PDZ Domain Recognition: Insight from Human Tax-Interacting Protein 1 (TIP-1) Interaction with Target Proteins
Abstract
:1. PDZ Domains
2. The PDZ Domain of TIP-1
3. PDZ Domain Structure and Mechanism of Ligand Binding

4. Structures of TIP-1 and TIP-1-Ligand Complexes

| PDB ID | Method of Structure Determination | Name of the Ligand † | Sequence of the Ligand | B-Factor (X-ray) /RMSD (NMR) ‡ | Average Depth of the Binding Pocket (Å) § | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4E3B | X-ray | iCAL36L | ANSRWPTSIL | 21.0 | 23.33 | [52] |
| 3SFJ | X-ray | iCAL36 | ANSRWPTSII | - | 16.42 | [51] |
| 2KG2 | NMR | No ligand | - | 0.473 | - | [48] |
| 3DJ1 | X-ray | No ligand | - | 27.1 | - | [47] |
| 3DJ3 | X-ray | No ligand | - | 37.6 | - | [47] |
| 3DIW | X-ray | β-catenin * | NGLAWFDTDL | 23.2 | 19.63 | [47] |
| 3GJ9 | X-ray | Kir2.3 * | NISYRRESAI | 65.8 | 13.89 | [45] |
| 2L4T | NMR | Glutaminase L * | KENLESMV | 0.67 | 14.12 | [49] |
| 2L4S | NMR | No ligand | - | 0.45 | - | [49] |
| 2VZ5 | X-ray | No ligand | - | - | - | [46] |
5. TIP-1 Recognition of Target Proteins with C-Terminal Recognition Motif

6. Novel Internal Motif for TIP-1
7. TIP-1 Recognition of Internal Motif: Structure-Based Models
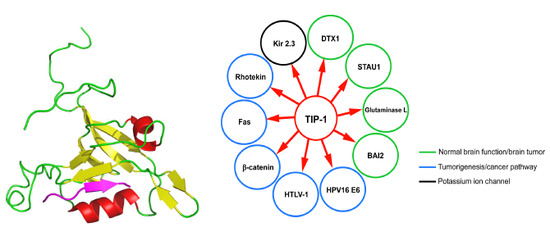
8. TIP-1 Interaction Network: Significance and Role in Diseases

9. TIP-1 as a Biomarker
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ponting, C.P.; Phillips, C. DHR domains in syntrophins, neuronal no synthases and other intracellular proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.B. Origin of Pdz (Dhr, Glgf) domains. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Zheng, J.J. PDZ domains and their binding partners: Structure, specificity, and modification. Cell Commun. Signal. 2010, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, K.; Charbonnier, S.; Trave, G. The emerging contribution of sequence context to the specificity of protein interactions mediated by PDZ domains. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2648–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallen, M.J.; Ponting, C.P. PDZ domains in bacterial proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 26, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponting, C.P. Evidence for PDZ domains in bacteria, yeast, and plants. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penkert, R.R.; DiVittorio, H.M.; Prehoda, K.E. Internal recognition through PDZ domain plasticity in the Par-6-Pals1 complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Appleton, B.A.; Wiesmann, C.; Lau, T.; Costa, M.; Hannoush, R.N.; Sidhu, S.S. Inhibition of Wnt signaling by dishevelled PDZ peptides. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, T.B.; Lee, H.J.; Shao, Y.; Zheng, J. Interaction between the internal motif KTXXXI of Idax and mDvl PDZ domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillier, B.J.; Christopherson, K.S.; Prehoda, K.E.; Bredt, D.S.; Lim, W.A. Unexpected modes of PDZ domain scaffolding revealed by structure of nNOS-syntrophin complex. Science 1999, 284, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songyang, Z.; Fanning, A.S.; Fu, C.; Xu, J.; Marfatia, S.M.; Chishti, A.H.; Crompton, A.; Chan, A.C.; Anderson, J.M.; Cantley, L.C. Recognition of unique carboxyl-terminal motifs by distinct PDZ domains. Science 1997, 275, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourry, C.; Grant, S.G.; Borg, J.P. PDZ domain proteins: Plug and play! Sci. STKE 2003, 2003, RE7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stricker, N.L.; Christopherson, K.S.; Yi, B.A.; Schatz, P.J.; Raab, R.W.; Dawes, G.; Bassett, D.E., Jr.; Bredt, D.S.; Li, M. PDZ domain of neuronal nitric oxide synthase recognizes novel C-terminal peptide sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, P.; Dente, L. PDZ domains: Troubles in classification. FEBS Lett. 2002, 512, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisguerin, P.; Leben, R.; Ay, B.; Radziwill, G.; Moelling, K.; Dong, L.; Volkmer-Engert, R. An improved method for the synthesis of cellulose membrane-bound peptides with free C termini is useful for PDZ domain binding studies. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamori, M.; Sandy, P.; Marzinotto, S.; Benetti, R.; Kai, C.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Schneider, C.; Suzuki, H. The PDZ protein Tax-interacting protein-1 inhibits beta-catenin transcriptional activity and growth of colorectal cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38758–38764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbaiah, V.K.; Kranjec, C.; Thomas, M.; Banks, L. PDZ domains: The building blocks regulating tumorigenesis. Biochem. J. 2011, 439, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, A.S.; Anderson, J.M. Protein-protein interactions: PDZ domain networks. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, M. Tandem PDZ repeats in glutamate receptor-interacting proteins have a novel mode of PDZ domain-mediated target binding. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.F.; Tochio, H.; Wang, P.; Fan, J.S.; Sala, C.; Niethammer, M.; Sheng, M.; Zhang, M. Supramodular structure and synergistic target binding of the N-terminal tandem PDZ domains of PSD-95. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 327, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lue, R.A.; Brandin, E.; Chan, E.P.; Branton, D. Two independent domains of hDlg are sufficient for subcellular targeting: The PDZ1-2 conformational unit and an alternatively spliced domain. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dev, K.K. PDZ domain protein-protein interactions: A case study with PICK1. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Maout, S.; Welling, P.A.; Brejon, M.; Olsen, O.; Merot, J. Basolateral membrane expression of a K+ channel, Kir 2.3, is directed by a cytoplasmic COOH-terminal domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10475–10480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Neubig, R.R. Regulator of G protein signaling proteins: Novel multifunctional drug targets. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Herman, M.A. Asymmetric localizations of LIN-17/Fz and MIG-5/Dsh are involved in the asymmetric B cell division in C. Elegans. Dev. Biol. 2007, 303, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeitler, J.; Hsu, C.P.; Dionne, H.; Bilder, D. Domains controlling cell polarity and proliferation in the drosophila tumor suppressor scribble. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.T.; Han, Z. Expression of TIP-1 confers radioresistance of malignant glioma cells. PLoS One 2012, 7, e45402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.T.; Han, Z. The PDZ protein TIP-1 facilitates cell migration and pulmonary metastasis of human invasive breast cancer cells in athymic mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.T.; Han, Z. Expression of Tax-interacting protein 1 (TIP-1) facilitates angiogenesis and tumor formation of human glioblastoma cells in nude mice. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olalla, L.; Aledo, J.C.; Bannenberg, G.; Marquez, J. The C-terminus of human glutaminase l mediates association with PDZ domain-containing proteins. FEBS Lett. 2001, 488, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olalla, L.; Gutierrez, A.; Jimenez, A.J.; Lopez-Tellez, J.F.; Khan, Z.U.; Perez, J.; Alonso, F.J.; de la Rosa, V.; Campos-Sandoval, J.A.; Segura, J.A.; et al. Expression of the scaffolding PDZ protein glutaminase-interacting protein in mammalian brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, A.W.; He, X.; Borthwick, K.; Donne, A.J.; Hampson, L.; Hampson, I.N. The HPV16 E6 binding protein TIP-1 interacts with ARHGEF16, which activates Cdc42. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alewine, C.; Olsen, O.; Wade, J.B.; Welling, P.A. TIP-1 has PDZ scaffold antagonist activity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 4200–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zencir, S.; Banerjee, M.; Dobson, M.J.; Ayaydin, F.; Fodor, E.A.; Topcu, Z.; Mohanty, S. New partner proteins containing novel internal recognition motif for human glutaminase interacting protein (HGIP). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 432, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zencir, S.; Ovee, M.; Dobson, M.J.; Banerjee, M.; Topcu, Z.; Mohanty, S. Identification of brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 2 as an interaction partner of glutaminase interacting protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besser, J.; Leito, J.T.; van der Meer, D.L.; Bagowski, C.P. TIP-1 induces filopodia growth and is important for gastrulation movements during zebrafish development. Dev. Growth Differ. 2007, 49, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, L.; Li, C.; Oliver, A.W.; Kitchener, H.C.; Hampson, I.N. The PDZ protein TIP-1 is a gain of function target of the HPV16 E6 oncoprotein. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 25, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, C.; Fabre, S.; Jalinot, P. The PDZ protein TIP-1 interacts with the Rho effector rhotekin and is involved in Rho signaling to the serum response element. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33962–33968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, M.; Zoetewey, D.L.; Ovee, M.; Mazumder, S.; Petrenko, V.A.; Samoylova, T.I.; Mohanty, S. Specificity and promiscuity in human glutaminase interacting protein recognition: Insight from the binding of the internal and C-terminal motif. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 6950–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, D.A.; Lee, A.; Lewis, J.; Kim, E.; Sheng, M.; MacKinnon, R. Crystal structures of a complexed and peptide-free membrane protein-binding domain: Molecular basis of peptide recognition by PDZ. Cell 1996, 85, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, D.L.; Cohen, A.R.; Anderson, J.M.; Brunger, A.T. Crystal structure of the hcask PDZ domain reveals the structural basis of class II PDZ domain target recognition. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Hoffmuller, U.; Krause, G.; Ashurst, J.; Macias, M.J.; Schmieder, P.; Schneider-Mergener, J.; Oschkinat, H. Specific interactions between the syntrophin PDZ domain and voltage-gated sodium channels. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochio, H.; Zhang, Q.; Mandal, P.; Li, M.; Zhang, M. Solution structure of the extended neuronal nitric oxide synthase PDZ domain complexed with an associated peptide. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Sala, C. PDZ domains and the organization of supramolecular complexes. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, C.; Xie, X.; Wu, Y.; Tian, C.; Shen, Y.; Long, J. Molecular mechanism of inward rectifier potassium channel 2.3 regulation by Tax-interacting protein-1. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 392, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.W.; Shafqat, N.; Yue, W.; Johannsson, C.; Salah, E.; Cooper, C.; Elkins, J.M.; Pike, A.C.; Roos, A.; Filippakopoulos, P.; von Delft, F.; Wickstroem, M.; Bountra, C.; Edwards, A.M.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Oppermann, U. Structure of the PDZ domain of Tax1 (human T-cell leukemia virus type 1) binding protein 3. 2008. Avaliable online: http://pdbj.org/mine/summary/2vz5 (accessed on 20 January 2015).
- Zhang, J.; Yan, X.; Shi, C.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Tian, C.; Long, J.; Shen, Y. Structural basis of beta-catenin recognition by Tax-interacting protein-1. J Mol Biol 2008, 384, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durney, M.A.; Birrane, G.; Anklin, C.; Soni, A.; Ladias, J.A. Solution structure of the human Tax-interacting protein-1. J Biomol NMR 2009, 45, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoetewey, D.L.; Ovee, M.; Banerjee, M.; Bhaskaran, R.; Mohanty, S. Promiscuous binding at the crossroads of numerous cancer pathways: Insight from the binding of glutaminase interacting protein with glutaminase l. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 3528–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, M.; Huang, C.; Marquez, J.; Mohanty, S. Probing the structure and function of human glutaminase-interacting protein: A possible target for drug design. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 9208–9219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushing, P.R.; Vouilleme, L.; Amacher, J.F.; Boisguerin, P.; Madden, D.R. Crystal structure of Tax-interacting protein-1 (TIP-1) PDZ domain bound to iCAL36 inhibitor peptide. RCSB PDB Protein Data Bank 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amacher, J.F.; Cushing, P.R.; Bahl, C.D.; Beck, T.; Madden, D.R. Stereochemical determinants of c-terminal specificity in PDZ peptide-binding domains: A novel contribution of the carboxylate-binding loop. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 5114–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Hutchinson, E.G.; Michie, A.D.; Wallace, A.C.; Jones, M.L.; Thornton, J.M. Pdbsum: A web-based database of summaries and analyses of all PDB structures. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1997, 22, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A. Pdbsum: Summaries and analyses of PDB structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A. Surfnet: A program for visualizing molecular surfaces, cavities, and intermolecular interactions. J. Mol. Graph. 1995, 13, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.C.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. Ligplot: A program to generate schematic diagrams of protein-ligand interactions. Protein Eng. 1995, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestan, N.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S.; Rakic, P. Contact-dependent inhibition of cortical neurite growth mediated by notch signaling. Science 1999, 286, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Joazeiro, C.; Fang, N.; Wang, H.Y.; Elly, C.; Altman, Y.; Fang, D.; Hunter, T.; Liu, Y.C. Recognition and ubiquitination of Notch by Itch, a hect-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 35734–35737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeau, G.; Maher-Laporte, M.; Topolnik, L.; Laurent, C.E.; Sossin, W.; Desgroseillers, L.; Lacaille, J.C. Staufen1 regulation of protein synthesis-dependent long-term potentiation and synaptic function in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2896–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, J.; de la Oliva, A.R.; Mates, J.M.; Segura, J.A.; Alonso, F.J. Glutaminase: A multifaceted protein not only involved in generating glutamate. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gomez, C.; Campos-Sandoval, J.A.; Alonso, F.J.; Segura, J.A.; Manzanares, E.; Ruiz-Sanchez, P.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Marquez, J.; Mates, J.M. Co-expression of glutaminase K and L isoenzymes in human tumour cells. Biochem. J. 2005, 386, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Tchernyshyov, I.; Chang, T.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Kita, K.; Ochi, T.; Zeller, K.I.; de Marzo, A.M.; van Eyk, J.E.; Mendell, J.T.; et al. C-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, F.A.; Kettunen, M.I.; Day, S.E.; Lerche, M.; Brindle, K.M. 13C MR spectroscopy measurements of glutaminase activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells using hyperpolarized 13C-labeled glutamine. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, N.; Nagata, S. A novel protein domain required for apoptosis. Mutational analysis of human fas antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 10932–10937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saras, J.; Engstrom, U.; Gonez, L.J.; Heldin, C.H. Characterization of the interactions between PDZ domains of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase ptpl1 and the carboxyl-terminal tail of fas. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20979–20981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S. Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 1997, 88, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, R.; Fabre, S.; Desbois, C.; Bantignies, F.; Jalinot, P. The C-terminus of the HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein mediates interaction with the PDZ domain of cellular proteins. Oncogene 1998, 16, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Fu, A.; Han, M.; Hallahan, D.; Han, Z. TIP-1 translocation onto the cell plasma membrane is a molecular biomarker of tumor response to ionizing radiation. PLOS ONE 2010, 5, e12051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Han, M.; Whetsell, W., Jr.; Wang, J.; Rich, J.; Hallahan, D.; Han, Z. Tax-interacting protein 1 coordinates the spatiotemporal activation of Rho gtpases and regulates the infiltrative growth of human glioblastoma. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohanty, S.; Ovee, M.; Banerjee, M. PDZ Domain Recognition: Insight from Human Tax-Interacting Protein 1 (TIP-1) Interaction with Target Proteins. Biology 2015, 4, 88-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010088
Mohanty S, Ovee M, Banerjee M. PDZ Domain Recognition: Insight from Human Tax-Interacting Protein 1 (TIP-1) Interaction with Target Proteins. Biology. 2015; 4(1):88-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohanty, Smita, Mohiuddin Ovee, and Monimoy Banerjee. 2015. "PDZ Domain Recognition: Insight from Human Tax-Interacting Protein 1 (TIP-1) Interaction with Target Proteins" Biology 4, no. 1: 88-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010088
APA StyleMohanty, S., Ovee, M., & Banerjee, M. (2015). PDZ Domain Recognition: Insight from Human Tax-Interacting Protein 1 (TIP-1) Interaction with Target Proteins. Biology, 4(1), 88-103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010088