Forensic Tools for Species Identification of Skeletal Remains: Metrics, Statistics, and OsteoID
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Morphometric Human Versus Nonhuman Classification
3.3. Morphometric Skeletal Species Identification
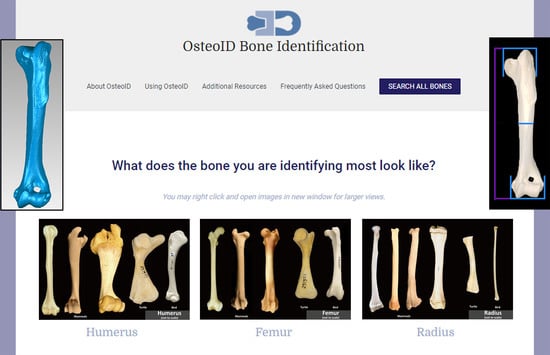
3.4. Web Tool for Species Identification
4. Discussion
4.1. Human Versus Nonhuman Determination
4.2. Species Identification
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pokines, J.T. Identification of nonhuman remains received in a medical examiner setting. J. Forensic Identif. 2015, 65, 223–246. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, W.M. Human Osteology—A Laboratory and Field Manual, 4th ed.; Missouri Archaeological Society: Columbia, MO, USA, 1995; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, A.M.; Passalacqua, N.V.; Bartelink, E.J. Forensic Anthropology: Current Methods and Practices, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 104–123. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, D.; Marks, M.M. Species: Human versus nonhuman. In Encyclopedia of Forensic Sciences, 2nd ed.; Siegel, J.A., Saukko, P.J., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, B.; Crabtree, P. Comparative Skeletal Anatomy—A Photographic Atlas for Medical Examiners, Coroners, Forensic Anthropologists, and Archeologists; Human Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, B.; Crabtree, P. Comparative Osteology—A Laboratory and Field Guide of Common North American Animals; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- France, D. Human and Nonhuman Bone Identification: A Color Atlas; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- France, D. Human and Nonhuman Bone Identification: A Concise Field Guide; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- France, D. Comparative Bone Identification—Human Subadult to Nonhuman; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hillson, S. Mammal Bones and Teeth—An Introductory Guide to Methods of Identification; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Beisaw, A.M. Identifying and Interpreting Animal Bones—A Manual; Texas A&M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Broughton, J.M.; Miller, S.D. Zooarchaeology and Field Ecology—A Photographic Atlas; University of Utah Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.J. Mammal Remains from Archaeological Sites; Papers of the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, President and Fellows of Harvard College: York, PA, USA, 1964; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- Saulsman, B.; Oxnard, C.E.; Franklin, D. Long bone morphometrics for human from non-human discrimination. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 202, 110.e1–110.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von den Dreisch, A. A Guide to the Measurement of Animal Bones from Archaeological Sites: As Developed by the Institut fur Palaeoanatomie, Domestikationsforschung und Geschichte der Tiermedizin of the University of Munich; Peabody Museum Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1976; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Eerkens, J.W.; Darwent, C.M.; Campbell-Grey, A.; Wildt, J.; Wheelis, B. Meaner than a junkyard dog: Osteological and isotopic insights into three canid burials from 1890s San Jose, California. SCA Proc. 2019, 33, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.J.M. Measurements of a group of adult female Shetland sheep skeletons from a single flock: A baseline for zooarchaeologists. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1996, 23, 593–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meachen, J.A.; Samuels, J.X. Evolution in coyotes (Canis latrans) in response to the megafaunal extinctions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4191–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitakarnnop, T.; Buddhachat, K.; Euppayo, T.; Kriangwanich, W.; Nganvongpanit, K. Feline (Felis catus) skull and pelvic morphology and morphometry: Gender-related difference? Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2017, 46, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoest, J.J.T. On the Morphology of the Domesticated Dog in Medieval Norway: An Osteometric Study. Master’s Thesis, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway, December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, K. Rezente Hunderassen. Eine Osteologische Untersuchung; Antropologische Abteilung: Oslo, Norway, 1930. [Google Scholar]
- Boonsri, B.; Pitakarnnop, T.; Buddhacat, K.; Changtor, P.; Nganvongpanit, K. Can feline (Felis catus) flat and long bone morphometry predict sex or skull shape? Anat. Sci. Int. 2019, 94, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeder, M.A. A metrical analysis of a collection of modern goats (Capra hircus aegagrus and C. h. hircus) from Iran and Iraq: Implications for the study of Caprine domestication. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2001, 28, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvia, W.J.; Peterson, R.O.; Vucetich, J.A.; Silvia, W.F.; Silvia, A.W. Variation in metatarsal morphology among subgroups of North American Moose (Alces alces). Alces J. Devoted Biol. Manag. Moose 2014, 50, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Saulsman, B. Long Bone Morphometrics for Human from Non-human Discrimination. Master’s Thesis, The University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Guintard, C.; Lallemand, M. Osteometric study of metapodial bones in sheep (Ovis aries, L. 1758). Ann. Anat. 2003, 185, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S.K. Scaling Patterns and Ecological Correlates of Postcranial Skeletal Robusticity in Canis and Ursus: Implications for Human Evolution. Ph.D. Thesis, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, B.M. Mammalian Osteology; Missouri Archaeological Society: Columbia, MO, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Salvagno, L.; Albarella, U. A morphometric system to distinguish sheep and goat postcranial bones. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, R.; Holmes, M.; Morris, J. “So bigge as bigge may be”: Tracking size and shape change in domestic livestock in London (AD 1220–1900). J. Arcchaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 3309–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfeiffer, S. Carpine skeletons can be “herd”. SCA Proc. 2013, 27, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, D.; Dollas, N.; DiMichele, D.; Robert, J. Terry Anatomical Human Skeletal Collection database. National Museum of Natural History. Dataset 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, B.M. Goldman Osteometric Data Set. Available online: https://web.utk.edu/~auerbach/GOLD.htm (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Samuels, J.X.; Meachen, J.A.; Sakai, S.A. Postcranial morphology and the locomotor habits of living and extinct carnivorans. J. Morphol. 2013, 274, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machuca, C.; Vettore, M.V.; Krasuka, M.; Baker, S.R.; Robinson, P.G. Using classification and regression tree modelling to investigate response shift patterns in dentine hypersensitivity. BRC Med. Res. Methodol. 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IBM SPSS Decision Trees 21; IBM Corporation: Armonk, NY, USA, 2012.
- Bartholdy, B.P.; Sandoval, E.; Hoogland, M.L.P.; Schrader, S.A. Getting rid of dichotomous sex estimations: Why logistic regression should be preferred over discriminant function analysis. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, P.L. Sexing skulls using discriminant function analysis of visually assessed traits. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2008, 136, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.C.; Mahoney, E.R.; Walker, P.L.; Everson, P.M. Prediction of sex based on five skull traits using decision analysis (CHAID). Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2009, 139, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, N.R.; Dudzik, B.; Cloutier, A. A decision tree for nonmetric sex assessment from the skull. J. Forensic Sci. 2018, 63, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikita, E.; Nikitas, P. Data mining and decision trees. In Statistics and Probability in Forensic Anthropology; Obertova, Z., Stewart, A., Cattaneo, C., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 88–105. [Google Scholar]
- Feldesman, M.R. Classification trees as an alternative to linear discriminant analysis. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2002, 119, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OsteoID. Available online: www.boneidentification.com (accessed on 29 October 2021).
- Morphosource OsteoID Project. Available online: https://www.morphosource.org/projects/000364427?locale=en (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Garvin, H.M.; Dunn, R.; Sholts, S. Postcranial osteometric data from human and 27 North American faunal species, Dryad. Dataset 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algee-Hewitt, B.; Coelho, C.; Navega, D.; Cunha, E. New and established methods for the quantification of cranial variation for forensic casework. In Statistics and Probability in Forensic Anthropology; Obertova, Z., Stewart, A., Cattaneo, C., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Nikita, E.; Nikitas, P. On the use of machine learning algorithms in forensic anthropology. Leg. Med. 2020, 47, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefner, J.T.; Ousley, S.D. Statistical classification methods for estimating ancestry using morphoscopic traits. J. Forensic Sci. 2014, 59, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navega, D.; Coelho, C.; Vicente, R.; Ferriera, M.T.; Wasterlain, S.; Cunha, E. AncesTrees: Ancestry estimation with randomized decision trees. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2015, 129, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savall, F.; Faruch-Bilfeld, M.; Dedouit, F.; Sans, N.; Rousseau, H.; Rouge, D.; Telmon, N. Metric sex determination using the human coxal bone on a virtual sample using decision trees. J. Forensic Sci. 2015, 60, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubelaker, D.H. The forensic evaluation of burned skeletal remains: A synthesis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2009, 183, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frayer, D.W.; Macchiarelli, R.; Mussi, M. A case of chondrodystrophic dwarfism in the Italian late Upper Paleolithic. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 1988, 75, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhern, D.M. A probable case of gigantism in a fifth dynasty skeleton from the Western Cemetery at Giza, Egypt. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2005, 15, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croker, S.L.; Clement, J.G.; Donlon, D. A comparison of cortical bone thickness in the femoral midshaft of humans and two non-human mammals. HOMO—J. Comp. Hum. Biol. 2009, 60, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croker, S.L.; Reed, W.; Donlon, D. Comparative cortical bone thickness between the long bones of humans and five common non-human mammal taxa. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 260, 104.e1–104.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rerolle, C.; Saint-Martin, P.; Dedouit, F.; Rousseau, H.; Telmon, N. Is the corticomedullary index valid to distinguish human from nonhuman bones: A multislice computed tomography study. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 231, 406.e1–406.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrieri, B.; Marquez-Grant, N. Using nutrient foramina to differentiate human from non-human long bone fragments in bioarchaeology and forensic anthropology. HOMO—J. Comp. Hum. Biol. 2019, 70, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, V.; Beckett, S.; Marquez-Grant, N. Differentiating human versus non-human bone by exploring the nutrient foramen: Implications for forensic anthropology. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2017, 131, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brits, D.; Steyn, M. A histomorphological analysis of human and non-human femora. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2014, 128, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillier, M.L.; Bell, L.S. Differentiating human bone from animal bone: A revie of histological methods. J. Forensic Sci. 2007, 52, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulhern, D.M.; Ubelaker, D.H. Differences in osteon banding between human and nonhuman bone. J. Forensic Sci. 2001, 46, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescimanno, A.; Stout, S.D. Differentiating fragmented human and nonhuman long bone using osteon circularity. J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, V.M.; Crowder, C.M. The utility of osteon shape and circularity for differentiating human and non-human Haversian bone. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2012, 149, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogner, E. Differentiating Black Bears (Ursus americanus) and Brown Bears (U. arctos) using Linear Tooth Measurements and Identification of Ursids from Oregon Caves National Monument. Master’s Thesis, East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN, USA, May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kantelis, T.M. Black Bears (Ursus americanus) versus Brown Bears (U. arctos): Combining Morphometrics and Niche Modeling to Differentiate Species and Predict Distributions Through Time. Master’s Thesis, East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN, USA, May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lariviere, S. Ursus americanus. Mamm. Species 2001, 64, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasitschniak-Arts, M. Ursus arctos. Mamm. Species 1993, 439, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boessneck, J. Osteological differences between sheep (Ovis aries Linne). In Science in Archaeology: A Comprehensive Survey of Progress and Research, 2nd ed.; Browthwell, D., Higgs, E., Eds.; Thames & Hudson: London, UK, 1969; pp. 311–358. [Google Scholar]
- Welker, M.H.; Byers, D.A.; McClure, S.B. “I wanna be your dog”: Evaluating the efficacy of univariate and multivariate methods for differentiating domestic and wild canids in North America. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2021, 31, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, R.K.; Geffen, E.; Girman, D.J.; Koepfli, K.P.; Lau, L.M.; Marshall, C.R. Molecular systematics of the Canidae. Syst. Biol. 1997, 46, 622–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannasch, D.L.; Baes, C.F.; Leeb, T. Genetic variants affecting skeletal morphology in domestic dogs. Trends Genet. 2020, 36, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frynta, D.; Baudysova, J.; Hradcova, P.; Faltusova, K.; Kratochvil, L. Allometry of sexual size dimorphism in domestic dog. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, M.; Hamerow, H.; Thomas, R. Close companions? a zooarchaeological study of the human-cattle relationship in Medieval England. Animals 2021, 11, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuschoft, H. Mechanisms for the acquisition of habitual bipedality: Are there biomechanical reasons for the acquisition of upright bipedal posture? J. Anat. 2004, 204, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardong, K.V. Vertebrates: Comparative Anatomy, Function, Evolution, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 348–371. [Google Scholar]
- Garvin, H.M.; Kenyhercz, M.W.; Dunn, R.; Sholts, S.; Litten, M.S. A Metric Approach to Human and Non-Human Species Identification of Skeletal Remains using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the American Academy of Forensic Sciences 73rd Annual Scientific Meeting, Virtual, 15–19 February 2021; p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Loyola-Gonzalez, O. Black-box vs. white-box: Understanding their advantages and weaknesses from a practical point of view. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 154096–154113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Class | Genus | Species | Common Name | Humerus | Femur | Radius | Tibia | Ulna 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aves | Anas | platyrhynchos | Mallard Duck | 31 | 28 | 31 | 30 | 31 |
| Aves | Aquila | chrysaetos | Golden Eagle | 21 | 23 | 20 | 19 | 23 |
| Aves | Branta | canadensis | Goose | 34 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 34 |
| Aves | Gallus | gallus | Chicken | 31 | 31 | 31 | 32 | 31 |
| Aves | Meleagris | gallopavo | Turkey | 35 | 35 | 32 | 35 | 34 |
| Mammalia | Alces | alces | Moose | 19 | 17 | 20 | 21 | 27 |
| Mammalia | Bos | taurus | Cow | 15 | 16 | 13 | 17 | 12 |
| Mammalia | Canis | familiaris | Domestic Dog | 84 | 147 | 75 | 147 | 76 |
| Mammalia | Canis | latrans | Coyote | 64 | 65 | 57 | 65 | 58 |
| Mammalia | Canis | lupus | Wolf | 44 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 |
| Mammalia | Capra | hircus | Goat | 83 | 3 | 79 | 80 | 3 |
| Mammalia | Cervus | canadensis | Elk | 34 | 33 | 31 | 32 | 31 |
| Mammalia | Didelphis | virginiana | Opossum | 34 | 34 | 35 | 33 | 33 |
| Mammalia | Ovis/capra 2 | aries/hircus | Sheep/Goat | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Mammalia | Equus | caballus | Horse | 31 | 33 | 33 | 30 | 33 |
| Mammalia | Felis | catus | Domestic Cat | 40 | 39 | 39 | 39 | 38 |
| Mammalia | Homo | sapiens | Human | 2714 | 2700 | 2672 | 2684 | 463 |
| Mammalia | Odocoileus | hemionus | Mule deer | 31 | 32 | 34 | 32 | 38 |
| Mammalia | Odocoileus | virginianus | White-Tailed Deer | 33 | 39 | 35 | 39 | 35 |
| Mammalia | Ovis | aries | Sheep | 77 | 18 | 147 | 104 | 63 |
| Mammalia | Procyon | lotor | Racoon | 36 | 37 | 36 | 39 | 37 |
| Mammalia | Sus | scrofa | Domestic Pig/Boar | 20 | 17 | 7 | 17 | 8 |
| Mammalia | Sylviagus | floridanus | Eastern Cotton-Tail Rabbit | 36 | 34 | 34 | 32 | 33 |
| Mammalia | Urocyon | cinereoargenteus | Gray Fox | 39 | 42 | 39 | 40 | 42 |
| Mammalia | Ursus | americanus | American Black Bear | 38 | 34 | 18 | 19 | 18 |
| Mammalia | Ursus | arctos | Brown Bear | 48 | 46 | 18 | 22 | 19 |
| Mammalia | Vulpes | vulpes | Red Fox | 43 | 41 | 41 | 42 | 40 |
| Testudines | Chelydra | serpentina | Snapping Turtle | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Testudines | Terrapene | carolina | Common Box Turtle | 31 | 31 | 27 | 31 | 31 |
| Totals | 3778 | 3685 | 3705 | 3787 | 1360 |
| Bone | Meas 1 | N | Min | Max | Ave | SD | −2SD | +2SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Humerus | MaxL | 2567 | 225 | 397 | 309 | 23 | 262 | 356 |
| MaxPD | 94 | 35 | 56 | 46 | 4 | 37 | 55 | |
| MaxPW | 411 | 38 | 62 | 49 | 4 | 41 | 58 | |
| MaxDD | 94 | 22 | 37 | 28 | 3 | 22 | 35 | |
| MaxDW | 1867 | 42 | 77 | 59 | 6 | 47 | 70 | |
| MidMaxD | 425 | 16 | 32 | 23 | 3 | 17 | 28 | |
| MidMinD | 440 | 11 | 24 | 18 | 2 | 13 | 23 | |
| Radius | MaxL | 2531 | 180 | 309 | 236 | 20 | 196 | 276 |
| MaxPD | 380 | 15 | 31 | 23 | 2 | 18 | 28 | |
| MaxPW | 380 | 15 | 31 | 23 | 2 | 18 | 27 | |
| MaxDD | 89 | 17 | 36 | 25 | 4 | 17 | 32 | |
| MaxDW | 89 | 21 | 42 | 33 | 4 | 25 | 41 | |
| MidMaxD | 454 | 10 | 21 | 16 | 2 | 12 | 19 | |
| MidMinD | 454 | 8 | 74 | 12 | 3 | 5 | 19 | |
| Ulna | MaxL | 406 | 211 | 334 | 263 | 20 | 222 | 303 |
| MaxPW | 257 | 14 | 35 | 26 | 3 | 19 | 32 | |
| MidMaxD | 477 | 10 | 24 | 17 | 2 | 12 | 21 | |
| MidMinD | 477 | 9 | 19 | 13 | 2 | 9 | 17 | |
| Femur | MaxL | 2630 | 344 | 550 | 433 | 33 | 367 | 499 |
| MaxPD | 89 | 37 | 59 | 46 | 5 | 36 | 56 | |
| MaxPW | 89 | 71 | 105 | 87 | 8 | 72 | 103 | |
| DiamH | 1077 | 35 | 61 | 44 | 4 | 37 | 52 | |
| MaxDD | 89 | 46 | 92 | 63 | 7 | 49 | 78 | |
| MaxDW | 2563 | 58 | 98 | 77 | 6 | 64 | 90 | |
| MidMaxD | 457 | 14 | 39 | 27 | 3 | 21 | 33 | |
| MidMinD | 457 | 17 | 39 | 27 | 3 | 21 | 33 | |
| Tibia | MaxL | 2589 | 159 | 472 | 357 | 32 | 294 | 421 |
| MaxPW | 1867 | 50 | 94 | 71 | 6 | 58 | 84 | |
| MaxDD | 82 | 30 | 52 | 39 | 4 | 31 | 47 | |
| MaxDW | 415 | 40 | 63 | 52 | 4 | 43 | 60 | |
| MidMaxD | 420 | 19 | 44 | 33 | 4 | 25 | 42 | |
| MidMinD | 82 | 15 | 28 | 21 | 3 | 16 | 26 | |
| Fibula | MaxL | 429 | 282 | 463 | 366 | 27 | 312 | 421 |
| Os Coxae | MaxL | 91 | 166 | 237 | 202 | 16 | 170 | 233 |
| DiamA | 1526 | 39 | 63 | 49 | 4 | 41 | 57 | |
| Sacrum | MaxL | 90 | 89 | 157 | 114 | 13 | 88 | 141 |
| MaxPW | 90 | 90 | 138 | 111 | 9 | 93 | 129 | |
| Scapula | MaxL | 92 | 127 | 210 | 178 | 17 | 145 | 212 |
| Var(s) | Pooled-Bone | Humerus | Femur | Radius | Tibia | Ulna |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MaxL | 79.5% Hum: 79.3%; Non: 80.0% NHum = 11,129; NNon = 5254 | 94.1% Hum: 99.9%; Non: 78.0% NHum = 2567; NNon = 920 | 95.4% Hum: 100.0%; Non: 83.2% NHum = 2630; NNon = 981 | 95.4% Hum: 99.8%; Non: 79.3% NHum = 2531; NNon = 697 | 95.0% Hum: 99.5%; Non: 83.9% NHum = 2589; NNon = 1062 | 78.5% Hum: 96.8%; Non: 69.1% NHum = 406; NNon = 797 |
| MaxPW | 74.8% Hum: 68.8%; Non: 79.2% NHum = 3383; NNon = 4668 | 75.4% Hum: 85.4% Non: 69.8% NHum = 410; NNon = 733 | 85.4% Hum: 100.0%; Non: 83.8% NHum = 89; NNon = 822 | 46.1% Hum: 61.8%; Non: 39.7% NHum = 380; NNon = 946 | 93.4% Hum: 99.7%; Non: 78.8% NHum: 1867; NNon = 817 | 74.3% Hum: 70.8%; Non: 76.5% NHum = 257; NNon = 404 |
| MaxDW | 87.9% Hum: 92.9%; Non: 82.1% NHum = 5021; NNon = 4345 | 92.0% Hum: 97.9%; Non: 81.2% NHum = 1868; NNon = 1024 | 94.8% Hum: 100.0%; Non: 80.3% NHum = 2560; NNon = 908 | 69.7% Hum: 83.1% Non: 68.1% NHum = 89; NNon = 745 | 89.6% Hum: 100.0%; Non: 84.9% NHum = 415; NNon = 923 | -- |
| MaxDD & MaxDW | 78.9% Hum: 64.3%; Non: 80.0% NHum = 230; NHn = 3007 | 96.3% Hum: 100.0%; Non: 96.21% NHum = 26; NNon = 850 | 96.1% Hum: 97.0%; Non: 96.1% NHum = 33; NNon = 720 | 86.4% Hum: 82.0%; Non: 87.3% NHum = 89; NNon = 448 | 86.2% Hum: 92.7% Non: 85.4% NHum = 82; NNon = 735 | -- |
| MidMaxD & MidMinD | 64.4% Hum: 49.0%; Non: 73.1% NHum = 1767; NNon = 3089 | 67.1% Hum: 62.0%; Non: 69.9% NHum = 347; NNon = 714 | 90.2% Hum: 86.4%; Non: 92.7% NHum = 457; NNon = 711 | 87.9% Hum: 88.3%; Non: 87.6% NHum = 436; NNon = 443 | 87.2% Hum: 84.8% Non: 87.5% NHum = 66; NNon = 537 | 90.0% Hum: 94.4%; Non: 85.3% NHum = 461; NNon = 428 |
| Stepwise 1 | 90.3% Hum: 95.6%; Non: 87.9% NHum = 1408; NNon = 3088 MaxL, MidMaxD, MidMinD | 96.7% Hum: 99.6%; Non: 90.7% NHum = 1862; NNon = 891 MaxL, MaxDW | 98.1% Hum: 99.9%; Non: 93.0% NHum = 2552 NNon = 906 MaxL, MaxDW | 91.4% Hum: 100.0%; Non: 86.8% NHum = 327; NNon = 621 MaxL, MaxPW | 89.4% Hum: 92.2%; Non: 83.4% NHum = 1773 NNon = 807 MaxL, MaxPW | 87.4% Hum: 93.7%; Non: 77.7% NHum = 254; NNon = 166 MaxL, MaxPW, MidMaxD, MidMinD |
| Bone | Input | Training Sample | Test Sample | Tree Variables | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Acc | Hum Acc | Non Acc | Hum N | Non N | Total Acc | Hum Acc | Non Acc | Hum N | Non N | |||
| Pooled | All 6 | 91.4% | 99.6% | 75.4% | 8211 | 4253 | 91.0% | 99.6% | 75.0% | 3487 | 1865 | MaxL, MidMaxD, MaxDW & MaxPW |
| Pooled | Distal | 83.3% | 98.8% | 64.8% | 3650 | 3052 | 82.9% | 98.9% | 64.5% | 1495 | 1300 | MaxDD & MaxDW |
| Pooled | Mid | 77.2% | 99.7% | 61.9% | 1603 | 2356 | 75.7% | 99.4% | 59.6% | 689 | 1016 | MidMaxD & MidMinD |
| Pooled | Length | 88.3% | 99.9% | 64.5% | 7696 | 3763 | 88.7% | 99.8% | 63.2% | 3433 | 1491 | MaxL |
| Humerus | ALL 6 | 99.1% | 99.3% | 98.4% | 1914 | 741 | 97.9% | 98.6% | 96.3% | 776 | 323 | MaxL & MidMinD |
| Femur | ALL 6 | 96.7% | 99.4% | 89.5% | 1853 | 694 | 96.4% | 99.6% | 86.9% | 837 | 290 | MaxL only |
| Radius | ALL 6 | 95.1% | 98.6% | 86.2% | 1894 | 734 | 94.9% | 98.6% | 85.2% | 778 | 298 | MaxL & MidMaxD |
| Tibia | ALL 6 | 94.9% | 98.4% | 86.5% | 1854 | 776 | 94.0% | 97.8% | 84.4% | 830 | 327 | MaxDW & MaxPW |
| Ulna | ALL 4 | 92.5% | 98.7% | 89.2% | 318 | 590 | 89.3% | 94.5% | 86.5% | 145 | 267 | MidMinD & MaxPW |
| Bone | N | Vars | Total Acc | Hum Acc | Number of Species | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <50% | 50–75% | 75–90% | >90% | |||||
| Pooled | 2737 | All 6 | 40.4% | 68.9% | 20 | 6 | 0 | 2 |
| Humerus | 735 | All 6 | 89.1% | 100.0% | 0 | 6 | 4 | 18 |
| Femur | 744 | All 6 | 79.3% | 100.0% | 1 | 4 | 14 | 8 |
| Radius | 462 | All 6 | 83.9% | 100.0% | 4 | 5 | 8 | 10 |
| Tibia | 548 | All 6 | 77.7% | 92.9% | 3 | 5 | 5 | 14 |
| Ulna | 420 | All 4 | 79.2% | 76.8% | 4 | 2 | 6 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garvin, H.M.; Dunn, R.; Sholts, S.B.; Litten, M.S.; Mohamed, M.; Kuttickat, N.; Skantz, N. Forensic Tools for Species Identification of Skeletal Remains: Metrics, Statistics, and OsteoID. Biology 2022, 11, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010025
Garvin HM, Dunn R, Sholts SB, Litten MS, Mohamed M, Kuttickat N, Skantz N. Forensic Tools for Species Identification of Skeletal Remains: Metrics, Statistics, and OsteoID. Biology. 2022; 11(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarvin, Heather M., Rachel Dunn, Sabrina B. Sholts, M. Schuyler Litten, Merna Mohamed, Nathan Kuttickat, and Noah Skantz. 2022. "Forensic Tools for Species Identification of Skeletal Remains: Metrics, Statistics, and OsteoID" Biology 11, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010025
APA StyleGarvin, H. M., Dunn, R., Sholts, S. B., Litten, M. S., Mohamed, M., Kuttickat, N., & Skantz, N. (2022). Forensic Tools for Species Identification of Skeletal Remains: Metrics, Statistics, and OsteoID. Biology, 11(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010025