W3N9_MUNRE SH3 domain-containing protein | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 8 (8) | 296 |
| A0A340XVM8_LIPVE Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 15 | Lipotes vexillifer Baiji | 10 (6) | 294 |
| A0A5N4CT25_CAMDR Histone H4 | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 5 (5) | 240 |
| A0A5N3XAC4_MUNRE Uncharacterized protein (Ig-like domain-containing protein) | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 7 (3) | 239 |
| A0A6J0ZDI0_ODOVR Serotransferrin | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 5 (5) | 234 |
| *ACTB_BOSMU Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | Bos mutus grunniens Wild yak | 6 (5) | 232 |
| A0A5N3WEA4_MUNMU Beta-1 metal-binding globulin | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 5 (5) | 232 |
| A0A6J0XRB4_ODOVR Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 oral-like | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 16 (6) | 228 |
| A0A2C9F3E9_PIG Junction plakoglobin | Sus scrofa | 6 (1) | 228 |
| A0A212DB90_CEREH Ig-like domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 6 (3) | 225 |
| *0A6I9IE32_VICPA Collagen alpha-1(III) chain isoform X1 | Vicugna pacos Alpaca | 6 (4) | 224 |
| A0A212D5P4_CEREH TAF domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 5 (5) | 222 |
| A0A643C4S8_BALPH Uncharacterized protein (IF rod domain-containing protein; KRT81; Keratin 85) | Balaenoptera physalus Fin Whale | 10 (6) | 215 |
| A0A5N3W8P2_MUNMU Uncharacterized protein (Ig-like domain-containing protein) | Muntiacus muntjac Reeves’s muntjac | 7 (3) | 212 |
| A0A212D7J2_CEREH Fibrinogen beta chain | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 3 (3) | 192 |
| A0A287B7K6_PIG IF rod domain-containing protein | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 9 (6) | 186 |
| A0A212DFA6_CEREH IF rod domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 11 (5) | 184 |
| A0A6J0XD83_ODOVR Fibrinogen alpha chain | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 5 (4) | 180 |
| *A0A2Y9MPQ9_DELLE Collagen alpha-1(III) chain | Delphinapterus leucas Beluga whale | 5 (4) | 163 |
| A0A452E8D3_CAPHI Ig-like domain-containing protein | Capra hircus Goat | 3 (2) | 149 |
| W5P2K5_SHEEP IF rod domain-containing protein | Ovis aries Sheep | 7 (4) | 147 |
| A0A5N3UHT3_MUNRE Ig-like domain-containing protein | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 2 (2) | 147 |
| A2P2I1_SHEEP VH region | Ovis aries Sheep | 1 (1) | 131 |
| *Q0VCX2|BIP_BOVIN Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | Bos taurus Cow | 2 (2) | 101 |
| A0A212CAL2_CEREH Elongation factor 1-alpha | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (2) | 100 |
| A0A5N3UV43_MUNMU IF rod domain-containing protein | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 5 (2) | 89 |
| A0A3Q1LUE9_BOVIN Ig-like domain-containing protein | Bos taurus Cow | 1 (1) | 87 |
| A0A6B9SDT6_BOVIN Ig lamda chain variable region | Bos taurus Cow | 1 (1) | 87 |
| A0A212CSZ9_CEREH Ig-like domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (1) | 83 |
| A0A2F0B9E6_ESCRO Trypsin | Eschrichtius robustus Gray whale | 2 (1) | 80 |
| *A0A286ZKC5_PIG HATPase_c domain-containing protein | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 2 (0) | 76 |
| A0A1L6BP13_BUBBU Beta-casein | Bubalus bubalis Water buffalo | 3 (2) | 75 |
| A0A6B0S2F2_9CETA Fibrinogen C-terminal domain-containing protein | Bos mutus Wild yak | 3 (2) | 68 |
| *P0C276|RL40_SHEEP Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40 | Ovis aries Sheep | 1 (1) | 67 |
| *A0A2Y9SBW8_PHYMC Histone H2B | Physeter macrocephalus Sperm Whale | 2 (2) | 65 |
| A0A6B0RTH8_9CETA Uncharacterized protein (obscurin) | Bos mutus Wild yak | 2 (2) | 63 |
| A0A6J3S691_TURTR Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 78 | Tursiops truncates Common bottlenose dolphin | 2 (2) | 63 |
| A0A383ZRF2_BALAS Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 24 | Balaenoptera acutorostrata scammony Minke whale | 1 (1) | 62 |
| *A0A0C5AGQ3_BUBBU Lysozyme | Bubalus bubalis Water buffalo | 1 (1) | 61 |
| A2P2I3_SHEEP VH region | Ovis aries Sheep | 1 (1) | 60 |
| A0A075B7I6_PIG Ig-like domain-containing protein | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 1 (1) | 59 |
| A0A0R4I993_SUSBA Tubulin alpha chain | Sus barbatus Bornean bearded pig | 1 (1) | 53 |
| A0A5N4EAI9_CAMDR Annexin | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 2 (2) | 50 |
| A0A2Y9EH04_PHYMC Fer-1-like protein 4 | Physeter macrocephalus Sperm Whale | 2 (2) | 50 |
| A0A5J5N0U1_MUNRE Uncharacterized protein (small proline-rich protein 2I-like; Type II small proline-rich protein) | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 1 (1) | 50 |
| A0A6B0R269_9CETA Ig-like domain-containing protein | Bos mutus Wild yak | 2 (1) | 49 |
| A0A452E907_CAPHI Uncharacterized protein (skin-specific protein 32; Chromosome 3 C1orf68 homolog; Chromosome 1 open reading frame 68) | Capra hircus Goat | 1 (1) | 48 |
| A0A4W2E476_BOBOX Ig-like domain-containing protein | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 1 (1) | 48 |
| A0A212CS30_CEREH Ig-like domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (1) | 47 |
| Protein ID Protein Name | Species Name Common Name | Matches (Sequences) | Total Score (p < 0.05) † |
|---|---|---|---|
| *A0A6J0ZEI2_ODOVR Complement C3 | Odocoileusvirginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 71 (51) | 3535 |
| *A0A6J0Y2W1_ODOV Fibronectin isoform X5 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 70 (50) | 3454 |
| *A0A5N3WRA9_MUNMU C3-beta-c | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 70 (51) | 3438 |
| *A0A6J0YF65_ODOVR alpha-2-macroglobulin | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 43 (37) | 2929 |
| A0A140T897_BOVIN Albumin | Bos taurus Cow | 81 (59) | 2831 |
| A0A5J5N929_MUNRE Uncharacterized protein(alpha-2-macroglobulin-like) | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 59 (42) | 2815 |
| L8ISP4_9CETA Serum albumin | Bos mutus Domestic Yak | 79 (58) | 2691 |
| *A0A6J0YGQ5_ODOVR Pregnancy zone protein-like isoform X1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 49 (38) | 2596 |
| A0A6J0WT46_ODOVR Serum albumin | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 99 (66) | 2581 |
| A0A6J0ZDI0_ODOVR Serotransferrin | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 77 (49) | 2452 |
| A0A5N3XN56_MUNRE Beta-1 metal-binding globulin | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 65 (44) | 2268 |
| A0A212D5P0_CEREH ALB | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 84 (56) | 2237 |
| X2GM95_CERNI Serum albumin | Cervus nippon Sika deer | 82 (54) | 2182 |
| A0A6J0XGG0_ODOVR Fibrinogen beta chain | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 63 (47) | 1890 |
| A0A6J0XD83_ODOVR Fibrinogen alpha chain | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 62 (42) | 1770 |
| A0A5N3WDS4_MUNMU Bradykinin | Muntiacus muntjac | 76 (49) | 1754 |
| *A0A6J0WDQ8_ODOVR Kininogen-1 isoform X1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus | 72 (46) | 1645 |
| *A0A6J0WBI9_ODOVR Histidine-rich glycoprotein isoform X1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus | 152 (95) | 1514 |
| A0A5N3WD93_MUNMU Fibrinogen C-terminal domain-containing protein | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 54 (43) | 1470 |
| *A0A212CD20_CEREH 2M | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 32 (24) | 1469 |
| A0A5N3XZ04_MUNRE IF rod domain-containing protein | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 37 (25) | 1466 |
| A0A5N3WGH1_MUNMU Uncharacterized protein (HRG) | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 142 (87) | 1393 |
| A0A6B0S2F2_9CETA Fibrinogen C-terminal domain-containing protein | Bos mutus Wild yak | 43 (29) | 1365 |
| A0A5N4DHW9_CAMDR Keratin | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 31 (21) | 1284 |
| *A0A212D8V0_CEREH FGG | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus | 47 (34) | 1235 |
| *A0A6J0YZJ7_ODOVR Ceruloplasmin isoform X2 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus European red deer | 28 (16) | 1227 |
| A0A5N3WB21_MUNMU Fibrinogen alpha chain | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 42 (24) | 1207 |
| W5PF65_SHEEP Beta-1 metal-binding globulin | Ovis aries Sheep | 32 (21) | 1206 |
| A0A212CMY9_CEREH Uncharacterized protein (immunoglobulin heavy constant mu; beta-2-microglobulin) | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 47 (30) | 1156 |
| A0A5N3XTY4_MUNRE Uncharacterized protein(complement factor H) | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 26 (21) | 1151 |
| *A0A6J0XY06_ODOVR Thrombospondin-1 isoform | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 21 (12) | 1076 |
| *A0A6J0XUD5_ODOVR Complement C4-A-like | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 20 (15) | 1074 |
| *A0A6J0WY92_ODOVR Complement factor H-like | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 22 (17) | 1026 |
| *A0A6J0W0N0_ODOVR Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 18 (14) | 944 |
| *A0A4W2C0F6_BOBOX C4a anaphylatoxin | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 16 (11) | 943 |
| *A0A212CJ19_CEREH CP | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 22 (13) | 935 |
| *A0A6J0XUP5_ODOVR Complement C4-A-like | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 15 (12) | 923 |
| *E1BH06_BOVIN C4a anaphylatoxin | Bos taurus Cow | 16 (11) | 921 |
| *A0A6J0WIC5_ODOVR Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 20 (14) | 879 |
| *A0A6J0YC26_ODOVR Heparin cofactor 2 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 17 (11) | 830 |
| A0A6I9IRH0_VICPA Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 | Vicugna pacos Alpaca | 23 (14) | 822 |
| A0A287B5W2_PIG Trypsinogen isoform X1 | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 145 (124) | 795 |
| *A0A6J0ZDS1_ODOVR C4b-binding protein alpha chain | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 15 (9) | 783 |
| A0A6J0VYI5_ODOVR Uncharacterized protein (complement C1q) | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 19 (14) | 774 |
| A0A341C5T8_NEOAA Serum albumin | Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis Narrow-ridged finless porpoise | 31 (11) | 734 |
| A0A6J0YVR0_ODOVR Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 15 isoform X1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 20 (13) | 720 |
| A0A4W2D3K5_BOBOX Keratin 75 | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 22 (14) | 716 |
| A0A287AEL2_PIG IF rod domain-containing protein | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 22 (12) | 708 |
| *A0A5N3XTJ5_MUNRE Antithrombin-III | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 14 (4) | 614 |
| *A0A220IGA4_RANTA Adult beta-globin | Rangifer tarandus Reindeer | 12 (11) | 603 |
| A0A212CMB3_CEREH Uncharacterized protein(Ig gamma-3 chain C region; IgG heavy chain) | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 20 (15) | 593 |
| *A0A6J0WIA8_ODOVR Prothrombin | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 12 (8) | 567 |
| A0A6I9I3P0_VICPA Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5-like | Vicugna pacos Alpaca | 16 (9) | 563 |
| *A0A6J0Y9J4_ODOVR Apolipoprotein A-I | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 10 (7) | 543 |
| *Q9TS85_BOVIN Histidine-rich GLYCOPROTEIN=FACTOR XIIIA substrate | Bos taurus Cow | 39 (18) | 536 |
| *A0A212DHP9_CEREH APOA1 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 9 (7) | 504 |
| *A0A0B8RTA2_PIG Actin, gamma 1 | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 10 (6) | 502 |
| *A0A212D467_CEREH C1QB | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 13 (9) | 498 |
| A0A2Y9SJP9_PHYMC Keratin, type II cytoskeletal | Physeter macrocephalus Sperm whale | 14 (7) | 495 |
| *A0A5N3VLU1_MUNMU Prothrombin | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 11 (6) | 482 |
| HRG_BOVIN Histidine-rich glycoprotein | Bos taurus Cow | 21 (14) | 480 |
| *S9Y253_CAMFR Kininogen-2 isoform I | Camelus ferus Wild Bactrian camel | 28 (11) | 451 |
| *A0A6J0XQV8_ODOVR Hemopexin | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 9 (5) | 450 |
| *A0A6J0WWF4_ODOVR Vitronectin isoform X1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 10 (7) | 438 |
| *A0A6J0W8S2_ODOVR Plasminogen isoform X1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 11 (3) | 434 |
| A0A5J5MM15_MUNRE Uncharacterized protein(immunoglobulin kappa light chain-like) | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 12 (7) | 425 |
| *A0A6J0Z5Q2_ODOVR Transcobalamin-2 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 8 (6) | 423 |
| *A0A5N3X8Z5_MUNRE Hemopexin | Muntiacus reevesi Reeves’s muntjac | 7 (5) | 422 |
| *A0A212CJF4_CEREH C1q domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 17 (10) | 415 |
| *C0LXP2_ODOVR Complement 1 subcomponent q polypeptide gamma | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 6 (5) | 408 |
| A0A5N3W8P2_MUNMU Uncharacterized protein(Ig-like domain-containing protein) | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 11 (9) | 398 |
| *A0A286ZIC1_PIG Actin-depolymerizing factor | Sus scrofa Wils boar | 8 (3) | 371 |
| *A0A5N3VK90_MUNMU Actin-depolymerizing factor | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 7 (3) | 369 |
| A0A212DB90_CEREH Ig-like domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 9 (5) | 364 |
| *A0A212DHZ3_CEREH HPX | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 7 (4) | 349 |
| *A0A6J0X6J4_ODOVR Selenoprotein P | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 9 (5) | 334 |
| *A0A6J0Y2T5_ODOVR Hemoglobin subunit alpha | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 7 (3) | 333 |
| *A0A480Y2E3_PIG Kininogen-1 isoform 1 | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 16 (5) | 333 |
| *A0A6J0YKX8_ODOVR Protein AMBP | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 6 (5) | 324 |
| A0A4W2DA54_BOBOX Uncharacterized protein (Heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2) | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 4 (3) | 314 |
| *A0A5J5MM09_MUNRE Plasminogen | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 9 (2) | 308 |
| *A0A212C7P2_CEREH PLG | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 8 (2) | 299 |
| *A0A5N3WQN5_MUNMU Vitellogenin domain-containing protein | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 8 (1) | 278 |
| *A0A5N3X9D4_MUNRE SERPIN domain-containing protein | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 6 (4) | 270 |
| *A0A6J0YIK3_ODOVR Vitamin D-binding protein | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 5 (4) | 267 |
| *A0A6J0XXC2_ODOVR Apolipoprotein B-100 isoform X1 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 7 (1) | 267 |
| *A0A6J0Y0A8_ODOVR Serpin A3-7-like | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 6 (4) | 267 |
| *A0A212CS37_CEREH SERPIN domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 6 (4) | 265 |
| A0A5N3XX47_MUNRE Uncharacterized protein (inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4) | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 5 (3) | 259 |
| *A0A6J0VV77_ODOVR CD5 antigen-like | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 5 (3) | 255 |
| *A0A5N3WVG9_MUNMU Apolipoprotein H | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 4 (3) | 252 |
| A0A4W2E1T0_BOBOX Uncharacterized protein (FZ domain-containing protein; collagen type XVIII alpha 1 chain; COL18A1 protein) | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 5 (3) | 244 |
| A0A2Y9N2V9_DELLE Bradykinin | Delphinapterus leucas Beluga whale | 19 (5) | 235 |
| *A0A212D5I5_CEREH DSP | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 6 (1) | 207 |
| A0A4U1EJD5_MONMO TAF domain-containing protein | Monodon monoceros Narwhale | 5 (3) | 204 |
| *A0A6B0SDR2_9CETA Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Bos mutus Wild yak | 6 (2) | 202 |
| *A0A5N3V0U6_MUNMU Peptidase_M14 domain-containing protein | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 5 (1) | 200 |
| A0A5N3VBS8_MUNMU Uncharacterized protein (insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex acid labile subunit) | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 4 (2) | 199 |
| A0A287AAL6_PIG Uncharacterized protein(four and a half LIM domains protein 1 isoform X3) | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 4 (2) | 198 |
| *A0A2U4C7Y7_TURTR Histidine-rich glycoprotein | Tursiops truncates Common bottlenose dolphin | 24 (2) | 186 |
| A0A3Q1M1M7_BOVIN Junction plakoglobin | Bos taurus Cow | 4 (3) | 186 |
| A0A212CSZ9_CEREH Ig-like domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 3 (1) | 181 |
| *A0A452FXZ3_CAPHI Apolipoprotein H | Capra hircus Goat | 3 (2) | 180 |
| *A0A5N3WZL8_MUNMU Complement C1q subcomponent subunit A | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 4 (3) | 179 |
| *A0A6J0XZP9_ODOVR Alpha-1-antitrypsin | Odocoileus virginianus texanus | 5 (2) | 179 |
| *A0A452E7A0_CAPHI Plasminogen | Capra hircus Goat | 5 (2) | 176 |
| A0A4V5P683_MONMO Uncharacterized protein (histone H2B type 1-L-like) | Monodon monoceros Narwhale | 4 (2) | 174 |
| A0A6B9SCH7_BOVIN Ig lamda chain variable region | Bos taurus Cow | 2 (2) | 160 |
| A0A452E8D3_CAPHI Ig-like domain-containing protein | Capra hircus Goat | 3 (2) | 157 |
| *A0A452F014_CAPHI SERPIN domain-containing protein | Capra hircus Goat | 4 (1) | 155 |
| *A0A2Y9LVH2_DELLE Amine oxidase | Delphinapterus leucas Beluga whale | 2 (2) | 141 |
| A0A6B0SAT2_9CETA Ig-like domain-containing protein | Bos mutus Wild yak | 4 (1) | 140 |
| A0A4W2CFX9_BOBOX Ig-like domain-containing protein | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 2 (1) | 139 |
| A2P2I1_SHEEP VH region | Ovis aries Sheep | 2 (1) | 139 |
| *A0A088Q0F1_9CETA Heat shock protein 90kDa alpha | Bos grunniens x Bos taurus Domestic yak x Cow | 2 (2) | 137 |
| A0A5N3UK72_MUNRE Ig-like domain-containing protein | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 2 (1) | 133 |
| FIBA_ALCAA Fibrinogen alpha chain | Alces alces alces Moose | 1 (1) | 122 |
| A0A643C7L4_BALPH Uncharacterized protein (desmoplakin) | Balaenoptera physalus Fin whale | 4 (1) | 120 |
| A6QM09_BOVIN Uncharacterized protein (Ig-like domain-containing protein; Ig lambda chain V-III region LOI-like protein) | Bos taurus Cow | 4 (1) | 118 |
| *A0A6B0R457_9CETA Activating signal cointegrator 1 complex subunit 3 | Bos mutus Wild yak | 3 (1) | 118 |
| *A0A212DB97_CEREH SERPINF2 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (1) | 117 |
| *A0A6J3PT56_TURTR Immunoglobulin lambda-1 light chain-like isoform X1 | Tursiops truncates Common bottlenose dolphin | 4 (1) | 116 |
| A0A3Q1LT19_BOVIN Ig-like domain-containing protein | Bos taurus Cow | 2 (2) | 113 |
| *A0A212CSZ1_CEREH SERPINA5 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 3 (1) | 112 |
| A0A5N4CT25_CAMDR Histone H4 | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 3 (1) | 107 |
| *A0A6J0XAN1_ODOVR Complement component C9 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 3 (1) | 104 |
| *A0A6J0Y2I3_ODOVR Alpha-1B-glycoprotein | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 2 (1) | 95 |
| A0A2F0AYU0_ESCRO Ig lambda chain V-III region SH | Eschrichtius robustus Gray whale | 2 (1) | 95 |
| A0A212CS30_CEREH Ig-like domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (1) | 93 |
| *A0A1L6BNZ0_BUBBU Alpha-S1-casein | Bubalus bubalis Water buffalo | 2 (1) | 93 |
| *A0A212D4C7_CEREH Ribosomal protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 1 (1) | 92 |
| *A0A212CIC4_CEREH FETUB | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (1) | 91 |
| A0A0R4I993_SUSBA Tubulin alpha chain | Sus barbatus Bornean bearded pig | 2 (1) | 89 |
| A2P2I3_SHEEP VH region | Ovis aries Sheep | 2 (1) | 89 |
| *A0A6J0WSX6_ODOVR Tubulin beta-3 chain | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 2 (1) | 88 |
| *A0A340WKS1_LIPVE Selenoprotein P | Lipotes vexillifer Baiji | 3 (1) | 87 |
| *A0A4W2BXS4_BOBOX Kallikrein B1 | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 2 (1) | 86 |
| R4R2H5_SHEEP Beta-casein | Ovis aries Sheep | 2 (1) | 84 |
| *A0A6J0Z7P6_ODOVR Apolipoprotein R-like | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 2 (1) | 84 |
| A0A6B9SDT6_BOVIN Ig lamda chain variable region | Bos taurus Cow | 1 (1) | 84 |
| *A0A5N3WWG2_MUNMU SERPIN domain-containing protein | Muntiacus muntjac Barking deer | 2 (1) | 83 |
| *A0A2Y9EXF5_PHYMC 2-phospho-D-glycerate hydro-lyase | Physeter macrocephalus Sperm whale | 1 (1) | 82 |
| *A0A212D4I5_CEREH C3/C5 convertase | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 3 (1) | 81 |
| *A0A212CM12_CEREH 40S ribosomal protein S18 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 1 (1) | 80 |
| A0A452G1G8_CAPHI Uncharacterized protein (msx2-interacting protein isoform X, X2, X3, X4) | Capra hircus Goat | 3 (1) | 79 |
| A0A212CAL2_CEREH Elongation factor 1-alpha | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (2) | 79 |
| *A0A212CI11_CEREH Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 1 (1) | 78 |
| A0A2F0B9E6_ESCRO Trypsin | Eschrichtius robustus Gray whale | 5 (2) | 78 |
| *A0A5J5MZJ4_MUNRE MACPF domain-containing protein | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 2 (1) | 74 |
| *A0A212C6Y8_CEREH Transthyretin | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 1 (1) | 73 |
| *A0A212D5R7_CEREH JCHAIN | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (1) | 73 |
| *A0A480MMJ7_PIG Heat shock 70 kDa protein | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 2 (2) | 72 |
| *A0A6J0Y8N1_ODOVR Angiopoietin-related protein 6 isoform X2 | Odocoileus virginianus texanus White-tailed deer | 2 (1) | 72 |
| *A0A5N4EH44_CAMDR Biorientation of chromosomes in cell division protein 1-like 1 | Camelus dromedarius Dromedary | 2 (1) | 71 |
| *S9WER1_CAMFR Biorientation of chromosomes in cell division protein 1-like protein | Camelus ferus Wild Bactrian camel | 2 (1) | 71 |
| A0A212D1P2_CEREH Uncharacterized protein (N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase) | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (1) | 70 |
| *A0A3Q1LUP1_BOVIN Uncharacterized protein(cilia- and flagella-associated protein 54) | Bos taurus Cow | 3 (1) | 69 |
| A0A212CM59_CEREH Ig-like domain-containing protein | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 4 (1) | 68 |
| *A0A2Y9EUI8_PHYMC Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase | Physeter macrocephalus Sperm whale | 3 (1) | 67 |
| A2P2H1_SHEEP VH region | Ovis aries Sheep | 2 (1) | 66 |
| *A0A0B8RZA9_PIG Proliferation-associated 2G4, 38kDa) | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 2 (2) | 66 |
| A0A4X1TXJ2_PIG Uncharacterized protein (IgG heavy chian constant region) | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 2 (1) | 63 |
| A0A2Y9EH04_PHYMC Fer-1-like protein 4 | Physeter macrocephalus Sperm whale | 3 (1) | 62 |
| *A0A286ZRK7_PIG 60S ribosomal protein L11 | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 1 (1) | 62 |
| A0A4W2CHE4_BOBOX IF rod domain-containing protein | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 3 (1) | 61 |
| *A0A287BDT6_PIG Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 2 (1) | 61 |
| *A0A287AFA5_PIG Endoplasmin | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 1 (1) | 61 |
| *BIP_BOVIN Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | Bos taurus Cow | 1 (1) | 58 |
| 0A6B0R269_9CETA Ig-like domain-containing protein | Bos mutus Wild yak | 1 (1) | 57 |
| A0A5N3UHJ8_MUNRE Ig-like domain-containing protein | Muntiacus reevesi Chinese muntjac | 1 (1) | 56 |
| *A0A2Y9M486_DELLE Protein PRRC2C isoform X8 | Delphinapterus leucas Beluga whale | 9 (1) | 55 |
| *A0A383Z8A9_BALAS Putative SEC14-like protein 6 | Balaenoptera acutorostrata scammony Minke whale | 2 (1) | 53 |
| *A0A212D225_CEREH TMED9 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 1 (1) | 53 |
| *A0A0B8RSX6_PIG Filamin A, alpha | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 2 (1) | 52 |
| *A0A452E6D4_CAPHI Complement C5-like | Capra hircus Goat | 2 (1) | 52 |
| A0A6B0RW97_9CETA Uncharacterized protein(Ig lamda chain variable region) | Bos mutus Wild yak | 1 (1) | 52 |
| *A0A212CJY0_CEREH Transferrin receptor protein 1 | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 1 (1) | 52 |
| *A0A4W2F326_BOBOX Anaphylatoxin-like domain-containing protein | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 2 (1) | 52 |
| A0A4U1EAQ3_MONMO Ig-like domain-containing protein | Monodon monoceros Narwhal | 2 (1) | 50 |
| A0A286ZJV6_PIG Annexin | Sus scrofa Wild boar | 1 (1) | 50 |
| A0A6B0RTH8_9CETA Uncharacterized protein (obscurin, cytoskeletal calmodulin and titin-interacting RhoGEF) | Bos mutus Wild yak | 2 (1) | 50 |
| *A0A212CKA1_CEREH Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 1 (1) | 50 |
| W5P6D4_SHEEP Uncharacterized protein (Integrator complex subunit 1) | Ovis aries Sheep | 2 (1) | 50 |
| *A0A4W2F827_BOBOX 60 kDa poly(U)-binding-splicing factor | Bos indicus x Bos taurus Zebu x Cow | 3 (1) | 50 |
| *A0A212CT53_CEREH Lactadherin | Cervus elaphus hippelaphus European red deer | 2 (1) | 50 |
| A0A6B9SDX6_BOVIN Ig lamda chain variable region | Bos taurus Cow | 1 (1) | 50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Alessio, S.; Thorgeirsdóttir, S.; Kraev, I.; Skírnisson, K.; Lange, S. Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Plasma and Plasma EVs of Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus). Biology 2021, 10, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030222
D’Alessio S, Thorgeirsdóttir S, Kraev I, Skírnisson K, Lange S. Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Plasma and Plasma EVs of Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus). Biology. 2021; 10(3):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030222
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Alessio, Stefania, Stefanía Thorgeirsdóttir, Igor Kraev, Karl Skírnisson, and Sigrun Lange. 2021. "Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Plasma and Plasma EVs of Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus)" Biology 10, no. 3: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030222
APA StyleD’Alessio, S., Thorgeirsdóttir, S., Kraev, I., Skírnisson, K., & Lange, S. (2021). Post-Translational Protein Deimination Signatures in Plasma and Plasma EVs of Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus). Biology, 10(3), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030222