The Capacity to Secrete Insulin Is Dose-Dependent to Extremely High Glucose Concentrations: A Key Role for Adenylyl Cyclase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
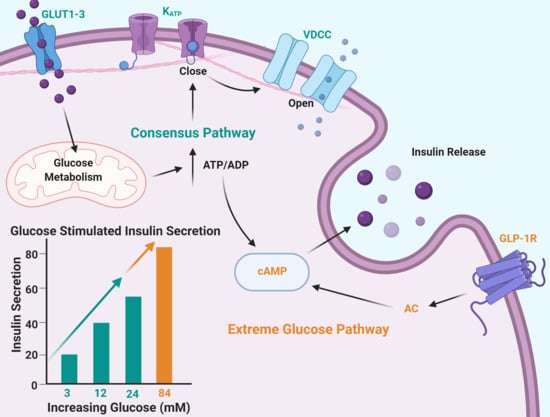
2.1. Insulin Secretion Is Maintained in Response to Extreme Glucose
2.2. Increased Osmolarity Does Not Alter Insulin Secretion or Islet Viability
2.3. Intracellular Calcium Is Maximally Stimulated in 24 mM Glucose
2.4. Glycolytic Capacity to Secrete Insulin Dose-Dependently Extends above 24 mM Glucose
2.5. The cAMP Pathway Provides Additional Capacity for Insulin Secretion in Extremely High Glucose
3. Discussion
3.1. Maximum Glucose Concentrations for Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion Are Much Higher Than Previously Reported
3.2. High Glucose Leads to Increased cAMP via Different Potential Mechanisms
3.3. Paracrine Effects of Extreme Glucose via Alpha Cells
3.4. Clinical Relevance
3.5. Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Islet Sources and Isolation
4.2. Calcium Imaging
4.3. Insulin Secretion
4.4. Cell Death Quantification
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Ethical Approval
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komatsu, M.; Takei, M.; Ishii, H.; Sato, Y. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: A newer perspective. J. Diabetes Investig. 2013, 4, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Rohrscheib, M.; Tzamaloukas, A.H. Extreme hyperglycemia with ketoacidosis and hyperkalemia in a patient on chronic hemodialysis. Hemodial. Int. 2008, 12, S43–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharroubi, A.T.; Darwish, H.M. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlsson, F.; Gedeborg, R.; Hesselager, G.; Tuvemo, T.; Enblad, P. Treatment of extreme hyperglycemia monitored with intracerebral microdialysis. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 5, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazar, O.; Buchwald, P. Concentration-Dependency and Time Profile of Insulin Secretion: Dynamic Perifusion Studies with Human and Murine Islets. Front. Endocrinol 2019, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druet, C.; Tubiana-Rufi, N.; Chevenne, D.; Rigal, O.; Polak, M.; Levy-Marchal, C. Characterization of Insulin Secretion and Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes of Adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.; Shepherd, R.M.; Gill, D.; Gorman, T.; Smith, D.M.; Dunne, M.J. Glucose-dependent modulation of insulin secretion and intracellular calcium ions by GKA50, a glucokinase activator. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, K.; Peng, X.; Bokvist, K.; Stehno-Bittel, L. Assessment of re-aggregated human pancreatic islets for secondary drug screening. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3010–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewandowski, S.L.; Cardone, R.L.; Foster, H.R.; Ho, T.; Potapenko, E.; Poudel, C.; VanDeusen, H.R.; Sdao, S.M.; Alves, T.C.; Zhao, X.; et al. Pyruvate Kinase Controls Signal Strength in the Insulin Secretory Pathway. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, M.; Manappallil, R.G.; Ramdas, D.; Jayaraj, J. The survival story of a diabetic ketoacidosis patient with blood sugar levels of 1985 mg/dL. Asian J. Med Sci. 2017, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Highest Blood Sugar Level. Guinness World Records. Available online: https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/highest-blood-sugar-level/ (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Gheni, G.; Ogura, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Yokoi, N.; Minami, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Harada, K.; Hastoy, B.; Wu, X.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Glutamate Acts as a Key Signal Linking Glucose Metabolism to Incretin/cAMP Action to Amplify Insulin Secretion. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henquin, J.C. Triggering and amplifying pathways of regulation of insulin secretion by glucose. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalwat, M.A.; Cobb, M.H. Mechanisms of the amplifying pathway of insulin secretion in the β cell. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 179, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenbeck, I.; Schulze, T.; Morsi, M.; Alshafei, M.; Panten, U. What Is the Metabolic Amplification of Insulin Secretion and Is It (Still) Relevant? Metabolites 2021, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengholm, A. Cyclic AMP dynamics in the pancreatic β-cell. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2012, 117, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-Molina, C.; Mirmira, R.G. Achieving ‘PeaK-A’ Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1389–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyot, M.-L.; Gray, J.P.; Lamontagne, J.; Smith, P.J.; Holz, G.G.; Madiraju, S.M.; Prentki, M.; Heart, E. Glucagon-like peptide-1 induced signaling and insulin secretion do not drive fuel and energy metabolism in primary rodent pancreatic β-cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenny, S.; Patel, R.; Thorell, W. Mannitolin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470392/ (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Lee, B.; Jonas, J.C.; Weir, G.C.; Laychock, S.G. Glucose regulates expression of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor isoforms in isolated rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonkers, F.C.; Guiot, Y.; Rahier, J.; Henquin, J.-C. Tolbutamide stimulation of pancreatic β-cells involves both cell recruitment and increase in the individual Ca2+ response. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henquin, J.C. Regulation of insulin secretion: A matter of phase control and amplitude modulation. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henquin, J.C.; Meissner, H.P. The ionic, electrical, and secretory effects of endogenous cyclic adenosine monophosphate in mouse pancreatic B cells: Studies with forskolin. Endocrinology 1984, 115, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yada, T.; Itoh, K.; Nakata, M. Glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36)amide and a rise in cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate increase cytosolic free Ca2+ in rat pancreatic beta-cells by enhancing Ca2+ channel activity. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Grapengiesser, E.; Gylfe, E.; Hellman, B. Crosstalk between the cAMP and inositol trisphosphate-signalling pathways in pancreatic beta-cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 334, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepurny, O.G.; Kelley, G.G.; Dzhura, I.; Leech, C.A.; Roe, M.W.; Dzhura, E.; Li, X.; Schwede, F.; Genieser, H.G.; Holz, G.G. PKA-dependent potentiation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by Epac activator 8-pCPT-2′-O-Me-cAMP-AM in human islets of Langerhans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 298, E622–E633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Yang, L. Targeting cAMP/PKA pathway for glycemic control and type 2 diabetes therapy. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 57, R93–R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seino, S.; Shibasaki, T. PKA-dependent and PKA-independent pathways for cAMP-regulated exocytosis. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1303–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, H.; Komatsu, M.; Schermerhorn, T.; Aizawa, T.; Kaneko, T.; Nagai, M.; Sharp, G.W.; Hashizume, K. cAMP enhances insulin secretion by an action on the ATP-sensitive K+ channel-independent pathway of glucose signaling in rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaihara, K.A.; Dickson, L.M.; Jacobson, D.A.; Tamarina, N.; Roe, M.W.; Philipson, L.H.; Wicksteed, B. β-Cell–Specific Protein Kinase A Activation Enhances the Efficiency of Glucose Control by Increasing Acute-Phase Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaisano, H.Y. Here come the newcomer granules, better late than never. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henquin, J.-C.; Nenquin, M. Activators of PKA and Epac Distinctly Influence Insulin Secretion and Cytosolic Ca2+ in Female Mouse Islets Stimulated by Glucose and Tolbutamide. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3274–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamontagne, J.; Al-Mass, A.; Nolan, C.J.; Corkey, B.E.; Madiraju, S.M.; Joly, E.; Prentki, M. Identification of the signals for glucose-induced insulin secretion in INS1 (832/13) β-cells using metformin-induced metabolic deceleration as a model. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 19458–19468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, G.; Sandler, S.; Gylfe, E.; Tengholm, A. Glucose- and hormone-induced cAMP oscillations in α- and β-cells within intact pancreatic islets. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Song, J.; Liu, H.; Yan, F.; He, T.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Hou, X.; Chen, L. Insulin regulates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion by pancreatic alpha cells. Endocrine 2018, 62, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thams, P.; Capito, K. L-arginine stimulation of glucose-induced insulin secretion through membrane depolarization and independent of nitric oxide. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 140, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.; Vieira, E.; Gylfe, E. Paradoxical stimulation of glucagon secretion by high glucose concentrations. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Shuai, H.; Ahooghalandari, P.; Gylfe, E.; Tengholm, A. Glucose controls glucagon secretion by directly modulating cAMP in alpha cells. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gylfe, E.; Gilon, P. Glucose regulation of glucagon secretion. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosmanov, A.R.; Gosmanova, E.O.; Kitabchi, A.E. Hyperglycemic Crises: Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS). In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279052/ (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Corbin, K.L.; West, H.L.; Brodsky, S.; Whitticar, N.B.; Koch, W.J.; Nunemaker, C.S. A Practical Guide to Rodent Islet Isolation and Assessment Revisited. Biol. Proced. Online 2021, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitticar, N.B.; Strahler, E.W.; Rajan, P.; Kaya, S.; Nunemaker, C.S. An Automated Perifusion System for Modifying Cell Culture Conditions over Time. Biol. Proced. Online 2016, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slepchenko, K.G.; Corbin, K.L.; Nunemaker, C.S. Comparing methods to normalize insulin secretion shows the process may not be needed. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 241, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammon, H.P.T.; Muller, A.B. Effect of forskolin on islet cyclic AMP, insulin secretion, blood glucose and intravenous glucose tolerance in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1984, 326, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, Q.; Gao, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Weng, J.; Li, Q.; et al. The Adenylyl Cyclase Inhibitor MDL-12,330A Potentiates Insulin Secretion via Blockade of Voltage-Dependent K+ Channels in Pancreatic Beta Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baskić, D.; Popović, S.; Ristić, P.; Arsenijević, N.N. Analysis of cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in human leukocytes: Fluorescence microscopy using annexin V/propidium iodide versus acridin orange/ethidium bromide. Cell Biol. Int. 2006, 30, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dula, S.B.; Jecmenica, M.; Wu, R.; Jahanshahi, P.; Verrilli, G.M.; Carter, J.D.; Brayman, K.L.; Nunemaker, C.S. Evidence that low-grade systemic inflammation can induce islet dysfunction as measured by impaired calcium handling. Cell Calcium 2010, 48, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gelin, L.; Li, J.; Corbin, K.L.; Jahan, I.; Nunemaker, C.S. Metformin Inhibits Mouse Islet Insulin Secretion and Alters Intracellular Calcium in a Concentration-Dependent and Duration-Dependent Manner near the Circulating Range. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 9163052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, C.M.; Lu, C.; Corbin, K.L.; Sharma, P.R.; Dula, S.B.; Carter, J.D.; Ramadan, J.W.; Xin, W.; Lee, J.K.; Nunemaker, C.S. Circulating Levels of IL-1B+IL-6 Cause ER Stress and Dysfunction in Islets from Prediabetic Male Mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Source | Isolation ID | Purity | Donor Age | BMI | Height (m) | Weight (kg) | HbA1c | Sex | Diabetes | Cold Ischemia Time (h) | Donation Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IsletCore, University of Alberta | R286 | 95% | 41 | 20.4 | 1.80 | 66 | 5.2 | M | No | 13.5 | Neurological |
| IsletCore, University of Alberta | R318 | 90% | 54 | 20.5 | 1.85 | 70 | 5.0 | M | No | 16 | Neurological |
| IsletCore, University of Alberta | R322 | 90% | 44 | 23.2 | 1.58 | 58 | 4.9 | F | No | 11.5 | Neurological |
| Clinical Islet Lab, University of Alberta | H#:2296 | 90% | 52 | 29.2 | 1.82 | 96.8 | 5.2 | F | No | 4.5 | Head trauma (fall) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gerber, K.M.; Whitticar, N.B.; Rochester, D.R.; Corbin, K.L.; Koch, W.J.; Nunemaker, C.S. The Capacity to Secrete Insulin Is Dose-Dependent to Extremely High Glucose Concentrations: A Key Role for Adenylyl Cyclase. Metabolites 2021, 11, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060401
Gerber KM, Whitticar NB, Rochester DR, Corbin KL, Koch WJ, Nunemaker CS. The Capacity to Secrete Insulin Is Dose-Dependent to Extremely High Glucose Concentrations: A Key Role for Adenylyl Cyclase. Metabolites. 2021; 11(6):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060401
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerber, Katherine M., Nicholas B. Whitticar, Daniel R. Rochester, Kathryn L. Corbin, William J. Koch, and Craig S. Nunemaker. 2021. "The Capacity to Secrete Insulin Is Dose-Dependent to Extremely High Glucose Concentrations: A Key Role for Adenylyl Cyclase" Metabolites 11, no. 6: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060401
APA StyleGerber, K. M., Whitticar, N. B., Rochester, D. R., Corbin, K. L., Koch, W. J., & Nunemaker, C. S. (2021). The Capacity to Secrete Insulin Is Dose-Dependent to Extremely High Glucose Concentrations: A Key Role for Adenylyl Cyclase. Metabolites, 11(6), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060401