Visual Positioning System Based on 6D Object Pose Estimation Using Mobile Web
Abstract
:1. Introduction
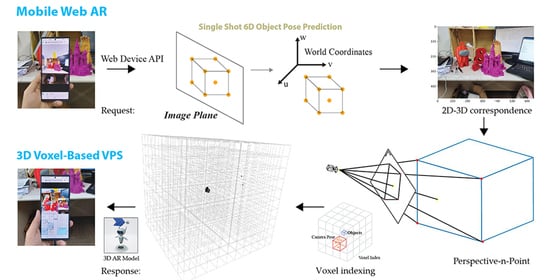
- We propose an indoor positioning system using a mobile web browser that users can easily access. The mobile client system uses a smartphone camera to acquire images and estimate the pose of the camera in the server system to ensure real-time indoor space.
- We improve a single-shot deep CNN based on 2D object recognition. The pose of the camera calculated using PnP is indexed to the voxel database. A visual positioning system is designed to determine the user location using a spatial voxel address.
- With the help of object pose estimation of single-shot Deep CNN, one object box in the camera pose is used as an anchor point for 3D AR to provide information on a 3D indoor space in 3D AR model.
2. Related Research
2.1. 6D Object Pose Prediction
2.2. 2D–3D Correspondence
3. System and Methodology
3.1. System Overview
3.2. 6D Object Pose Estimation
3.3. 2D–3D Correspondence—3D Position Estimation Utilizing Perspective-n-Point
3.4. Voxel Index Database Using Camera Pose Optimization
3.5. Voxel Addressing vs. VPS Distance Error
4. Evaluation
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. System Setup
4.1.2. LineMOD Dataset
4.2. Comparison of 6D Pose Estimation Convolutional Neural Network Using RGB
4.3. VPS Results of Voxel Index
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, H.; Garther, G. A survey of mobile indoor navigation systems. In Central and Eastern Europe; Section III: Multimedia Cartography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 305–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Su, Y. Visual place recognition: A survey from deep learning perspective. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 113, 107760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachmann, E.; Krull, A.; Michel, F.; Gumhold, S.; Shotton, J.; Rother, C. Learning 6D Object Pose Estimation Using 3D Object Coordinates. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 536–551. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.; Christensen, H.I. RGB-D Object Pose Estimation in Unstructured Environments. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 595–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, W.; Milletari, F.; Tombari, F.; Ilic, S.; Navab, N. Deep Learning of Local RGB-D Patches for 3D Object Detection and 6D Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 205–220. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Qi, C. Pose Estimation by Key Points Registration in Point Cloud. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Symposium on Autonomous Systems (ISAS), Shanghai, China, 29–31 May 2019; pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Schmidt, T.; Narayanan, V.; Fox, D. Posecnn: A convolutional neural network for 6d object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.00199. [Google Scholar]
- Sundermeyer, M.; Marton, Z.C.; Durner, M.; Triebel, R. Augmented Autoencoders: Implicit 3D Orientation Learning for 6D Object Detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 714–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Huang, M.; Prasad, N.R.; Mihovska, A.D. A survey of image-based indoor localization using deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on 2019 22nd International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC), Lisbon, Portugal, 24–27 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Bao, H. Pvnet: Pixel-wise voting network for 6dof pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4556–4565. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Song, J.; Huang, Q. Hybridpose: 6d object pose estimation under hybrid representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 428–437. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Parra, Á.; Cao, J.; Li, N.; Chin, T.J. End-to-end learnable geometric vision by backpropagating PnP optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8097–8106. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, R.; Vincent, L. BB8: A scalable, accurate, robust to partial occlusion method for predicting the 3D poses of challenging objects without using depth. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3848–3856. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, B.; Sinha, S.N.; Fua, P. Real-time seamless single shot 6d object pose prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 292–301. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharov, S.; Ivan, S.; Slobodan, I. Dpod: 6d pose object detector and refiner. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1941–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Gu, W.; Xiangyang, J. Cdpn: Coordinates-based disentangled pose network for real-time rgb-based 6-dof object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7677–7686. [Google Scholar]
- Kiru, P.; Timothy, P.; Markus, V. Pix2pose: Pixel-wise coordinate regression of objects for 6d pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7667–7676. [Google Scholar]
- Lepetit, V.; Moreno-Noguer, F.; Fua, P. EPnP: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the PnP Problem. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 81, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Xu, C.; Xie, M. A Robust O(n) Solution to the Perspective-n-Point Problem. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Press, W.; Teukolsky, S.; Vetterling, W.; Flannery, B. Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, J.L. A Tutorial on se (3) Transformation Parameterizations and on-Manifold Optimization. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.468.5407&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Hinterstoisser, S.; Holzer, S.; Cagniart, C.; Ilic, S.; Konolige, K.; Navab, N.; Lepetit, V. Multimodal templates for real-time detection of texture-less objects in heavily cluttered scenes. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV’11, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 858–865. [Google Scholar]
- Bukschat, Y.; Vetter, M. EfficientPose: An efficient, accurate and scalable end-to-end 6D multi object pose estimation approach. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.04307. [Google Scholar]
- Shun, I.; Xingyu, L.; Rawal, K.; Rio, Y.; Kris, M.K. RePOSE: Fast 6D Object Pose Refinement via Deep Texture Rendering. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.00633. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; Gu, W.; Xiangyang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Fox, D. DeepIM: Deep Iterative Matching for 6D Pose Estimation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.00175. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Medhi, J.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Gupta, V. End-to-End Differentiable 6DoF Object Pose Estimation with Local and Global Constraints. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.11078. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.; Lars, P.; Richard, H. Cullnet: Calibrated and pose aware confidence scores for object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 2758–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Wadim, K.; Fabian, M.; Federico, T.; Slobodan, I.; Navab, N. SSD-6D: Making rgb-based 3D detection and 6D pose estimation great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1530–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Peng, G.; Wang, H.; Fang, H.S.; Li, C.; Lu, C. Estimating 6D pose from localizing designated surface keypoints. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.01387. [Google Scholar]
- Sundermeyer, M.; Marton, Z.C.; Durner, M.; Brucker, M.; Triebel, R. Implicit 3D Orientation Learning for 6D Object Detection from RGB Images. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.01275. [Google Scholar]






| 6D Object Pose | Efficient Pose [25] (FPS) | SSD-6D [30] (FPS) | Single-Shot Deep CNN [15] (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ape | 20.56 | 11.98 | 54.36 |
| Bench vise | 20.50 | 11.32 | 53.99 |
| Cam | 20.69 | 11.45 | 54.30 |
| Can | 20.87 | 11.87 | 54.49 |
| Cat | 21.01 | 11.94 | 54.69 |
| Driller | 20.91 | 11.57 | 54.53 |
| Duck | 19.88 | 11.74 | 54.47 |
| Eggbox | 19.53 | 12.43 | 54.56 |
| Glue | 20.29 | 12.03 | 55.50 |
| Hole puncher | 19.84 | 11.83 | 54.16 |
| Iron | 21.67 | 11.78 | 53.96 |
| Lamp | 20.32 | 11.10 | 54.04 |
| Phone | 20.47 | 11.59 | 53.95 |
| Average FPS | 20.50 | 11.74 | 54.38 |
| Request + Response | Detect | 2D–3D Correspondence | Perspective-n-Point | Voxel Indexing | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700 ms | 28.84 ms | 0.069 ms | 0.2178 ms | 0.4 ms | 733.1268 ms |
| Voxel | Ape | Bench Vise | Cam | Can | Cat | Driller | Duck | Eggbox | Glue | Hole Puncher | Iron | Lamp | Phone | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance | 10 cm | 5 cm | 7 cm | 5 cm | 8 cm | 7 cm | 9 cm | 9 cm | 8 cm | 8 cm | 11 cm | 14 cm | 11 cm | 8.61 cm |
| Voxel Index Error (20 cm) | Ape | Bench Vise | Cam | Can | Cat | Driller | Duck | Eggbox | Glue | Hole Puncher | Iron | Lamp | Phone | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Voxel (%) | 34.8 | 27.3 | 35.5 | 27 | 36.5 | 32.9 | 36.4 | 36.3 | 31.8 | 35.8 | 37.9 | 33.6 | 38.4 | 34.2 |
| 2 Voxel (%) | 10.2 | 4.7 | 6.9 | 4.1 | 10 | 8.6 | 10 | 10.8 | 8.4 | 7.6 | 13.5 | 9.9 | 13.4 | 9.1 |
| 3 Voxel (%) | 2.2 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 1.2 |
| 4 Voxel + (%) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Voxel Index Error (50 cm) | Ape | Bench Vise | Cam | Can | Cat | Driller | Duck | Eggbox | Glue | Hole Puncher | Iron | Lamp | Phone | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Voxel (%) | 19.4 | 11.7 | 15.4 | 12.5 | 19.7 | 14.1 | 16.6 | 19 | 17.4 | 16.8 | 23.5 | 14.7 | 21 | 17.1 |
| 2 Voxel (%) | 2.1 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.9 | 1 | 0.9 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.2 |
| 3 Voxel (%) | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| 4 Voxel + (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Voxel Index Error (100 cm) | Ape | Bench Vise | Cam | Can | Cat | Driller | Duck | Eggbox | Glue | Hole Puncher | Iron | Lamp | Phone | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Voxel (%) | 4.6 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 3.9 | 6.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 4.8 |
| 2 Voxel (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| 3 Voxel (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 4 Voxel + (%) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Voxel Index Error (50 cm) | Ape | Bench Vise | Cam | Can | Cat | Driller | Duck | Eggbox | Glue | Hole Puncher | Iron | Lamp | Phone | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Voxel (%) | 13.3 | 13.2 | 10.0 | 14.0 | 12.8 | 11.3 | 12.3 | 3.2 | 7.7 | 11.5 | 9.4 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.8 |
| 2 Voxel (%) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 15.3 | 12.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 2.7 |
| 3 Voxel (%) | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 5.8 | 4.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 |
| 4 Voxel + (%) | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 61.7 | 34.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 7.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, I.-S.; Yun, D.-Y.; Jung, T.-W.; Kwon, S.-C.; Jung, K.-D. Visual Positioning System Based on 6D Object Pose Estimation Using Mobile Web. Electronics 2022, 11, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060865
Kim J-Y, Kim I-S, Yun D-Y, Jung T-W, Kwon S-C, Jung K-D. Visual Positioning System Based on 6D Object Pose Estimation Using Mobile Web. Electronics. 2022; 11(6):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060865
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ju-Young, In-Seon Kim, Dai-Yeol Yun, Tae-Won Jung, Soon-Chul Kwon, and Kye-Dong Jung. 2022. "Visual Positioning System Based on 6D Object Pose Estimation Using Mobile Web" Electronics 11, no. 6: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060865
APA StyleKim, J. -Y., Kim, I. -S., Yun, D. -Y., Jung, T. -W., Kwon, S. -C., & Jung, K. -D. (2022). Visual Positioning System Based on 6D Object Pose Estimation Using Mobile Web. Electronics, 11(6), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060865