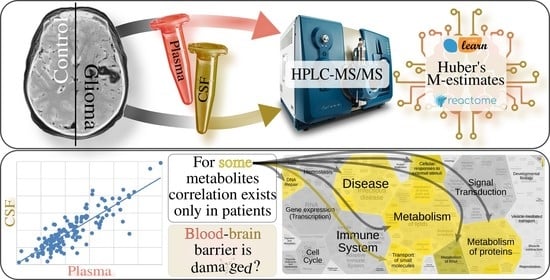
Correlation of Metabolic Profiles of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid of High-Grade Glioma Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Subjects
3.2. Compliance with Ethical Standards
3.3. Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Collection and Processing
3.4. Sample Preparation
3.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3.6. Data Processing and Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Stetson, L.; Virk, S.M.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Epidemiology of gliomas. Cancer Treat. Res. 2015, 163, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omuro, A.; DeAngelis, L.M. Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA 2013, 310, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silantyev, A.S.; Falzone, L.; Libra, M.; Gurina, O.I.; Kardashova, K.S.; Nikolouzakis, T.K.; Nosyrev, A.E.; Sutton, C.W.; Mitsias, P.D.; Tsatsakis, A. Current and Future Trends on Diagnosis and Prognosis of Glioblastoma: From Molecular Biology to Proteomics. Cells 2019, 8, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.D.; Shao, S.X.; Jiang, H.P.; Cao, Y.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Yang, X.C.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, X.S.; Niu, H.T. Warburg effect or reverse Warburg effect? A review of cancer metabolism. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2015, 38, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qian, Y.; Wu, S. The Warburg effect: Evolving interpretations of an established concept. Free Radic. Biol Med. 2015, 79, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinnaiyan, P.; Kensicki, E.; Bloom, G.; Prabhu, A.; Sarcar, B.; Kahali, S.; Eschrich, S.; Qu, X.; Forsyth, P.; Gillies, R. The metabolomic signature of malignant glioma reflects accelerated anabolic metabolism. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5878–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yen, K.E.; Bittinger, M.A.; Su, S.M.; Fantin, V.R. Cancer-associated IDH mutations: Biomarker and therapeutic opportunities. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6409–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, L.; Yen, K.; Attar, E.C. IDH mutations in cancer and progress toward development of targeted therapeutics. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tumani, H.; Huss, A.E.; Bachhuber, F. Chapter—The cerebrospinal fluid and barriers—anatomic and physiologic considerations. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 3rd ed.; Deisenhammer, F., Teunissen, C.E., Tumani, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 146, pp. 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhov, P.G.; Trifonova, O.P.; Maslov, D.L.; Lichtenberg, S.; Balashova, E.E. Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease by A Metabolomics-Based Laboratory-Developed Test (LDT). Diagnostics 2020, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, R.; Sayago, A.; Fernández-Recamales, Á. High-Throughput Direct Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics to Characterize Metabolite Fingerprints Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis. Metabolites 2018, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poddighe, S.; Murgia, F.; Lorefice, L.; Liggi, S.; Cocco, E.; Marrosu, M.G.; Atzori, L. Metabolomic analysis identifies altered metabolic pathways in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 93, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, G.; Ellul, S.; Narayana, V.K.; Kanojia, K.; Ha, H.T.T.; Li, S.; Renoir, T.; Cao, K.L.; Hannan, A.J. An integrated metagenomics and metabolomics approach implicates the microbiota-gut-brain axis in the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 148, 105199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locasale, J.W.; Melman, T.; Song, S.; Yang, X.; Swanson, K.D.; Cantley, L.C.; Wong, E.T.; Asara, J.M. Metabolomics of human cerebrospinal fluid identifies signatures of malignant glioma. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2012, 11, M111.014688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jürchott, K.; Guo, K.T.; Catchpole, G.; Feher, K.; Willmitzer, L.; Schichor, C.; Selbig, J. Comparison of metabolite profiles in U87 glioma cells and mesenchymal stem cells. Biosystems 2011, 105, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Teo, C.; McDonald, K.L.; Zinger, A.; Bustamante, S.; Lim, C.K.; Sundaram, G.; Braidy, N.; Brew, B.J.; Guillemin, G.J. Involvement of the kynurenine pathway in human glioma pathophysiology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mörén, L.; Wibom, C.; Bergström, P.; Johansson, M.; Antti, H.; Bergenheim, A.T. Characterization of the serum metabolome following radiation treatment in patients with high-grade gliomas. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, K.R.; Lim, C.K.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Chatterjee, P.; Martins, R.N.; Brew, B.J.; Guillemin, G.J.; Lovejoy, D.B. Correlation between plasma and CSF concentrations of kynurenine pathway metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease and relationship to amyloid-β and tau. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 80, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Breitkopf, S.B.; Yang, X.; Asara, J.M. A positive/negative ion–switching, targeted mass spectrometry–based metabolomics platform for bodily fluids, cells, and fresh and fixed tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becht, E.; McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Dutertre, C.A.; Kwok, I.W.; Ng, L.G.; Ginhoux, F.; Newell, E.W. Dimensionality reduction for visualizing single-cell data using UMAP. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, F.A.; Angerer, P.; Theis, F.J. SCANPY: Large-scale single-cell gene expression data analysis. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huber, P.J. Robust Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; p. 523. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, T.P. The graph-tool python library. Dataset. Figshare. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, A.M.; Wrensch, M.R.; Jenkins, R.B.; Eckel-Passow, J.E. Statistical considerations on prognostic models for glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Booth, T.C.; Williams, M.; Luis, A.; Cardoso, J.; Ashkan, K.; Shuaib, H. Machine learning and glioma imaging biomarkers. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arvanitis, C.D.; Ferraro, G.B.; Jain, R.K. The blood-brain barrier and blood-tumour barrier in brain tumours and metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B.; Ghosh, M.K. Extracellular Vesicles in Glioma: From Diagnosis to Therapy. BioEssays 2019, 41, e1800245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Dieppa, D.R.; Gonda, D.D.; Cheung, V.J.; Steinberg, J.A.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Extracellular Vesicles as a Platform for Glioma Therapeutic Development. Progr. Neurol. Surg. 2018, 32, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallawaaratchy, D.M.; Hallal, S.; Russell, B.; Ly, L.; Ebrahimkhani, S.; Wei, H.; Christopherson, R.I.; Buckland, M.E.; Kaufman, K.L. Comprehensive proteome profiling of glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles identifies markers for more aggressive disease. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 131, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Čuperlović-Culf, M.; Khieu, N.H.; Surendra, A.; Hewitt, M.; Charlebois, C.; Sandhu, J.K. Analysis and Simulation of Glioblastoma Cell Lines-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Metabolome. Metabolites 2020, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, D.J.; Pinu, F.R.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Poojary, M.M.; Narayana, V.K.; Boughton, B.A.; Kanojia, K.; Dayalan, S.; Jones, O.; Dias, D.A. Review of recent developments in GC-MS approaches to metabolomics-based research. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, B.C.; Grootveld, M.; Gibson, M.; Osman, Y.; Molinari, M.; Jafari, F.; Sahota, T.; Martin, M.; Casanova, F.; Mather, M.L.; et al. Low-Field, Benchtop NMR Spectroscopy as a Potential Tool for Point-of-Care Diagnostics of Metabolic Conditions: Validation, Protocols and Computational Models. High-Throughput 2019, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bujak, R.; Struck-Lewicka, W.; Markuszewski, M.J.; Kaliszan, R. Metabolomics for laboratory diagnostics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Metabolomics for Biomarker Discovery: Moving to the Clinic. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 354671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trushina, E.; Dutta, T.; Persson, X.M.T.; Mielke, M.M.; Petersen, R.C. Identification of altered metabolic pathways in plasma and CSF in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using metabolomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, S.F.; Chevallier, O.P.; Elliott, C.T.; Hölscher, C.; Johnston, J.; McGuinness, B.; Kehoe, P.G.; Passmore, A.P.; Green, B.D. Untargeted metabolomic analysis of human plasma indicates differentially affected polyamine and L-arginine metabolism in mild cognitive impairment subjects converting to Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupp, M.; Jonsson, P.; Öhrfelt, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Obudulu, O.; Malm, L.; Blennow, K.; Antti, H. Metabolite and peptide levels in plasma and CSF differentiating healthy controls from patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson’s disease. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2014, 4, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, D.; Pesaresi, M.; Abbiati, F.; Calabrese, D.; Giatti, S.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Melcangi, R.C. Comparison of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of neuroactive steroids with their brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerve levels in male and female rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolomic Profile in Glioma Patients. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03865355 (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- pyopls—Orthogonal Projection to Latent Structures in Python. Available online: https://github.com/BiRG/pyopls (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Pathway Identifier | Pathway Name | Entities Found | Entities Total | Entities FDR | Submitted Entities Found |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-HSA-425366 | Transport of bile salts and organic acids, metal ions and amine compounds | 4 | 165 | 0.02317 | C00719; C00791; C00158; C00366 |
| R-HSA-71291 | Metabolism of amino acids and derivatives | 4 | 661 | 0.02875 | C00719; C00791; C00956; C00005 |
| R-HSA-425407 | SLC-mediated transmembrane transport | 4 | 418 | 0.02875 | C00719; C00791; C00158; C00366 |
| R-HSA-71403 | Citric acid cycle (TCA cycle) | 2 | 50 | 0.02875 | C00005; C00158 |
| R-HSA-549132 | Organic cation/anion/zwitterion transport | 2 | 51 | 0.02875 | C00791; C00366 |
| R-HSA-382551 | Transport of small molecules | 5 | 967 | 0.03432 | C00719; C00791; C00005; C00158; C00366 |
| R-HSA-71406 | Pyruvate metabolism and Citric Acid (TCA) cycle | 2 | 98 | 0.034312 | C00005; C00158 |
| R-HSA-112310 | Neurotransmitter release cycle | 2 | 99 | 0.04432 | C00189; C00719 |
| R-HSA-917937 | Iron uptake and transport | 2 | 83 | 0.04500 | C00005; C00158 |
| R-HSA-1428517 | The citric acid (TCA) cycle and respiratory electron transport | 2 | 233 | 0.04705 | C00005; C00158 |
| Name | Patients | Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huber R | Huber p | Huber R | Huber p | |
| Methylcysteine | −0.12 | 0.53 | 0.96 | 9.75 × 10−15 |
| N-Acetyl-L-alanine | 0.34 | 0.10 | −0.74 | 2.82 × 10−2 |
| N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate | −0.01 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 1.10 × 10−2 |
| deoxyuridine | 0.17 | 0.62 | 0.97 | 6.08 × 10−12 |
| Acetylcarnitine | 0.14 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 2.22 × 10−3 |
| 4-Pyridoxic acid | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.85 | 1.56 × 10−3 |
| S-methyl-5-thioadenosine | 0.51 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 2.29 × 10−2 |
| Name | Patients | Control Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huber R | Huber p | Huber R | Huber p | |
| biotin | 0.92 | 7.69 × 10−31 | −0.27 | 0.57 |
| phenylalanine | 0.86 | 2.14 × 10−12 | −0.29 | 0.54 |
| leucine-isoleucine | 0.79 | 2.05 × 10−5 | −0.36 | 0.63 |
| Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate (SBP) | 0.53 | 4.60 × 10−5 | −0.52 | 0.31 |
| hypoxanthine | 0.71 | 9.50 × 10−9 | −0.24 | 0.62 |
| cysteine | 0.85 | 1.69 × 10−7 | −0.04 | 0.92 |
| creatine | 0.50 | 0.0021 | −0.34 | 0.44 |
| purine | 0.84 | 1.12 × 10−6 | 0.077 | 0.91 |
| alanine | 0.44 | 0.0071 | −0.32 | 0.49 |
| 2,3-Diphosphoglyceric acid | 0.85 | 2.97 × 10−6 | 0.102 | 0.86 |
| Group | Gender (M/F) | Min. | 1st Qu. | 2nd Qu. | 3rd Qu. | Max. | Average | Median | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6/5 | 28.0 | 52.0 | 52.0 | 52.0 | 77.0 | 53.0 | 53.0 | 12.2 |
| Glioma | 11/9 | 21.0 | 50.5 | 50.5 | 50.5 | 65.0 | 55.2 | 56.0 | 10.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rogachev, A.D.; Alemasov, N.A.; Ivanisenko, V.A.; Ivanisenko, N.V.; Gaisler, E.V.; Oleshko, O.S.; Cheresiz, S.V.; Mishinov, S.V.; Stupak, V.V.; Pokrovsky, A.G. Correlation of Metabolic Profiles of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid of High-Grade Glioma Patients. Metabolites 2021, 11, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030133
Rogachev AD, Alemasov NA, Ivanisenko VA, Ivanisenko NV, Gaisler EV, Oleshko OS, Cheresiz SV, Mishinov SV, Stupak VV, Pokrovsky AG. Correlation of Metabolic Profiles of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid of High-Grade Glioma Patients. Metabolites. 2021; 11(3):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030133
Chicago/Turabian StyleRogachev, Artem D., Nikolay A. Alemasov, Vladimir A. Ivanisenko, Nikita V. Ivanisenko, Evgeniy V. Gaisler, Olga S. Oleshko, Sergey V. Cheresiz, Sergey V. Mishinov, Vyacheslav V. Stupak, and Andrey G. Pokrovsky. 2021. "Correlation of Metabolic Profiles of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid of High-Grade Glioma Patients" Metabolites 11, no. 3: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030133
APA StyleRogachev, A. D., Alemasov, N. A., Ivanisenko, V. A., Ivanisenko, N. V., Gaisler, E. V., Oleshko, O. S., Cheresiz, S. V., Mishinov, S. V., Stupak, V. V., & Pokrovsky, A. G. (2021). Correlation of Metabolic Profiles of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid of High-Grade Glioma Patients. Metabolites, 11(3), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030133